
Заглавная страница Избранные статьи Случайная статья Познавательные статьи Новые добавления Обратная связь FAQ Написать работу КАТЕГОРИИ: ТОП 10 на сайте Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрацииТехника нижней прямой подачи мяча. Франко-прусская война (причины и последствия) Организация работы процедурного кабинета Смысловое и механическое запоминание, их место и роль в усвоении знаний Коммуникативные барьеры и пути их преодоления Обработка изделий медицинского назначения многократного применения Образцы текста публицистического стиля Четыре типа изменения баланса Задачи с ответами для Всероссийской олимпиады по праву 
Мы поможем в написании ваших работ! ЗНАЕТЕ ЛИ ВЫ?
Влияние общества на человека
Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрации Практические работы по географии для 6 класса Организация работы процедурного кабинета Изменения в неживой природе осенью Уборка процедурного кабинета Сольфеджио. Все правила по сольфеджио Балочные системы. Определение реакций опор и моментов защемления |
Construction Industry Glossary.Содержание книги
Поиск на нашем сайте
Acoustics The science of sound. In housing, acoustical materials used to keep down noise within a room or to prevent it from passing through walls. Adobe construction Construction using sun-dried units of adobe soil for walls; usually found in the southwestern United States. Air conditioner An apparatus that can heat, cool, clean, and circulate air. Air-dried lumber Lumber that is left in the open to dry rather than being dried by a kiln. Air duct A pipe, usually made of sheet metal, that conducts air to rooms from a central source. Air trap A U-shaped pipe filled with water and located beneath plumbing fixtures to form a seal against the passage of gases and odors. Alcove A recessed space connected at the side of a larger room. Alteration A change in, or addition to, an existing building. Amortization An installment payment of a loan, usually monthly for a home loan. Ampere The unit used in the measure of the rate of flow of electricity. Anchor bolt A threaded rod inserted in masonry construction for anchoring the sill plate to the foundation. Angle iron A structural piece of rolled steel shaped to form a 90° angle. Appraisal The estimated price of a house which a buyer would pay and the seller accept for a property. An appraisal is a detailed evaluation of the property. Apron The finish board immediately below a window sill. Also the part of the driveway that leads directly into the garage.
Arcade A series of arches supported by a row of columns. Arch A curved structure that will support itself by mutual pressure and the weight above its curved opening. Architect A person who plans and designs buildings and oversees their construction. Area wall A wall surrounding an area way. Areaway A recessed area below grade around the foundation to allow light and ventilation into a basement window or doorway. Ashlar A facing of squared stones. Ashpit The area below the hearth of a fireplace which collects the ashes. Asphalt Bituminus sandstones used for paving streets and waterproofing flat roofs. Asphalt shingles Composition roof shingles made from asphalt-impregnated felt covered with mineral granules. Assessed value A value set by governmental assessors to determine tax assessments. Atrium An open court within a building. Attic The space between the roof and the ceiling. Awning window An out-swinging window hinged at the top.
Backhearth The part of the hearth inside the fireplace. Baffle A partial blocking against a flow of wind or sound. Balcony A deck projecting from the wall of a building above the ground. Balloon framing The building-frame construction in which each of the studs is one piece from the foundation to the roof of a two-story house. Balustrade A series of balusters or posts connected by a rail, generally used for porches and balconies. Banister A handrail. Base The finish of a room at the junction of the walls and floor. Baseboard The finish board covering the interior wall where the wall and floor meet. Base course The lowest part of masonry construction. Base line A located line for reference control purposes. Basement The lowest story of a building, partially or entirely below ground. Base plate A plate, usually of steel, upon which a column rests. Base shoe A molding used next to the floor in interior baseboards. Batt A blanket insulation material usually made of mineral fibers and designed to be installed between framing members. Batten A narrow strip of board, used to cover cracks between the boards in board-and-batten siding.
Batter Sloping a masonry or concrete wall upward and backward from the perpendicular. Batter boards Boards at exact elevations nailed to posts just outside the corners of a proposed building. Strings are stretched across the boards to locate the outline of the foundation. Bay window A window projecting out from the wall of a building to form a recess in the room. Beam A horizontal structural member that carries a load. Beam ceiling A ceiling in which the ceiling beams are exposed to view. Bearing plate A plate that provides support for a structural member. Bearing wall or partition A wall supporting any vertical load other than its own weight. Bench mark A metal or stone marker placed in the ground by a surveyor with the elevation on it. This is the reference point to determine lines, grades, and elevations in the area. Bending moment A measure of the forces that break a beam by bending. Bent A frame consisting of two supporting columns and a girder or truss used in vertical position in a structure. Bevel siding Shingles or other siding board thicker on one edge than the other. The thick edge overlaps the thin edge of the next board. Bib A threaded faucet allowing a hose to be attached. Bill of material A parts list of material accompanying a structural drawing. Blanket insulation Insulation in rolled-sheet form, often backed by treated paper that forms a vapor barrier. Blocking Small wood framing members that fill in the open space between the floor and ceiling joists to add stiffness to the floors and ceiling. Blueprint An architectural drawing used by workers to build from. The original drawing is transferred to a sensitized paper that turns blue with white lines when printed. Also, prints of blue lines on white paper. Board measure A system of lumber measurement having as a unit a board foot. One board foot is the equivalent of 1 foot square by 1 inch thick. Brace Any stiffening member of a framework. Braced framing Frame construction with posts and braces used for stiffening. Morerigid than balloon framing. Breezeway A roofed walkwaywith open sides. It connects the house and garage. If large enough, it can be used as a patio. Broker An agent in buying and selling property. BTU Abbreviation for British thermal unit, a standard unit for measuring heat gain or loss. Buck Frame for a door, usually made of metal, into which the finished door fits. Building code A collection of legal requirements for buildings designed to protect the safety, health, and general welfare of people who work and livein them. Building line An imaginary line on a plot beyond which the building cannot extend. Building paper A heavy, waterproof paper used over sheathing and sub floorsto prevent passage of air and water. Building permit A permit issued by a municipal government authorizing the construction of a building or structure. Built-up beam A beam constructed of smaller members fastened together. Built-up roof A roofing male-rial composed of several lasers of fell and asphalt. Butterfly roof A roof with two sides sloping down tow cud the interior ot the house. Butt joint A joint formed by placing the end of one member against another member. Buttress A mass of masonry projecting beyond a wall to take thrust or pressure. A projection from a wall to create additional strength and support. BX cable Armored electric cable wrapped in plastic and protected by a flexible steel covering.
Canopy A projection over windows and doors to protect them from the weather. Cantilever A projecting member supported only at one end. Cant strip An angular board used to eliminate a sharp right angle on roofs or flashing. Carport An automobile shelter not fully enclosed. Carriage The horizontal part of the stringers of a stair that supports the treads. Casement window A hinged window that opens out, usually made of metal. Casing A metal or wooden member around door and window openings to give a finished appearance. Catch basin An underground structure for drainage into whichthe water from a roof or floor will drain. It is connected with a sewer or drain. Caulking A waterproof material used to seal cracks. Cavity wall A hollow wall usually made up of two brick walls built a few inches apart and joined together with brick or metal ties. Cedar shingles Roofing and siding shingles made from western red cedar. Cement A masomy adhesive material purchased in the form of pulverized powder. Any substance used in its soft state to join other materials together and which afterward dries and hardens. Central heating A single source of heat that is distributed by pipes or ducts. Certificate of title A document given to the home buyer with the deed, stating that the title to the property named in the deed is clearly established. Cesspool A pit or cistern to hold sewage. Chalk line A string that is heavily chalked, held tight, then plucked to make a straight guideline against boards or other surfaces. Chase A vertical space within a building for ducts, pipes, or wires. Checks Splits or cracks in a board, ordinarily caused by seasoning. Check valve A valve that permits passage through a pipe in only one direction. Chimney A vertical flue for passing smoke and gases outside a building. Chimney stack A group of flues in the same chimney. Chord The principal members of a roof or bridge truss. The upper members are indicated by the term upper chord. The lower members are identified by the term lower chord. Cinder block A building block made of cement and cinder. Circuit The path of an electric current. The closed loop of wire in which an electric current can flow. Circuit breaker A device used to open and close an electrical circuit. Cistern A tank or other reservoir to store rainwater that has run off the roof. Clapboard A board, thicker on one side than the other, used to overlap an adjacent board to make house siding. Clearance A clear space to allow passage. Clerestory A set of high windows often above a roof line. Clinch To. bend over the protruding end of a nail. Clip A small connecting angle used for fastening various members of a structure. Collar beam A horizontal member fastening opposing rafters below the ridge in roof framing. Column In architecture: a perpendicular supporting member, circular in section; in engineering: a vertical structural member supporting loads acting on or near and in the direction of its longitudinal axis. Common wall A wall that serves two dwelling units. Compression A force that tends to make a member fail because of crushing. Concrete A mixture of cement, sand, and gravel with water. Concrete block Precast hollow or solid blocks of concrete. Condemn To legally declare unfit for use. Condensation The formation of frost or drops of water on inside walls when warm vapor inside a room meets a cold wall or window. Conductor In architecture: a drain pipe leading from the roof; in electricity: anything that permits the passage of an electric current. Conductor pipe A round, square, or rectangular metal pipe used to lead water from the roof to the sewer. Conduit A channel built to convey water or other fluids; a drain or sewer. In electrical work, a channel that carries wires for protection and for safety. Construction loan A mortgage loan to be used to pay for labor and materials going into the house. Money is usually advanced to the builder as construction progresses and is repaid when the house is completed and sold. Continuous beam A beam that has three or more supports. Contractor A person offering to build for a specified sum of money. Convector A heat-transfer surface that uses convection currents to transfer heat. Coping The top course of a masonry wall that projects to protect the wall from the weather.
Corbel A projection in a masonry wall made by setting courses beyond the lower ones. Corner bead A metal molding built into plaster corners to prevent the accidental breaking off of the plaster. Cornice The part of a roof that projects out from the wall. Counterflashing A flashing used under the regular flashing. Course A continuous row of stone or brick of uniform height. Court An open space surrounded partly or entirely by a building. Crawl space The shallow space below the floor of a house built above the ground. It is surrounded by the foundation walls. Cricket A roof device used at intersections to divert water.
Cripple A structural member that is cut less than full length, such as a studding piece above a window or door. Cross bracing Boards nailed diagonally across studs or other boards to make framework rigid. Cross bridging Bracing between floor joists to add stiffness to the floors.
Crosshatch Lines drawn closely together at an angle of 45 degrees, to show a section cut. Cull Building material rejected as below standard grade. Culvert A passage for water below ground level. Cupola A small structure built on top of a roof. Curb A very low wall. Cure To allow concrete to dry slowly by keeping it moist to allow maximum strength. Curtain wall An exterior wall that provides no structural support.
Damper A movable plate that regulates the draft of a stove, fireplace, or furnace. Datum A reference point of starting elevations used in mapping and surveying. Deadening Construction intended to prevent the passage of sound. Dead load All the weight in a structure made up of unmovable materials. See also Loads. Decay The disintegration of wood through the action of fungi. Dehumidify To reduce the moisture content in the air. Density The number of people living in a calculated area of land such as a square mile or square kilometer. Depreciation Loss of value. Designer A person who designs houses but is not a registered architect. Detail To provide specific instruction with a drawing, dimensions, notes, or specifications. Dimension building material Building material that has been precut to specific sizes. Dimension line A line with arrowheads at either end to show the distance between two points. Dome A hemispherical roof form. Doorstop The strips on the doorjambs against which the door closes. Dormer A structure projecting from a sloping roof to accommodate a window. Double glazing A pane made of two pieces of glass with air space between and sealed to provide insulation. Double header Two or more timbers joined for strength. Double-hung A window having top and bottom sashes each capable of movement up and down. Downspout A pipe for carrying rainwater from the roof to the ground.
Drain A pipe for carrying waste water. Dressed lumber Lumber machined and smoothed at the mill. Usually Drip A projecting construction member or groove below the member to prevent rainwater from running down the face of a wall or to protect the bottom of a door or window from leakage. Dry rot A term applied to many types of decay, especially an advanced stage when the wood can be easily crushed to a dry powder. The term is actually inaccurate because all fungi require considerable moisture for growth. Dry-wall construction Interior wall covering other than plaster, usually referred to as gypsum-board surfacing. Dry well A pit located in porous ground and lined with rock that allows water to seep through the pit. Used for the disposal of rainwater or the effluent from a septic tank. Ducts Sheet-metal conductors for warm- and cold-air distribution.
Eave That part of a roof that projects over a wall.
Efflorescence Whitish powder that forms on the surface of bricks or stone walls due to evaporation of moisture containing salts. Effluent The liquid discharge from a septic tank after bacterial treatment. Elastic limit The limit to which a material can be bent or pulled out of shape and still return to its former shape and dimensions. Elbow An L-shaped pipe fitting.
Elevation The drawings of the front, side, or rear face of a building. Ell An extension or wing of a building at right angles to the main section. Embellish To add decoration. Eminent domain The right of the local government to condemn for public use. Enamel Paint with a considerable amount of varnish. It produces a hard, glossy surface. Equity The interest in or value of real estate the owner has in excess of the mortgage indebtedness. Escutcheon The hardware on a door to accommodate the knob and keyhole. Excavation A cavity or pit produced by digging the earth in preparation for construction.
Facade The face or front elevation of a building. Face brick A brick used on the outside face of a wall. Facing A finish material used to cover another. Fascia A vertical board nailed on the ends of the rafters. It is part of the cornice. Fatigue A weakening of structural members. Federal Housing Administration (FHA) A government agency that insures loans made by regular lending institutions. Felt papers Papers, sometimes tar-impregnated, used on roofs and side walls to give protection against dampness and leaks. Fenestration The arrangement of windows. Fiberboard A building board made with fibrous material – used as an insulating board. Filled insulation A loose insulating material poured from bags or blown by machines into walls. Finish lumber Dressed wood used for building trim. Firebrick A brick that is especially hard and heat-resistent. Used in fireplaces. Fireclay A grade of clay that can withstand a large quantity of heat. Used for firebrick. Fire cut The angular cut at the end of a joist designed to rest on a brick wall. Fire door A door that will resist fire. Fire partition A partition designed to restrict the spread of fire. Fire stop Obstruction across air passages in buildings to prevent the spread of hot gases and flames. A horizontal blocking between wall studs. Fished A splice strengthened by metal pieces on the sides. Fixed light A permanently sealed window. Fixture A piece of electric or plumbing equipment. Flagging Cut stone, slate, or marble used on floors. Flagstone Flat stone used for floors, steps, walks, or walls. Flashing The material used for and the process of making watertight the roof intersections and other exposed places on the outside of the house. Flat roof A roof with just enough pitch to let water drain. Flitch beam A built-up beam formed by a metal plate sandwiched between two wood members and bolted together for additional strength. Floating Spreading plaster, stucco, or cement on walls or floors with use of a tool called a float. Floor plan The top view of a building at a specified floor level. A floor plan includes all vertical details at or above win-dowsill levels. Floor plug An electrical outlet flush with the floor. Flue The opening in a chimney through which smoke passes. Flue lining Terra-cot ta pipe used for the inner lining of chimneys. Flush surface A continuous surface without an angle. Footing An enlargement at the lower end of a wall, pier, or column, to distribute the load into the ground. Footing form A wooden or steel structure placed around the footing that will hold the concrete to the desired shape and size. Framing (western) The wood skeleton of a building. Frieze The flat board of cornice trim that is fastened to the wall.
Frost line The depth of frost penetration into the soil. Fumigate To destroy harmful insect or animal life with fumes. Furring Narrow strips of board nailed upon walls and ceilings to form a straight surface for the purpose of attaching wallboards or ceiling tile. Fuse A strip of soft metal inserted in an electric circuit and designed to melt and open the circuit should the current exceed a predetermined value.
Gable roof A roof that slopes from two sides only. Galvanize A lead and zinc bath treatment to prevent rusting. Gambrel roof A symmetrical roof with two different pitches or slopes on each side. Garret An attic. Girder A horizontal beam supporting the floor joists.
Glazing Placing of glass in windows or doors. Grade The level of the ground around a building. Gradient The slant of a rod, piping, or the ground, expressed in percent. Graphic symbols Symbolic representations used in drawing that simplify presentations of complicated items. Gravel stop A strip of metal with a vertical lip used to retain the gravel around the edge of a built-in roof. Green lumber Lumber that still contains moisture or sap. Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI) An electrical device that breaks an electric circuit when an excessive leakage current is detected. Intended to eliminate shock hazards to people. Grout A thin cement mortar used for leveling and filling masonry holes. Gusset A plywood or metal plate used to strengthen the joints of a truss. Gutter A trough for earning off water. Gypsum board A board made of plaster with a covering of paper.
Hanger An iron strap used to support a joist beam or pipe. Hardpan A compacted layer of soils. Head The upper frame on a door or window. Header The horizontal supporting member above openings that serves as a lintel. Also one or more pieces of lumber supporting ends of joists. Used in framing openings of stairs and chimneys. Headroom The clear space between floor line and ceiling, as in a stairway. Hearth That part of the floor directly in front of the fireplace, and the floor inside the fireplace on which the fire is built. It is made of fire-resistant masonry. Heel plate A plate at the ends of a truss. Hip rafter The diagonal rafter that extends from the plate to the ridge to form the hip. Hip roof A roof with four sloping sides. House drain Horizontal sewer piping within a building that receives wastes from the soil stacks. House sewer The watertight soil pipe extending from the exterior of the foundation wall to the public sewer. Humidifier A mechanical device that controls the amount of water vapor to be added to the atmosphere. Humidistat An instrument used for measuring and controlling moisture in the air.
Indirect lighting Artificial light that is bounced off ceiling and walls for general lighting. Insulating board Any board suitable for insulating purposes, usually manufactured board made from vegetable fibers, such as fiberboard. Insulation Materials for obstructing the passage of sound, heat, or cold from one surface to another. Interior trim General trim for all the finish molding, casing, baseboard, etc.
Jalousie A type of window consisting of a number of Ions, thin, hinged panels. Jamb The sides of a doorway or window opening. Jerry-built Poorly constructed. Joints The meeting of two separate pieces of material for a common bond. Joist A horizontal structural member that supports the floor system or ceiling system.
Keystone The top, wedge-shaped stone of an arch. Kiln A heating chamber for drying lumber. King post In a roof truss, the central upright piece. Knee brace A corner brace, fastened at an angle from wall stud to rafter, stiffening a wood or steel frame to prevent angular movement. Knee wall Low wall resulting from one-and-one-half-story construction. Knob and tube Electric wiring through walls where insulated wires are supported with porcelain knobs and tubes when passing through wood construction members.
Laminated beam A beam made by bonding together several layers of material. Landing A platform in a flight of steps. Landscape architect A professional person who utilizes and adapts land for people's use. Lap joint A joint produced by lapping two pieces of material. Lath (metal) Sheet-metal screening used as a base for plastering. Lath (wood) A wooden strip nailed to studding and joists to which plaster is applied. Lattice A grille or openwork made by crossing strips of wood or metal. Lavatory A washbasin or a room equipped with a washbasin. Leaching bed A system of trenches that carries wastes from sewers. It is constructed in sandy soils or in earth filled with stones or gravel. Leader A vertical pipe or downspout that carries rainwater from the gutter to the ground. Lean-to A shed whose rafters lean against another building or other part of the same building. Ledger A wood strip nailed to the lower side of a girder to provide a bearing surface for joists.
Lessee The tenant who holds a lease. Lessor The owner of leased property. Lien A legal claim on a property that may be exercised in default of payment of a debt. Lineal foot A measurement of 1 foot along a straight line. Lintel A horizontal piece of wood, stone, or steel across the top of door and window openings to bear the weight of the walls above the opening. Loads Live load: the total of all moving and variable loads that may be placed upon a building. Dead load: the weight of all permanent, stationary construction included in a building. Load-bearing walls Walls that support weight from above as well as their own weight. Loggia A roofed, open passage along the front or side of a building. It is often at an upper level, and it often has a series of columns on either or both sides. Lookout A horizontal framing member extending from studs out to end of rafters. Lot line The line forming the legal boundary of a piece of property. Louver A set of fixed or movable slats adjusted to provide both shelter and ventilation.
Mantel A shelf over a fireplace. Market price The amount that property can be sold for at a given time. Market value The amount that property is worth at a given time. Masonry Anything built with stone, brick, tiles, or concrete. Meeting rail The horizontal rails of a double-hung sash that fit together when the window is closed. Member A single piece in structure that is complete in itself. Metal tie A strip of metal used to fasten construction members together. Metal wall ties Strips of corrugated metal used to tie a brick veneer wall to framework. Mildew A mold on wood caused by fungi. Millwork The finish woodwork in a building, such as cabinets and trim. Mineral wool An insulating material made into a fibrous form from mineral slag. Modular construction Construction in which the size of the building and the building materials are based on a common unit of measure. Moisture barrier A material such as specially treated paper that retards the passage of vapor or moisture into walls and prevents condensation within the walls. Monolithic Concrete construction poured and cast in one piece without joints. Monument A boundary marker set by surveyors to locate property lines. Mortar A mixture of cement, sand, and water, used as a bonding agent by the mason for binding bricks and stone. Mortgage A pledging of property, conditional on payment of the debt in full. Mortgagee The lender of money to the mortgagor. Mortgagor The owner who mortgages property in return for a loan. Mosaic Small colored tile, glass, stone, or similar material arranged on an adhesive ground to produce a decorative surface. Mud room A small room or en-tranceway where muddy overshoes and wet garments can be removed before entering other rooms. Mullion A vertical bar in a window that separates the window into sections. Muntin A small bar separating the glass lights in a window.
Nominal dimension Dimensions for finished lumber in which the stated dimension is usually larger than the actual dimension. These dimensions are usually larger by an amount required to smooth a board. Nonbearing wall A dividing wall that does not support a vertical load other than its own weight. Nonferrous metal Metal containing no iron, such as copper, brass, or aluminum. Nosing The rounded edge of a stair tread.
On center Measurement from the center of one member to the center of another (noted oc). Open-end mortgage A mortgage that permits the remaining amount of the loan to be increased, as for improvements, by mutual agreement of the lender and borrower, without rewriting the mortgage. Orientation The positioning of a house on a lot in relation to the sun, wind, view, and noise. Outlet Any kind of electrical box allowing current to be drawn from the electrical system for lighting or appliances. Overhang The horizontal distance that a roof projects beyond a wall.
Parapet A low wall or railing around the edge of a roof. Parging A thin coat of plaster applied to masonry surfaces for smoothing purposes. Parquet flooring Flooring, usually of wood, laid in an alternating or inlaid pattern to form various designs. Partition An interior wall that separates two rooms. Party wall A wall between two adjoining buildings in which both owners share, such as common wall between row houses. Patio An open court. Pediment The triangular space forming the gable end of a low-pitched roof. A similar form is often used as a decoration over doors in classic architecture. Penny A term for the length of a nail, abbreviated d. Periphery The entire outside edge of an object. Perspective A drawing of an object in a three-dimensional form on a plane surface. An object drawn as it would appear to the eye. Pier A block of concrete supporting the floor of a building. Pilaster A portion of a square column, usually set within or against a wall for the purpose of strengthening the wall. Also a decorative column attached to a wall. Piles Long posts driven into the soil in swampy locations, or whenever it is difficult to secure a firm foundation, upon which the foundation footing is laid. Pillar A column used for supporting parts of a structure. Pinnacle Projecting or ornamental cap on the high point of a roof. Plan A horizontal, graphic representational section of a building, showing the walls, doors, windows, stairs, chimneys, and surrounding objects as walks and landscape. Planks Material 2 or 3 inches (50 or 75 mm) thick and more than 4 inches (100 mm) wide, such as joists, flooring, and the like. Plaster A mortarlike composition used for covering walls and ceilings. Usually made of port-land cement mixed with sand and water. Plasterboard A board made of plastering material covered on both sides with heavy paper. It is often used instead of plaster. Also called gypsum board. Plaster ground A nailer strip included in plaster walls to act as a gage for thickness of plaster and to give a nailing support for finish trim around openings and near the base of the wall. Plat A map or chart of an area showing boundaries of lots and other pieces of property. Plate The top horizontal member of a row of studs in a frame wall to earn1 the trusses of a roof or to carry the rafters directly. Also a shoe or base member, as of a partition or other frame. Plate cut The cut in a rafter that rests upon the plate. It is also called the seat cut or bird-mouth. Plate glass A high-quality sheet of glass used in large windows. Platform or Western Framing Multistory house framing in which each story is built upon the other. Plenum system A system of heating or air conditioning in which the air is forced through a chamber connected to distributing ducts. Plot The land on which a building stands. Plow To cut a groove running in the same direction as the grain of the wood. Plumb Said of an object when it is in true vertical position as determined by a plumb bob. Plywood A piece of wood made of three or more layers of veneer joined with glue and usually laid with the grain of adjoining piles at right angles. Porch A covered area attached to a house at an entrance. Portico A roof supported by columns, whether attached to a building or wholly by itself. Portland cement A hydraulic cement, extremely hard, formed by burning silica, lime, and alumina together and then grinding up the mixture. Post A perpendicular supporting member. Post-and-beam construction Wall construction consisting of posts rather than studs. Precast Concrete shapes made separately before being used in a structure. Prefabricated houses Houses that are built in sections or component parts in a factors', and then assembled at the site. Primary coat The first coat of paint. Principal The original amount of money loaned. Purlin A structural member spanning from truss to truss and supporting the rafters.
Quarry tile A machine-made, unglazed tile. Quoins Large squared stones set in the corners of a masonry building foi" appearance.
Rafters Structural members used to frame a roof. Several types are common: hip, jack, valley, and cripple. Raglin The open joint in masonry to receive flashing. Realtor A real-estate broker who is a member of a local chapter of the National Association of Real Estate Boards. Register The open end of a duct in a room for warm or cool air. Reinforced concrete Concrete in which steel bars or webbing has been embedded for strength. Rendering The art of shading or coloring a drawing. Restoration Rebuilding a structure so it will appear in its original form. Restrictions Limitations on the use of real estate as set by law or contaned in a deed. Retaining wall A wall to hold back an earth embankment. Rheostat An instrument for regulating electric current. Ribbon A support for joists. A board set into studs that are cut to support joists. Ridge The top edge of the roof where two slopes meet. Ridge cap A wood or metal cap used over roofing at the ridge. Riprap Stones placed on a slope to prevent erosion. Also broken stone used for foundation fill. Rise The vertical height of a roof. Riser The vertical board in a stairway between two treads. Rock wool An insulating material that looks like wool but is composed of suchsubstances as granite or silica. Rodding Stirring freshly poured concrete with a vibrator to remove air pockets. Roll roofing Roofing material of fiber and asphalt. Rough floor The sub floor on which the finished floor is laid. Rough hardware All the hardware used in a house, such as nails and bolts, that cannot be seen in the completed house. Roughing in Putting up the skeleton of the building. Rough lumber Lumber as it comes from the saw. Rough opening Any unfinished opening in the framing of a building. Run Stonework having irregular-shaped units and no indicalion of systemic course work. The horizontal distance covered by a (light of stairs. The length of a rafter.
Safety factor The ultimate strength of the material divided by the allowable working load. The element of safety needed to make certain that there will be no structural failures. Sand finish A final plaster coat; a skim coat. Sap All the fluids in a tree. Sash The movable framework in which window panes are set. Scab A small wood member, used to join other members, which is fastened on the outside face.
Scarfing A joint between two pieces of wood that allows them to be spliced lengthwise. Schedule A list of parts or details. Scratch coat The first coat of plaster. It is scratched to provide a good bond for the next coat. Screed A guide for the correct thickness of plaster or concrete being placed on surfaces. Scuttle A small opening in a ceiling to provide access to an attic or roof. Seasoning Drying out of green lumber, either in an oven or kiln or by exposing it to air. Second mortgage A mortgage made by a home buyer to raise money for a down payment required under the first mortgage. Section The drawing of an object that is cut to show the interior. Also, a panel construction used in walls, floors, ceilings, or roofs. Seepage pit A pit or cesspool into which sewage drains from a septic tank, and which is so constructed that the liquid waste seeps through the sides of the pit into the ground. Septic tank A concrete or steel tank where sewage is reduced partially by bacterial action. About half the sewage solids become gases that escape back through the vent stack in the house. The other solids and liquids flow from the tank into the ground through a tile bed. Service connection The electric wires to the building from the outside power lines.
Set The hardening of cement or plaster. Setback A zoning restriction on the location of the home on a lot. Settlement Compression of the soil or the members in a structure. Shakes Thick hand-cut shingles. Sheathing The structural covering of boards or wallboards, placed over exterior studding or rafters of a structure. Sheathing paper A paper barrier against wind and moisture applied between sheathing and outer wall covering. Shed roof A flat roof slanting in one direction.
Shim A piece of material used to level or fill in the space between two surfaces.
Shingles Thin pieces of wood or other materials that overlap each other in covering a roof. The number and kind needed depend on the steepness of the roof slope and other factors. Kinds of shingles include tile, slate shingles, and asphalt shingles. Shiplap Boards with lapped joints along their edges. Shoe mold The small mold against the baseboard at the floor. Shoring Lumber placed in a slanted position to support the structure of a building temporarily. Siding The outside boards of an exterior wall. Sill The horizontal exterior member below a window or door opening. Also the wood member placed directly on top of the foundation wall in wood-frame construction.
Skeleton construction Construction where the frame carries all the weight. Skylight An opening in the roof for admitting light. Slab foundation A reinforced concrete floor and foundation system. Sleepers Strips of wood, usually
Smoke chamber The portion of a chimney flue located directly лег the fireplace. Soffit The undersurface of a projecting structure.
Softwood Wood from trees having needles rather than broad leaves. The term does not necessarily refer to the softness of the wood. Soil stack The main vertical pipe that receives waste from all fixtures. Solar heat Heat from the sun's rays. Sole The horizontal framing member directly under the studs, Spacing The distance between structural members. Spackle To cover wallboard joints with plaster. Span The distance between structural supports. Specification The written or printed direction regarding the details of a building or other construction. Spike A large, heavy nail. Splice Joining of two similar members in a straight line. Stack A vertical pipe. Stakeout Marking the foundation layout with stakes. Steel framing Skeleton framing with structural steel beams. Steening Brickwork without mortar. Stile A vertical member of a door, window, or panel. Stirrup A metal U-shaped strap used to support framing members.
Stock Common sizes of building materials and equipment available from most commercial industries. Stool An inside windowsill. Stop A small strip to hold a door or window sash in place. Storm door or window An extra door or extra window placed outside an ordinary door or window for added protection against cold. Storm sewer A sewer that is designed to carry away water from storms, but not sewage. Stress Any force acting upon a part or member used in construction. Stress-cover construction Construction consisting of panels or sections with wood frameworks to which plywood or other sheet material is bonded with glue so that the covering carries a large part of the loads. Stretcher course A row of masonry in a wall with the long side of the units exposed to the exterior. Stringer One of the sides of a flight of stairs. The supporting member cut to receive the treads and risers. Stripping Removal of concrete forms from the hardened concrete. Stucco Any of various plasters used for covering walls, especially an exterior wall covering in which cement is used. Stud Upright beams in theframework of a building. Usually referred to as Subfloor The rough flooring under the finish floor that rests on the floor joists. Sump A pit in a basement floor to collect water, into which a sump pump is placed to remove the water through sewer pipes. Surfaced lumber Lumber that is dressed by running it through a planer. Surveyor A person skilled in land measurement. Swale A drainage channel formed where two slopes meet.
Tar A dark heavy oil used in roofing and roof surfacing. Tempered Thoroughly mixed cement or mortar. Tensile strength The greatest stretching stress a structural member can bear without breaking or cracking. Termite shield Sheet metal used to block the passage of termites. Thermal conductor A substance capable of transmitting heat. Thermostat A device for automatically controlling the supply of heat. Threshold The beveled piece of stone, wood, or metal over which the door swings. It is sometimes called a carpet strip, or a saddle. Throat A passage directly above the fireplace opening where a damper is set. Tie A structural member used to bind others together. Timber Lumber with a cross section larger than 4 by 6 inches (100 by 150 mm), for posts, sills, and girders. Title insurance An agreement to pay the buyer for losses in title of ownership. Toe nail To drive nails at an angle. Tolerance The acceptable variance of dimensions from a standard size. Tongue A projection on the edge of wood that joins with a similarly shaped groove.
Total run The total of all the tread widths in a stair. Transom A small window over a door. Tread The step or horizontal member of a staii. Trimmers Single or double joists or rafters that run around an opening in framing construction. Truss A triangular-shaped unit for supporting roof loads over long spans.
Undressed lumber Lumber that is not squared or finished smooth. Unit construction Construction that includes two or more preas-sembled walls, together with floor and ceiling construction, for shipment to the building site.
Valley jacks Rafters that run from a ridgeboard to a valley rafter. Valley rafter The diagonal rafter forming the intersection of two sloping roofs. Valve A device that regulates the flow of material in a pipe.
Vapor barrier A watertight material used to prevent the passage of moisture or water vapor into and through walls. Veneer A thin covering of valuable material over a less expensive material. Vent A screened opening for ventilation. Ventilation The process of supplying and removing air by natural or mechanical means to or from any space. Vent pipes Small ventilating pipes extending from each fixture of a plumbing system to the vent stack. Vent stack The upper portion of a soil or waste stack above the highest fixture. Vergeboard The board that serves as the eaves finish on the gable end of a building. Vestibule A small lobby or entrance room. Vitreous Pertaining to a composition of materials that resemble glass. Volume The amount of space occupied by an object. Measured in cubic units.
Wallboard Wood pulp, gypsum, or similar materials made into large rigid sheets that may be fastened to the frame of a building to provide a surface finish. Warp Any change from a true or plane surface. Warping includes bow, crook, cup, and twist. Warranty deed A guarantee that the property is as promised. Wash The slant upon a sill, capping, etc., to allow the water to run off. Waste stack A vertical pipe in a plumbing system that carries the discharge from any fixture. Waterproof Material or construction that prevents the passage of water. Water table A projecting mold near the base on the outside of a building to turn the rainwater outward. Also the level of subterranean water. Watt A unit of electrical energy. Weathering The mechanical or chemical disintegration and discoloration of the surface of exterior building materials. Weather strip A strip of metal or fabric fastened along the edges of windows and doors to reduce drafts and heat loss. Weep hole An opening at the bottom of a wall to allow the drainage of water. Well opening A floor opening for a stairway.
TEST KEYS Test № 1 (Units 1,2,3). 1 – 1; 2 – 2; 3 – 2; 4 – 2; 5 – 2; 6 – 2; 7 – 1; 8 – 2; 9 – 2; 10 – 2; 11 – 2; 12 – 2; 13 – 1; 14 – 3; 15 – 2; 16 – 2; 17 – 3; 18 – 1; 19 – 3; 20 – 1.
Test № 2 (Units 4,5,6). 1 – 3; 2 – 3; 3 – 3; 4 – 2; 5 – 2; 6 – 2; 7 – 2; 8 – 2; 9 – 1; 10 – 1; 11 – 1; 12 – 3; 13 – 2; 14 – 1; 15 – 1; |

 Abstract of title A summary of all deeds, wills, and legal actions to show ownership.
Abstract of title A summary of all deeds, wills, and legal actions to show ownership.
 Backfill Earth used to fill in areas around exterior foundation walls.
Backfill Earth used to fill in areas around exterior foundation walls.
 Cabinet work The finish interior woodwork.
Cabinet work The finish interior woodwork.


 Damp course A layer of waterproof material.
Damp course A layer of waterproof material.
 inch less than nominal (rough) size.
inch less than nominal (rough) size. Easement The right to use land owned by another, such as a utility company's right-of-way.
Easement The right to use land owned by another, such as a utility company's right-of-way.

 Fabrication Work done on parts of a structure at the factory before delivery to the building site.
Fabrication Work done on parts of a structure at the factory before delivery to the building site.

 Gable The triangular end of an exterior wall above the eaves.
Gable The triangular end of an exterior wall above the eaves.
 Half timber A frame construction of heavy timbers in which the spaces are filled in with masonry.
Half timber A frame construction of heavy timbers in which the spaces are filled in with masonry. I beam A steel beam with an I-shaped cross section.
I beam A steel beam with an I-shaped cross section. Jack rafter A short rafter, usually used on hip roofs.
Jack rafter A short rafter, usually used on hip roofs.
 Kalamein door A fireproof door with a metal covering.
Kalamein door A fireproof door with a metal covering. Lally column A steel column used as a support for girders and beams.
Lally column A steel column used as a support for girders and beams.

 Mansard roof A roof with two slopes on each side, with the lower slope much steeper than the upper.
Mansard roof A roof with two slopes on each side, with the lower slope much steeper than the upper.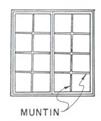
 Newel A post supporting the handrail at the top or bottom of a stairway.
Newel A post supporting the handrail at the top or bottom of a stairway. Obscure glass Sheet glass that is made translucent instead of transparent.
Obscure glass Sheet glass that is made translucent instead of transparent. Panelboard The center for controlling electrical circuits.
Panelboard The center for controlling electrical circuits.
 Quad An enclosed court.
Quad An enclosed court.
 Radiant heating A system using heating elements in the floors, ceilings, or walls to radiate heat into the room.
Radiant heating A system using heating elements in the floors, ceilings, or walls to radiate heat into the room. Saddle The ridge covering of a roof designed to carry water from the back of chimneys. Also called a cricket. A threshold.
Saddle The ridge covering of a roof designed to carry water from the back of chimneys. Also called a cricket. A threshold.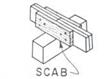




 's, laid over a slab floor to which finished wood Mooring is nailed.
's, laid over a slab floor to which finished wood Mooring is nailed.


 's, and spaced at 16 inches from center to center.
's, and spaced at 16 inches from center to center. Tamp To ram and concentrate soil.
Tamp To ram and concentrate soil.
 Underpinning A foundation replacement or reinforcement for temporary braced supports.
Underpinning A foundation replacement or reinforcement for temporary braced supports. Valley The internal angle formed by the two slopes of a roof.
Valley The internal angle formed by the two slopes of a roof.
 Wainscot Facing for the lower part of an interior wall.
Wainscot Facing for the lower part of an interior wall. Zoning Building restrictions as to size, location, and type of structures to be built in specific areas.
Zoning Building restrictions as to size, location, and type of structures to be built in specific areas.


