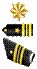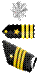Заглавная страница Избранные статьи Случайная статья Познавательные статьи Новые добавления Обратная связь FAQ Написать работу КАТЕГОРИИ: ТОП 10 на сайте Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрацииТехника нижней прямой подачи мяча. Франко-прусская война (причины и последствия) Организация работы процедурного кабинета Смысловое и механическое запоминание, их место и роль в усвоении знаний Коммуникативные барьеры и пути их преодоления Обработка изделий медицинского назначения многократного применения Образцы текста публицистического стиля Четыре типа изменения баланса Задачи с ответами для Всероссийской олимпиады по праву 
Мы поможем в написании ваших работ! ЗНАЕТЕ ЛИ ВЫ?
Влияние общества на человека
Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрации Практические работы по географии для 6 класса Организация работы процедурного кабинета Изменения в неживой природе осенью Уборка процедурного кабинета Сольфеджио. Все правила по сольфеджио Балочные системы. Определение реакций опор и моментов защемления |
Вербування, набір, найом, прийомСодержание книги
Поиск на нашем сайте heavy enrolment – великий набір light enrolment – невеликий набір open enrolment – вільний прийом до навчального закладу (незалежно від формальних обмежень, як-то від місця проживання)
Серед основних заходів удосконалення системи комплектування ЗС треба відзначити такі: − створення принципово нового сержантського корпусу; − створення більш досконалої системи визначення придатності громадян України до професійної військової служби. Система визначення придатності громадян до військової служби розглядатиме такі аспекти: − відбір за станом здоров’я; − відбір за морально-професійними якостями; − відбір за рівнем освіти. Вирішення питань військово-технічної політики прямо пов’язане зі способом комплектування військ. Зрозуміло, що без підвищення якісних параметрів особового складу не можна забезпечити належну ефективність реформування Збройних Сил.
В Україні запроваджено якісно нову систему комплектування посад військовослужбовців, а також супроводження служби військовослужбовців на всіх її етапах. Важливими елементами зазначеної системи стануть формування дійсно дієздатного резерву кандидатів для проходження служби. Передбачається покращання військово-професійної орієнтації та психофізіологічного відбору військовослужбовців, застосування більш ефективної системи мотивації до військової служби, стимулювання професійного росту і планування кар’єри військовослужбовця. Перехід Збройних Сил України на професійну основу та створення відповідних умов її функціонування зроблять військову службу більш привабливою для молоді. Важливим кроком є забезпечення соціально-правового захисту військовослужбовців, членів їх сімей та пенсіонерів Збройних Сил.
The Army's claim for effectiveness of the “Army of One” campaign is based mostly on an increase in recruiting contacts. Even before September 11, the site had about 26,000 hits per day, a level that the Army says is 238 percent higher than in the previous year. Recruits who first contacted the Army on-line were up 81 percent. All of the services claim even more dramatic increases in the number of contacts with young people in the aftermath of the 9/11 tragedy. Although the military considers its "Army of One" campaign to be a success, anti-militarism activists can still take heart. In the past, enlistments have taken a nose-dive when the public has come to understand that military service is about more than getting benefits. War means war, complete with the possibility of injury, death, friendly fire, exposure to environmental hazards, and Gulf War-like syndromes. The new US policy of expanded war − which knows no geographical boundaries or time limits − is already causing many young people to lose enthusiasm for military service. Besides "reality television" is a fad that's soon to pass, and with it will go the resonance and entertainment value of the military's current recruiting drive.
Lesson 12
*****
Military Ranks (US Views) One big problem throughout military history has been identifying who's in charge. From the earliest days of warfare to the present, special rank badges meant survival. In the heat of battle, knowing who to listen to was as important as the fighting skills soldiers and sailors developed. They had to know at a glance whose shouted orders to obey. The U.S. military services still use many of the ranks they started with when they began in 1775 at the outbreak of the Revolutionary War. The leaders adopted the organization, regulations and ranks of the British army and navy with just minor changes. This is not surprising because the Revolutionary Army was made up of colonial militia units that had been organized and drilled by British methods for many years. Revolutionary Army rank insignia, however, did not follow the British patterns but was similar to the insignia used by the French. After the war the U.S. Army often used the uniform styles and some insignia of the British as well as the French armies. Military rank is more than just who salutes whom. Military rank is a badge of leadership. Responsibility forpersonnel, equipment, and mission grows with each increase in rank. Officer ranks in the United States military consist of commissioned officers (ComOs) and warrant officers (WOs). The commissioned ranks are the highest in the military. These officers hold presidential commissions and are confirmed at their ranks by the Senate. Army, Air Force and Marine Corps officers are called company grade officers in the pay grades of O-1 to O-3, field grade officers in pay grades O-4 to O-6 and general officers in pay grades O-7 and higher. The equivalent officer groupings in the Navy are called junior grade, mid-grade and flag. Warrant officers hold warrants from their service secretary and are specialists and experts in certain military technologies or capabilities. The lowest ranking warrant officers serve under a warrant, but they receive commissions from the president upon promotion to chief warrant officer 2. These commissioned warrant officers are direct representatives of the president of the United States. They derive their authority from the same source as commissioned officers but remain specialists, in contrast to commissioned officers, who are generalists. There are no warrant officers in the Air Force. Non-commissioned officers (NCOs) are servicepeople who have received neither a commission nor a warrant but hold positions requiring responsibility for personnel and its training. They may be sergeants or petty officers in the Navy. The lowest in the rank are the enlisted personnel. However, depending on their qualification and service aptitudes they are also differentiated in rank. Do not confuse rank with pay grades, such as E-1, W-2 and O-5. Pay grades are administrative classifications used primarily to standardize compensation across the military services. The "E" in E-1 stands for "enlisted" while the “1” indicates the pay grade for that position. The other pay categories are “W” for warrant officers and "O" for commissioned officers. Some enlisted pay grades have two ranks. The Army, for example, has the ranks of corporal and specialist at the pay grade of E-4. A corporal is expected to fill a leadership role and has a higher rank than a specialist even though both receive the same amount of pay. Pay grade is used in the US military as to normalize the equivalent enlisted and officer ranks respectively. For example, the base pay of an E-8 are the same in the Air Force and the Army. In theory, those two E-8s will have equivalent levels of seniority and responsibility. The table shows current ranks in the US military service branches, but they can serve as a fair guide throughout the twentieth century. [53]
1. What groupings of officers do you know? 2. What is the difference between commissioned and non-commissioned officers? 3. What is a warrant? 4. What is the pay scale used for? 5. Are there any ranks for enlisted personnel?
GA; BG; VADM; MSGT; GAF; GEN; SCPO; LTG; MG; COL; LTJG; LTC; MAJ; CPT; RADM; 1LT; 2LT; PO1; MWO; RCT; SMAJ; 1SGT; CPT; SFC; MCPO; SSGT; SGT; CPL; PFC; PVT; FADM; ADM; COMMO; CDR; LCDR; LT; ENS; CPO; NCO.
Badge of leadership; derive one’s authority; administrative classification; compensation; base pay; service aptitudes; fill a leadership role; hold a warrant; develop fighting skills; identify who's in charge; in the heat of battle; special rank badge; know at a glance; be differentiated in rank; at the outbreak of the Revolutionary War; depending on one’s qualification; follow the British patterns; military experience; confuse rank with pay grades; equivalent officer groupings; hold positions; responsibility for personnel and its training; minor change; shouted order; receive the same amount of pay.
Розрізнятися у військовому званні; відповідальність за особовий склад та його бойову підготовку; службові здібності; в залежності від кваліфікації; службова класифікація; усний наказ; отримувати повноваження; виконувати командні функції; отримувати однакове грошове утримання; грошове забезпечення/утримання; впізнавати командира; незначні зміни; перебувати на посаді; військовий досвід; на початку війни за незалежність; спеціальна ознака військового звання; плутати військове звання зі штатно-посадовою категорією; мінімальне грошове утримання; миттєво впізнавати; використовувати британські зразки; в розпалі битви; розвивати бойові навички; ознака командира; відповідні категорії офіцерського складу; отримувати наказ міністра (СВ, ВПС, ВМС) про присвоєння військового звання ворент-офіцера.
Виконувати накази; rank insignia; військове вітання; віддавати військове вітання; increase in rank; офіцерське звання; commissioned officer (ComO); ворент-офіцер; hold presidential commission; штатно-посадова категорія (за грошовим утриманням); тарифний розряд; company grade officers; старші офіцери; general officers; молодші офіцери (ВМС); mid-grade officers; адмірали; non-commissioned officers (NCOs); сержант; petty officer (РО); наказ про присвоєння військового звання ворент-офіцера; receive commission; підвищення у військовому званні; specialist; фахівець широкого профілю; enlisted personnel; посада; seniority; одержувати підтвердження Сенатом військового звання; be a direct representative of the president of the United States; військове звання; obey orders; знаки розрізнення за військовим званням; salute; підвищення у військовому званні; officer rank; офіцер; warrant officer (WO); отримати офіцерське звання від президента; pay grade; молодші офіцери; field grade officers; генерали; junior grade officers; старші офіцери (ВМС); flag officers; сержантський і старшинський склад; sergeant (SGT); старшина (ВМС); warrant; отримати офіцерське звання; promotion; спеціаліст (фахівець вузького профілю); generalist; рядовий склад; position; старшинство; be confirmed at one’s rank by the Senate; прямо призначатися президентом США.
rank 1. n. ряд, лінія to form up in three ranks – розташувати в три ряди to close ranks – зімкнути ряди
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Последнее изменение этой страницы: 2016-06-22; просмотров: 322; Нарушение авторского права страницы; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! infopedia.su Все материалы представленные на сайте исключительно с целью ознакомления читателями и не преследуют коммерческих целей или нарушение авторских прав. Обратная связь - 216.73.216.214 (0.01 с.) |