
Заглавная страница Избранные статьи Случайная статья Познавательные статьи Новые добавления Обратная связь FAQ Написать работу КАТЕГОРИИ: ТОП 10 на сайте Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрацииТехника нижней прямой подачи мяча. Франко-прусская война (причины и последствия) Организация работы процедурного кабинета Смысловое и механическое запоминание, их место и роль в усвоении знаний Коммуникативные барьеры и пути их преодоления Обработка изделий медицинского назначения многократного применения Образцы текста публицистического стиля Четыре типа изменения баланса Задачи с ответами для Всероссийской олимпиады по праву 
Мы поможем в написании ваших работ! ЗНАЕТЕ ЛИ ВЫ?
Влияние общества на человека
Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрации Практические работы по географии для 6 класса Организация работы процедурного кабинета Изменения в неживой природе осенью Уборка процедурного кабинета Сольфеджио. Все правила по сольфеджио Балочные системы. Определение реакций опор и моментов защемления |
In the USA and Great BritainСодержание книги
Похожие статьи вашей тематики
Поиск на нашем сайте МИНИСТЕРСТВО ВНУТРЕННИХ ДЕЛ РОССИЙСКОЙ ФЕДЕРАЦИИ
КАЛИНИНГРАДСКИЙ ФИЛИАЛ САНКТ-ПЕТЕРБУРГСКОГО УНИВЕРСИТЕТА
И.Ф. Кардаш POLICING: ISSUES AND TRENDS УЧЕБНО-МЕТОДИЧЕСКОЕ ПОСОБИЕ
Калининград Кардаш И.Ф. Policing: Issues and Trends. Деятельность полиции: проблемы и направления деятельности: Учебно-методическое пособие по английскому языку. Калининград: Калининградский филиал Санкт-Петербургского университета МВД России, 2015. 116 с. Автор-составитель: Кардаш Ирина Федоровна, старший преподаватель кафедры социально-экономических и гуманитарных дисциплин Калининградского филиала Санкт-Петербургского университета МВД России.
Рецензенты: Алафьева Е.Н., начальник отделения НЦБ Интерпола УМВД России по Калининградской области. Лобжанидзе Г.И., врио начальника кафедры психологии и педагогики ФГКОУ ВИО «Дальневосточный юридический институт МВД России», кандидат филологических наук, доцент.
Цель данного учебного пособия – формирование и совершенствование навыков различных видов речевой деятельности (чтения, говорения, аудирования, письма) на основе аутентичных текстов. Учебное пособие предназначено для курсантов и слушателей второго года обучения высших учебных заведений МВД России, приступающих к чтению юридических материалов, содержащих трудности лексического и грамматического характера, желающих совершенствовать свои знания, умения и навыки в профессионально ориентированной лексике. Оно дает возможность изучить и отработать профессиональную терминологию в сфере юриспруденции и правоохранительной деятельности, повторить, обобщить и систематизировать основные грамматические структуры и лексику, относящуюся к правоприменительной деятельности. Пособие может быть использовано для профессионального обучения и совершенствования навыков различных видов чтения, аудирования, говорения и письма. Пособие предназначено для работы в аудитории под руководством преподавателя, а также для самостоятельной работы.
ВВЕДЕНИЕ Учебно-методическое пособие “Policing: Issues and Trends” предназначено для курсантов и слушателей второго года обучения высших учебных заведений МВД России. Цель пособия – обеспечить практическое владение всеми видами речевой деятельности в рамках программы по дисциплине «Иностранный язык». В учебно-методическом пособии использованы современные аутентичные материалы. Правовая лексика вводится тематически, закрепляется в разнообразных упражнениях и находит свое применение в профессионально ориентированных ситуациях. Учебно-методическое пособие состоит из следующих разделов: 1. Полиция США, Великобритании 2. Интерпол 3. Европол 4. Международное сотрудничество полицейских Каждый раздел включает определенную часть лексико-грамматического материала, обрабатываемого дифференциально для устной речи и чтения с помощью упражнений. Во всех разделах имеются тексты для изучающего, просмотрового, поискового чтения, а также предусмотрены задания на дотекстовом, текстовом и послетекстовом этапах. В пособие также включены тексты для аудирования, которые способствуют формированию навыка восприятия иноязычной речи на слух. Дополнительные тексты для чтения по вышеперечисленным разделам пособия можно использовать как для самостоятельной работы, так и на аудиторных занятиях в группах с различным уровнем подготовки по усмотрению преподавателя.
UNIT 1 Police Force In the USA and Great Britain Every policeman knows that, though Governments may change, the police remain Leon Trotsky Part I The American Police Force Grammar: Infinitive Passive Infinitive Complex Subject Texts: Structure ofPolice Force in the United States Police in the United States The Most Glamorous Aspect of Police Work The history of the American Women Police The Federal Bureau of Investigation John Edgar Hoover Training Division FBI National Academy Nomination of Law Enforcement officers to Attend the National Academy Program of the FBI I. GRAMMAR
INFINITIVE Инфинитив – это неличная форма глагола, которая называет действие и в русском языке соответствует неопределенной форме глагола, которая отвечает на вопросы «что делать?» и «что сделать?».
to read – читать to investigate – расследовать Формальным признаком инфинитива является частица “ to ”. Инфинитив в предложении может быть: 1. Подлежащим: (что?) To detect the criminal is very often not an easy task. (Разыскать преступника – это часто очень нелегкая задача.) 2. Составной частью сказуемого: (что делать?) On of the basic tasks of the police is to maintain order. (Одна из основных задач милиции – это поддерживать порядок.) 3. Дополнением: (чему?) At our Criminalistics classes we are also taught to find evidence. (На занятиях по криминалистике нас учат также находить улики.) 4. Определением: (какого?) I had no intention to commit a crime. (У меня не было намерения совершить преступление.) 5. Обстоятельством цели: в этом случае инфинитив стоит в начале или конце предложения. Чтобы отличить инфинитив–обстоятельство, стоящее вначале предложения, от инфинитива–подлежащего надо найти сказуемое и по нему определить подлежащее. Кроме того, инфинитив–обстоятельство можно перенести в конец предложения без потери предложением структуры и смысла. To reduce the risk theyevacuated everybody from the danger zone.
Инфинитив имеет формы залога (Active, Passive), а также формы времени (Indefinite, Continuous, Perfect).
Наиболее распространенными являются формы Indefinite Infinitive Active и Passive. Остальные формы инфинитива встречаются значительно реже.
Ex. 1. A: Read the sentences, find Infinitive and translate the sentences into Russian. 1. He wanted to be present at the trial. 2. To know everything is to know nothing. 3. The criminal waited for the judge to pass a sentence. 4. It is important to begin investigating a crime as soon as possible. 5. A man is never too old to learn (Middleton). 6. To begin prosecution it is necessary to have evidence establishing (устанавливающий) the fact of the crime having been committed. B: Pay attention to the difference in the function of Infinitive and translate the sentences into Russian. 1. To decrease crime in our society is necessary nowdays. 2. To decrease crime in our society you are to do much preventive work. 3. To understand the actions of the criminal the operative is to examine the crime scene properly. 4. To understand the actions of the investigator is difficult sometimes. 5. To get all the necessary information an operative is to do much work. 6. To get all the necessary information was very difficult in that case. 7. In order to prove the case the operative and the investigator were to interrogate many witnesses. 8. To prove that case was not a simple matter.
PASSIVE INFINITIVE в функции определения
Пассивный инфинитив, стоящий после существительного, обычно переводится придаточным предложением с оттенком модальности, в котором действие, выраженное инфинитивом, совершается над лицом или предметом, к которому оно относится. The case to be investigated by this young officer is rather difficult. Дело, которое должно быть расследовано этим молодым следователем, довольно трудное.
Ex. 2. Read the sentences. Find Passive Infinitive and translate the sentences into Russian. 1. The evidence to be found at a crime scene is very important for the investigation. 2. The report to be written by the investigator must include all the facts collected during the investigation. 3. The crime to be investigated by Scotland Yard occurred on the Thames. 4. The crime case to be tried by our district court next week is much spoken of in our city. 5. He spoke of the problems to be settled in the nearest future. 6. The article to be discussed by the students is about the American Constitution.
COMPLEX SUBJECT (Сложное подлежащее или Именительный падеж с инфинитивом)
Подлежащее (существительное или местоимение) с инфинитивом, стоящим после сказуемого, выраженного одним из глаголов, to know (знать), to suppose (предполагать), to believe (полагать), to see (видеть), to hear (слышать), to say (говорить), to report (сообщать), to seem (казаться), to happen (случаться) и др., в страдательном залоге представляет собой оборот «именительный падеж с инфинитивом» или «сложное подлежащее». Перевод предложения со сложным подлежащим следует начинать со сказуемого, которое переводится на русский язык безличным или неопределенно–личным предложением (говорят, известно, считают, полагают, кажется, случается и т. п.); в придаточном предложении инфинитив становится сказуемым. Придаточное предложение в большинстве случаев вводится союзом «что». 2 1 3
Графически этот оборот можно изобразить следующим образом:
a)
(was, were) expected – Ожидают said – Говорят, что… considered – Считают found – Полагают believed – Полагают supposed - Предполагают
б)
smth. seems – Кажется appears – По - видимому proves – Оказалось, что … is (un) likely – (Мало) вероятно is sure (certain) – Обязательно
Ex. 3. Read the sentences. Find Complex Subject and translate the sentences into Russian. 1. The evidence proved to be very important. 2. This case is unlikely to be investigated quickly. 3. Good detectives are believed to be able to solve most crimes. 4. He proved to be a good lawyer. 5. The bank is believed to have been robbed by a group of armed men. 6. That man was reported to have committed a minor offence. 7. He is sure to come.
Ex. 4. Write these sentences in another way, beginning as shown. Use the underlined word in your sentences. Translate the new sentences. Model: It is believed that the thieves got in through the kitchen window. The thieves are believed to get in through the kitchen window.
1. It is reported that the building has been badly damaged by fire. The building… 2. It is thought that the prisoner escaped by climbing over a wall. The prisoner… 3. It is said that the man drove through the town at 90 miles an hour. The man… 4. It is believed that the criminal is wearing a white pullover and blue jeans. The criminal… 5. It is said that the young man has kicked a policeman. The young man…
Ex.5. Read the text, find sentences with Complex Subject and translate them into Russian. What are the main attributes of a policeman?
The Policeman in the United States Nothing is more difficult than being a police officer nowadays. The policeman is supposed to solve family disputes, enforce hundreds of laws, identify the suspected criminal when little or no evidence exists. This work requires a variety of skills and abilities. A policeman should be a guardian of law and order and he has the greatest responsibility in the society. In the United States the policeman is considered to be a public servant. The policeman has a difficult job, because he is to tell people what they cannot be. It is very difficult to perform this function and maintain the image of respect and friendliness. People don’t like this. The image of the police is not good today. It is very important that every police officer recognizes his role in developing the police image. The police officer should be courteous (вежливый, учтивый), truly interested in the welfare of others and should possess broad knowledge. Sincere (искренний) interest will communicate to those people with whom he comes in contact.
II. TEXTS Warming Up
Text 1 Text 2 Text 2 Police in the United States Vocabulary for reading the text:
Police in the United States The United States inherited England’s common law and its system of policing. The colonists had the night watch under constables, with all able-bodied men over 16 serving without pay. Most cities and towns used this system well into the 19th century. The use of daytime police started in Boston in 1838 with a force of 6 men. In Boston and New York the old night watch and the day force continued, with the mayor in charge of day force and the constable in charge of night watchmen. In 1844 New York City created the first police department in the United States, using the London Metropolitan Police as a model. Boston and Philadelphia followed. The model for American police originated in England: police were organized in a quasi-military command structure; there were no detectives; their task was prevention of crime and disorder. There are five major types of police agencies: 1) the federal system, consisting of agencies attached to the Department of Justice (the Federal Bureau of Investigation, together with 700 U.S. marshals), the Bureau of Internal Revenue (investigating tax invasions), the U.S. Secret Service, the Drug Enforcement Administration, the Postal Inspection Service, and many others. Their task is to enforce federal laws. 2) the police forces and criminal investigation agencies established by each of the 50 states of the union. State police is headed by commissioner superintendent who is usually appointed by the governor of the state. The mission of the state police is to preserve law and order, to enforce criminal, traffic and regulatory laws, and to provide security and safety services; 3) sheriffs and deputy sheriffs in more than 3,000 counties, plus a few county police forces. The county sheriff is elected to office and employs a staff of deputies performing duties as uniformed policemen. The sheriff is also responsible for prisoners kept in the county jails; 4) the police forces of about 1,000 cities and more than 20,000 townships and New England towns. Town and city police are municipal agencies; 5) the police of some 15,000 villages, boroughs, and incorporated towns. To this list must be added special categories, such as the police of the District of Columbia; various forces attached to authorities governing bridges, tunnels, parks and parkways; university police forces; and some units for policing special districts formed for the protection, soil conservation and other purposes. The above-mentioned police forces are controlled in different ways. The federal bodies are responsible to the federal authorities, and the state forces – to the governors of their states. At local levels there are variations. States are divided into counties, and every county has its sheriff with responsibilities for the investigation of crime and the supervision of the custody of prisoners. In some states there are county police forces under the control of county boards. In some places county police forces are completely independent of the sheriff’s office.
Text 3 Text 4
Vocabulary for reading the text: intelligence agent – агент службы разведки personal security guard – телохранитель military secret service – военная спецслужба receive a commission – получить офицерское звание hire, v – нанимать juveniles, n – подростки be assigned, v – быть назначенным Ex. 34. Agree or disagree. 1. Women can be as physically fit as men. 2. Women officers can handle stress as well as men. 3. Women if trained properly, are as willing as men to use force.
Text 5 Text 6 John Edgar Hoover
John Edgar Hoover was born in 1855. He was a native of Washington, D.C. He went to school there and then to George Washington University where he studied law. As a student he was brilliant and had a great choice after graduating from the University. But Hoover got a job in the Department of Justice. Very soon they sent him to the Federal Bureau of Investigation. That was in 1924 when J.E. Hoover was forty. For many years he was the head of the FBI and made it the world’s greatest law enforcement organization. He opened a technical and scientific laboratory, identification division, set up a lot of training schools. He was also the initiator of the National Police Academy where he taught as the chief instructor. John Hoover had a photographic mind: he called agents by their first name; he remembered all investigations and their results. He said: “The main task of the FBI is the protection of people against crime”. As to his personal life, he had no time to get married. When he was not busy with his service in the FBI, he usually went fishing or hunting. Hoover played tennis very well. He also liked good music.
Text 7 Training Division Training Division All FBI Agents are trained at facilities in Washington, D. C., and at the FBI Academy in Quantico, Virginia. Today, the new Agents receive fourteen weeks of instruction. Two-week retraining courses are held periodically for all Agents. Although the theory of the various law enforcement arts and sciences is taught, the greater emphasis is placed on those practical skills and techniques demanded by day-to-day investigation. The courses range from the Constitution and Federal Criminal Procedure to Investigative Techniques and the Collection, Identification and Preservation of Physical Evidence. Thorough training is given in firearms and defensive tactics in order that an agent may defend himself in those extreme situations where life may be in danger. The Training Division also provides instructors for thousands police schools conducted by local enforcement agencies in communities across the Nation.
Notes: 1. facilities – оборудование 2. retraining courses – курсы переподготовки 3. practical skills – практические навыки 4. firearms, n – огнестрельное оружие 5. defensive tactics – самбо 6. range, v – колебаться (в определенных пределах) 7. law enforcement arts – методы деятельности правохранительных органов
Text 8 FBI National Academy Ex. 44.Read the text without a dictionary and write the summary of the text. FBI National Academy The FBI National Academy has long been a vital element in the continuing improvement of law enforcement standards, knowledge, and cooperation throughout the world. The national Academy experience and its sister program, “Field Police Training”, provide a wide range of leadership and specialized training, as well as an opportunity for professional law enforcement officers to share ideas, techniques, and experiences. It is with the above concept that the National Academy Program was founded on July 29, 1935, with 23 students in attendance. Since that early beginning, the National Academy program has graduated 30,517 qualified students with the graduation of the 190th Session on September 12, 1997. The program has enjoyed a world-wide reputation among international law enforcement and 1,689 officers representing 120 foreign countries have taken advantage of this training program. Following graduation each officer has the opportunity to join the FBI National Academy Associates, a dynamic organization of more than 25,000 law enforcement professionals who have played a significant role in developing a higher level of competency, cooperation, and integrity within the law enforcement community. Notes: 1. vital – жизненный, насущный 2. experience – опыт 3. leadership – руководство 4. share, v – делить, разделять 5. advantage – преимущество 6. integrity – целостность Text 9 Ex. 45.Read the text with a dictionary. Write the summary of the text. Ex. 46. Check yourself. Задание 1. Дополните предложения, выбрав правильный вариант. 1). The basic responsibility of the police is... A - to make and pass laws. B - to fight crime and maintain order. C - to train police officers. 2) The mission of a detective is... A - to prepare a preliminary report. B - to secure the crime scene. C - to apprehend the offender. 3) The two major stages of the investigation process are... A - interviewing of witnesses and interrogating of suspects. B - apprehending and arresting offender. C - preliminary investigation and follow-up investigation. 4) To obtain information about suspected criminal activity, the police make use of... A - the FBI agents. B – informants. C - criminalistics technicians. Задание 2. Выберите слова сходные по значению (синонимы) для следующих слов. 1) responsibility A – ability B – duty C - quality 2) a criminal A – offender B – informant C - detective 3) to handle A - to fight B - to deal with C - to maintain 4) basic A – main B – preliminary C - separate Задание 3. Заполните пропуски в предложениях, используя указанные слова и словосочетания. 1. The FBI is one of the best investi- A - Department of Justice gative (...) in the world. B - bodies 2. It (...) in 1924. C - the strength 3. Its (...) is to handle criminal D - mission investigation for the (...). E - Training Division 4. FBI (...) is situated in Washington. F - divisions 5. (...) of the FBI is 21000 men. G - fingerprints 6. There are 11 (...) in the FBI. H - General Investigation Division 7. (...) handles criminal investigations. 8. Identification division (...) the I - scientific examinations largest collection of (...). J - Headquarters 9. Laboratory Division makes (...). K - was created 10. (...) trains agents for the FBI. L - contains
Ex. 47. Speak about the police system of the USA using the questions given below as a plan.
1. Whеn was the US Police created? 2. How many police agencies are there now? 3. What functions do the police perform in society? 4. What types of police agencies are there in the USA? 5. What is the main aspect of policing? 6. What are the two major stages of investigation? 7. What are the main duties of a patrol officer at a crime scene? 8. What is the largest police agency on the federal level? 9. When was the FBI created? 10. What is the motto of the FBI? 11. What can you say about FBI responsibilities? 12. What divisions is the FBI composed of? 13. Where are the FBI agents trained? 14. How long does the training last? 15. What do the agents learn?
Part II The British Police Service
Grammar: Word Formation Homonyms Conversion Phrasel Verbs There be construction Texts: Structure of British Police Police Service. The Metropolitan Police Force of London. Scotland Yard. I. GRAMMAR
WORD FORMATION Improve your wordpower. Translate the words into Russian, using a dictionary if necessary. Nouns Co- poly- trans- dis- ex- co-administrator poliacid transaction disability ex-convict co-defendant polygraph transactor disadvantage ex-president co-insuranse polyclinic transformation dislike ex-factory co-executor polygamy transcription disaccord ex-minister co-applicant polygene transgene disaffection ex-offender co-guardian polymer transistor disagreement ex-prisoner co-creditor polyalcochol transnational disappearance ex-serviceman
HOMONYMS Омонимы Омоним (греч. homónyma, от homós – одинаковый и ónyma – имя), одинаково звучащие единицы языка, в значении которых (в отличие от значений многозначных единиц) нет общих семантических элементов. Лексические омонимы возникают: вследствие звукового совпадения различных по происхождению слов, например, «рысь» (бег) и «рысь» (животное); в результате полного расхождения значений многозначного слова, например, «мир» (вселенная) и «мир» (отсутствие войны, вражды); при параллельном словообразовании от той же основы, например, «тройка» (лошадей) и «тройка» (отметка). Понимание омонимов определяется контекстом, однако отсутствие у омонимов общих семантических элементов делает невозможным совмещение их значений. Case – 1) something that has happened (случай); 2) a question or problem that will be dealt with by a law court (дело); 3) an example of a particular situation, problem, etc. (случай, пример); 4) a large box or container in which things can be stored or moved (ящик); 5) the way in which the form of the word changes, showing its relationship to other words in a sentence (падеж). Criminal – 1) related to or connected with crime (преступный, уголовный); 2) someone who is involved in illegal activity or has been proved guilty of a crime (престкпник).
CONVERSION Конверсия Приконверсииот существительного слова без изменения его звуковой или графической формы образуется новое слово, относящееся к другой части речи. В современном английском языке от существительного с конкретным значением могут быть образованы глаголы, причем последние иногда изменяются по значению, а иногда переводятся описательно, например: place – место, to place – помещать, land – земля, to land – приземляться, садиться на землю.
Criminal (adj.) – related to or connected with crime (преступный, уголовный). The boy has shown criminal tendencies since his early childhood. Мальчик проявлял преступные наклонности с раннего детства. Criminal (n) - someone who is involved in illegal activity or has been proved guilty of a crime (престкпник). My suspicious neighbour turned out to be a real criminal. Мой подозрительный сосед оказался настоящим преступником. В некоторых случаях при переходе глагола в существительное происходит и перенос ударения: Con` ٰ duct – to carry out a particular process, especially in order to get information or prove facts (проводить). The company conducted a survey to find out local reaction to the leisure centre. Компанияпровела исследование, чтобы узнать отношение местного населения к развлекательному центру. ٰ` Conduct - the way someone behaves, especially in public, in their job, etc. (поведение). The reporter was accused of unprofessional conduct. Репортёр был обвинен в непрфессиональном поведении. Sus′pect – to think that someone is probably guilty (подозревать). She strongly suspected her husband of murder. Она настойчиво подозревала своего мужа в убийстве. ′Suspect – someone who is thought to be guilty of a crime (подозреваемый). Two suspects were arrested today in connection with the robbery. Двое подозреваемых были арестованы сегодня в связи с грабежом. PHRASAL VERBS Составные глаголы Составной глагол – это сочетание, состоящее из двух компонентов, написанных раздельно. Первый компонент такого сочетания является глаголом, а второй – словообразовательным элементом (послелогом), придающим глаголу новое значение: to carry – нести; to carry out – выполнять. Послелоги по внешнему виду полностью совпадают с предлогами (out, up, on, etc.), поэтому их часто пытаются перевести отдельно, что приводит к ошибкам. Следует помнить, что составные глаголы переводятся на русский язык одним словом и в словаре их следует искать в гнезде глаголов, e.g.: carry (v) – нести; ~ out - выполнять. Некоторые предлоги изменяют полностью значение глагола: e.g. to carry – нести; to carry out – выполнять. Другие послелоги лишь уточняют или дополняют значение глагола: e.g. to work – работать; to work out – разрабатывать. Признаки составных глаголов: 1) наличие предлога, стоящего после послелога: e.g. to carry out with the help … - выполнять при помощи …; 2) местоположение послелога в конце предложения: e.g. The mission is to be carried out. – Эта задача должна быть выполнена. Warming Up Text 1 Structure of British Police Ex. 7.Read the text and find the answers to following questions. 1. Is the police in Great Britain organized in the same way as in other countries? 2. How many police forces are there in Great Britain? 3. How is the British policeman called?
Vocabulary for reading the text: 1. police force – полицейские силы, полиция 2. separate, adj. – отдельные 3. Metropolitan Police – столичная полиция 4. City of London police – полиция Лондонского Сити 5. county police – полиция графств 6. county borough police – полиция города-графства 7. combined police – объединенные полицейские формирования 8. Home Office – МВД 9. Home Secretary – министр внутренних дел 10. Chief Constable – главный констебль, начальник полиции (назначается мировыми судьями и членами местного совета) 11. most senior police officer – старший полицейский чин 12. Commissioner of Police of the Metropolis – комиссар столичной полиции 13. road accident – дорожное происшествие 14. give first-aid – оказать первую помощь
British Police Force The police in Great Britain are organized differently from many other countries. There is no national police force in Great Britain. Instead there are 52 separate police forces. Among them there is the Metropolitan Police, the City of London police, county police, county borough police and combined police. The forces cooperate with each other and are controlled by Home Office with Home Secretary at the head. The head of county, county borough and combined police is Chief Constable. Chief Constable is the most senior police officer of a force. The head of Metropolitan Police is the Commissioner of Police of the Metropolis. The British police officer is often called “the bobby” after Sir Robert Peel – the founder of the police force. The tasks of British police are varied. They maintain public order, deal with road accidents, give first-aid and information to anybody who asks for help. Ex. 8.Complete the following sentences. 1. Britain has no … 2. Police forces consist of… 3. There are … police forces … 4. Police forces cooperate with each other and are controlled by … 5. Chief Constable is at the head of … 6. Chief Constable is … 7. The head of the Metropolitan Police is … 8. British police deal with …
Text 2 Police Service
Vocabulary for reading the text:
Police Service Policemen and policewomen today have to deal with very serious problems such as continuing crime, drug misuse, terrorism as well as a number of other problems like relations with ethnic communities and an increasingly complex society. The civilian police are responsible in Britain for the maintenance of law and order. The duties of the police are varied, ranging from assisting at accidents to safeguarding public order and dealing with lost property. One their main function is, of course, the control of crime. Though the duties and functions of the British police are broadly similar to many other countries, it is organised very differently in that Britain has no national police force controlled by central government. The oldest police force in Britain is the Metropolitan Police which was founded in 1829 by Sir Robert Peel to combat crime in London, and from which the modern forces have grown. Outside London the police are all local forces, there are 52 separate police forces for each area (43 in England and Wales, eight in Scotland and one in Northern Ireland), which corresponds either to county council or to regional areas. Each regional force has a local police authority – a police committee of local councillors and magistrates, which are charged with law enforcement in their localities. In the 41 police areas outside London, they normally have 17 members – nine locally elected councillors, three magistrates and five independent members. The professional head of each regional force is the Chief Constable, who is responsible for all operational and administrative decisions including the actions of the force. The police authorities, in consultation with the chief constables and local community, set local policing objectives, while the Government sets key objectives for the police as a whole. The Home Secretary and the Scottish and Northern Ireland Secretaries, together with police authorities and chief constables, are responsible for providing an efficient police service in the UK. The Metropolitan Police zone of operation covers Greater London, and is currently under the direct responsibility of the Home Secretary, although the Government has put forward proposals for a new body with a majority of elected representatives. The “Met” as it is popularly called, also provides certain national police services, including the maintenance of a national record of all criminals and crimes, to which local police forces may refer. The famous “Scotland Yard” is the Criminal Investigation Department (CID), which gets its popular name from the New Scotland Yard, where its offices are situated. The central government gives the local authorities grants towards the cost of policing. Inspectors from the Home Office direct and control the local forces, reporting to the Home Secretary who can approve and disapprove the appointments and removals of Chief Constables, but the actions of a local police force are normally not the responsibility of any minister. There are over 150,000 policemen and policewomen in the UK, which means one officer for every 400 people in the total population. Text 3 Text 4 Scotland Yard Ex. 20. Read the text about the Criminal Investigation Department of the Metropolitan Police and say what Department of Russian police performs the same functions. Vocabulary for reading the text: 1. headquarters, n – штаб-квартира 2. ambassador, n – посол 3. palace, n – дворец 4. consist of, v – состоять из… 5. staff, n – штат 6. to be charged with, v – вменять в обязанности, возлагать ответственность 7. subversive, adj. – подрывной 8. criminal record office – отдел криминалистического учета 9. fingerprint department – дактилоскопический отдел 10. flying squad – отряд быстрого реагирования
Scotland Yard Though Scotland Yard is in fact the headquarters of Metropolitan Police Force, the name is almost always associated with the Criminal Investigation Department (C. I. D.) of the Metropolitan Police. The C. I.D. was set up in 1878. The name Scotland Yard comes from the fact that originally there was a palace used by the Scottish kings and their ambassadors when they visited London. Later the palace was replaced by the building of the Metropolitan Police. But the name of Scotland Yard sticked to it. The Criminal Investigation Department consists of about 1.500 detectives, of which 1.300 do ordinary detective work. The remaining 200 detectives work in the Special Branch, which in many respects is national first, because it has a staff at every airport and seaport, and secondly, because it is charged with protecting very important persons (VIPs) and dealing with actions which may be regarded as subversive to the state. Other branches of the C. I. D. which operate on a nation wide scale are as follows: 1) the criminal record office, which is the only office in the country that maintains a central record of all criminals. 2) the fingerprint department, which by status, maintains all fingerprint records. 3) the flying squad, which is used all over the country by chief constables when necessary. Although the C. I. D. usually operates on a nation wide scale it can go to the help of a provincial police force only if it is invited. In serious cases it is usually invited.
Task 3. Listen to the text.
Bobbies Before 1829, there were no police anywhere in Britain. In that year, the Prime Minister, Robert Peel, set up a force in London; they were often called bobbies, and the nickname is still occasionally used today. (Bobby is the familiar form of the name Robert). There was considerable resistance to the idea of a permanent police force, rather than groups of citizens brought together to deal with particular problems. The early 19th century was a time of political unrest in Britain as elsewhere in Europe, and workers suspected (rightly, as it turned out) that the police would be used against them. A writer named J. P. Smith warned in 1812 that the police would mean: “... a system of tyranny; an organized army of spies and informers, for the destruction of all public liberty, and the disturbance of all private happiness.” There is no national police service in Britain. Each region has its own independent service; for example, the west Midlands Police, Devon and Cornwall Police, or (in London) the Metropolitan Police. If there are serious complaints about one service, an officer from another service is brought to investigate.
Notes: 1. set up – учреждать 2. nickname – прозвище 3. familiar – знакомый 4. resistance – сопротивление 5. unrest – волнение 6. suspect – подозревать, предполагать 7. warn – предупреждать 8. spy – шпион 9. destruction – уничтожение 10. disturbance – нарушение
Task 1. Find in the text the synonyms for the following words: founded; sometimes; known; to handle; somewhere.
Task 2. Answer the questions.
Ex.32. Check yourself. I. Дополните предложения, выбрав правильный вариант. 1) The police in Britain are organized... A - in the same way as in other countries. B - differently from many other countries. C - in the same way as in the USA. 2) Britain has... A - a national police force. B - no national police force. C - no police force. 3) The British police officer is sometimes called... A – cop B – panda C - bobby 4) The job of the traffic wardens is... A - to make sure that drivers obey the parking regulations B - to fine drivers for speeding C - to apprehend criminals II. Выберите слова, сходные по значению (синонимы) для следующих слов. 1) is vested in A - belongs to B - consists of C - is divided into 2) was created A - was occupied B - was set up C - was situated 3) a branch A - a department B - a group C - an office 4) an aid A - a job B - a help C - a service
UNIT 2 INTERPOL
Grammar: The Passive Voice Понятие отрицания в английском языке и некоторые способы его выражения Texts: Establishment of Interpol What is Interpol? Interpol Interpol and Eastern Europe Interpol and Bilateral Cooperation
I. GRAMMAR
THE PFSSIVE VOICE Залог выражает отношение между подлежащим и сказуемым в предложении. В английском языке, как и в русском, существует два залога – действительный (Active Voice) и страдательный (Passive Voice). Глагол-сказуемое в действительном залоге показывает, что подлежащее предложения само совершает действие, выраженное глаголом: I speak English. – Я говорю по-английски. I asked questions. – Я задавал вопросы. Глагол-сказуемое в страдательном залоге показывает, что подлежащее предложения является объектом действия, выраженного глаголом: English is spoken all over the world. – На английском языке говорят во всём мире. I was asked a few questions. – Мне задали несколько вопросов. Формы глагола в страдательном залоге образуются с помощью вспомогательного глагола to be в соответствующем времени и числе и причастия прошедшего времени (Participle II) смыслового глагола.
Страдательный залог употребляется в следующих случаях: 1)Когда неизвестно (неважно или непонятно из контекста), кто выполнил действие: The Parthenon was built in the 5th century BC (Before Christ). – Парфенон был построен в 5 веке до нашей эры. 2)Когда само действие важнее, чем тот, кто выполняет его (часто используется в газетных статьях, рекламных объявлениях, инструкциях, новостях): Two teenagers were seriously injured in a car accident last night. - Двое подростков были серьезно ранены в ДТП прошлой ночью. С конструкцией в страдательном залоге используются два предлога – by (если указано, кем произведено действие) и with ( если указано,чем произведено действие): America was discovered by Columbus. – Америка была открыта Колумбом. The victim was killed with a knife. – Потерпевшего убили ножом.
II. TEXTS Warming Up Text 1 Establishment of Interpol Vocabulary for reading the text: 1. postpone, v – отложить postpone smth, till/until/to – отложить что-либо до… 2. particular, adj. – особенный 3. to necessitate smth., v – вызвать необходимость чего-либо 4. Belgian – бельгийский 5. revive, v – оживлять, возрождать 6. attend, v – посещать 7. statute, n – устав
Ex. 12. Translate these nouns into Russian and write down the corresponding verbs. postponement _________ support _____________ attendance ____________ cooperation __________ revival _______________ growth ______________ establishment__________ meeting _____________ approval _____________ change ______________ popularity ____________ title ________________
Establishment of Interpol
The first International Police Congress was held in Monaco in 1914 and delegates, who included lawyers, judges, criminologists, academics and civil servants as well as police officers, came from 17 countries. The Congress supported calls for greater tran
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Последнее изменение этой страницы: 2017-01-19; просмотров: 1377; Нарушение авторского права страницы; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! infopedia.su Все материалы представленные на сайте исключительно с целью ознакомления читателями и не преследуют коммерческих целей или нарушение авторских прав. Обратная связь - 216.73.216.137 (0.02 с.) |

 (Чтобы уменьшить риск, они эвакуировали всех из опасной зоны.)
(Чтобы уменьшить риск, они эвакуировали всех из опасной зоны.)

 Our laws are known to protect the interests of all the people.
Our laws are known to protect the interests of all the people.
 Известно, что наши законызащищают интересы всех граждан.
Известно, что наши законызащищают интересы всех граждан.
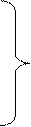 smb known – Известно
smb known – Известно smth. is (are) reported – Сообщают
smth. is (are) reported – Сообщают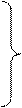 smb.
smb. Ex. 32. Do you know how many (%) women serve in the police in Russia? What police departments do they work at? What are their functions? Read the Text 3 and compare the activity of women police in the USA and Russia.
Ex. 32. Do you know how many (%) women serve in the police in Russia? What police departments do they work at? What are their functions? Read the Text 3 and compare the activity of women police in the USA and Russia.




