Заглавная страница Избранные статьи Случайная статья Познавательные статьи Новые добавления Обратная связь FAQ Написать работу КАТЕГОРИИ: ТОП 10 на сайте Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрацииТехника нижней прямой подачи мяча. Франко-прусская война (причины и последствия) Организация работы процедурного кабинета Смысловое и механическое запоминание, их место и роль в усвоении знаний Коммуникативные барьеры и пути их преодоления Обработка изделий медицинского назначения многократного применения Образцы текста публицистического стиля Четыре типа изменения баланса Задачи с ответами для Всероссийской олимпиады по праву 
Мы поможем в написании ваших работ! ЗНАЕТЕ ЛИ ВЫ?
Влияние общества на человека
Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрации Практические работы по географии для 6 класса Организация работы процедурного кабинета Изменения в неживой природе осенью Уборка процедурного кабинета Сольфеджио. Все правила по сольфеджио Балочные системы. Определение реакций опор и моментов защемления |
Sidestand Switch ConnectionsСодержание книги
Поиск на нашем сайте
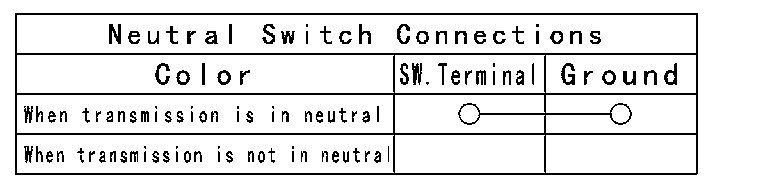
Neutral Switch Connections
*: Engine lubrication system is in good condition.
Water Temperature Sensor Inspection
• Suspend the sensor [A] in a container of coolant so that the temperature-sensing projection [C] and threaded por- tion [C] are submerged. • Suspend an accurate thermometer [B] with temperature -sensing projection located in almost the same depth. NOTE ○The sensor and thermometer must not touch the con- tainer side or bottom. • Place the container over a source of heat and gradu- ally raise the temperature of the coolant while stirring the coolant gently. • Using the hand tester, measure the internal resistance of the sensor.
Water Temperature Sensor Resistance
*: Reference Information
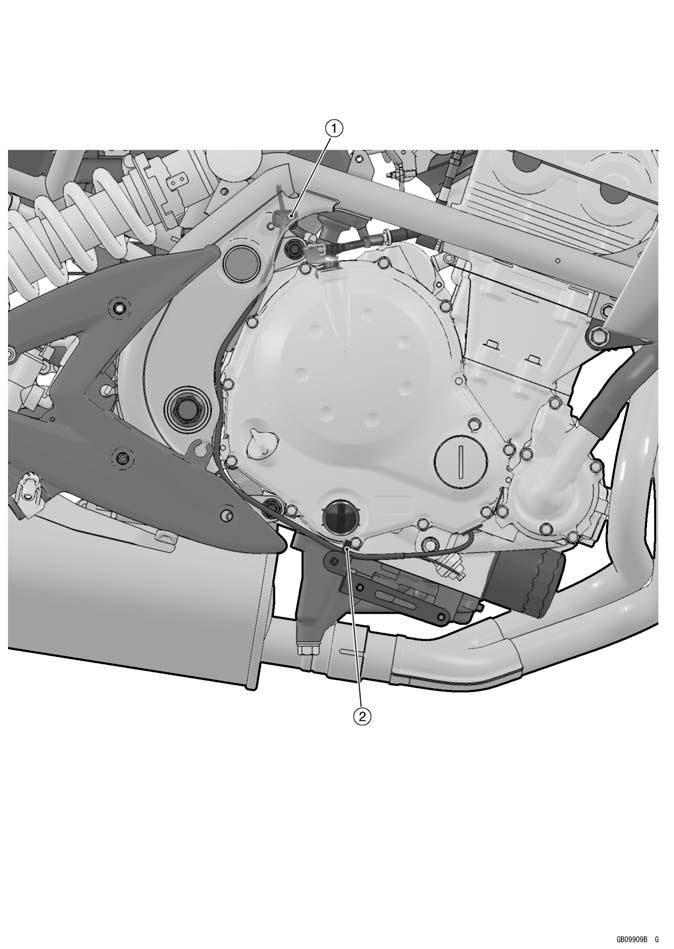
• Remove the left center fairing (see Center Fairing Re- moval in the Frame chapter). • Disconnect the speed sensor lead connector [A]. • Remove the engine sprocket cover (see Engine Sprocket Removal in the Final Drive chapter).
Speed Sensor [B]
Speed Sensor Installation • Installation is the reverse of removal. • Apply a non-permanent locking agent to the sensor bolt, and tighten it. Torque - Speed Sensor Bolt: 7.8 N·m (0.80 kgf·m, 69 in·lb)
• Remove the speed sensor (see Speed Sensor Removal). • Connect the speed sensor connector [A] with the battery [B], 10 kΩ resistor [C] and hand tester [D] as shown. • Set the tester to the DC 25 V range. Special Tool - Hand Tester: 57001-1394
○Then the tester indicator should flick [B].
sensor.
• Remove: Left Lower Fairing (see Lower Fairing Removal in the Frame chapter) • Disconnect the oxygen sensor lead connector [A].
 Oxygen Sensor Installation (Europe Models) Oxygen Sensor Installation (Europe Models)
• Tighten: Torque - Oxygen Sensor: 44.1 N·m (4.50 kgf·m, 32.5 ft·lb) • Run the oxygen sensor lead correctly (see Cable, Wire, and Hose Routing section in the Appendix chapter).
Oxygen Sensor Inspection (Europe Models) • Refer to the Oxygen Sensor Inspection in the Fuel System (DFI) chapter.
• Fill the fuel tank with fuel. • Close the fuel tank cap surely. • Remove the fuel tank (see Fuel Tank Removal in the Fuel System (DFI) chapter). • Connect the test light [A] (12 V 3.4 W bulb a socket with leads) and the 12 V battery [B] to the fuel pump connector [C]. Connections: Battery (+) → 12 V 3.4 W Bulb (One Side) 12 V 3.4 W Bulb (Other Side) → BL Lead Terminal Battery (–) → BK Lead Terminal
• Connect the test light (12 V 3.4 W bulb in a socket with leads) and the 12 V battery to the fuel pump connector as shown. 12 V Battery [A] Test Light [B] Fuel Pump Connector [C] Fuel Reserve Switch [D]
NOTE ○It may take a long time to turn on the test light in case that the fuel reserve switch is inspected just after the fuel pump is removed. Leave the fuel reserve switch with leads for inspection connected for few minutes.
The relay box [A] has relays and diodes. The relays and diodes can not be removed.
• Remove: Fuel Tank (see Fuel Tank Removal in the Fuel System (DFI) chapter) • Take out the relay box [A] and disconnect the connectors [B].
Relay Circuit Inspection • Remove the relay box (see Relay Box Removal). • Check conductivity of the following numbered terminals by connecting the hand tester and one 12 V battery to the relay box as shown (see Relay Box Internal Circuit in this section).
Relay Circuit Inspection (with the battery disconnected)
*: The actual reading varies with the hand tester used.
Relay Circuit Inspection (with the battery connected)
(+): Apply positive lead. (–): Apply negative lead.
Diode Circuit Inspection • Remove the relay box (see Relay Box Removal). • Check conductivity of the following pairs of terminals (see Relay Box Internal Circuit in this section).
Diode Circuit Inspection The resistance should be low in one direction and more than ten times as much in the other direction. If any diode shows low or high in both directions, the diode is defective and the relay box must be replaced.
○The actual meter reading varies with the meter or tester used and the individual diodes, but generally speaking, the lower reading should be from zero to one half the scale.
A: Headlight Relay B: ECU Main Relay C: Fuel Pump Relay D: Starter Circuit Relay E: Fan Relay
30 A Main Fuse Removal
Left Side Cover (see Side Cover Removal in the Frame chapter) Cover (see Starter Relay Inspection) Connector [A] • Pull out the main fuse [B] from the starter relay with needle nose pliers.
• Remove the seat (see Seat Removal in the Frame chap- ter). • Unlock the hook [A] to lift up the lid [B].
• Remove: Seat (see Seat Removal in the Frame chapter) • Unlock the hook [A] to pull the lid [B].
Fuse Installation • If a fuse fails during operation, inspect the electrical sys- tem to determine the cause, and then replace it with a new fuse of proper amperage. • Install the fuse box fuses on the original position as spec- ified on the lid.
• Remove the fuse (see 30 A Main/Fuse Box /15 A ECU Fuse Removal). • Inspect the fuse element.
blown fuse, always check the amperage in the affected circuit. If the amperage is equal to or greater than the fuse rating, check the wiring and related components for a short circuit. Housing [A]
Fuse Element [B] Terminals [C] Blown Element [D]
Appendix Table of Contents Cable, Wire, and Hose Routing.............................................................................................. 17-2 Troubleshooting Guide................................................................................................................... 17-46
17
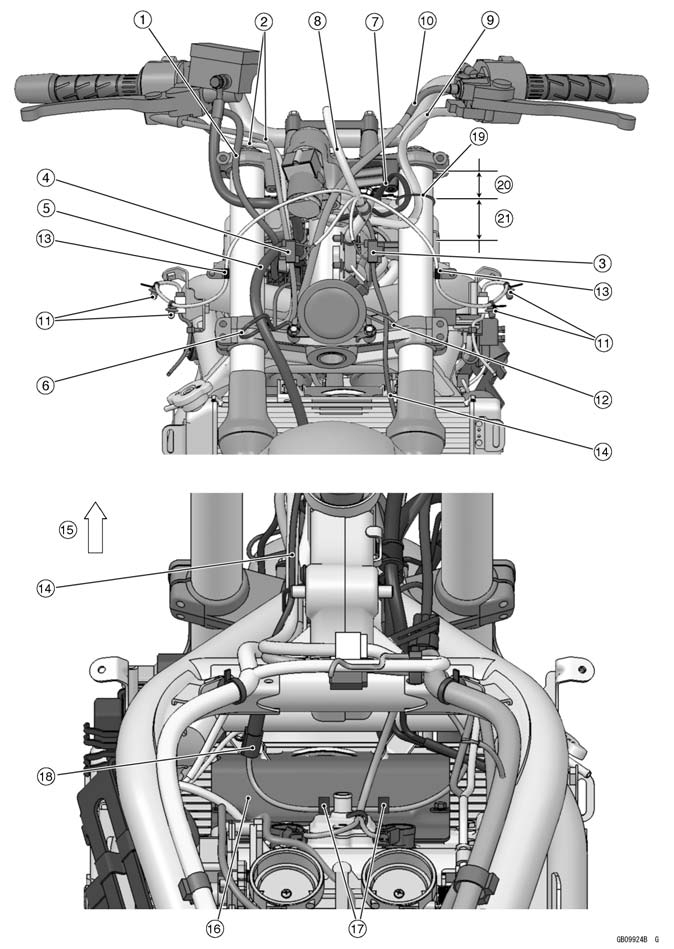
1. Clamp (From the on sequentially, through the ignition switch lead, left switch housing lead and main harness.) 2. Left Switch Housing Lead Connector 3. Clamp (Insert the clamp from air cleaner side.) 4. Air Switching Valve Lead Connector 5. Main Harness 6. Clamp 7. Clamp (Insert the clamp in the frame.) 8. Clamp (Insert the clamp in the frame.) 9. Clamp 10. Inlet Temperature Sensor Lead Connector 11. Clamp (Insert the clamp from air cleaner side.) 12. Ignition Switch Lead Connector 13. Clamp (Clamp the left switch housing lead (main harness side), ignition switch lead (main har- ness side) and air switching valve lead.) 14. Through the air switching valve lead on the left switch housing lead.
1. Relay Box 2. Main Harness 3. Clamp (Insert the clamp in the bracket.) 4. Battery Negative Cable 5. Battery Positive Cable 6. ECU Connectors 7. Clamp 8. Clamp 9. Tail Light Connector 10. License Plate Light Connector 11. Rear Left Turn Signal Light Connector 12. Rear Right Turn Signal Light Connector 13. Clamp (Insert the clamp in the rear fender rear.) 14. Frame Ground 15. Clamp 16. Water-proof Joint 17. Clamp 18. Fuse Box 19. Clamp 20. Clamp 21. Band 22. Band 23. Clamp 24. To the Vehicle-down Sensor, Crankshaft Sensor and Rear Brake Switch 25. Clamp (Clamp the regulator/rectifier lead, and insert the clamp in the rear fender front.) 26. Battery Negative Lead Connector 27. Fuel Pump Lead 28. Starter Motor Cable 29. To Starter Relay 30. Regulator/Rectifier Lead 31. View A
EX650B Models
1. To Main Harness 2. Battery Positive Cable 3. ABS Kawasaki Self-diagnosis System Connector (Insert the connector to the bracket.) 4. ABS Motor Relay Fuse 5. ABS Solenoid Valve Relay Fuse
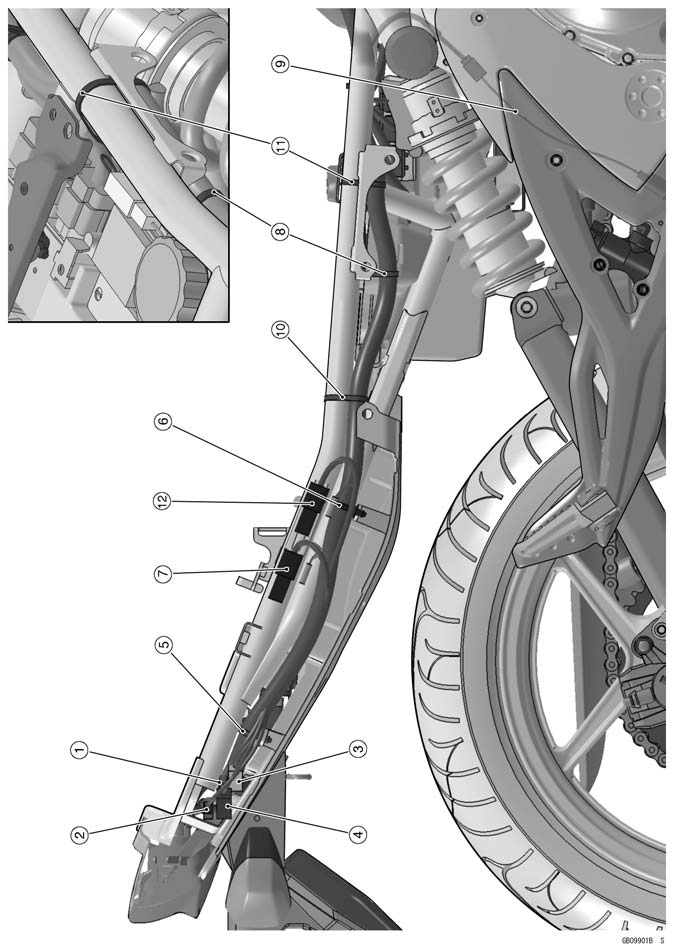
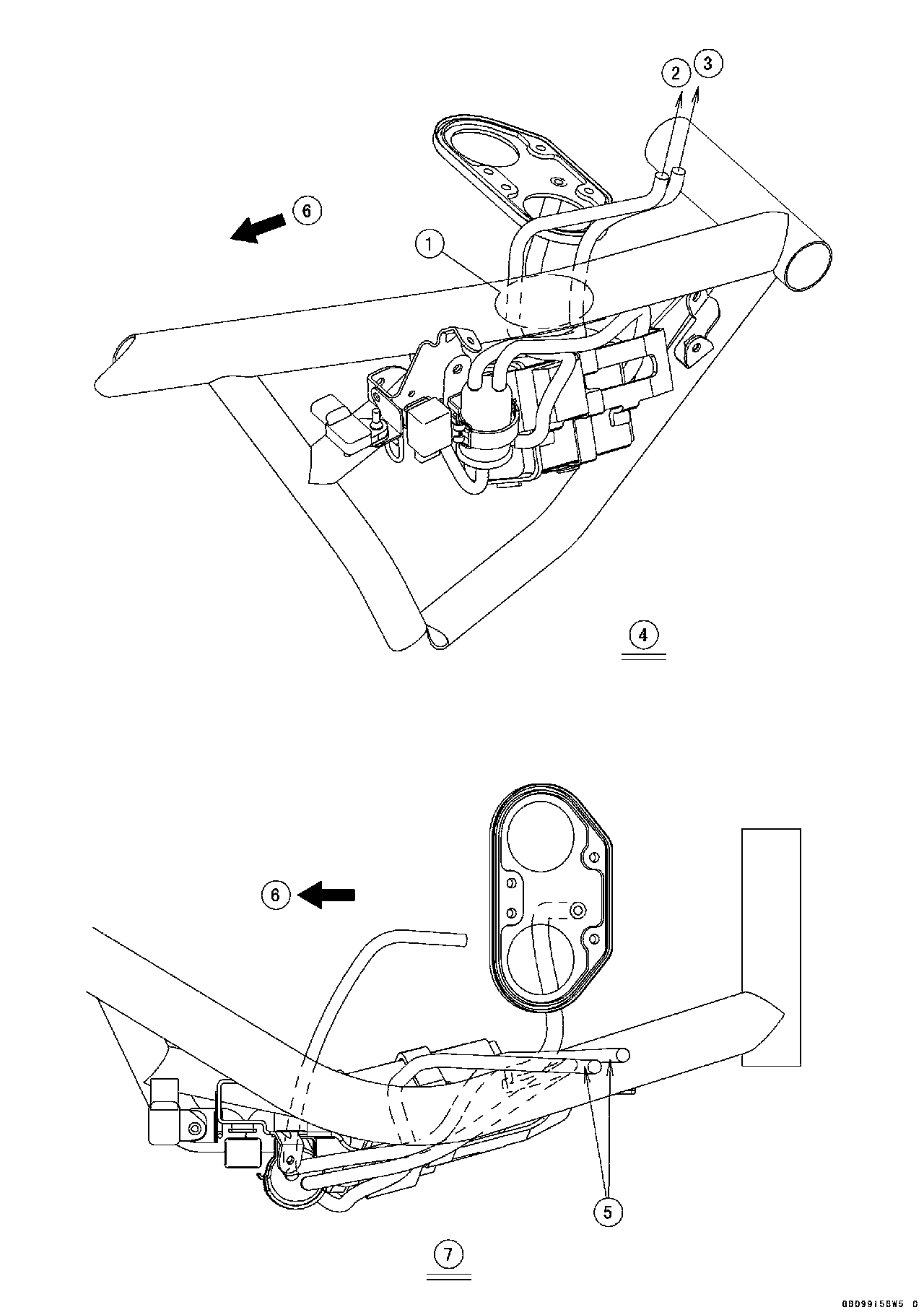
1. Inlet Pressure Sensor 2. Turn Signal Relay 3. Air Cleaner Drain Tube 4. From this side, through the fuel tank drain tube, corrugated tube and air cleaner drain tube between chain guide and engine. 5. To the Water Temperature Sensor 6. Oxygen Sensor Lead Connector 7. Clamp (Through the sidestand switch lead and oxygen sensor lead in the clamp.) 8. Oxygen Sensor Lead 9. Clamp (Through the drain hose in the clamp.) 10. Drain Hose 11. Sidestand Switch Lead 12. Corrugated Tube 13. Alternator Lead Connector 14. Sidestand Switch Lead Connector 15. Speed Sensor Lead Connector 16. Main Throttle Sensor Lead Connector 17. Tube 18. Neutral Switch Lead 19. Drain Hose (Through the drain hose between main harness and air cleaner.) 20. Clamp (Insert the clamp in the cross pipe.)
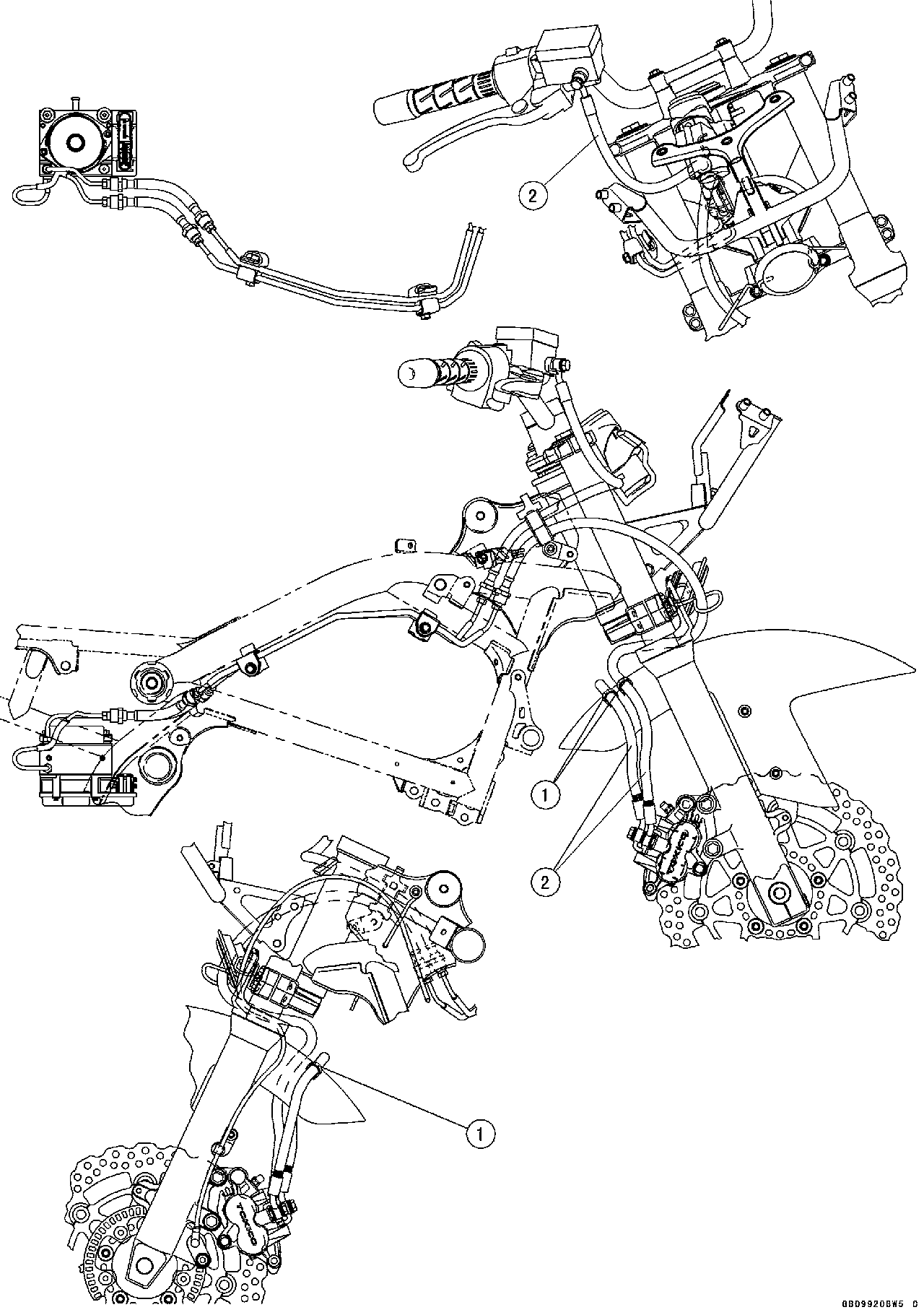
1. Clamp (Through the right switch housing lead, and insert the clamp in the frame.) 2. Clutch Cable 3. Throttle Cables 4. Clamp 5. Right Switch Housing Lead 6. Clamp (Through the clutch cable in the clamp.) 7. Frame (Through the coolant hose in the frame.) 8. Coolant Hose 9. Clamp
1. Brake Hose 2. Clutch Cable 3. Throttle Cables 4. Clamp 5. Right Switch Housing Lead 6. Clamp (Through the clutch cable in the clamp.) 7. Frame (Through the coolant hose in the frame.) 8. Coolant Hose 9. Clamp 10. Clamp (Clamp the right switch housing lead connector.) 11. Bracket 12. Throttle Cables 13. Through the brake hose at the right side of the throttle cables.
1. Right Switch Housing Lead 2. Throttle Cable (Decelerator) 3. Throttle Cable (Accelerator) 4. Through the brake hose at the right side of the throttle cables.
1. Crankshaft Sensor Lead Connector 2. Clamp (Insert the clamp in the bracket.)
1. Tail Light Connector 2. License Plate Light Connector 3. Rear Right Turn Signal Light Connector 4. Rear Left Turn Signal Light Connector 5. Clamp (Insert the clamp in the rear fender rear.) 6. Clamp (Insert the clamp in the rear fender rear.) 7. Diagnosis Connector 8. Clamp (Insert the clamp in the rear fender front.) 9. Rear Brake Light Switch Lead 10. Band (Clamp the main harness with the frame.) 11. Band 12. ABS Kawasaki Self-diagnosis System Connector (EX650B Models)
5. Brake Hose 6. Clamp 7. Ignition Switch Lead 8. Main Harness 9. Left Switch Housing Lead 10. Clutch Cable 11. Clamp (Insert the clamp to the inner fairing.) 12. Clamp 13. Clamp 14. Clamp (Clamp the left switch housing lead and ignition switch lead.) 15. 20 mm (0.79 in.) 16. 50 mm (1.97 in.)
EX650B Models
5. Brake Hose (Through the brake hose at the right side of the throttle cables.) 6. Clamp 7. Ignition Switch Lead 8. Main Harness 9. Left Switch Housing Lead 10. Clutch Cable 11. Clamp (Insert the clamp to the inner fairing.) 12. Clamp 13. Clamp 14. Front Wheel Rotation Sensor Lead 15. Front 16. Baffle Plate 17. Clamp (Insert the clamp to the baffle plate.) 18. Front Wheel Rotation Sensor Lead Connector 19. Clamp (Clamp the left switch housing lead and ignition switch lead.) 20. 20 mm (0.79 in.) 21. 50 mm (1.97 in.)
1. Clamp 2. Clamp 3. Clamp 4. Clamp (Clamp the subthrottle sensor lead and subthrottle valve actuator lead to the delivery pipe.) 5. Ground Lead 6. Clamp 7. Subthrottle Sensor Lead Connector 8. Subthrottle Valve Actuator Lead Connector 9. Clamp (Clamp the harness.) 10. Clamp 11. Clamp 12. Stick Coil Lead Connector 13. Clamp (Clamp the stick coil lead.) 14. Clamp (Push the subthrottle valve actuator lead, and clamp the subthrottle sensor lead and subthrottle valve actuator lead to the delivery pipe.)
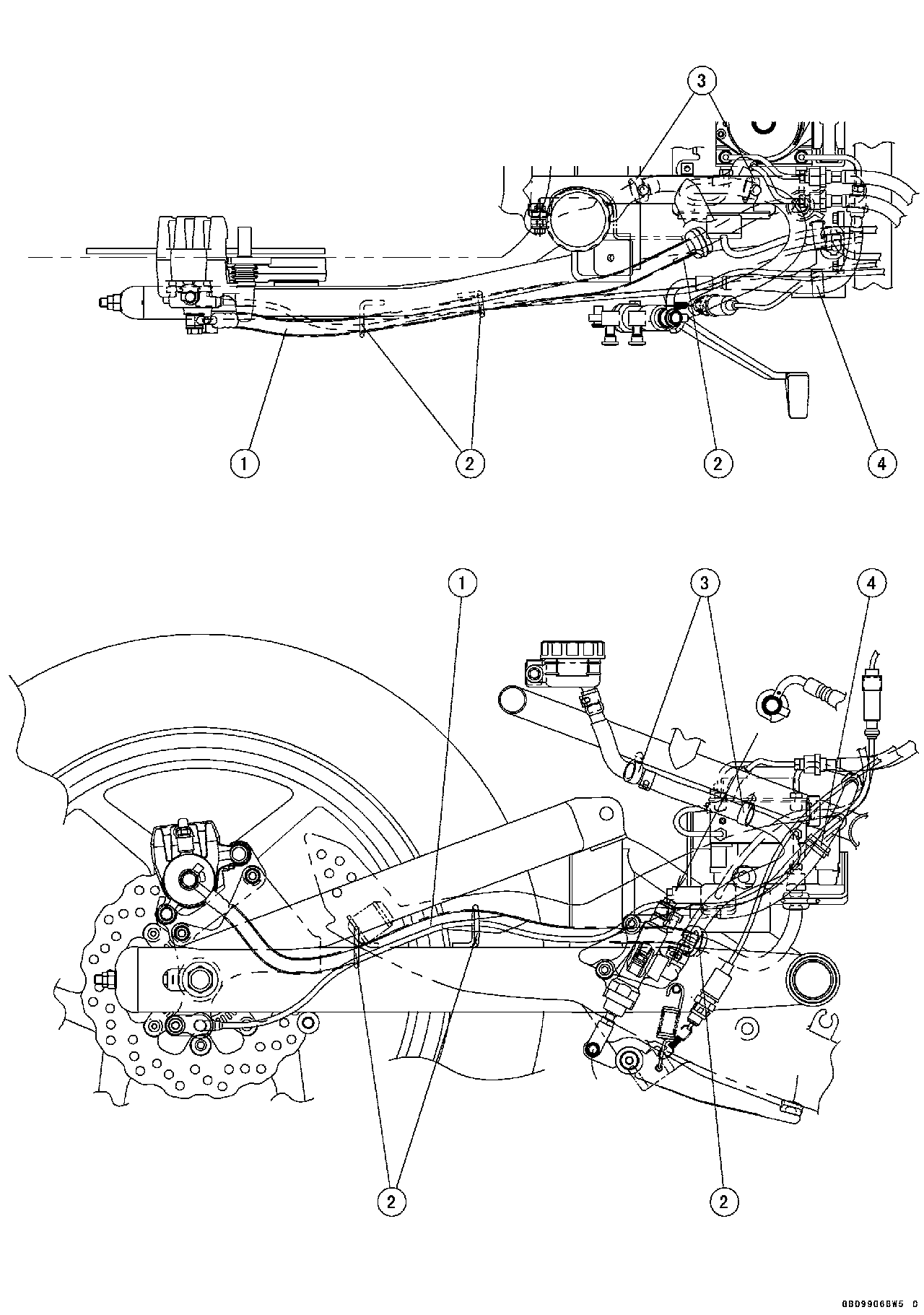
1. Regulator/Rectifier Lead 2. Clamp (Insert the clamp in the frame.) 3. Rear Brake Light Switch Lead Connector 4. Through the rear brake light switch lead and vehicle-down sensor lead from the front side of the rear shockabsorber installation part. 5. Through the regulator/rectifier lead to the front opening of the rear fender front. 6. Vehicle-down Sensor Lead 7. Fuel Pump Lead Connector 8. Through the fuel pump lead to the hook of the rear fender front (Routing is done so that there is no slack.). 9. Through the fuel pump lead to the slit of the cover.
1. ABS Hydraulic Unit Lead (ECU) (Through the lead to the forward of frame cross pipe.) 2. ABS Hydraulic Unit 3. Through the rear wheel rotation sensor lead upper the starter motor cable and engine ground cable. 4. Through the regulator/rectifier lead in the clamp. 5. Through the rear wheel rotation sensor lead upper the brake hose. 6. Rear Wheel Rotation Sensor Lead 7. Through the regulator/rectifier lead under the brake fluid reservoir hose. 8. Through the vehicle-down sensor lead under the brake hose. 9. Clamp (Clamp the brake hose and rear wheel rotation sensor lead.) 10. Through the rear wheel rotation sensor lead upper the rear brake light switch lead. 11. Through the rear wheel rotation sensor lead under the brake hose.
1. Front Wheel Rotation Sensor Lead 2. Ignition Switch Lead 3. Left Switch Housing Lead 4. Clamp (Clamp the front wheel rotation sensor lead.) 5. Main Harness 6. Clamp (Clamp the front wheel rotation sensor lead.)
1. To Meter Unit 2. Clamp 3. To Front Right Turn Signal Light Lead 4. Left Switch Housing Lead 5. Ignition Switch Lead 6. Main Harness 7. To Front Left Turn Signal Light Lead
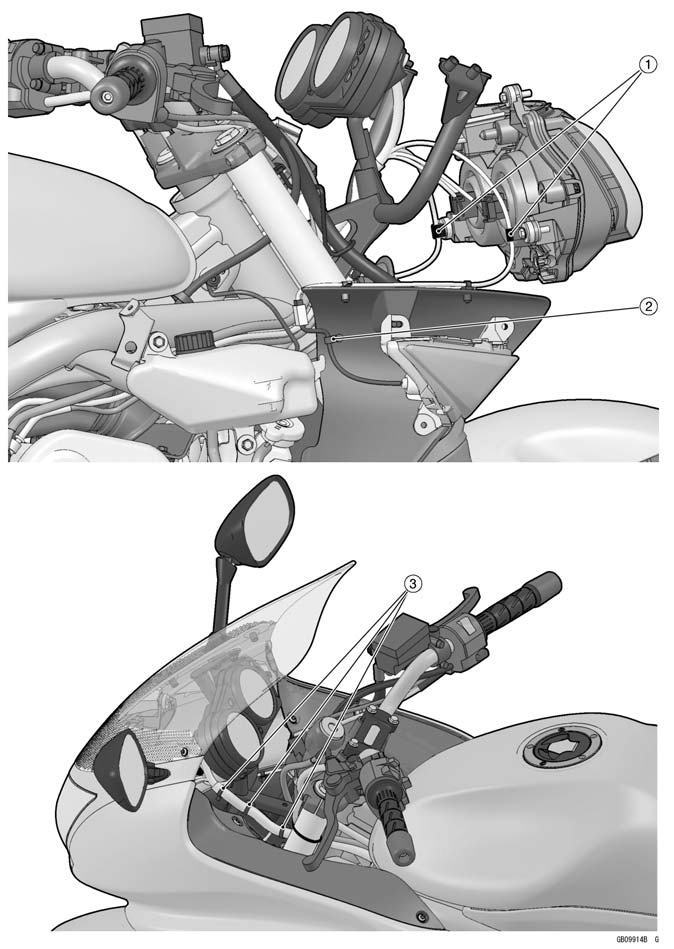
1. Clamp 2. Clamp (Insert the clamp to the inner fairing.) 3. Clamp (Insert the clamp to the upper fairing bracket.)
California Model
1. Through the hose between main harness and air cleaner housing. 2. To Fuel Tank (Red) 3. To Fuel Tank (Blue) 4. Left Side View 5. Through the hose between main harness and air cleaner housing. 6. Front 7. Lower Side View
3. Clamp 4. Clamp
EX650B Models
EX650B Models
4. Clamp
NOTE ○Refer to the Fuel System chapter for most of DFI trouble shooting guide. ○This is not an exhaustive list, giving every possible cause for each problem listed. It is meant simply as a rough guide to assist the troubleshooting for some of the more common difficulties. Engine Doesn’t Start, Starting Difficulty: Starter motor not rotating: Starter lockout switch or neutral switch trou- ble Starter motor trouble Battery voltage low Starter relay not contacting or operating Starter button not contacting Wiring open or shorted Ignition switch trouble Engine stop switch trouble Fuse blown Starter motor rotating but engine doesn’t turn over: Starter clutch trouble Vehicle-down sensor (DFI) coming off Engine won’t turn over: Valve seizure Valve lifter seizure Cylinder, piston seizure Crankshaft seizure Connecting rod small end seizure Connecting rod big end seizure Transmission gear or bearing seizure Camshaft seizure Starter idle gear seizure No fuel flow: No fuel in tank Fuel pump trouble Fuel tank air vent obstructed Fuel filter clogged Fuel line clogged Engine flooded: Clean spark plug and adjust plug gap Starting technique faulty (When flooded, do not crank the engine with the throttle fully opened. This promotes engine flood because more fuel is supplied automatically by DFI.) No spark; spark weak: Vehicle-down sensor (DFI) coming off Ignition switch not ON Engine stop switch turned OFF Clutch lever not pulled in or gear not in neu- tral Battery voltage low Spark plug dirty, broken, or gap malad- justed Stick coil shorted or not in good contact Stick coil trouble Spark plug incorrect IC igniter in ECU trouble Neutral, starter lockout, or side stand switch trouble Crankshaft sensor trouble Ignition switch or engine stop switch shorted Wiring shorted or open Fuse blown Fuel/air mixture incorrect: Bypass screw and/or idle adjusting screw maladjusted Air passage clogged Air cleaner clogged, poorly sealed, or miss- ing Compression Low: Spark plug loose Cylinder head not sufficiently tightened down No valve clearance Cylinder, piston worn Piston ring bad (worn, weak, broken, or sticking) Piston ring/groove clearance excessive Cylinder head gasket damaged Cylinder head warped Valve spring broken or weak Valve not seating properly (valve bent, worn, or carbon accumulation on the seating surface)
Poor Running at Low Speed: Spark weak: Battery voltage low Spark plug dirty, broken, or maladjusted Stick coil wiring trouble Stick coil not in good contact Spark plug incorrect IC igniter in ECU trouble Crankshaft sensor trouble Stick coil trouble Fuel/air mixture incorrect: Bypass screw maladjusted Air passage clogged Air bleed pipe bleed holes clogged Pilot passage clogged Air cleaner clogged, poorly sealed, or miss- ing Fuel tank air vent obstructed Fuel pump trouble Throttle body assy holder loose Air cleaner duct loose
Compression low: Spark plug loose Cylinder head not sufficiently tightened down No valve clearance Cylinder, piston worn Piston ring bad (worn, weak, broken, or sticking) Piston ring/groove clearance excessive Cylinder head warped Cylinder head gasket damaged Valve spring broken or weak Valve not seating properly (valve bent, worn, or carbon accumulation on the seating surface) Other: IC igniter in ECU trouble Throttle body assy not synchronizing Engine oil viscosity too high Drive train trouble Brake dragging Air suction valve trouble Air switching valve trouble Engine overheating Clutch slipping
Poor Running or No Power at High Speed: Firing incorrect: Spark plug dirty, broken, or maladjusted Stick coil wiring trouble Stick coil not in good contact Spark plug incorrect Camshaft position trouble IC igniter in ECU trouble Crankshaft sensor trouble Stick coil trouble Fuel/air mixture incorrect: Air cleaner clogged, poorly sealed, or miss- ing Air cleaner O-ring damaged Air cleaner duct loose Water or foreign matter in fuel Throttle body assy holder loose Fuel to injector insufficient (DFI) Fuel tank air vent obstructed Fuel line clogged Fuel pump trouble Compression low: Spark plug loose Cylinder head not sufficiently tightened down No valve clearance Cylinder, piston worn Piston ring bad (worn, weak, broken, or sticking) Piston ring/groove clearance excessive Cylinder head gasket damaged Cylinder head warped Valve spring broken or weak Valve not seating properly (valve bent, worn, or carbon accumulation on the seating surface) Knocking: Carbon built up in combustion chamber Fuel poor quality or incorrect Spark plug incorrect IC igniter in ECU trouble Crankshaft sensor trouble Miscellaneous: Throttle valve won’t fully open Brake dragging Clutch slipping Engine overheating Engine oil level too high Engine oil viscosity too high Drive train trouble Air suction valve trouble Air switching valve trouble Catalytic converter melt down due to muffler overheating (KLEEN)
Overheating: Firing incorrect: Spark plug dirty, broken, or maladjusted Spark plug incorrect IC igniter in ECU trouble Muffler overheating: For KLEEN, do not run the engine even if with only one cylinder misfiring or poor running (Request the nearest service fa- cility to correct it) For KLEEN, do not push-start with a dead battery (Connect another full-charged battery with jumper cables, and start the engine using the electric starter) For KLEEN, do not start the engine under misfire due to spark plug fouling or poor connection of the stick coil For KLEEN, do not coast the motorcycle with the ignition switch off (Turn the igni- tion switch ON and run the engine) IC igniter in ECU trouble Fuel/air mixture incorrect: Throttle body assy holder loose Air cleaner duct loose Air cleaner poorly sealed, or missing Air cleaner O-ring damaged Air cleaner clogged Compression high: Carbon built up in combustion chamber Engine load faulty: Clutch slipping Engine oil level too high
Engine oil viscosity too high Drive train trouble Brake dragging Lubrication inadequate: Engine oil level too low Engine oil poor quality or incorrect Gauge incorrect: Water temperature gauge broken Water temperature sensor broken Coolant incorrect: Coolant level too low Coolant deteriorated Wrong coolant mixed ratio Cooling system component incorrect: Radiator fin damaged Radiator clogged Thermostat trouble Radiator cap trouble Radiator fan relay trouble Fan motor broken Fan blade damaged Water pump not turning Water pump impeller damaged
Over Cooling: Gauge incorrect: Water temperature gauge broken Water temperature sensor broken Cooling system component incorrect: Radiator fan relay trouble Thermostat trouble
Clutch Operation Faulty: Clutch slipping: Friction plate worn or warped Steel plate worn or warped Clutch spring broken or weak Clutch hub or housing unevenly worn No clutch lever play Clutch inner cable trouble Clutch release mechanism trouble Clutch not disengaging properly: Clutch plate warped or too rough Clutch spring compression uneven Engine oil deteriorated Engine oil viscosity too high Engine oil level too high Clutch housing frozen on drive shaft Clutch hub nut loose Clutch hub spline damaged Clutch friction plate installed wrong Clutch lever play excessive Clutch release mechanism trouble Gear Shifting Faulty: Doesn’t go into gear; shift pedal doesn’t return: Clutch not disengaging Shift fork bent or seized Gear stuck on the shaft Gear positioning lever binding Shift return spring weak or broken Shift return spring pin loose Shift mechanism arm spring broken Shift mechanism arm broken Shift pawl broken Jumps out of gear: Shift fork ear worn, bent Gear groove worn Gear dogs and/or dog holes worn Shift drum groove worn Gear positioning lever spring weak or bro- ken Shift fork guide pin worn Drive shaft, output shaft, and/or gear splines worn Overshifts: Gear positioning lever spring weak or bro- ken Shift mechanism arm spring broken
Abnormal Engine Noise: Knocking: IC igniter in ECU trouble Carbon built up in combustion chamber Fuel poor quality or incorrect Spark plug incorrect Overheating Piston slap: Cylinder/piston clearance excessive Cylinder, piston worn Connecting rod bent Piston pin, piston pin hole worn Valve noise: Valve clearance incorrect Valve spring broken or weak Camshaft bearing worn Valve lifter worn Other noise: Connecting rod small end clearance exces- sive Connecting rod big end clearance exces- sive Piston ring/groove clearance excessive Piston ring worn, broken, or stuck Piston ring groove worn Piston seizure, damage Cylinder head gasket leaking Exhaust pipe leaking at cylinder head con- nection Crankshaft runout excessive
Engine mount loose Crankshaft bearing worn Primary gear worn or chipped Camshaft chain tensioner trouble Camshaft chain, sprocket, guide worn Air suction valve damaged Air switching valve damaged Alternator rotor loose Catalytic converter melt down due to muffler overheating (KLEEN)
Abnormal Drive Train Noise: Clutch noise: Clutch housing/friction plate clearance ex- cessive Clutch housing gear worn Wrong installation of outside friction plate Transmission noise: Bearings worn Transmission gear worn or chipped Metal chips jammed in gear teeth Engine oil insufficient Drive line noise: Drive chain adjusted improperly Drive chain worn Rear and/or engine sprocket worn Chain lubrication insufficient Rear wheel misaligned
Abnormal Frame Noise: Front fork noise: Oil insufficient or too thin Spring weak or broken Rear shock absorber noise: Shock absorber damaged Disc brake noise: Pad installed incorrectly Pad surface glazed Disc warped Caliper trouble Other noise: Bracket, nut, bolt, etc. not properly mounted or tightened
Oil Pressure Warning Light Goes On: Engine oil pump damaged Engine oil screen clogged Engine oil filter clogged Engine oil level too low Engine oil viscosity too low Camshaft bearing worn Crankshaft bearing worn Oil pressure switch damaged Wiring faulty Relief valve stuck open O-ring at the oil passage in the crankcase damaged
Exhaust Smokes Excessively: White smoke: Piston oil ring worn Cylinder worn Valve oil seal damaged Valve guide worn Engine oil level too high Black smoke: Air cleaner clogged Brown smoke: Air cleaner duct loose Air cleaner O-ring damaged Air cleaner poorly sealed or missing
Handling and/or Stability Unsatisfactory: Handlebar hard to turn: Cable routing incorrect Hose routing incorrect Wiring routing incorrect Steering stem nut too tight Steering stem bearing damaged Steering stem bearing lubrication inade- quate Steering stem bent Tire air pressure too low Handlebar shakes or excessively vibrates: Tire worn Swingarm pivot bearing worn Rim warped, or not balanced Wheel bearing worn Handlebar holder bolt loose Steering stem nut loose Front, rear axle runout excessive Engine mounting bolt loose Handlebar pulls to one side: Frame bent Wheel misalignment Swingarm bent or twisted Swingarm pivot shaft runout excessive Steering maladjusted Front fork bent Right and left front fork oil level uneven Shock absorption unsatisfactory: (Too hard) Front fork oil excessive Front fork oil viscosity too high Rear shock absorber adjustment too hard Tire air pressure too high Front fork bent (Too soft) Tire air pressure too low Front fork oil insufficient and/or leaking Front fork oil viscosity too low
Rear shock adjustment too soft Front fork, rear shock absorber spring weak Rear shock absorber oil leaking
Brake Doesn’t Hold: Air in the brake line Pad or disc worn Brake fluid leakage Disc warped Contaminated pad Brake fluid deteriorated Primary or secondary cup damaged in master cylinder Master cylinder scratched inside Battery Trouble: Battery discharged: Charge insufficient Battery faulty (too low terminal voltage) Battery lead making poor contact Load excessive (e.g., bulb of excessive wattage) Ignition switch trouble Alternator trouble Wiring faulty Regulator/rectifier trouble Battery overcharged: Alternator trouble Regulator/rectifier trouble Battery faulty
MODEL APPLICATION
□:This digit in the frame number changes from one machine to another.
Part No.99924-1361-01 Printed in Japan
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Последнее изменение этой страницы: 2016-08-10; просмотров: 278; Нарушение авторского права страницы; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! infopedia.su Все материалы представленные на сайте исключительно с целью ознакомления читателями и не преследуют коммерческих целей или нарушение авторских прав. Обратная связь - 3.143.237.203 (0.007 с.) |



 • Remove the water temperature sensor (see Removal/In- stallation in the Fuel System (DFI) chapter).
• Remove the water temperature sensor (see Removal/In- stallation in the Fuel System (DFI) chapter). If the hand tester does not show the specified values, re- place the sensor.
If the hand tester does not show the specified values, re- place the sensor. Speed Sensor Removal
Speed Sensor Removal • Remove: Bolt [A]
• Remove: Bolt [A] Speed Sensor Inspection
Speed Sensor Inspection • Trace [A] each side of the speed sensor surface with the screw driver.
• Trace [A] each side of the speed sensor surface with the screw driver. If the tester indicator does not flick, replace the speed
If the tester indicator does not flick, replace the speed Oxygen Sensor Removal (Europe Models)
Oxygen Sensor Removal (Europe Models) • Remove the oxygen sensor [A].
• Remove the oxygen sensor [A]. Fuel Reserve Switch Inspection
Fuel Reserve Switch Inspection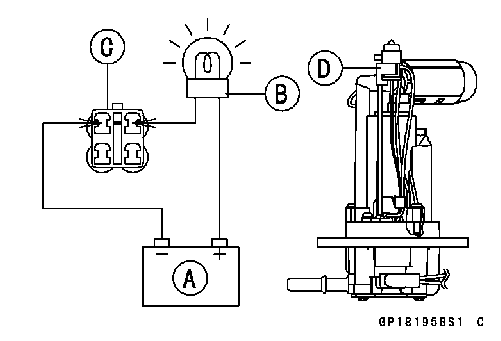 • Remove the fuel pump (see Fuel Pump Removal in the Fuel System (DFI) chapter).
• Remove the fuel pump (see Fuel Pump Removal in the Fuel System (DFI) chapter).
 Relay Box Removal
Relay Box Removal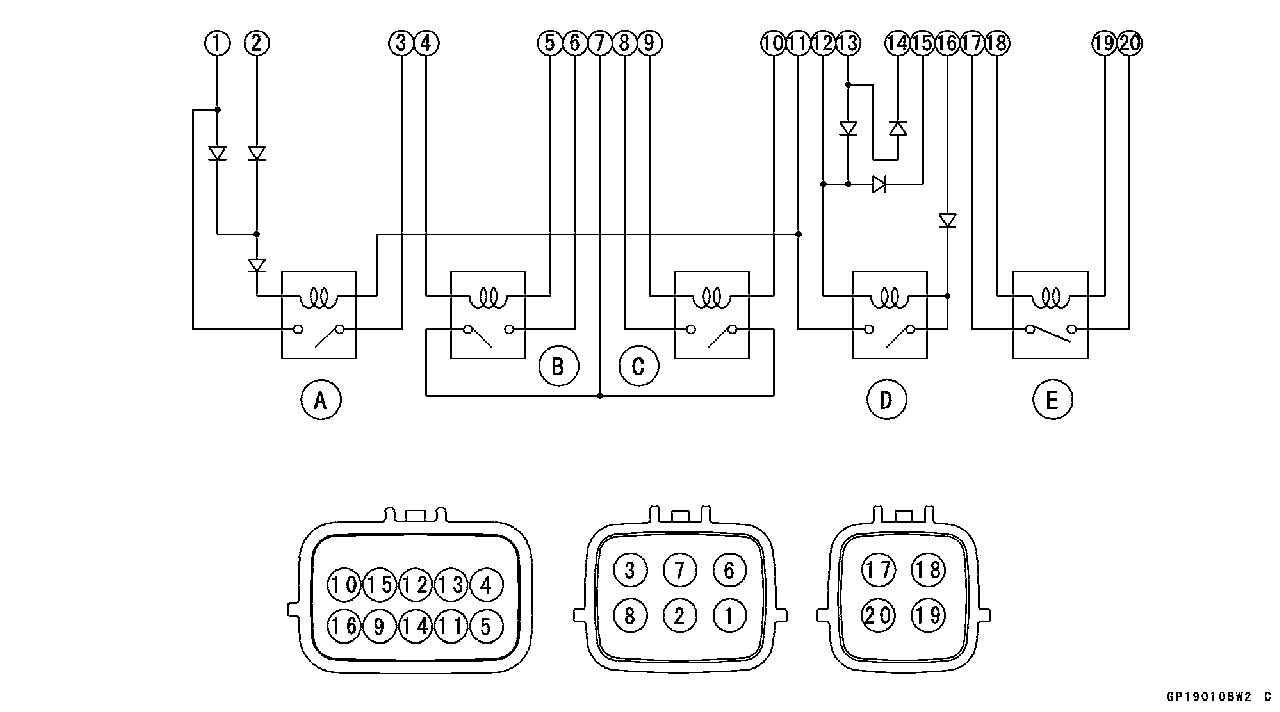
 • Remove:
• Remove: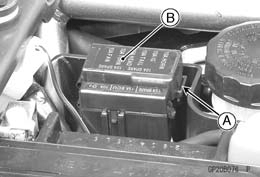 Fuse Box Fuse Removal
Fuse Box Fuse Removal • Pull the fuses [A] straight out of the fuse box with needle nose pliers.
• Pull the fuses [A] straight out of the fuse box with needle nose pliers. 15 A ECU Fuse Removal
15 A ECU Fuse Removal • Pull out the ECU fuse [A] from the fuse box.
• Pull out the ECU fuse [A] from the fuse box. Fuse Inspection
Fuse Inspection