Заглавная страница Избранные статьи Случайная статья Познавательные статьи Новые добавления Обратная связь FAQ Написать работу КАТЕГОРИИ: ТОП 10 на сайте Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрацииТехника нижней прямой подачи мяча. Франко-прусская война (причины и последствия) Организация работы процедурного кабинета Смысловое и механическое запоминание, их место и роль в усвоении знаний Коммуникативные барьеры и пути их преодоления Обработка изделий медицинского назначения многократного применения Образцы текста публицистического стиля Четыре типа изменения баланса Задачи с ответами для Всероссийской олимпиады по праву 
Мы поможем в написании ваших работ! ЗНАЕТЕ ЛИ ВЫ?
Влияние общества на человека
Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрации Практические работы по географии для 6 класса Организация работы процедурного кабинета Изменения в неживой природе осенью Уборка процедурного кабинета Сольфеджио. Все правила по сольфеджио Балочные системы. Определение реакций опор и моментов защемления |
Complete the sentences (1-7) with the words in the box.Содержание книги
Похожие статьи вашей тематики
Поиск на нашем сайте
The computer Before you start 1 Match the computer parts with the words below. floppy disk □ scanner □ mouse □ keyboard □ tower □ monitor □ CD-rewriter □ printer
Reading 2 Read the text quickly. Match the headings (a-d) with the paragraphs (1-4). a Memory □ c PCs and Notebooks □ b Speed □ d Hardware/Software □ 1 The parts of a computer you can touch, such as the monitor or the Central Processing Unit (CPU) are hardware. All hardware except the CPU and the working memory are called peripherals. Computer programs are software. The operating system (OS) is software that controls the hardware. Most computers run the Microsoft Windows OS. MacOS and Linux are other operating systems. 2 The CPU controls how fast the computer processes data, or information. We measure its speed in megahertz (MHz) or gigahertz (GHz). The higher the speed of the CPU, the faster the computer will run. You can type letters and play computer games with a 500 MHz CPU. Watching movies on the Internet needs a faster CPU and a modem. 3 We measure the Random Access Memory (RAM) of the computer in megabytes (MB). RAM controls the performance of the computer when it is working and moves data to and from the CPU. Programs with a lot of graphics need a large RAM to run well. The hard disk stores data and software programs. We measure the size of the hard disk in gigabytes (GB). 4 Computer technology changes fast, but a desktop PC (Personal Computer) usually has a tower, a separate monitor, a keyboard and a mouse. The CPU, modem, CD-ROM and floppy disk drives are usually inside the tower. A notebook is a portable computer with all these components inside one small unit. Notebooks have a screen, not a monitor, and are usually more expensive than desktops with similar specifications
3 Look at these words from the text. Write H (hardware), P (peripheral), S (software) or M (measurement) next to each one.
Vocabulary 4 Match the highlighted words and phrases in the text with the definitions (1-8). 1 parts ___________________ 2 pictures and images___________________ 3 a way of doing something___________________ 4 reads and uses data___________________ 5 measurements___________________ 6 use a computer program___________________ 7 keeps data in the memory___________________ 8 how well a computer does something___________________
Speaking 5 Work in pairs. Look at the chart and compare the two computers. Use fast, slow, cheap, expensive, big, small Hi-Tech 2010 Series X Wi-Fi Type PC Notebook CPU 933 MHz 1.5GHz RAM 256 MB 512 MB Monitor/Screen 17 inch 15 inch Hard disk 20 GB 40 GB Price?2,000?2,999
Get real Look at new computers on the Internet or in magazines. Find one you like. Make a note of its specifications. Bring your notes to class and say why you like it. Build a class file of computers with information about them.
The desktop Before you start 1 What do you see first when you turn on a computer? How do you open a program? Reading 2 Read the text quickly and match the headings (a-d) with the paragraphs (1-4).
a The control panel с The desktop
1 The desktop is the screen that appears after you boot up, or turn on, your computer. It shows a number of icons on a background picture or color, When you buy a new computer and boot up for the first time, the desktop will only show a small number of icons. In the Windows operating system, these usually include My Computer and the Recycle Bin. 2 Double-clicking on an icon with the mouse opens a computer program, a folder or a file. Folders usually contain other files. You can move icons around the desktop add new ones or remove them by deleting them. Deleted files go to the Recycle Bin. People usually put the programs they use most often on the desktop to find them quickly. 3 When you double-click on My Computer another screen appears. This screen shows the A: drive icon, for floppy disks; the C: drive icon, which usually contains all of the main programs and folders on your computer; the D: drive icon, which is usually the CD- ROM drive, and the Control Panel folder. 4 When you double-click on Control Panel, another screen appears that shows many other icons, such as the Display icon and the Date/Time icon. Double-clicking on Display opens a box that lets you personalize your desktop by changing the screen saver (the moving image that appears when no one is using the computer) or the background picture.
3 Decide if the sentences are true (T) or false (F). 1 The desktop appears before you boot up. T/F 2 Files are usually inside folders. T/F 3 People usually put their favourite programs on the desktop. T/F 4 Use the C: drive to open floppy disks. T/F 5 You cannot change the background picture of the desktop. T/F 6 The Control Panel folder contains the Date/Time icon. T/F
Vocabulary 4 Find the words in the text that mean: 1 comes into view so you can see it (paragraph1) _________ 2 the picture or color on your screen (1) _________ 3 clicking the mouse two times quickly (2)_________ 4 something that holds documents or files (2) _________ 5 most important (3)____________________________ 6 make something the way you want it (4) _________
Speaking Get real Go to the menu bar and look at File, Edit, View, Insert, Format and Tools. Find out the function of two other commands or tools and use them j in your document from Exercise 9. Report back j to the class and make a class file of the new commands and tools.
Word processing: for and against Before you start Creating a folder Before you start 1 1 pointer □ 2 cursor □ 3 C: drive icon □ 4 folder □5 close □6 drop-down menu □ 7 minimize□8 maximize □ 9 restore □
Reading 2 Read the text quickly. What do you use from Exercise 1 to make a folder? 1. To make a new folder in the Windows OS, go to the Desktop, find the My Computer icon with the pointer and double-click it using the left mouse button. The My Computer window appears, showing the different drives. Maximize the screen if necessary. 2. Double-click the C: drive icon. The C: drive window appears showing the folders in your C: drive, either in a row or in a list. 3. Move the pointer to the menu bar. Click on File and a drop-down menu appears. You can only click the words New or Close. 4. Move the pointer to the word New. Another menu appears with Folder at the top of the list. 5. Click on Folder. This creates a new folder that appears at the end of the list of folders on the C: drive. The words New Folder are highlighted. The cursor also flashes on and off to show you where to type. 6. Click on New Folder and type the name you want in the box. This can be up to 250 characters long, but you cannot use the characters ‘\ /:*?“<> I’ in your folder name. 7. Click anywhere on the window to see your new folder name. If you do not click on the window, you will save your new folder as New Folder, not with the name you want. 8. Close the window. 9. Your new folder is now listed in the C: drive in alphabetical order.
3.Match the diagrams (a-d) with the instruction numbers from Exercis 2.
4.Complete the sentences with words from Exercise 1. 1. _________Double-click the to view a list offolders and files. 2. You will find the Undo command in the Edit _________ menu. 3. The shows you where to type on thescreen. 4. The mouse controls both the___________andthe cursor. 5. If you click____________, the window will coverall of the computer screen. 6. Clicking_______________________ changes the size andlocation of the window.
Writing 5 Write down the instructions you need to operate one of the following:
Get real Imagine that your class is going to store all the information from your English lessons on computer, so that any student can use it. How could you organize the information into folders (e.g. grammar) and files (e.g. the present simple)? Create a list of folders and files, and name them all.
Saving files Before you start Work in pairs. Bring to your class six photographs of your family, Mends, city or pets that you would like to store on your computer. Decide on file names to give them. Use the most important part of the photograph, but try to keep the names short. I’d call this file ‘Dad Sleeping 50’, because I took the picture on his 50th birthday and he’s sleeping in a chair. I wouldn’t call this ‘Picture 27’because the file name doesn’t describe the picture.
Get real Type Photographs in your search engine. Visit at least three websites that contain photographs or other visual images. Look at the categories that the sites use to group their photographs. Report back to class to say what each category contains. Write up the category list for your next class. The Internet Before you start THE INTERNET Originated in the early 1970s when the United States wanted to make sure that people could communicate after a nuclear war. This needed a free and independent communication network without a centre and it led to a network of computers that could send each other e-mail through cyberspace Tim Berners-Lee invented the World Wide Web (WWW) when he discovered a way to jump to different files on his computer using the random, or unplanned, links between them. He then wrote a simple coding system, called HTML (Hyper Text Markup Language), to create links to files on any computer connected to the network. This was possible because each file had an individual address, or URL (Uniform Resource Locator). He then used a set of transfer rules, called HTTP (Hyper Text Transfer Protocol), to link Web files together across the Internet. Berners-Lee also invented the world’s first browser. This lets you locate and view Web pages and also navigate from one link to another. The WWW became available to everyone in 1991 and the number of Internet users grew from 600,000 to 40 million in five years. Today, that number is much larger and there are now many browsers that provide Web pages, information and other services. You can also do research, download music files, play interactive games, shop, talk in chat rooms and send and receive e- mail on the WWW.
3.Find the correct word or abbreviation in the text. 1 an address for Web pages_______________________________ 2 a coding system that creates links___________________________________ 3 this finds and shows Web pages__________________________________ 4 rules for transferring files_______________________________ 5 a group of computers joined together____________________________________
Vocabulary 4.Match the groups of verbs below with their general meaning from the box.
1 browse, surf, view___________________________ 2 download, navigate, transfer_________________________________ 3 connect, link__________________________ 4 discover, locate___________________________ 5 originate, create, invent_______________________________
5.Complete the sentences (1-7) with the words from the text. 1 Some people spend too much time playing ___________ games on the Internet. 2 You can sometimes have a computer________________________________ that is not connected to the Internet. 3 It is easy to________________________ around a screen with a mouse. 4 Berners-Lee discovered how to_________________________________ links between computers in new ways. 5 Some people surf the Internet at________________________________, just to see what they can find. 6 People use the Internet to _______________ information from one place to another. 7 When you surf the Internet, you are travelling in___________,
Speaking 6.Work in groups. Say which of the following ideas about the Internet are good or bad.
Get real Use a browser to surf the Internet at random. Find five interesting websites to tell the class about. Write down the URL of each website and bring the list to class. Build a class file of interesting sites so that other students can visit them.
Research on the Internet Before you start 1. Where is the best place to find information on these topics? • European history • the price of mobile phones • your favourite pop star 2. What are the advantages and disadvantages of finding information from these sources? books ■ magazines ■ newspapers ■ libraries ■ encyclopedias ■ friends or family ■ teachers ■ CD-ROMs ■ television ■ radio ■ the Internet
Reading 3. Read the text quickly and choose the correct answer. 1 Google is a keyword / search engine. 2 This WORD is in upper / lower case. 3 AND / WHEN is a logical operator. Finding information on the World Wide Web needs an Internet search engine such as Google, Alta Vista or Excite. Search engines have a text box where you type in a keyword or words. A search engine is a software program that reads the keywords in the text box and searches the Internet for Web pages, websites and other Internet files that use them. These documents are shown on the computer screen in a results listing. When carrying out searches, you should usually be specific and brief in your choice of words. If the keyword is too general, or includes too many different meanings, the results listing may not be useful. Different search engines categorize information in different ways, which changes the way they store and retrieve it. Using upper case letters (capital letters) in a keyword search will only retrieve documents that use upper case. Typing in lower case (no capitals) is usually better because search engines will retrieve documents that use both upper case and lower case letters. You can narrow a search using logical operators such as AND, OR and NOT. AND retrieves all the words typed in the text box, OR retrieves either of the words and NOT excludes words. Spelling is important when typing in keywords, but a search engine will not usually read punctuation, prepositions and articles. 4. Tick (√) the good things to do to find information on the Internet. 1 Choose keywords that are different to the item you want. □ 2 Give the best keyword to describe what you want. □ 3 Use as many general keywords as possible. □ 4 Try to use a keyword that can have only one meaning □ 5 Type your keywords in lower case only. □ 6 Use logical operators to narrow your search, □ 7 Use full stops and commas. □ 8 Do not use words like at, in, on, a/anand the. □
Vocabulary 5. Find the words and phrases in the text that mean: 1 clear and exact (paragraph 2)______________________ 2 put into similar groups (2) ______________________ 3 to bring back (2) ______________________ 4 make smaller (4) ______________________ 5 mathematical words (4) ______________________ 6 does not use (4) ______________________
6. Are the words in the groups below listed from general to specific or specific to general? Write G->S or S->G. 1 telephone -> mobile phone -> Nokia______________________ 2 mother -> family -> humans______________________ 3 writing -> essay -> sentence______________________ 4 Big Ben -> London -> UK______________________ 5 cars -> vehicles -> transport______________________ 6 cars -> German cars -> BMW______________________
Speaking 7. Talk about the keywords you should use to find information on the following topics. • information on cheap hotels in the UK • what the weather will be like tomorrow • an essay on the history of the European Economic Union • mobile phones that connect to the Internet • a nice present for your mother’s birthday.
Get real Carry out the searches in Exercise 7. Then: • note the words you used in the search • note the top five results for each search • visit each site and find out if it is useful.
Do the search using a different search engine. Bring the list of keywords and your notes on the search results back to class. Lida, 28 For me it has to be e-mail, it's very fast, cheap and modern - you can download music and video, send letters and pictures, and it's informal, which I like, I know privacy and security can be problems but who sends important documents by e-mail? I get annoyed if I get hundreds of e-mails at work and they all expect an instant response, and obviously I hate getting spam, or even worse, a virus. Jarek, 65 Well, I use all three, but I prefer the phone. It's more expensive, especially for long-distance calls, but I like the instant interaction and I think you can understand more when you hear a person's voice, I like the informality and speed and you can also use your mobile phone for e-mail and sending images. With mobile phones you don't get a lot of unwanted communication, apart from the occasional wrong number. Andrea, 39 I like modern things, but I still prefer the post. I know postal delivery is slow, but it's cheap, and you can be sure no one will read your mail or listen to your conversations. You can send anything by post, which you can't do with e-mail. Personally, I like receiving handwritten letters - they look, feel and smell different from e-mails. I think it's sad that young people don't write letters now - they're usually more formal than e-mail and students can practice their grammar and spelling. Now, what I don't like is getting is bills and junk mail!
3 Read the quotes again. Tick (\/) the features of each type of communication. Vocabulary Which of the words in the box do people usually think of as positive? Which do they think of as negative?
Speaking 4 Work in pairs. How do you feel about getting these unwelcome messages? Why? Add other types of unwanted communication to the list.
I don’t mind getting... I don’t really like getting... I really don’t like / can’t stand / (really) hate...
Writing 5 Write a paragraph describing the advantages and disadvantages of e-mail or telephones or the postal service. Get real Work in pairs. Send each other a handwritten letter in English through the post. Also send each other an e-mail. (They can have the same content.) Describe how the letter looked, how it felt and how it smelt when you received it. Compare the letter to the e-mail you have received. Tell the class which you preferred and why.
Mobile phones Before you start 1.Answer the questions. Then discuss in pairs. 1 Do you use a mobile phone? 2 What do you use it for? Make a list. 3 When is it a good or bad time to make/receive mobile phone calls? Reading 2.Label the parts of the mobile phones with the words in the box.
3. Read the adverts to check your answers to Exercise 2. Which phone is best for a business person and which is best for a student? Then write the correct names by Model 1 and Model 2 above.
4.Which mobile phone has these features? Write QT1, SP5 or Both, 1 can work anywhere_____________ 2 a diary_____________ 3 a camera_____________ 4 no cables_____________ 5 faceplates you can change_____________ 6 a one-week standby time_____________ 7 ring tones you can program_____________ 8 games you can download_____________
Vocabulary 5.Which of the words in the box are specific to phones/IT and which are used in general English? band mode ■ connection ■ detachable ■ dimensions ■ dual ■ navigation ■ ring tones ■ text messages ■ transmission ■ voice mail
Speaking 6.Work in pairs. Text messages or SMS (Short Message Service) use abbreviations. Match the text messages (1-5) with their meanings. 1 gtg 2 brb 3 thx 4 J4F 5 I k%d meet u @ 7 I could meet you at 7.00. ■Be right back. ■ Thank you. ■Got to go. ■ Just for fun.
Writing 7.Write a paragraph about the mobile phone you have or the one you would like to have. Get read Use the Internet or magazines to find a new, up-to-date mobile phone. Make a list of the features it has and report back to the class.
Writing e-mails Before you start 1.Which of these things do you do with e-mail and which do you do with letters? Compare your answers with another student. write a subject ■ send copies ■ write an address ■ add attachments ■ sign in ■ sign your name ■ go to your inbox ■ use a post box m click on a name 2.E-mails, like letters, should have a start and an end. Which phrases usually start a message and which end one? Write S (start) or E (end) next to the phrase. 1 Yours sincerely,______________________ 2 Love and kisses to all._________________________ 3 Dear Sir or Madam,________________________ 4 Thanks for your e-mail.__________________________ 5 Give my regards to your family._____________________________ 6 Good to hear from you._______________________________ Which are formal (F)? Which are informal (I)? Write F or I.
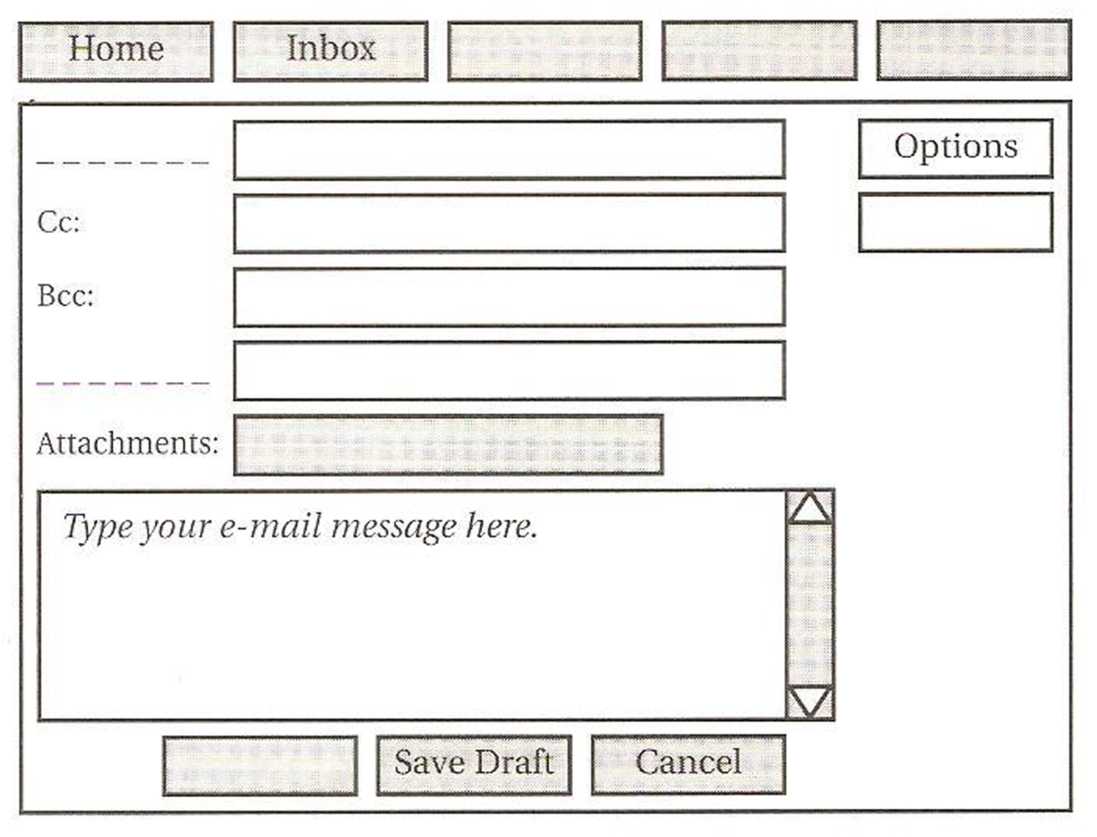
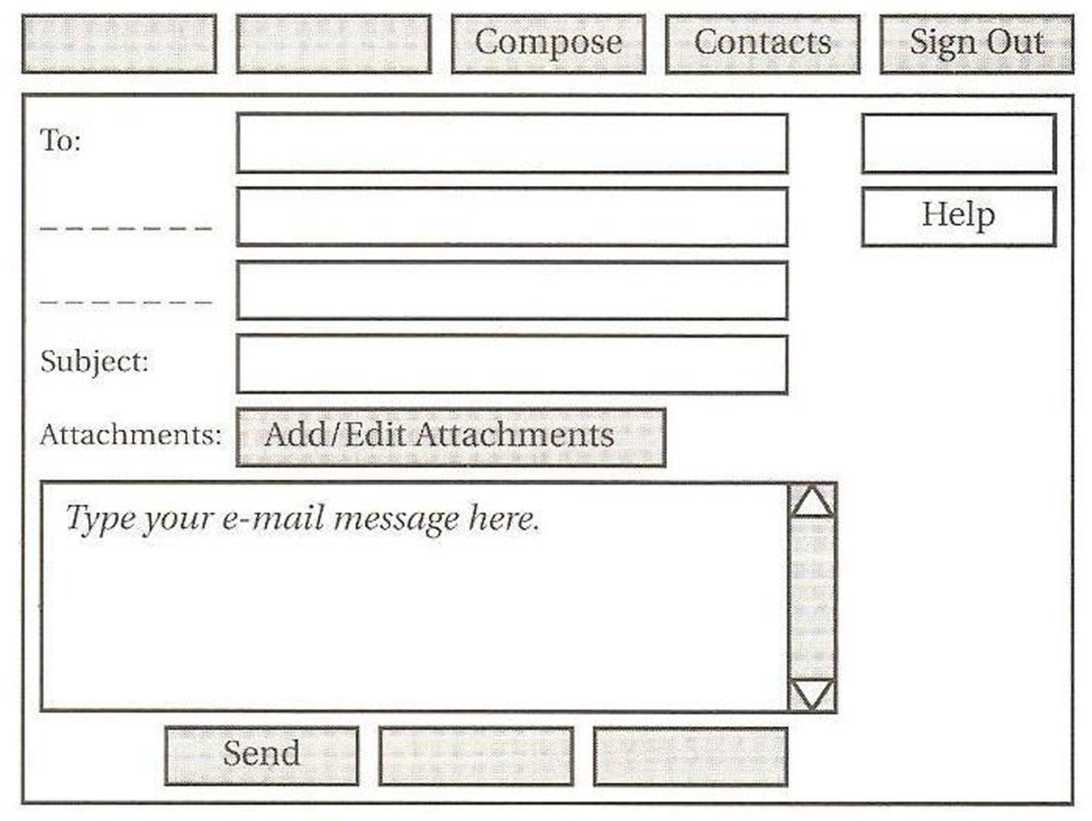
3.Write these messages in the correct order. Which are formal and which are informal? 1 e-mail 21st your August. I to refer dated 2 your I e-mail thanks, yesterday, got 3 you. can’t I see wait to 4 seeing look to you. forward I 5 me a Give if you need ring me. 6 Reading/Speaking 4.Work in pairs, A and B. Each of you has a box of commands and fields and a diagram of a typical e-mail. Compose window with some of the commands and fields missing. You also have information about the commands and fields in your diagram. • Look at your tables and diagrams before you start the activity. • Take it in turns to ask and answer questions about your missing commands and fields. • Write them in the spaces on your diagram. Student A Find out where to write the command or field in the box by asking questions like these: Where is the Compose command? What does it do? Where is the To: field? What do I type? Command: Compose Sign Out Help Send Add/Edit Attachments Contacts Field: To: Subject: Now use your table to answer Student B’s questions. Give answers like these: The Home command is t he first one top left. It takes you back to... The Bcc: field is the third one. You type...
Student B Student A will ask you questions about his/her missing commands and fields. Use the table below to give answers like these: The Compose command is the third box. It gives you a new screen... The To: field is the top field. You type...
Now complete your diagram by asking Student A about the missing commands and fields in your table. Use questions like these: Where is the Home command? What does it do? Where is the Bcc: field? What do I type? Command: Home Inbox Options Save Draft Cancel
Speaking 6.Work in pairs. Look at the following European country codes. Discuss which countries they could stand for. .at ■.be ■.bg ■.de ■.dk ■.es ■.fr■.gr ■.hu■.it ■.lu ■.nl ■.pt ■.ro ■.si ■.uk Get real Use an Internet search engine to find a list of Internet Country Codes. Pick any five countries that you do not know and find out where they are. Chose one country and find some information about it using your search engine. Report back to the class.
E-post Express You can attach a file while you are online or offline. Open the program and click Create a new mail massage to go to you compose window. Click on the paperclip icon with the word Attach below it. An Insert Attachment dialog box appears, which shows your computer directory. Click on the file you want to send and then click the Attach button. The file and an icon appear in the Attach field. Send can be any size but some servers will not accept files of more than one megabyte. To remove a file, click on the attachment with the right mouse button then click Remove. When you are finished, click Send. MEGA MAIL Connect to the Internet to open your program and go to the compose screen. Click on Attach Files. A screen opens showing three Browse buttons. You can only send three attachments up to three megabytes in total. Click on the first Browse button. A Choose File dialog box appears, which shows your computer directory. Click on the file you want to send. The file name appears in the File name drop-down list box. Click Open. The Choose File dialog box disappears and the file appears in the file field of the Attach Files screen. Click Attach files. A screen appears telling you that the file is being attached and then another screen appears when the program has attached the file. To add more files, click Attach More Files and the Attach Files screen will reappear. When you have finished, click Done. Your compose screen reappears, listing the name of the attached file with an icon next to it. Click Send.
3. Which information (1-6) is the same for E-post Express and Mega Mail, and which is different? Write S (same) or D (different). 1 You can send up to three megabytes of data. □ 2 A dialog box appears, showing the computer directory. □ 3 You can attach and send up to three files. □ 4 You have to be online to attach files. □ 5 Click Send when you want to send your e-mail. □ 6 The program shows an icon next to the attached file. □
Vocabulary 4.Find the words in the text that mean: 1 a series of steps (E-post Express)_________________________________ 2 take off or take away (E-post Express) 3 something you click to start an action (E-post Express) 4 goes away suddenly (Mega Mail)__________________________________ 5 come back into view (Mega Mail)__________________________________ 6 finished (Mega Mail)_____________________________ Get real Either review two or three e-card websites or go to a shop with a good selection of cards. Which occasions are there cards and e-cards for? What do the cards and e-cards offer (e.g. pictures and sounds)? Were the websites easy to use? Report back to the class and discuss what you found. Music on the Internet Before you start 1. Tick () the kind of music you like. Make a list of other types of music. pop □ rock □ classical □ jazz □ 2. What is good or bad about downloading music from the Internet? Make a list. Reading 3. Milos (M) is a music fan. Kamila (K) works in the music industry. They are in a chat room. Read the dialogue and tick (√) the topics they talk about. 1 Making copies of songs from the Internet. 2 How much money the music industry loses. 3 How Napster sent music to people. 4 What peer-to-peer music sharing is. 5 How to stop peer-to-peer sharing. 6 Which are the best legal music websites. M Downloading music is great. I can get all the songs I like, when I want to get them. K That’s true, but if you don’t pay for it, you’re breaking copyright law. M Really? Why is it against the law? K Well, getting music for free costs the music industry billions in lost income, so we have less to spend on new bands and singers. M Was that the problem with Napster? K Yes. Napster created a file-sharing system using the MP3 audio format. People could connect to a central location and others could then download their files using the server. Napster closed down in 2001 because it was breaking the law. M I see, but peer-to-peer music swapping is legal, isn’t it? It’s just two people sharing music - they’re not using a central server. K No, it’s still illegal, I’m afraid. M Actually, peer-to-peer isn’t that great - you don’t get much choice because it depends on who’s online at the same time as you. Can you download music legally? K Yes, there are several Web-based music services that charge a fee. It’s really worth paying. The choice and quality of the music is better and they offer other services such as music reviews and chat rooms. Try one!
4.Label the diagrams central location and peer-to-peer. 5. Match the first part of the sentence (1-6) with the second part (a-f). 1 The record industry loses money a to join a legal music website. 2 Napster used b give a lot of music services. 3 You have to pay c is illegal, money 4 The best music d the MP3 audio websites format. 5 Peer-to-peer sharing e because of peer-to-peer sharing. Vocabulary 6. Find the words in the text that mean: 1 money people receive for work______________________________ 2 related to sound___________________________ 3 someone of the same type/group________________________________ 4 exchanging something with someone 5 dividing something between people_____________________________________ 6 against the law__________________________ 7 money you pay for a service________________________________ Speaking Desktop publishing (DTP) Before you start 1
2 Noun Adjective Noun and adjective __________ ______________ _________________ __________ ______________ _________________ __________ ______________ _________________ __________ ______________ _________________ __________ ______________ _________________ Reading 3. A computer virus has damaged this text and put the paragraphs in the wrong order! The headings (1-6) are in the correct order. Use them to number the paragraphs. 1 DTP programs and what they do 2 Templates and Web pages 3 Making changes to text 4 DTP programs and word processors 5 Using graphics 6 Moving text and graphics on a page □ DTPprograms let you work with graphics: you can draw shapes, fill them with text or colour, insert graphics or special characters from the program, or import them from another program, and you can move them all easily around the page. □ While DTP programs and word-processing programs have a lot of similar commands and tools, DTP programs have one important advantage: what you see on the screen is exactly what you get when you print your document. □ There are many things you can do with text and graphics: you can use an align command to put them in a straight line, horizontally or vertically, and a rotate tool lets you turn them around. You can bring text to the front of a shape or graphic or send it to the back so that you can't see it. You can also wrap text around a picture or inside a shape, like in this reading. □ Desktop Publishing (DTP) programs, such as Adobe PageMaker and QuarkXpress, let you combine text and graphics in creative ways to produce stylish greeting cards, holiday brochures, business cards, newsletters, sales catalogues, calendars and many other documents. □ The tools and commands in DTP programs give you a great deal of control over text. For example, you can make word and character changes, such as changing the space between words in a text without changing the font size, or changing the space between characters to make them look neater. These choices are useful when you only have a small space to work in. □ These programs also let you make a template of your document so you do not have to remake the whole document each time you want to change the text or the pictures. Many DTP programs let you change the file format of your design into a Web page, too.
4. Read the text in the correct order. Decide if the sentences are true (T) or false (F). 1 You cannot type letters in a DTP program.T/F 2 You can use a template to save time.T/F 3 DTP programs print exactly what you see on the screen.T/F 4 It is difficult to control the text in a DTP program.T/F 5 It is impossible to change the spaces between words.T/F 6 A rotate tool lets you turn text around.T/F 5 align horizontally ■ increase space between words ■ align vertically ■ bring to front ■ rotate ■ fill ■ text wrap ■ decrease space between characters
Vocabulary 6. Complete the puzzle with words from the text. 1 looking smart and new 2 letters and words 3 a document pattern or plan 4 join together 5 bring from another program 6 get from the program you are using 7 a drawing or plan of something new 7. Match the document types (1-7) with the descriptions (a-g). 1 greeting card a information for tourists showing hotels, resorts, etc. 2 holiday brochure b a table that shows days and months 3 business card c a small card with a person’s name and a company name 4 newsletter d a card for a special occasion 5 sales catalogue e a page on the World Wide Web 6 Web page f a small newspaper for a specific group of people 7 Calendar g a book of advertisements from a commercial company Speaking 8. Work in pairs. Describe the picture.
Get real Bring in some holiday brochures, newsletters, business cards, sales catalogues or any other printed documents. Look the design of the documents. Discuss how you could change and improve them using the commands and tools of a DTP program.
Image editing Before you start Get real Look at some of the pictures and images in magazines and some created by computer programs (type ‘computer generated art’ in your search engine). Which colours go well together? Report back to class on your favourite images and websites.
Reviewing Websites Before you start 1.What things don’t you like or annoy you about websites? Make a list.
Reading 2.Look at Matej’s Top 10 Web page annoyances on his home page. Which ones are similar to the annoyances you talked about in Exercise 1? My TOP 10 Web page annoyances 1. Frames Don't you hate those silly boxes in Web pages? Sometimes the text doesn't fit in the frame and you have to use the horizontal scroll bar. This makes it very hard to read. Downloading plug-ins The little programs that you have to download to get an audio or video message before you can enter the site - they make me want to go somewhere else! Pop-up ads The horrible advertisements that suddenly appear-they drive me crazy. Bad design Too many buttons and links on different parts of the page are confusing. Blinking fonts Brightly-coloured texts are difficult to read, but fonts that blink on and off? Ugh! Counters It's wonderful to know that I'm visitor number 345,345,218, but I feel terrible finding out I'm visitor number 11. Why not put counters in a separate link? Then, if you want to know your number, you can just click there. Flash These animations are good if they download quickly, but please make them relevant to the website, and not just there to make the site look No Privacy Policy I never give my e-mail address to a website that does not have a privacy policy. I want to be sure that they won't sell or send it to another site. Silly sound files Sound files that start with a bang, or a dog barking make me jump! They're really annoying, and you can't turn them off. Why only English? Doesn't anyone realize that we live in a multilingual world?
3. Write the number of the annoyance that matches each sentence. a. Websites should have rules about giving e-mail addresses to other sites. □ b. Web pages should have options for different languages. □ c. Animations should be about the same subject as the Web page. □ d.Web pages should not need special programs to run. □ e.The text should not blink on and off. □ f.Dividing a Web page into a lot of small frames is bad design. □
Vocabulary 4.Find the opposites of the adjectives (1-6) in the text. 1 clear 2 very bad____________________ 3 unrelated_____________________ 4 ugly 5 uncertain_____________________ 6 monolingual______________________ 5.Complete the sentences (1-5) with the words in the box. confusing ■ else ■ fits ■ relevant ■ scroll bar 1 This is a well-designed Web page. Everything ________well on the screen. 2 Web surfers will go somewhere ______if the page doesn’t appear quickly. 3 That animation is good because it is pretty and it is ___ to the Web page. 4 That website is very _________ because I couldn’t find the Back button. 5 It’s annoying when you have to use the horizontal____ see all of the text. Speaking 6. Work in pairs. Do you agree or disagree with Matej’s list? Rank your top five annoyances from the text: 1 = most annoying, 5 = least annoying. Get real Work in groups. Look at some websites for business, education, entertainment, or information. Make notes on the differences in design between them. Look at how they organize navigation bars, the categories they use, and how many pictures and animations they use. Report back to the class and make a class list of design features for each category.
Designing Web pages Before you start Beginning HTML Web designers use Hyper Text Markup Language (HTML) to create and format Web pages. HTML uses a set of codes, called tags, to structure a Web document that will run in a browser. There are hundreds of tags you can use to format text, insert graphics, animations, sound and video. But you do not need to understand HTML to make your own personal home page. Many word-processing, desktop publishing and Web-authoring programs will generate HTML tags for you. To upload, or copy, your Web page to a Web server, use the server's File Transfer Protocol (FTP).
Home Page Hints It's your 'cyberhome', but remember that websites are different from books or magazines. Think about these suggestions to make people want to stay. 1) Use a navigation bar to organize your hyperlinks to other pages. 2) Hyperlinks also let visitors navigate up or down long pages. 3) Keep your use of colour and buttons consistent. If a Next Pade button is a pink circle, all Next Page buttons should be the same, and in the same place on the screen. 4) If you use a lot of animations, your Web page will take a long time to download. 5) If you use a lot of graphics, animations and text your Web page will be too busy. 6) It's difficult to read a text that's next to an animation. 7) Keep texts short and simple! Surfers don't like reading on a computer screen much. 8) It's not easy to read multi-coloured text. 9) Lots of bright colours look nice at first, but often give people headaches! 10) Make sure you use a spell check and use good grammar. 11) Try not to use too much slang. People who visit your site may not understand. 12) Don't be afraid to be original. Good websites have something that is different about them and that comes from you!
Vocabulary 5 Match the highlighted words and phrases in the text with the definitions (1-7). 1 connections to a Web page or part of a Web page_________________ 2 make or produce____________________________ 3 plan or build a Web page_______________________________ 4 a group of organized Web links, usually in a line ____________________ 5 does not change, always the same___________________________________ 6 the type of software that helps create Web pages___________________ 7 new, not done before_____________________________
Complete the sentences (1-8) with the words in the box. busy ■ consistent ■ generate ■ home pages ■ structure ■ surfers ■ upload ■ Web-authoring 1 That Web page is much too _________________. I don’t know what to look at. 2 An FTP server is a computer that lets you ______________ files to the Internet. 3 The buttons on this page are not ___________ with the button on the last page. 4 Net_________________ never like reading a lot of text on the screen. 5 __________ software means you don't have to learn HTML to make a Web page. 6 Many students have their own ________________ on the World Wide Web. 7 HTML creates the____________________ for Web pages to run on a browser. 8 Web-authoring programs________________________ HTML tags for you. 6 Tick (√) the sentences that use informal English. 1. Get real, people. Frames are a big no-no. □ 2. Designing a Web page needs careful planning. □ 3. I think sound files are cool. □ 4. Multi-coloured blinking fonts look terrible. □ 5. That Web page is mega ugly. □ 6. The text has too many grammatical errors. □
Speaking 7 Work in groups. How would you design your personal website? What graphics, images and colours would you use? What would you say in your text? How many pages would you have? What would you call the links on your navigation bar to show the different pages? Use the sample pages in Exercise 9 to help you. Writing 8 Look at the two home pages below. Write two paragraphs, describing what is good and bad about each home page. Freddy’s home page is fun but badly designed because it has/uses... It is confusing because it is.../there are... Jana’s home page is well designed because it has...
Get real Review the texts in Unit 19 and in this unit. Visit a website or home page of your choice. Make notes on what is good and bad about it. Report back to the class and make a class file of good and badly designed sites for people to visit.
Multimedia Before you start 1.Work in groups and discuss the questions. 1 How are books and CD-ROMs different? 2 Have you ever used CD-ROMs to help you study? Do you prefer them to books? Reading 2.Match the parts of the CD-ROM with the information they provide. a The history of multimedia b Education and entertainment c What is multimedia? d Business and industry 1. Multimedia is any computer application that integrates text, graphics, animation, video,audio or other methods of communication. Multimedia is different from television, books or cassettes because it lets you interact with the application. You can click on a word to make a picture appear, or click on a picture to start a video. 2. Multimedia became more popular after the mid-1990s when the price of hardware began to fall. Then people started using it in industry, business, education, entertainment and for other purposes. Today, we can find multimedia at home, in school, at work, in public places, such as libraries, and on the Internet. 3. In business, advertisers use virtual reality in multimedia applications to advertise their products in three dimensions (3-D). Using multimedia for graphs and tables is now the best way for managers to present company results. In industry, pilots learn to fly using multimedia simulations of real situations, and scientists simulate experiments with dangerous chemicals in safety. Publishers are also producing interactive magazines, called e-zines, and e-books online. 4. In education, students study interactive CD- ROMs at their own speed and explore topics creatively by clicking on related links. Teenagers have played computer games for years, but many multimedia applications combine education and entertainment and they let them visit virtual worlds or change the ending of films. Work in pairs. Describe your favourite CD-ROM (or other method of studying). What can you learn from it? Describe how it integrates text, images, and other features such as animations, video, audio and Internet links.
Get real Find an e-zine on the WWW on a topic you are interested in. Note how it is different to reading a paper magazine. Report back to the class.
E-commerce Before you start 1 Work in pairs and discuss the questions. 1 Have you ever heard of e-shopping? What do you know about it? 2 Do you know anyone who has bought anything online? What did they buy? 3 What do you think are the advantages and disadvantages of e-shopping? Make a list. Reading 2.Read part of an interview about e-commerce. Match the questions (a-e) with the correct paragraphs (1-5). a How does e-commerce work? □ b What’s the future for e-commerce? □ c Do customers like shopping online? □ d What kind of business do you run? □ e What do e-tail stores need to succeed? □ 1 We sell mobile phones and accessories, and we only operate online. We're a B2C business. That means 'business to customer', so we don't sell to other businesses - that's B2B. We're obviously not C2C either, which is individual people selling to each other online. 2 Yes, it's becoming very popular and successful. It's world-wide shopping, 24 hours a day, 365 days a year. It's so convenient - people can browse through online catalogues, compare prices easily, and there's less paperwork, so it's cheaper for the retailer. We can pass these savings onto the consumer. 3 Well, the best sites, or e-tail stores, have an electronic storefront giving categories that are easy to understand. You can read reviews about the products, go to chat rooms to talk about them, and when you've made your choice, simply click your mouse and add it to your electronic shopping cart. 4 The retailer needs to build consumer confidence. You need a website that is easy to navigate and it must download quickly. You need customer support services, things like FAQs (frequently asked questions), information about the order, and guarantees about delivery. A secure server for transactions using credit cards and a privacy policy are also very important. 5 I think everyone will shop online soon. All e- tail stores will use virtual reality to sell their goods - it's going to generate billions of euros.
3.Tick (√) the features of the best e-tail stores. 1 have slow downloads □ 2 have an electronic shop window □ 3 have somewhere to put to your goods □ 4 inform the customer about the order □ 5 need a lot of paperwork □ 6 have a place for people to talk □ 7 give product reviews □ 8 use a safe Web server for payment □ 9 cannot say when goods will arrive □ 10 let people ask questions □
Vocabulary 4.Find the words in the text that mean: 1 extra, additional products (paragraph 1)___________________________ 2 work, do business (1)_____________________________ 3 matches someone’s needs (2)_________________________________ 4 someone who sells (2)______________________________ 5 customer (2)_________________________ 6 help (4)_______________________ 7 promises (4)_________________________ 8 buying and selling (4)_____________________________ Chat rooms Before you start 1 Work in groups. Make a list of: • five topics you can talk about when you first meet people • five topics you shouldn’t talk about when you first meet people. Reading 2 Read the opinions about chat rooms. Which ones do you agree with? We got a lot of letters in response to our article last week on Internet chat rooms. Here is a random selection. 1. Why do people like them? They're boring! It's just a group of people talking nonsense! My son doesn't go out or meet real people any more! 2. Some make you register for a free trial membership, so you have to send your real name and e-mail address. You have to read the agreement carefully - sometimes if you don't cancel before your trial ends, they send you a bill! I think this is unfair. 3. You should warn parents about them. People use nicknames – they call them ‘handles’ – so you don’t know who they are. Tell teenagers never to give out personal information, especially their name, home or school address or telephone number 0 and they must never agree to meet anyone from a chat room. It could be dangerous. 4. I think they're good for practicing English in real time - that's when everyone is online and 'talking' at the same time as you. I like expressing my feelings with those cute emoticons, too. If you only talk about your family, the weather, sport, school subjects and other small talk topics, I think they are amusing and harmless. 5. Most only have text boxes for messages, but chat rooms that support voice and video chat are the best, if you have the right hardware and software that is! 6. If people can't find a chat room they like, they can create one of their own. I set up my own online community. I think this is fantastic and more people should do the same. 3.Decide if the sentences are true (T) or false (F). 1 You can set up your own chat room. T/F 2 You must be online to go into a chat room. T/F 3 Anyone can use a video chat room. T/F 4 You can say how you feel with a symbol. T/F 5 You have to pay for some chat rooms. T/F
Get real Ask the people in your family what they talk about when they first meet somebody. Take each topic and think of questions in English that you can ask about them. Make a class list of small talk topics and questions.
Netiquette Before you start 1.Look at the definition of etiquette. What do you think Netiquette is? etiquette /'etiket, -ket/ n [U] formal rules of correct and polite behaviour in society or among members of a profession Reading 2.Read the Web page about Netiquette and check your answer to Exercise 1. Then write the he
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Последнее изменение этой страницы: 2017-02-10; просмотров: 3018; Нарушение авторского права страницы; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! infopedia.su Все материалы представленные на сайте исключительно с целью ознакомления читателями и не преследуют коммерческих целей или нарушение авторских прав. Обратная связь - 3.147.77.51 (0.015 с.) |


 Match the icons (a-i) with the words (1-9) below.
Match the icons (a-i) with the words (1-9) below.







 .Complete the chart with the correct command or description of each action from the box.
.Complete the chart with the correct command or description of each action from the box.