Заглавная страница Избранные статьи Случайная статья Познавательные статьи Новые добавления Обратная связь FAQ Написать работу КАТЕГОРИИ: ТОП 10 на сайте Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрацииТехника нижней прямой подачи мяча. Франко-прусская война (причины и последствия) Организация работы процедурного кабинета Смысловое и механическое запоминание, их место и роль в усвоении знаний Коммуникативные барьеры и пути их преодоления Обработка изделий медицинского назначения многократного применения Образцы текста публицистического стиля Четыре типа изменения баланса Задачи с ответами для Всероссийской олимпиады по праву 
Мы поможем в написании ваших работ! ЗНАЕТЕ ЛИ ВЫ?
Влияние общества на человека
Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрации Практические работы по географии для 6 класса Организация работы процедурного кабинета Изменения в неживой природе осенью Уборка процедурного кабинета Сольфеджио. Все правила по сольфеджио Балочные системы. Определение реакций опор и моментов защемления |
Features and Tools Usage How to RunСодержание книги
Поиск на нашем сайте
Users and Groups Assigns access rights to individual
users or groups
Use the (Local) Users and Groups category in Computer Management.
Chapter 6: Operating Systems 115
Figure 6-5 Computer Management (Windows 7).
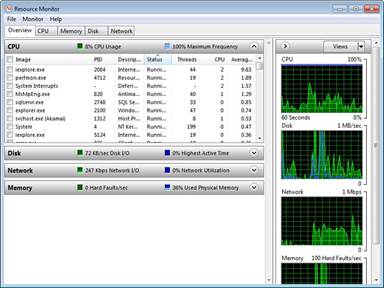
Figure 6-6 Resource Monitor (Windows 7).
MSCONFIG (Table 6-8) provides startup management features. MSConfig can be started from the Run menu in Windows XP, or by using the integrated Instant Desktop Search feature in Windows Vista and 7. Note that the Windows XP version of MSConfig also includes tabs for managing sys-tem.ini and win.ini configuration files used by legacy programs. 116 CompTIA A+ Quick Reference
Table 6-8 MSCONFIG Tabs
Windows includes a Task Manager feature (Table 6-9) to provide real-time information about com-puter activity. To start Task Manager in Windows XP, press Ctrl+Alt+Del. In Windows Vista and 7, press Ctrl+Alt+Del to display a menu that includes a Start Task Manager option.
Table 6-9 Task Manager Tabs
Windows Disk Management (see Figure 6-8) is a subnode of the Storage node in Computer Management. It is used to perform the following tasks:
Drive status —Lists the status for hard disks, solid-state disks (SSD), and flash drives con-nected to the computer. (Windows XP’s Disk Management also lists optical drives and removable-media drives if removable storage management is enabled.)
Assigning drive letters —Assign one or more drive letters to a drive.
Drive mount paths —Mounting a drive for access via an empty NTFS folder. Creating partitions —Create and format disk partitions.
Split partitions —Shrink an existing partition and assign the empty space to a new volume(drive letter).
Adding array —Create disk array from two or more selected drives.
Convert to dynamic disk —Dynamic disks can be expanded and can be added to arrays. Chapter 6: Operating Systems 117
Figure 6-7 The Services tab of Windows 7’s Task Manager.
Figure 6-8 Windows 7’s Disk Management.
Windows includes various run line programs used for system management. Table 6-10 provides a quick reference. 118 CompTIA A+ Quick Reference
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Последнее изменение этой страницы: 2017-02-08; просмотров: 404; Нарушение авторского права страницы; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! infopedia.su Все материалы представленные на сайте исключительно с целью ознакомления читателями и не преследуют коммерческих целей или нарушение авторских прав. Обратная связь - 216.73.216.33 (0.006 с.) |