

Мы поможем в написании ваших работ!
ЗНАЕТЕ ЛИ ВЫ?
|
Degrees of comparison of adjectives and adverbs
| Adjectives and Adverbs
| Positive
| Comparative
| Superlative
| Formation
| | One-syllable adjectives
and adverbs
| old
wise
hot
easy
fast
early
| older, elder wiser
hotter
easier
faster
earlier
| oldest, eldest
wisest
hottest
easiest
fastest
earliest
| For most
one-syllable adjectives and adverbs, -er and -est are added.
| | Two-syllable adjectives and adverbs
| famous
slowly
| more famous
more slowly
| most famous
most slowly
| For most two- syllable adj. and adv., more and most are used.
| |
| busy
pretty
| busier
prettier
| busiest
prettiest
| -Er / -est are used with two-syllable adjectives that end in -y. The -y is changed to -i.
| |
| clever
gentle
friendly
| cleverer
more clever
gentler
more gentle
friendlier
more friendly
| cleverest
most clever
gentlest
most gentle
friendliest
most friendly
| Some two-syllable adjectives use -er / -est or more / most:able, pleasant, angry,
handsome,simple, common, quiet,
narrow, sour, polite, cruel.
| | Adjectives and adverbs with three
or more
syllables
| important
productive
carefully
| more important
more productive
more
carefully
| most
important
most productive
most
carefully
| More and most are used with long adjectives and adverbs.
| | Irregular Adjectives and Adverbs
| | good/well
bad/badly
far
much/many
little
| better
worse
farther/further
more
less
| best
worst
farthest/furthest
most
least
|
Numerals
| Cardinal Numerals (how many?)
| Ordinal Numerals (Which?)
| |
1,000 1,000,000
| one
two
three
four
five
six
seven
eight
nine
ten
eleven
twelve
thirteen
fourteen
fifteen
sixteen
seventeen
eighteen
nineteen
twenty
twenty-one
twenty-two
twenty-three
twenty-four
twenty-five
twenty-six
twenty-seven
twenty-eight
twenty-nine
thirty
forty
fifty
sixty
seventy
eighty
ninety
a hundred
a thousand
a million
| first
second
third
fourth
fifth
sixth
seventh
eighth
ninth
tenth
eleventh
twelfth
thirteenth
fourteenth
fifteenth
sixteenth
seventeenth
eighteenth
nineteenth
twentieth
twenty-first
twenty-second
twenty-third
twenty-fourth
twenty-fifth
twenty-sixth
twenty-seventh
twenty-eighth
twenty-ninth
thirtieth
fortieth
fiftieth
sixtieth
seventieth
eightieth
ninetieth
hundredth
thousandth
millionth
| |
1,006
5,000
260,127
| a/one hundred and forty
four hundred
a/one thousand and six
five thousand
two hundred and sixty thousand, one hundred and twenty-seven
| | Dates
| March 10, 1998 ¾ the tenth of March nineteen ninety-eight or March the tenth nineteen ninety-eight
| | Fractional Numerals
| Common Fractions: 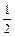 ¾ a half; ¾ a half;  ¾ a quarter; ¾ a quarter;
 ¾ a/one fifth; ¾ a/one fifth;  ¾ three fifths; ¾ three fifths;
 ¾ one and a half; ¾ one and a half;
 ¾ three and four fifths;
Decimal Fractions: 0.1 ¾ nought point one;
10.92 ¾ ten point nine two;
8.04 ¾ eight point nought four; ¾ three and four fifths;
Decimal Fractions: 0.1 ¾ nought point one;
10.92 ¾ ten point nine two;
8.04 ¾ eight point nought four;
| | Percentage
| a kind of decimal fraction, denominator of which is always 100: 2 % ¾ 2 per cent ¾ 2 p.c. ¾ two per cent.
| | Roman
Numerals
| 1 ¾I
2¾II
3 ¾III
4¾IV
5 ¾ V
6 ¾ VI
7 ¾ VII
8 ¾ VIII
9 ¾ IX
10 ¾ X
11 ¾ XI
12 ¾ XII
13 ¾ XIII
14 ¾ XIV
15 ¾ XV
| 16 ¾ XVI
17 ¾ XVII
18 ¾ XVIII
19 ¾ XIX
20 ¾ XX
21 ¾ XXI
30 ¾ XXX
40 ¾ XL
50 ¾ L
60 ¾ LX
70 ¾ LXX
80 ¾ LXXX
90 ¾ XC
100 ¾ C
1000 ¾ M
| | | | | |
NUMBERS IN MEASUREMENT
| Weight
Measure
Міри ваги
| 1 dram
1 ounce
1 pound
1 stone
1 quarter
1 hundredweight
1 ton
| драхма
унція
фунт
стон
квартер
хандредвейт
тонна
| dr
oz (16 dr)
lb (16 oz)
st (14 lb)
gr (28 lb)
hwt (112 lb)
tn (20 hwt)
| 1.77 g
28.35 g
453.59 g
6.35 kg
12.7 kg
50.8 kg
1016 kg
| | Linear Measure
Лінійні міри
| 1 inch
1 foot
1 yard
1 mile
1 International
Nautical Mile
| дюйм
фут
ярд
миля
миля морська
| in
ft (12 in)
yd (3 ft)
ml (1760 yd)
INM (6076 ft)
| 2.54 cm
30.48 cm
91.44 cm
1609.33 m
1.852 km
| | Dry Measure
Міри сипких речовин
| 1 gill
1 pint
1 quart
1 gallon
1 bushel
1 quarter
| джил
пінта
кварта
галон
бушель
квартер
| gi
pt (4 gills)
qt (2pt)
gal (4qt)
bu
qr (8 bu)
| 0.14 l
0.57 l
1.14 l
4.55 l
36.35 l
290.94 l
| | Square Measure
Міри площини
| 1 square inch
1 square foot
1 square yard
1 acre
1 square mile
| кв. дюйм
кв. фут
кв. ярд
акр
кв. миля
| sq in
sq ft (144 sq in)
sq yd (9 sq ft)
ac (4.8 sq yd)
sq ml (640 ac)
| 6.45 cm2
9.29 dm2
0.836 m2
0.4 hectare
2.59 km2
| | Cubic Measure
Міри об’єму
| 1 cubic inch
1 cubic foot
1 cubic yard
1 register ton
| куб. дюйм
куб. фут
куб. ярд
тонна
реєстрова
| cu in
cu ft (1728
cu in)
cu yd (27 cu ft)
reg t (100 cu ft)
| 16.39 cm3
28.32 cm3
764.53 cm3
2.83 m3
| | Time Measure
Міри часу
| 1 minute
1 hour
1 day
1 week
| хвилина
година
день
тиждень
| 60 seconds
60 minutes
24 hours
7 days
| | Angles Measure
Міри кута
| 1 minute
1 degree (1)
1 right angle
1 circle
| хвилина
градус
прямий кут
розгорнений
кут
| 60 seconds (60¢¢)
60 minutes (60¢)
90 degrees (90°)
360 degrees (360°)
4 right angles
|
ОСОБОВІ ФОРМИ ДІЄСЛОВА
FINITE FORMS OF THE VERB
| Дійсний спосіб The Indicative Mood
| | Активний стан Active Voice to ask
| | Пасивний стан Passive Voice to be asked
| | Неозначені часи Indefinite Tenses
to ask
| Доконані часи Perfect Tenses
to have asked
| | to be asked
| to have been asked
| | Present
| Past
| Future
| Present
| Past
| Future
| | ask
asks
|
asked
| shall
ask
will
| have
asked
has
|
had asked
| shall
have
will asked
| | am
is asked
are
| was
asked
were
| shall
be
will asked
| have
been
has asked
| had been
asked
| shall have
been
will asked
| | Тривалі часи
Continuous Tenses
to be asking
| Перфектно-тривалі часи
Perfect Continuous Tenses
to have been asking
| | to be being asked
| —
| | Present
| Past
| Future
| Present
| Past
| Future
| | am
is asking
are
| was
asking
were
| shall be asking
will
| have
been
has asking
| had been
asking
| shall have
been
will asking
| | am
is being
are asked
| was
being
asked
were
| —
| —
| —
| —
|
INDEFINITE TENSES
(to work, to write)
| Present Indefinite
| | work (s), write (s)
| | Affirmative
| Interrogative
| Negative
| Interrogative-
Negative
| | I work, write
He/she works, writes
We/you/they work, write
| Do I work, write?
Does he/she work, write?
Do we/you/
they work, write?
| I do not work, write
He/she does not work, write
We/you/they do not work, write
| Do I notwork,
write?
Does he/she not work, write?
Do we/you/they not work, write?
| | Past Indefinite
| | worked, wrote
| | Affirmative
| Interrogative
| Negative
| Interrogative-
Negative
| | I worked, wrote
He/she worked, wrote
We/you/they worked, wrote
| Did I work, write?
Did he/she work, write?
Did we/you/
they work, write?
| I did not work,
write
He/she did not work, write
We/you/they/
did not work, write
| Did I not work,
write?
Did he/she not work, write?
Did we/you/they not work, write?
| | Future Indefinite
| | shall/will + work, write
| | Affirmative
| Interrogative
| Negative
| Interrogative-
Negative
| | I/we shall work, write
He/she/you/
they will work, write
| Shall I/we work, write?
Will he/she/
you/they work, write?
| I/we shall not work, write
He/she/you/
they will not work, write
| Shall I/we not work, write?
Will he/she/
you/they not work, write?
| | | | | | |
CONTINUOUS TENSES
(to work, to write)
| Present Continuous
| | am, is, are + working, writing
| | Affirmative
| Interrogative
| Negative
| Interrogative-
Negative
| | I am working,
writing
He/she is
working, writing
We/you/they are working, writing
| Am I working,
writing?
Is he/she working,
writing?
Are we/you/
they working, writing?
| I am not working,
writing
He/she is not
working, writing
We/you/they are not working, writing
| Am I not working,
writing?
Is he/she not
working, writing?
Are we/you/they not working, writing?
| | Past Continuous
| | was, were + working, writing
| | Affirmative
| Interrogative
| Negative
| Interrogative-
Negative
| | I/he/she was working, writing
We/you/they were working, writing
| Was I/he/she working, writing?
Were we/you/
they working, writing?
| I/he/she was not working, writing
We/you/they/
were not working, writing
| Was I/he/she not working, writing?
Were we/you/
they not working, writing?
| | Future Continuous
| | shall/will + be working, writing
| | Affirmative
| Interrogative
| Negative
| Interrogative-
Negative
| | I/we shall be working, writing
He/she/you/
they will be working, writing
| Shall I/we be working, writing?
Will he/she/
you/they be working, writing?
| I/we shall not be working, writing
He/she/you/
they will not be working, writing
| Shall I/we not be working, writing?
Will he/she/
you/they not be working, writing?
|
PERFECT TENSES
(to work, to write)
| Present Perfect
| | have, has + worked, written
| | Affirmative
| Interrogative
| Negative
| Interrogative-
Negative
| | I/we/you/they
have worked, written
He/she has
worked, written
| Have I/we/
you/they worked, written?
Has he/she worked, written?
| I/we/you/they have not worked, written
He/she has not worked, written
| Have I/we/
you/they not worked, written?
Has he/she notworked, written?
|
|
Past Perfect
| | had+ worked, written
| | Affirmative
| Interrogative
| Negative
| Interrogative-
Negative
| | I/he/she/we/
you/they had worked, written
| Had I/he/she/
we/you/they worked, written?
| I/he/she/we/
you/they had not worked, written
| Had I/he/she/
we/you/they notworked, written?
|
| Future Perfect
| | shall/will have + worked, written
| | Affirmative
| Interrogative
| Negative
| Interrogative-
Negative
| | I/ We shallhave worked, written
He/she/you/
they will have worked, written
| Shall I/we have worked, written?
Will he/she/
you/they have worked, written?
| I/ We shall not have worked,
written
He/she/you/
they will not have worked, written
| Shall I/we not have worked, written?
Will he/she/
you/they not
haveworked, written
|
PERFECT CONTINUOUS TENSES
(to work, to write)
| Present Perfect Continuous
| | have, has + been + working, writing
| | Affirmative
| Interrogative
| Negative
| Interrogative-
Negative
| | I/we/you/they have been working, writing
He/she has been working, writing
| Have I/we/
you/they been working, writing?
Has he/she been working, writing?
| I/we/you/they have not been working, writing
He/she has not been working, writing?
| Have I/we/
you/ they not been working, writing?
Has he/she not been working, writing?
| | Past Perfect Continuous
| | had + been + working, writing
| | Affirmative
| Interrogative
| Negative
| Interrogative-
Negative
| | I/he/she/we/
you/they had been working, writing
| Had I/he/she/
we/you/they been working, writing?
| I/he/she/we/
you/they had not been working, writing
| Had I/he/she/
we/you/they not been working, writing?
| | Future Perfect Continuous
| | shall/will + have been working, writing
| | Affirmative
| Interrogative
| Negative
| Interrogative-
Negative
| | I/we shall have been working, writing
He/she/you/
they will have been working, writing
| Shall I/we have been working, writing?
Will he/she/
you/they have been working, writing?
| I/we shall not have been working, writing
He/she/you/
they will not have been working, writing
| Shall I/we not have been working, writing?
Will he/she/
you/they not have been working, writing?
| THE FUNCTIONS OF THE VERB «TO BE»
| Functions
| Examples
| | 1. The Notional Verb
| He is at home now. The students are in the classroom.
| | 2. An Auxiliary Verb
| He is writing a letter. I was asked a difficult question.
| | 3. A Link Verb
| Jhon is a student. He is intelligent. He is the best student in our group.
| | 4. A Modal Verb
| We are to meet at noon. They are to begin this work at once.
| THE FUNCTIONS OF THE VERB «TO HAVE»
| Functions
| Examples
| | 1. The Notional Verb
| She has a large family. We have got a comfortable flat.
| | 2. An Auxiliary Verb
| He has graduated from the University. I have been waiting for you for half an hour.
| | 3. A Modal Verb
| I have to get up early on Mondays. They had to go there. He will have to do it.
|
THE FUNCTIONS OF THE VERB «TO DO»
| Functions
| Examples
| | 1. The Notional Verb
| The exercise was done well. You didn't do anything to help her.
| | 2. An Auxiliary Verb
a) The Present and Past Indefinite (interrogative and negative forms)
b) The Imperative Mood (negative form)
c) to express emphasis
|
He doesn'twork here.
Did you see him yesterday? — Yes, I did.
Don't be late for the lessons.
But I do know him.
|
General Questions
| Predicate or auxiliary verb
| Sub-
ject
| Part of
the Predicate
| Object
| Adverbial Modifiers
| Short Answers
| |
|
|
|
|
| Affirmative
| Negative
| | Is
Do
Does
Did
Will
Are
Was
Can
| he
you
she
it
he
you
Ann
you
|
take
live
rain
be living?
studying?
swim?
|
books
French?
| at home?
here?
in Kyiv?
last night?
there?
in class?
| Yes, he is.
Yes, I do.
Yes,she does
Yes, it did.
Yes, he will.
Yes, I am.
Yes, she was.
Yes, I can.
| No, he isn't.
No, I don't.
No, she doesn't.
No, it didn't.
No, he won't.
No, I'm not.
No, she wasn't.
No, I can't.
|
Tag questionS
| Jack cancome, can't he?
Fred can't come, can he?
| A tag question is a question added at the end of
a sentence. Speakers use tag questions chiefly to make sure their information is correct or to seek agreement.
| | Affirmative Sentence + Negative tag = Affirmative answer expected
Mary is here, isn't she? Yes, she is.
You like tea, don't you? Yes, I do.
Theyhave left,haven't they? Yes, they have.
| | Negative Sentence + Affirmative tag = Negative answer expected
Mary isn't here,is she? No, she isn't.
You don't like tea, do you? No, I don't.
They haven't left, have they? No, they haven't.
| | This/Thatis your book, isn't it?
These/Those are yours, aren't they?
| The tag pronoun for this/that = it
The tag pronoun for these/those= they
| | There is a meeting tonight, isn't there?
| In sentences with there + be, there is used in the tag.
| | Everything is okay, isn't it?
Everyonetook the test, didn'tthey?
| Personal pronouns are used to refer to indefinite pronouns. They is usually used in a tag to refer to everyone,someone,everybody,somebody,no one, nobody.
| | Nothing is wrong, isit?
Nobody calledon the phone, did they?
You've never beenthere, have you?
| Sentences with negative words take affirmative tags.
| | I amsupposed to be here, am I not?
I am supposed to be here, aren't I?
| am I not? is formal English.
aren't I? is common in spoken English.
| | | | |
Question words
When
| When did they arrive?
Whenwill you come?
| Yesterday.
Next Monday.
| When is used to ask questions about time.
|
Where
| Where is she?
Where can I find a pen?
| At home.
In that drawer.
| Where is used to ask questions about place.
|
Why
| Why did he leave early?
Why aren't you coming with us?
| Because he's ill.
I'm tired.
| Why is used to ask questions about reason.
|
How
| How did you come to school?
How does he drive?
| By bus.
Carefully.
| How generally asks about manner.
| | How muchmoney does it cost?
How manypeople came?
| Ten dollars.
Fifteen.
| Howis used with much and many.
| | How old are you?
How coldis it?
How soon can you get there?
How fast were you driving?
How long has he been here?
How often do you write home?
How far is it to Paris from here?
| Eighteen.
Ten below zero.
In ten minutes.
50 miles an hour.
Two years.
Every week.
500 miles.
| Howis also used with adjectives and adverbs.
How long asks about length of time.
How oftenasks about frequency.
How farasks about distance.
|
More questions with How
| Question
| Answer
|
| | a) How do you spell «coming»? c-o-m-i-n-g.
b) How do you say «yes» in Japanese?Hai.
c) How do you say/pronounce this word?
| To answer a): Spell the word.
To answer b): Say the word.
To answer c): Pronounce the word.
| | d) How are getting along? Great.
e) How are you doing? Fine.
f) How's it going? Okay.
So-so.
| In d), e), and f): How is your life?
Is your life okay? Do you have any problems?
NOTE: f) is often used in greetings:
Hi, Bob. How's it going?
| | g) How do you feel? Terrific!
How are you feeling? Wonderful!
Great!
Fine.
Okay.
So-so.
A bit under
the weather.
Not so good.
Terrible!
Awful!
| The questions in g) ask about health or about general emotional state.
| | h) How do you do? How do you do?
| How do you do? is used by both speakers when they are introduced to each other in a somewhat formal situation.
|
Who
| Whocan answer that question?
Whocame to visit you?
| I can.
Jane and Tom.
| Who is used as the subject of a question.
It refers to people.
| | Who is coming to dinner tonight?
Who wantsto come with me?
| Ann and Tom.
We do.
| Who is usually followed by
a singular verb even if
the speaker is asking about more than one person.
|
Whose
| Whose bookdid you borrow?
Whose keyis this? (Whose is this?)
| David's.
It's mine.
| Whose ask questions about possession.
|
What
| Whatmade you angry?
What went wrong?
| His rudeness.
Everything.
| What is used as the subject of
a question.
It refers to «things».
| | Whatdo you need?
Whatdid Alice buy?
Whatdid he talk about?
About what did he talk? (formal)
| I need a pencil.
A book.
His vacation.
| What is also used as an object.
| | What kind ofsoup is that?
What kind ofshoes did he buy?
| It's bean soup.
Sandals.
| What kind ofasks about particular variety or type of something.
| | What did you do last night?
What is Mary doing?
| I studied.
She is reading a book.
| What + a form of dois used to ask questions about activities.
| | What countries did you visit?
What timedid she come?
What colour is his hair?
| Italy and Spain.
Seven o'clock.
Dark brown.
| What may accompany a noun.
| | What is Tom like?
What is the weather like?
| He's kind and friendly.
Hot and humid.
| What + be likeasks for
a general description of qualities.
| | What does Tom look like?
What does her house look like?
| He is tall and has dark hair.
It's a large, red brick house.
| What + look like asks for
a physical description.
|
Which
| I have two pens.
Which pendo you want?
Which onedo you want?
Whichdo you want?
Which book should I buy?
| The blue one.
That one.
| Whichis used instead ofwhatwhen a question concerns choosing from a definite, known quantity or group.
| | Which countriesdid he visit? What countriesdid he visit?Which classare you in?
What classare you in?
| Paris and Canada.
This class.
| In some cases, there is little difference in meaning between which and what when they accompany a noun.
|
|



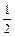 ¾ a half;
¾ a half;  ¾ a quarter;
¾ a quarter;
 ¾ a/one fifth;
¾ a/one fifth;  ¾ three fifths;
¾ three fifths;
 ¾ one and a half;
¾ one and a half;
 ¾ three and four fifths;
Decimal Fractions: 0.1 ¾ nought point one;
10.92 ¾ ten point nine two;
8.04 ¾ eight point nought four;
¾ three and four fifths;
Decimal Fractions: 0.1 ¾ nought point one;
10.92 ¾ ten point nine two;
8.04 ¾ eight point nought four;



