Заглавная страница Избранные статьи Случайная статья Познавательные статьи Новые добавления Обратная связь FAQ Написать работу КАТЕГОРИИ: ТОП 10 на сайте Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрацииТехника нижней прямой подачи мяча. Франко-прусская война (причины и последствия) Организация работы процедурного кабинета Смысловое и механическое запоминание, их место и роль в усвоении знаний Коммуникативные барьеры и пути их преодоления Обработка изделий медицинского назначения многократного применения Образцы текста публицистического стиля Четыре типа изменения баланса Задачи с ответами для Всероссийской олимпиады по праву 
Мы поможем в написании ваших работ! ЗНАЕТЕ ЛИ ВЫ?
Влияние общества на человека
Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрации Практические работы по географии для 6 класса Организация работы процедурного кабинета Изменения в неживой природе осенью Уборка процедурного кабинета Сольфеджио. Все правила по сольфеджио Балочные системы. Определение реакций опор и моментов защемления |
Exercise 6. Find corresponding equivalentsСодержание книги
Похожие статьи вашей тематики
Поиск на нашем сайте
Exercise 7. Match the terms with their definitions:
Exercise 8. Translate the following words and word combinations into English: Двостороннє запалення легень, подальша робота, довгострокові фізіологічні процеси, новий вид досліджень, обдарований молодий фізіолог, шлункова функція собак, фізіологічна лабораторія, вівісекція, передавати від покоління до покоління, створити унікальне свідчення, науково-дослідна робота, мимовільні реакціі, голова клініки, проходити вівісекцію, бути схильним до виділення слини, рефлекторні дії, отримати Нобелівську премію.
Exercise 9. Read information about “The Four Temperaments” and match the paragraph with a correct type:
This temperament is fundamentally introverted and thoughtful. People with this type can be highly creative in activities such as poetry and art - and can become preoccupied with the tragedy and cruelty in the world. Often they are perfectionists. They are self-reliant and independent.
This temperament is impulsive and pleasure-seeking; people are sociable and charismatic. They tend to enjoy social gatherings and making new friends. They are usually quite creative, often daydream, sensitive and thoughtful. Personalities of this type are chronically late, and tend to be forgetful and sometimes a little sarcastic. They are talkative and not shy.
This temperament is fundamentally relaxed and quiet, tend to be content with themselves and are kind. They are ashy and often prefer stability to uncertainty and change. They are consistent, relaxed, calm, rational, curious, and observant, qualities that make them good administrators. They can also be passive-aggressive.
This temperament is fundamentally ambitious and leader-like. They have a lot of aggression, energy, and/or passion, and try to instill it in others. They can dominate people of other temperaments. They like to be in charge of everything. They do not have in-between setups, only one extreme to another. People with this type are very much prone to mood swings.
Exercise 10. Look at the table. Pay attention to the Sequence of Tenses. Translate the sentences into your native language:
1. The physician said that the sanatorium treatment would be helpful. 2. I didn’t know you had had practice at the hospital. 3. The patient said that 2 hours before the admission he had felt an unbearable pain in epigastria area. 4. I was told that the conjunctiva was infected. 5. The doctor supposed that antibiotic treatment would be changed. 6. The patient was told that the life in subtropical climate would be very helpful. 7. Our teacher told us that Pavlov had carried out his experiments on dogs. 8. The woman said that her stomachache was unbearable. Exercise 11. Put questions to the underlined words: 1. Pavlov performed and directed experiments on digestion. 2. Pavlov and his researchers observed and began the study of transmarginal inhibition (TMI). 3. TMI is the body's natural response of shutting down when exposed to overwhelming stress or pain by electric shock 4. Carl Jung continued Pavlov's work on TMI. He correlated the observed shutdown types in animals with his own introverted and extroverted temperament types in humans. 5. The concept for which Pavlov is famous is the " conditioned reflex ". 6. It is popularly believed that Pavlov always signaled the occurrence of food by ringing a bell. 7. Pavlov’s writings record the use of a wide variety of stimuli, including electric shocks, whistles, metronomes, tuning forks, and a range of visual stimuli, in addition to the ring of a bell. 8. It is less widely known that Pavlov's experiments on the conditional reflex extended to children. Some of the children underwent surgical procedures, similar to those performed on the dogs, for the collection of saliva.
Завдання для самостійної роботи студентів (СРС)
Exercise 1. Topical vocabulary:
Exercise 2. Read the following word-combinations and translate them. Make up 3 sentences of your own with any of them: canal: alimentary canal, musculomembraneous canal, nasal canal, root canal cavity: oral cavity, abdominal cavity, pulp cavity, nasal cavity, thoracic cavity gland: salivary gland, endocrine gland, urethral gland, mucous gland, lymph gland tube: thin-wall muscular tube, inner-tube, test-tube, Fallopian tube, drainage tube palate: hard palate, soft palate, cleft palate, to have a delicate palate, depraved palate
Exercise 3. Translate the following word combinations into your native language: To extend from the oral cavity to the anus, the first division, to pass through the pharynx to the esophagus, the upper part of the abdomen, to be composed of, a thin-walled muscular tube, to absorb water,the largest gland in the human body, a major role in metabolism, a number of functions in the body, decomposition of red blood cells, a hollow sac, a long thin gland.
Exercise 4. Put words in the appropriate column: Ileum, heart, vessel, anus, jejunum, artery, duodenum, tongue, vein, pharynx, stomach, capillary, esophagus, intestine, aorta, atria, rectum, oral cavity, salivary glands, mouth, chamber, caecum, colon, teeth, ventricle.
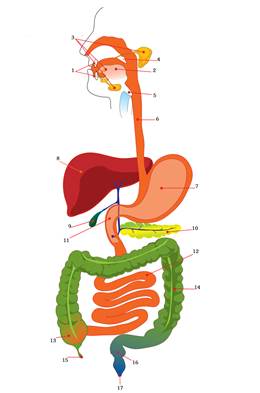
Exercise 5. Read and translate the text: Anatomy of Alimentary Tract The alimentary tract is a musculomembraneous canal about 8½ metres in length. It extends from the oral cavity to the anus. It consists of the mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and large intestine. The liver with gallbladder and pancreas are the large glands of the alimentary tract. The first division of the alimentary tract is formed by the mouth. Important structures of the mouth are the teeth and the tongue, which is the organ of taste. The soft and hard palates and the salivary glands are also in the oral cavity. From the mouth food passes through the pharynx to the esophagus and then to the stomach. The stomach is a muscular, hollow, dilated portion of the alimentary canal. It is in the upper part of the abdomen under the diaphragm. It measures about 21-25 cm in length, 8-9 cm in its greatest diameter. It has a capacity of from 2.14 to 4.28 litres. The small intestine is a thin-walled muscular tube about 6.5 metres long. It is located in the middle portion of the abdominal cavity. The small intestine is composed of the duodenum, jejunum and ileum. The large intestine is the last part of the alimentary tract. Its function is to absorb water from the remaining indigestible food matter, and then to pass useless waste material from the body. It is about 1.5 metres long. It is divided into caecum, colon and rectum. The liver is the largest gland in the human body. It is in the right upper part of the abdominal cavity under the diaphragm. The weight of the liver is 1,500 g. This organ plays a major role in metabolism and has a number of functions in the body, including glycogen storage, decomposition of red blood cells, plasma protein synthesis, hormone production, and detoxification. The gallbladder is a hollow sac lying on the lower surface of the liver, where bile is stored, before it is released into the small intestine. The pancreas is a long thin gland lying behind the stomach.
Exercise 6. Answer the questions to the text: 1. What is the alimentary tract? 2. What does the alimentary tract consist of? 3. What is the 1st division of the alimentary tract formed by? 4. What is the stomach? 5. What is the small intestine? 6. What is the function of the large intestine? 7. What largest glands in the human body do you know? 8. What is the function of the gallbladder? Exercise 7. Translate the following word combinations into English: Травний тракт, глотка та стравохід, черевна порожнина, простягатися від порожнини рота до ануса, під діафрагмою, мати ємкість, тонкостінна м'язова трубка, середня частина черевної порожнини, дванадцятипала та порожниста кишки, найбільша залоза в тілі людини, залишки неперетравленої їжі, ряд функцій в організмі, розкладання еритроцитів, тонка довга залоза, відігравати важливу роль в обміні речовин, товста та пряма кишки.
Exercise 8. Match the terms with their definitions:
Exercise 9. Write down organs in their appropriate position:
Stomach caecum colon appendix liver teeth esophagus rectum gallbladder epiglottis tongue soft palate pancreas ileum rectum anus salivary glands
Exercise 10. Say what organ is spoken about: I. This organ is the largest gland in the human body. It is in the upper part of the abdominal cavity under the diaphragm in the right side of the abdomen. Its upper surface is convex. This organ consists of small lobules connected together by connective tissue, different vessels and nerves.
II. This organ is pyriform (грушевидный) in shape. It is a dilated portion of the alimentary canal. It is in the upper part of the abdomen under the diaphragm. The liver is above this organ, and the colon is below it. The pancreas is behind this organ.
III. It is the beginning of the alimentary tract and the digestion starts here when taking the first bite of food. Chewing breaks the food into pieces that are more easily digested, while saliva mixes with food to begin the process of breaking it down into a form your body can absorb and use.
IV. This organ is the portion of the alimentary tract that is located between the stomach and rectum. In the human being it is divided in to two parts. Its function is to digest food and to enable the nutrients released from that food to enter into the bloodstream.
V. It is a tubular organ that lies behind the trachea and heart and in front of the spinal colomn; it passes through the diaphragm before entering the stomach.
VI. This organ is a part of two different systems of the body, digestive system and respiratory system. It is a passageway leading from the mouth and nose to the esophagus and larynx.
VII. This is a long, narrow gland that is located across the upper abdomen, behind the stomach and the spleen. It produces important digestive enzymes and hormone called insulin.
VIII. This is a hollow organ located beneath the right lobe of the liver and measures 8 centimeters in length. Its function is to store bile.
IX. This is a thin cartilaginous flap that covers the entrance to the larynx during swallowing, preventing food from entering the trachea.
X. It is the last part of the digestive system. Water is absorbed here and the remaining waste material is stored as feces before being removed by defecation.
Exercise 11. Fill in prepositions from the box below where necessary and translate into your native language:
One of the most common locations ____ a foreign body is the alimentary tract. It is possible ___ foreign bodies to enter the tract from the mouth, or from the rectum. The objects most commonly swallowed ____ children are coins. Meat impaction is more common ____ adults. Swallowed objects are more likely to lodge ____ the esophagus or stomach than ____ the pharynx or duodenum. ____ the person who swallowed the foreign body is doing well, usually a x-ray image will be taken. It will show any metal objects, and should be repeated a few days later to confirm that the object has passed all the way _____ the alimentary tract. Also it needs to be confirmed that the object is not stuck _____ the airways, in the bronchial tree. Most objects that are swallowed will pass all the way ____ the gastrointestinal tract unaided. ____ the foreign body causes problems like pain, vomiting ____ bleeding it must be removed.
Exercise 12. Arrange the following sentences in a correct order to describe the following term “stomach”: 1. The stomach has three tasks in digestion: mixing foods with gastric juices, storing swallowed food and liquid, moving food into the small intestine. 2. It is located in the upper part of the abdomen under the diaphragm. 3. The stomach is a hollow, saclike organ enclosed in a muscular wall. 4. The stomach receives food from the esophagus. 5. These flexible muscles allow the stomach to extend when you eat. 6. As food reaches the end of the esophagus, it enters the stomach through a muscular valve called the lower esophageal sphincter.
Exercise 13. Continue the following sentences using the text to describe the following term “intestine”: 1. Intestine is the last part of the alimentary tract and consist of ….. and …... 2. The small intestine is composed of ….., ….., …... 3. The large intestine is divided into ….., ….. and …... 4. The function of intestine is ….. and then …...
Exercise 14. Translate word-combinations with Participle into your native language: Saliva moistening the food; disease, spreading rapidly; food, containing a lot of vitamins; organ playing an important role; blood containing digested nutrients; teeth grinding the food; patient suffering from different diseases; tract extending from the mouth to the anus; food matters remaining indigestible; walls of the intestine absorbing water.
Exercise 15. Join two parts of the sentences and translate:
Exercise 16. Put questions to the underlined words: 1. First step in the digestive system take place in the mouth. 2. The soft palate is a continuation of the soft tissues covering the hart palate. 3.The weight of the largest of the salivary glands is 28gr. 4. The shape of the stomach changes when it dilates. 5. The duodenum is called so because its length measures about the length of twelve fingers. 6. The liver consisting of lobes is covered with a fibrous coat. 7. Foreign body that enters the alimentary tract can cause different problems. 8. Gastroendoscopy shows all the damages in the stomach.
Exercise 17. Open the brackets using the verb in the appropriate form: 1. The mechanical digestion of the food (to start) by the action of mastication and the wetting contact of saliva. 2. The esophagus (to line) with smooth muscle, which forces the food down the pipe to the stomach. 3. When food is swallowed, the stomach (to produce) hydrochloric acid. 4. The shape of the stomach (to change) when it delates and its borders greatly extend. 5. The liver (to play) a major role in metabolism and (to have) a number of functions in the body. 6. Discharged from the liver bile (to store) in the gallbladder. 7. 95% of absorption of nutrients (to occur) in the small intestine. 8. Waste material (to eliminate) from the rectum during defecation.
Завдання для самостійної роботи студентів (СРС)
Exercise 1. Topical vocabulary:
Exercise 2. Make nouns from the verbs with the help of suffix -tion and translate into your native language: to absorb, to product, to masticate, to create, to excrete, to digest, to stimulate, to salivate, to activate, to distribute, to penetrate, to irritate, to inhale. Exercise 3. Some of the following words don’t form adjectives with the help of suffixes. Try to form adjectives from the given nouns and translate them:
Exercise 4. Combine the adjectives with the proper nouns given below. Translate your word combinations: Adjectives: inner, serous, salivary, hard, exact, vital, connective, pale; Nouns: length, palate, coat, capacity, tissue, gland, layer, face.
Exercise 5. Fill the dialogue with necessary words from the “Anatomy of Alimentary tract” and act it! - Hello. How do you do! - How do you do! - Are you free now? - Yes, I’m. I’m trying to prepare my anatomy lesson on alimentary tract! But I don’t know it well. Can you help me? - Sure. To begin with, the alimentary tract is a ….................. canal about 8.5 meters in length. It extends from …............. to …................. - I know this. If I’m not mistaken it consists of the …...........,...............,................., …..............., …................. and …..................... - Yes, you are right. - Where does the food go from the mouth? - It passes through the pharynx to the esophagus and then to the stomach. - Certainly. - I’ve already mentioned that there is the small intestine and the large intestine in the alimentary tract. The small intestine is composed of the ….............., …...............and ….......... Do you want me to tell you about the large intestine? - No, thanks. As far as I know it is divided into …............, …........... and ….............. - Right. Do you know that the largest gland in the human body is …...............? - Yes, I do. I know that the gallbladder and …..............are also the large glands of the alimentary tract. - You are absolutely right. - Thank you very much for helping me.
Exercise 6. Translate the following word combinations into your native language: To start to salivate, the digestive process, the body's source of fuel, to be broken down into tiny pieces, to break down fats into fatty acids and glycerol, the mechanical digestion, the chemical digestion, to absorb more efficiently, to distribute throughout the body, a brain reflex triggers the flow of saliva, to break down starch into simpler sugars, to require stimulation of receptors, sensory impulses to the brain stem, to prevent food from entering the trachea and choking. Exercise 7. Read and translate the text:
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Последнее изменение этой страницы: 2016-08-14; просмотров: 594; Нарушение авторского права страницы; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! infopedia.su Все материалы представленные на сайте исключительно с целью ознакомления читателями и не преследуют коммерческих целей или нарушение авторских прав. Обратная связь - 216.73.216.214 (0.008 с.) |