
Заглавная страница Избранные статьи Случайная статья Познавательные статьи Новые добавления Обратная связь FAQ Написать работу КАТЕГОРИИ: ТОП 10 на сайте Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрацииТехника нижней прямой подачи мяча. Франко-прусская война (причины и последствия) Организация работы процедурного кабинета Смысловое и механическое запоминание, их место и роль в усвоении знаний Коммуникативные барьеры и пути их преодоления Обработка изделий медицинского назначения многократного применения Образцы текста публицистического стиля Четыре типа изменения баланса Задачи с ответами для Всероссийской олимпиады по праву 
Мы поможем в написании ваших работ! ЗНАЕТЕ ЛИ ВЫ?
Влияние общества на человека
Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрации Практические работы по географии для 6 класса Организация работы процедурного кабинета Изменения в неживой природе осенью Уборка процедурного кабинета Сольфеджио. Все правила по сольфеджио Балочные системы. Определение реакций опор и моментов защемления |
Информационные технологии и компьютерные системыСодержание книги
Похожие статьи вашей тематики
Поиск на нашем сайте ИНФОРМАЦИОННЫЕ ТЕХНОЛОГИИ И КОМПЬЮТЕРНЫЕ СИСТЕМЫ НА АНГЛИЙСКОМ ЯЗЫКЕ Учебное пособие для развития навыков устной речи на английском языке для студентов факультета Информационных технологий и компьютерных систем Омск 2009 УДК 004:811. – 111(075) ББК 32.81 + 81.2 Англ-923 А – 44
Рецензенты:
Т.В. Ощепкова, канд. филол. наук, доцент, зав. каф. английского языка факультета информатики ОмГПУ; К.Ю. Симонова, канд. филол. наук, доцент, зав. кафедрой связи с общественностью СибГУФК
Акулинина Т.В., Андреева Н.П., Ложникова Л.Н. «Информационные технологии и компьютерные системы на английском языке» А–44 Учебное пособие для развития навыков устной речи на английском языке для студентов факультета информационных технологий и компьютерных систем./ учеб. пособие/ Т.В. Акулинина, Н.П.Андреева, Л.Н. Ложникова – Омск Изд-во ОмГТУ, 2009 – 80с.
Данное учебное пособие содержит оригинальные тексты по специальности на английском языке для студентов II курса факультета информационных технологий и компьютерных систем. Каждый раздел (Unit) содержит познавательный материал для изучения терминологии, словообразования компьютерных терминов, обучения чтению с последующим обсуждением, а следовательно развитию навыков устной речи по специальности.
Печатается по решению редакционно-издательского совета Омского государственного технического университета
УДК 004:811. – 111(075) ББК 32.81 + 81.2 Англ-923
Омский государственный технический университет,2009 ПРЕДИСЛОВИЕ
Настоящее учебное пособие предназначено для студентов II курса дневного отделения факультета информационных технологий и компьютерных систем и аспирантов. Целью данного пособия является: развитие навыков устной коммуникации на английском языке по специальностям факультета, основанных на глубоких знаниях терминологии, использовании творческих заданий при работе с лексическим минимумом по профессиональным темам, а также на использовании разнообразных клише и разговорных формул при обсуждении оригинальных текстов. При отборе текстового материала в качестве основного критерия послужила информативная ценность текстов и их соответствие интересам студентов данной специальности. Большинство текстов взято из оригинальных английских и американских источников. Данное пособие представляет материал, способствующий взаимосвязанному обучению основным видам иноязычной речевой деятельности, готовит обучаемых к монологической и диалогической речи по темам специальностей для сферы профессионального общения. Пособие состоит из двух частей: I часть включает введение в специальности и 5 разделов (Units) по основным профессиональным направлениям факультета информационных технологий и компьютерных систем. Структура каждого раздела(Unit) включает в себя: вокабуляр, который закрепляется упражнениями; оригинальные тексты, диалоги, которые сопровождаются упражнениями, направленными на выработку умений устной коммуникации. Разделы содержат также и грамматический справочный материал, который затем отрабатывается в упражнениях направленных на усвоение вокабуляра, а также на развитие коммуникативных навыков. Каждый раздел завершается контрольными вопросами по данной тематике. II часть включает в себя алгоритм составления описательных аннотаций к дополнительным текстам по специальностям факультета, список базовых клише для обсуждения дополнительных текстов, дополнительные оригинальные тексты для внеаудиторной проработки, а также упражнения способствующие развитию навыков разговорной речи в сфере профессиональной коммуникации. Дополнительные тексты сопровождаются контрольными вопросами.
СОДЕРЖАНИЕ
Предисловие………………………………………………………………… Часть I Introduction…………………………………………………………………. Unit I Programming languages…………………………………………….. Unit II Software Engineering………………………………………………. Unit III Recent Developments in Information Technology………………… Unit IV The future of Information Technology…………………………….. Unit V People in Information Technology…………………………………. Часть II Supplementary Material…………………………………………………… Text I………………………………………………………………………. Text II……………………………………………………………………… Text III…………………………………………………………………….. Text IV……………………………………………………………………. Text V…………………………………………………………………….. Text VI……………………………………………………………………. Text VII…………………………………………………………………… Text VIII………………………………………………………………….. Text IX……………………………………………………………………. Text X……………………………………………………………………... Text XI…………………………………………………………………….. I. INTRODUCTION The information technologies and computer system facility I. Прочтите и запомните слова и словосочетания:
bachelor – бакалавр the course of studies – курс обучения broad engineering education – широкое техническое образование skills – навыки to get skills – приобрести навыки general education subjects – общеобразовательные предметы both … and – как … так и algebra of logic – алгебра логики research of operation – исследование операций theory of automatic regulation – теория автоматического управления to train – обучать to master – осваивать to get practice – проходить практику to have practice – проходить практику to make course projects – делать курсовые проекты to defend a diploma project – защищать дипломный проект topic – тема
II. Установите соответствие между русскими и английскими эквивалентами: 1. Всестороннее техническое образование 2. Общеобразовательные предметы 3. Приобрести навыки 4. Алгебра логики 5. Теория автоматического управления 6. Осваивать, овладевать 7. Проходить практику 8. Тема 9. Защищать дипломный проект 10. Обучать
1. To train 2. Broad engineering education 3. To have, to get practice 4. Theory of automatic regulation 5. Algebra of logic 6. To get skills 7. To master 8. General educational subjects 9. Topic 10. To defend a diploma project III. Прочтите следующие интернациональные слова и переведите их на русский язык: 1. Bachelor 2. Course 3. Algebra of logic 4. Theory 5. Practice 6. A diploma project
IV. Составьте предложения. 1. A diploma project, in the fifth year, to defend. 2. Last summer, had, students, computer center, practice. 3. To train, our faculty, specialists, in different fields. 4. Course projects, usually, have, students, in the fourth year, of their study. 5. To master, a profession, means, in this field, to get skills. 6. Is not considered, general educational subject, algebra of logic, to be. 7. To study, both and, general, subjects, special, subjects, students. 8. To get, at the university, students, broad engineering education. 9. Our professor, in the theory of automatic regulation, said, would, that, read, lectures, he. 10. The research of operation, topic, our, new, is.
V. Переведите и сделайте обратный перевод следующих предложений: 1. My future speciality is closely connected with the faculty of information technologies and computer systems. 2. The faculty trains specialists for advanced branches of science and industry. 3. Our faculty provides broad engineering education and practical skills. 4. The students study both general educational subjects and engineering ones. 5. The course of studies for engineers lasts 5 years and for bachelors it lasts 4 years. 6. To get skills in mastering new methods students have practice both in different laboratories and computer centers. 7. In the 5th year students can make contracts with industrial and economic enterprises. 8. In the last year of their studies students are to defend diploma projects. 9. The students make course projects to acquire profound knowledge in different subjects. 10. The students of the faculty of information technologies and computer systems take an active part in the world championships on internet. 11. Our students have all the possibilities to become excellent specialists in different branches of science, information technologies and computer aided design.
VI. Завершите предложения используя следующие выражения: 5 years, both laboratories and computer centers, make contracts, to acquire profound knowledge, to become excellent specialists, information technologies and computer systems, broad engineering education and practical skills, trains specialists, to defend diploma projects.
1. The faculty……… for advanced branches of science and industry. 2. Our faculty provides………………………………………………. 3. In the last year students are……………………………………….. 4. The students make course projects to……………………………... 5. The course of studies for engineers lasts………………………….. 6. To get skills in mastering new methods students have practice………. 7. In the 5th year students can…………………………………………… 8. Our students have all the possibilities……………………………………. 9. My future speciality is……………………………………………………… 10. Our faculty provides………………………………………………………..
VII. Прочтите и переведите словосочетания: To study in the information technologies and computer systems facility, To train specialists a course of studies, To get practical skills, To design and test computer elements, To study engineering subjects, To make new methods, To have practice at the computing center, To make course projects, To make contracts, To defend a diploma project, To get necessary data.
VIII. Ответьте на вопросы по тексту. 1. What specialists does the faculty of information technologies and computer system train? 2. What subjects do the students study? 3. What skills do the graduates get? 4. How long does the course of studies for engineers last? 5. What is the course of studies for bachelors? 6. What about teaching staff? 7. What does a prediploma practice help to get? My speciality I am a student of the Omsk State Technical University. My future speciality is closely connected with the facility of information technologies and computer systems. The faculty trains specialists for advanced branches of science and industry linked with modern information technologies and automatic control. The faculty provides broad engineering education and practical skills in designing and testing computer elements and systems. The students study both general educational subjects and engineering ones. Among those they study higher mathematics, algebra of logic, machine languages (Pascal, C, C ++), technology of programming, research of operation, theory of cooling, foreign languages, theory of automatic regulation electronics and microelectronics, elements of computers and so on. In the first year students are divided into engineers and bachelors. The course of studies of engineers lasts 5 years, for bachelors – 4 years. After that bachelors can continue their studies and receive magister diploma. To get skills in mastering new methods students have practice both in different laboratories and in the university computer center. Some students can do practice with the help of home computers. Our university computing center is equipped with IBM PC 486 computers. These computers have very good software and peripherals. Besides the students make course projects in all the years to acquire profound knowledge in different subjects. In the third year students can make contracts with industrial or economic enterprises. The training of the future specialists is performed by highly qualified teaching staff. The graduates get skills in mastering new methods of system analysis and designing by new information technologies and information processing. They can work in different areas of human activity with modern computers, workstations, computer networks and Internet. In the last year the students are to defend diploma projects. A prediploma practice helps them to get necessary data for a diploma project, the topic being chosen according to their interests and future work. The students of the facility of information technologies and computer system take an active part in the world championships on Internet, and they have all the possibilities to become excellent specialists in different branches of science, information technologies and computer aided design.
IX. Запросите дополнительную информацию у своего товарища: 1. Do you work in Internet? 2. What do you think new technologies of the information processing? 3. What computer networks are used in the computing center? 4. Where do you want to work in future? 5. What helps you to acquire profound knowledge in different subjects? 6. What about diploma project? 7. Do you take part in world championships on Internet?
X. Перескажите текст. XI. Представьте, что вы агитируете абитуриента, говорящего только по-английски, подать заявление на вашу специальность, рекламируя ее актуальность. Не пользуясь записями, постарайтесь сказать несколько фраз на эту тему.
XII. Контрольные вопросы: 1. What does your future speciality include? 2. In what fields of industry can you be involved after graduating from the university? 3. What is the difference between a specialist and a bachelor? 4. What special subjects do you study? 5. How is the computer center equipped? 6. Where can the students get practical skills? 7. Have you already chosen the topic of your diploma project? 8. What is necessary to take part in the world championships on Internet? 9. Is it difficult to master your speciality? 10. Where would you like to work in future?
Unit 1.Program, design and computer language.
I. Прочтите и выучите новые термины и терминосочетания: Programming – программирование Program – программа Set of instructions – набор инструкций Solution – решение To execute – выполнять Specific task – определенная задача Machine code – машинный код Symbolic languages – символические языки Assembly language – язык «Ассемблер» Software – программное обеспечение Low-level languages – языки низкого уровня программирования Hardware – аппаратное обеспечение High-level languages – языки высокого уровня программирования To resemble – быть похожим Compiler, interpreter – компилятор, интерпретатор Fortran – язык программирования для выполнения научных и математических приложений Cobol – язык программирования, используемый в бизнесе Basic - язык программирования как обучающий язык Visual basic – язык программирования, используемый для создания windows-приложений С – язык программирования, используемый для написания программного обеспечения систем, графиков и коммерческих программ Java - язык программирования, используемый для работы на web-страницах Java applets – небольшие программы, которые работают автоматически на web-страницах и позволяют Вам включать музыку и игры Markup languages – языки, которые используются для создания web-документов HTML – код, используемый для создания web-страниц Voice XML- предлагает доступ в интернет посредством узнавания речи по телефону (Вы можете использовать телефон для доступа к звуковым web-сайтам) Pascal - язык программирования, используемый для обучения основам программирования Object code – код, который преобразует программу в машинный код за один шаг Markup tags – инструкции для форматирования текстовых файлов
XV. Перескажите текст.
Steps in writing a program
· First they try to understand the problem and define the purpose of the program. · They design a flowchart, a diagram which shows the successive logical steps of the program. · Next they write the instructions in a high-level language (Pascal, C, etc.). This is called coding. The program is then compiled. · When the program is written, they test it: they run the program to see if it works and use special tools to detect bugs, or errors. Any errors are corrected until it runs smoothly. This is called debugging, or bug fixing. · Finally, software companies write a detailed description of how the program works, called program documentation. They also have a maintenance program. They get reports from users about any errors found in the program. After it has been improved, it is published as an updated version.
XVII. Пользуясь информацией задания XVI распределите шаги программирования в правильном порядке:
Test the program and detect bugs Make flowchart Write code and compile Analyze the problem Debug and correct it if necessary
XVIII. Прочитайте информацию о том, как написать программу и составьте диалог между разработчиком программного обеспечения и студентами группы подготовительных курсов по работе с компьютером пользуясь данной информацией: I’d like to begin the course by giving you a very basic overview of the programming process. We'll then move to the details. So, to write a program, we normally follow these steps: A program usually provides a solution to a given problem - for example, how to calculate wages and income tax in a big company. First of all, you have to understand exactly what the problem is and define it clearly. This means you have to decide, in a general way, how to solve the problem. The next step is to design a step-by-step plan of instructions. This usually takes the form of a flowchart, a diagram that uses special symbols to show how the computer works through the program - where it makes decisions, where it starts and ends, where data is input, things like that. Next, you write the instructions in a programming language, like BASIC, Pascal or C. These computer instructions are called source code. Then you have to use a compiler, a special program that converts the source code into machine code - the only language understood by the processor, which consists of 1 s and Os. Once you've written the program, you have to test it with sample data to see if there are any bugs or errors. The process of correcting these errors is called debugging. Computer programmers have to find the origin of each error, write the correct instruction, compile the program again, and test it until it works correctly. Finally, you have to write program documentation, a detailed description of how to use the program. A great program is not much good unless people know how to use it.
Unit 2 Software Engineering I. Прочтите и запомните новые термины и терминосочетания:
program code – код программы to design a solution – спроектировать решение to clarify the problem – выявить проблему to test the problem – испытать(проверить) задачу to document and maintain the problem – задокументировать и обеспечить техническую поддержку программы form of output – форма вывода object-oriented programming – объектно-ориентированное программирование; multimedia data types – типы мультимедийных данных rectangle – прямоугольник reusability code – код, который можно использовать вновь executable modules – исполнительные(рабочие) модули diverse data types – разнообразные типы(виды) данных Triangles icon – изображение треугольника a menu – меню to synchronize – синхронизировать Squares – квадраты Rectangles – прямоугольники debugging – настройка user-interface – пользователь интерфейса polymorphism – полиморфизм graphical user interface – графический пользователь интерфейс desktop – фоновый экран, представляющий картинки и файлы files, folders – файлы Unix – программное обеспечение Unix Linux – программное обеспечение Linux user-friendly – удобный, легкий в использовании PALM OS – handheld operating system – переносная операционная система RIM – research in motion The Symbian OS – операционная система Симбиан, используемая изготовителями телефонов Nokia и Siemens to launch a program – запустить программу menu bar – ряд слов меню scroll bar – горизонтальная или вертикальная полоса server platform – платформа сервера dock – набор картинок внизу на экране applicant software – прикладная программа operating system – операционная система system software – системное программное обеспечение
IV. Составьте предложения. 1. is, the most, thing, important, in, information technology, object-oriented programming. 2. refers, in order to, to, to interact computer, with, the term, the standard procedure, that follows, user-interface, the user. 3. graphical user-interface, in, 1984, appeared, in Macintosh computer. 4. makes use of, GUI, windows, icons, and pointers. 5. including, Nokia and Siemens, the Symbian OS, by some, is used, phone makers. 6. an open-source software, Linux, is. 7. found, Unix, a multi-user system, is, on mainframes, and workstations. 8. PALM OS, on PALM, devices, handheld, is used. 9. might, called, be, an icon, a display screen, on Triangles. 10. behind, OOP, a third, key feature, polymorphism, is. What is multitasking? GUI operating system The term user interface refers to the standard procedures that the user follows in order to interact with а computer. In the late 1970’s and early 80’s, the way users accessed computer systems was very complex. They had to memorize and type а 1ot of commands just to see the contents of а disk, to сору files or to respond to а single prompt. In fact, it was only experts who used computers, so there was no need for а user-friendly interface. In 1984, Apple produced the Macintosh, the first computer with а mouse and а graphical user interface (GUI). Macs were designed with one clear aim: to facilitate interaction with the computer. А few years later, Microsoft launched Windows, another operating system based on graphics and intuitive tools. Nowadays, computers аге used by all kinds of people, and as а result there is а growing emphasis on accessibility and user-friendly systems. А GUI makes use of а WIMP environment: w indows, i cons, m enus and p ointer. The background of the screen is callеd the desktop, which contains lаbellеd pictures callеd icons. These icons represent files or folders. Double-clicking а folder opens а window which contains programs, documents, or more nested folders. When you аге in а folder, yоu can launch а program or document by double clicking the icon, or yоu can dгаg it to another location. When yоu run а program, your РС opens а window that lets yоu work with different tools. All the programs have а high 1еvе1 of consistency, with similar toolbars, menu bars, buttons and dialog boxes. А modern OS also provides access to networks and allows multitasking, which means yоu can run several programs - and dо various tasks - at the same time. The most popular operating systems are: The Windows family - designed by Microsoft and used on most PCs. The most recent version is Windows Vista. Mаc OS -created by Apple and used on Macintosh computers. Unix - а multi-user system, found on mainframes and workstations in corporate installations. Linux - open-source software dеvеlоpеd under the GNU General Public License. This meansanybody can сору its source соdе, change it and distribute it. It is used in computers, appliances and small devices. Windows Mobile -used on most PDAs and smartphones (PDAs incorporating mobile phones). Раlm OS -used on Раlm handheld devices. R1M - used on BlackBerry communication devices. Developed by Research In Motion. The Symbian OS - used by some phone makers, including Nokia and Siemens. These computer platforms differ in areas such as device installation, network connectivity or compatibility with application software. VIII. Прочитайте и запомните определения терминов. OBJECT-ORIENTED PROGRAMMING One of the principal motivations for using ООР is to handle multimedia applications in which such diverse data types as sound and video сап be packaged together into executable modules. Another is writing program соде that's more intuitive and reusable; in other words, соде that shortens program-development time. Perhaps the key feature of ООР is encapsulation - bundling data and program instructions into modules called “objects”. Here's an example of how objects work. An icon on а display screen might be called ‘Triangles'. When the user selects the Triangles icon - which is аn object composed of the properties of triangles (see fig. below) and other data and instructions - а menu might appear on the screen offering several choices. The choices mау be (1) create а new triangle and (2) fetch а triangle already in storage. The menu, too, is an object, as are the choices оn it. Each time а user selects an object, instructions inside the object are executed with whatever properties or data the object holds, to get to the next step. For instance, when the user wants to create a triangle, the application might execute а set of instructions that displays several types of triangles - right, equilateral, isosceles, and so on. Many industry observers feel that the encapsulation feature of ООР is the natural tool for complex applications in which speech and moving images are integrated with text and graphics. With moving images and voice built into the objects themselves, program developers avoid the sticky problem of deciding how each separate type of data is to be integrated and synchronized into а working whole. А second key feature of ООР is inheritance. This allows ООР developers to define one class of objects, say “Rectangles”, and а specific instance of this class, say “Squares” (а rectangle with equal sides). Thus, all properties of rectangles –“Has 4 sides” and “Contains 4 right angles” are the two shown here - are automatically inherited by Squares. Inheritance is а useful property in rapidly processing business data. For instance, consider а business that has а class called “Employees at the Dearborn Plant” and а specific instance of this class, “Welders”. If employees at the Dearborn plant are eligible for а specific benefits package, welders automatically qualify for the package. If а welder named John Smith is later relocated from Dearborn to Birmingham, Alabama, where а different benefits package is available, revision is simple. An icon representing John Smith - such as John Smith's face - cаn be selected on the screen and dragged with а mouse tо аn icon representing the Birmingham plant. He then automatically `inherits' the Birmingham benefit package. А third principle behind ООР is polymorphism. This means that different objects can receive the same instructions but deаl with them in different ways. For instance, consider again the triangles example. If the user right clicks the mouse оn “Right triangle”, а voice clip might explain the properties of right triangles. However, if the mouse is right clicked оп 'Equilateral triangle' the voice instead explains properties of equilateral triangles. The combination of encapsulation, inheritance and polymorphism leads to соде reusability. “Reusable соdе” means that new programs can easily be copied and pasted together from old programs. All one has to dо is access а library of objects and stitch them into а working whole. This eliminates the nееd to write соdе from scratch and then debug it. Соdе reusability makes both program development and program maintenance faster.
Java Developed by Sun Microsystems in the mid-1990s, Java is widely used for developing interactive applications for the Internet. Ada Named after Countess Аdа Lovelace (оnе of the first programmers); it is а superset of Pascal. Аdа is а structured language developed and used by the US Department of Defense. Logo Logo is an easy-to-use language that is primarily used to teach children how to program. LISP Stands for LISt Processor; L1SP is designed to process nonnumeric data - that is, symbols such as characters оr words. It is used to develop applications in the field of artificial intelligence. FORTRAN Stands for FORmu1a TRANslator, FORTRAN was designed by scientists in 1954 and is oriented toward manipulating formulas for scientific, mathematical, and engineering problem-solving applications HTML Stands for HyperText Markup Language; HTML is а pagedescription language used to prераrе а text for display in а browser program. Perl Its nаmе comes from Practical Report and Extraction Language. It first appeared in 1987 as а Unix-based tool for producing reports but is now widely used for creating interactive webpages. Prolog Stands for PROgramming LOGic; Prolog is used to develop applications in the field of artificial intelligence. It is а popular tool for natural-language programming. XML Stands for extensible Markup Language; XML is а metalanguage for creating webpages with meaningful data that cаn bе used by а variety of programs. С++ С++ is an object-oriented superset of С which combines the best features of а structured high-level language and an assembly language - that is, it’s relatively easy to соdе and uses computer resources efficiently. С was originally designed to write systems software but is now considered а general purpose language. Visual Basic BAS1C stands for Beginners' All-purpose Symbolic Instruction Соdе; Visual Basic is а simple-to-use language that has а graphical interface. It makes it particularly easy for an inexperienced programmer to create database programs. Pascal Pascal, nаmеd after the mathematician Blaise Pascal, was created primarily to fill the need for а teaching vehicle that would encourage structured programming. It is often used in college computing courses. COBOL Stands for СОmmоn Business-Oriented language; it has been around for а long number of years but is still an important transaction-processing language used to process the records of large organizations on mainframe computers. 1. А schoolteacher wants his young pupils to learn some basic mathematics by controlling а simple robot. 2. The owner of а small business wants to create а simple database program to kееp track of his stock. 3. An engineer wants to develop а program for calculating the stresses in а mechanical device. 4. А student wants to create webpages for а personal website. 5. А systems programmer wants to add some new modules to an operating system. 6. А programmer working for the US army wants to create а program for controlling а new type of weapon. 7. А finance company needs to process data from its branch offices on its mainframe computer. 8. А website designer wants to enable the data on his website to be easily processed by а number of different programs. 9. А student studying artificial intelligence wants to write some programs for а course project. 10. А college lecturer wants his students to learn the principles of programming. 11. А professional programmer wants to create and sell а program for use in language learning. 12. А website designer wants to password-protect а section of а website.
UNIT 3 RECENT DEVELOPMENTS IN IT I. Прочтите и запомните новые термины и терминосочетания:
information technology (IT) – информационные технологии intranet – интрасеть visual computer – компьютер с визуальными функциями artificial brain implants – имплантат искусственного мозга multiple channels – множественные каналы domestic appliances – бытовые приборы robotics – робототехника barcodes – штрих коды radio–frequency tags – тег радио-частот via email – посредством электронной почты screen fridge – холодильник с экраном to surf the Web – искать информацию на страницах Интернет surveillance camera – камера слежения address pad – блокнот адресата notepad – блокнот для записей built-in – встроенный to launch – выпускать, запускать to download – загружать to control remotely – управлять на расстоянии to log on – подключиться WPAP-web-Ready Appliances Protocol obstacle – преграда, препятствие to be unlikely – быть маловероятным EVA – Electronic Virtual Assistance avator – суперпользователь, привилегированный пользователь online – в режиме dynamic data base – динамическая база данных artificial intelligence – искусственный интеллект neural nets – нейросети Aibo – a small electronic dog input level – уровень входа input signal - входной сигнал to retrieve information – восстанавливать информацию digital newsreader – цифровой потребитель интернет-новостей to sense chemical – обнаруживать химические вещества cyborg – киборг chip – микросхема, микрочип to activate sensors – приводить в действие датчики transponder – прибор, принимающий радиосигналы range of tasks – спектр, набор задач to tackle – решать проблемы
II. Установите соответствие между терминами на русском и английском языках: 1. neural nets 2. сyborg 3. chip 4. transponder 5. artificial intelligence 6. dynamic data base 7. domestic appliances 8. avators 9. robotics 10. notepad
a). робототехника b). микросхема c). искусственный интеллект d). динамическая база данных e). бытовые приборы f). нейросети g). суперпользователи h). киборг i). прибор, принимающий радиосигналы j). блокнот III. Прочтите следующие интернациональные слова и переведите их на русский язык: 1. Intranet; 2. Cyborg; 3. Robotics; 4. Information technology; 5. Visual computer; 6. Implant; 7. Channel
IV. Составьте предложения. 1. replaced, barcodes, by radio-frequency tags, will, be, soon; 2. the newest of computer science, is, information technology; 3. gives, screen fridge, an idea, in stook, you, what have; 4. can, that, communicate, its own, built-in; 5. to log on, you, Internet, can, and, remotely control, appliances, domestic, your.
V. Переведите с английского на русский, а затем с русского на английский предложения: 1. The technology behind EVA companies two global friends in website design. 2. EVA provides the ability to give Web images the impression of three dimensions. 3. Ana nova was created to front an Internet 24 hours, a day news servise by digital Animations groups. 4. Aibo is a small electronic dog. 5. The robotics use neural nets connected processor that have an input level associated with each processor. 6. Such technology will enable us to interact with machines in a completely different way. 7. The aim behind the Robocup is to promote the development of robots which can work together. 8. Professor Warwick will soon have transponder surgically implanted in his arm to record electrical signals controlling his movements, which can be played back. 9. The advantages of having robots which can tackle a range of tasks together are obvious.
VI. Завершите предложения, используя следующие выражения: License to chill Barcodes in the packaging of groceries will soon be replaces with radio-frequency tags that can be read at a distance and with greater reliability. As well as indicating what the product is, the data in the tags will include additional information such as the ‘best before’ date and even nutritional data. Now, imagine that a fridge could read these tags and keep track of the items placed there. If an item is about to exceed its ‘use by’ date, the fridge tells you, and you can either use it or throw or out. Fancy something different for dinner? No problem, ask the fridge to suggest some menus based on the ingredients it knows you have in stock. Or tell the fridge the menu you require and it will provide you with a shopping list of the items you don’t have or order the items via email. This is the Screen fridge from Electrolux. But why ‘Screen fridge’? On the door is a touch-sensitive panel or screen that provides a means of communicating with the users. For many households, life revolves around the kitchen. This is the assumption Electrolux made in designing the Screen fridge. The same screen is a messaging centre. Since the fridge is equipped with a microphone, speaker and video-camera, you’re not limited to textual information. The fridge is connected to the Internet so it can be used to send and receive email or you could surf the Web to find a new recipe. Many people gave a TV in the kitchen, but if you already have a screen on the fridge, why clutter up the work surface with a TV? Call the Screen fridge’s TV mode and watch your favourite program on the fridge. The Screen fridge can be interfaced to a surveillance camera to check out visitors or to keep an eye on the children. Finally, the Screen fridge can perform some of the household management tasks normally associated with a PC. For example, it has a diary, address pad and a notepad.
Talking to the washing A washing machine that can communicate with the Internet using is own built-in mobile phone has been launched by Ariston. The margherita2000.com machine will be able to send breakdown reports for repair and download new washing cycles from its own website. And the householder will be able to control the washing cycle remotely using a mobile phone or by logging on to the machine's own website. But the importance of the machine is that it is the first of a line-up of Web-connected domestic appliances that will be able to talk to each other using a new open communication system called WRAP - Web-Ready Appliances Protocol. Ariston will be launching a dishwasher, fridge and oven using WRAP early next year according to Francesco Caio, head of Ariston's parent company Merloni Elettrodomestici. Eventually it will be joined by Leonardo, a touch-screen kitchen computer. All the machines will communicate through the house's ring main, and to the Web through the washing machine's mobile phone. Mr Caio believes he can sell 30 to 50,000 washing machines each year in Europe. But he must leap some big hurdles before the system can become widely accepted. WRAP is a proprietary Merloni standard, and people are unlikely to buy if locked in to Ariston for other networked appliances. Caio claims the standard is open to other manufacturers to adopt but so far none have signed up, whereas the huge Japanese manufacturers are adopting rival systems. The main obstacle is the cost – the margherita2000.com will cost much more than a traditional washing machine.
Dawn of the cyberbabes Stratumsoft are developing the first electronic virtual assistant, or EVA. If EVA’s live up to the developers' claims, they could provide the illusion of personal service without the cost. Call centres, online advertisers and Internet service providers are among the initial targets. Eighty per cent of call centre requests could, Stratum soft argues, be dealt with by an EVA. E-commerce is another application. 'The best experience you can have as a shopper is personal contact, and EVA is designed to give that', says Stratumsoft's director of marketing. The technology behind EVA combines two global trends in website design. One, developed out of the computer animation and gaming industry, is the ability to give Web images the impression of three dimensions. The other is the use of dynamic database skills and artificial intelligence-style searching to retrieve information from data banks. Each EVA can be programmed with information such as a product catalogue, answers to frequently asked questions or an online encyclopedia. It is also equipped with a search engine to interpret customer requests made in colloquial language. Queries are typed in and answered via on-screen text boxes. If the EVA does not have an answer, it will interrogate the questioner, record the response, and add the answer to its database for future enquiries. EVA’s are not fully animated to imitate human features but they can be programmed to gesture and imitate different moods. An EVA в run via a Java applet - a small, self-contained program coded to download on to any type of personal computer rather than being transmitted over the Internet. Ananova Ananova is the world's first digital newsreader. She was created to front an Internet 24 hours a day news service by Digital Animations Group, a Scottish 3D digital entertainment company and PA New Media. Mark Hird, Director of PA New Media said, ‘We have given her a full range of human characteristics after researching the personality most people want to read news and other information. Ananova has been programmed to deliver breaking news 24 hours a day via the Internet, and later on mobile phones, televisions and other digital devices’. The Ananova character fronts a computer system which is constantly updated with news, sport, share prices, weather and other information. This is converted into speech while another program simultaneously creates real-time animated graphics. This ensures that the virtual newscaster can be on top of the news as it breaks, with very little delay at all. People using the service can also tailor their own news bulletins by using search words to hear the latest information on their chosen subjects. Mr.Hird believes the invention will dramatically change the role of the traditions newscaster, 'In 20 years time we could be seeing that type of job being replaced by computer-generated images.' But not everyone agree: Professor Bill Scott said that people prefer people to teach them things and in a world where information was increasingly important, an established face was important in terms trust. 'You don't get that confidence with computer characters’.
The rise of the robots Japan produced the first commercially available robotic pet, called Aibo, a small electronic dog that several owners on Aibonet.com describe as part of the family. Aibo is not alone. Dr Thomas Consi MIT has produced the 'robolobster' which is of imitating lobsters' abilities to sense chemicals in the water surrounding them. Researchers at Edinburgh's Mobile Robot Group have made the world's first cyber-cricket. These machines are important because they demonstrate that simple processes can result in complex behaviours. The robots use 'neural nets', erred processors that have an input level associated with each processor. When an input signal exceeds a certain value, the processor 'fires' a signal processors as output. Because neural nets can recognize patterns in data, they can be ‘trained’ with samples of data which are then revised to improve the response. The most important crossover, however, is not between animal and robot but between man and machine. Quadriplegics and paraplegics have been testing computer connections for some time to bypass injured nerves, but Professor Kevin Warwick, head of the Department of Cybernetics at the University of Reading, is currently conducting experiments which could lead to more of us becoming cyborgs. Professor Warwick has previously had a chip fitted into his arm which could activate sensors in doors and computers as he approached. He will soon have another transponder surgically implanted in his arm to record electrical signals controlling his movements, which can be played back so that he is then controlled by a prerecorded self. He predicts that such a technology could, one day, enable us to interact with machines in a completely different way. For example, we could soon be driving cars without steering wheels.
Sporting robots Each ear teams take part in an international football competition. The teams are organised into five leagues and the prize is a cup. Not just any cup, but the Robocup, for the players are all robots. They don't play on turf but the objective is the same, to hit a ball into a goal. The aim behind the Robocup is to promote the development of robots which can work together. Football is a good test of co-operation for any team and the robots are no exception. Although robot footballers are poor competition for a human team, each year their performance gets better and each the standards expected are raised so that competitors must constantly develop better hardware and software. The top league is the Sony legged robot division. They use modified versions of the well-known Sony robodog AIBO. A humanoid league will start as soon as there are sufficient two-legged players. The organiser of the Robocup is confident in the future of robotics, 'By mid-21st century, a team of fully autonomous humanoid soccer players will win a soccer game, complying with the official rules of FIFA, against the winner of the most recent World Cup.' Other sporting events for robots exist. For example, The British Association for the Advancement of Science organises a two-a-side event called Robot Volley Ball. The players' task is simply to return a ball within 60 seconds of its being served. The objective again, is to promote the development of robots which can work cooperatively. The advantages of having robots which can tackle a range of tasks together rather than constructing single expensive robots designed for one task only are obvious.
X. Обсудите информацию в группах. Распределите роли: 1). The Speaker (Using only his notes). 2). The reporter (listens carefully and reports back to the speaker). 3). The judge (listens carefully to both speaker and Reporter and points out any mistakes).
XI. Прочитайте информацию о модальном глаголе can и его эквиваленте be able to; выполните упражнение, вставляя правильные формы глагола. Study these ways to describe ability: 1. Swarming robots can work together to perform searches. 2. Washing machines will be able to report any breakdowns for repair. 3. Imagine being able to send music files to your MP3 player without a wire connection. 4. Professor Warwick had a chip fitted into his arm which could activate sensors in doors and computers as he approached. 5. Marconi was able to send a radio signal from Britain to Newfoundland. We use can and be able to to describe ability in the present but can is more common. We use could for general abilities in the past but was/were able to describe an ability on a specific occasion. This table summarises their uses:
Ability ___________________________________________________________ Present can be able to _____________________________________________________________ future X will be able to _____________________________________________________________ present perfect X has/have been able to _____________________________________________________________ -ing form X____________ being able to _____________________________________________________________ past (specific action) X was/were able to _____________________________________________________________ past (general and with verbs of sensation) could X
For past negatives and questions both verbs are possible. For example: Early computers could not/were not able to operate at high speeds. Could they/were they able to store much data? Imagine..................................... 1 open doors and switch on computers as you approach them. Professor Warwick…………..2 because he had an electronic chip fitted into his arm for a month. He…………....3 demonstrate to the press how computers would greet him with, 'Good morning, Professor Warwick' as he walked past. Next he wants to record the signals from his brain to his arm to see if he.…........ 4 program a computer to operate his arm. In the long term, this may help people who………...5 use their limbs. His wife too will have a chip implanted. They hope……….6 feed messages into each other's brains. According to the Professor, one day we……….7 communicate directly with machines. If he is right, we…………..8 drive a car from the passenger seat and we…………………9 operate a computer without using a mouse or keyboard. However, there is also the alarming prospect that someone………………10 hack into your brain. Turn on / switch on (= start the operation of something) turn off/switch off (= stop the operation of something) - Other common phrasal verbs in computing include: plug into (= connect) Plug one end of the phone cord into the phone jack. set up (= establish) What do I need to set up a wireless LAN? sign up (= register, enrol in a service) Once connected, you can sign up for RSS feeds, newsletters, etc. try out (= test or use experimentally) You can try out new software on their site. find out (= learn, discover) Search the Web to find out more information about WiMAX. take up (= occupy) Fibro optic cables take up less space than copper cables. make up (= constitut
|
||
|
Последнее изменение этой страницы: 2016-09-17; просмотров: 1289; Нарушение авторского права страницы; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! infopedia.su Все материалы представленные на сайте исключительно с целью ознакомления читателями и не преследуют коммерческих целей или нарушение авторских прав. Обратная связь - 216.73.216.214 (0.015 с.) |

 To write a program, software developers usually follow these steps.
To write a program, software developers usually follow these steps.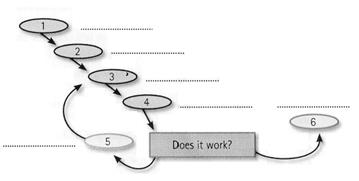 Document and maintain the program
Document and maintain the program


