Заглавная страница Избранные статьи Случайная статья Познавательные статьи Новые добавления Обратная связь FAQ Написать работу КАТЕГОРИИ: ТОП 10 на сайте Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрацииТехника нижней прямой подачи мяча. Франко-прусская война (причины и последствия) Организация работы процедурного кабинета Смысловое и механическое запоминание, их место и роль в усвоении знаний Коммуникативные барьеры и пути их преодоления Обработка изделий медицинского назначения многократного применения Образцы текста публицистического стиля Четыре типа изменения баланса Задачи с ответами для Всероссийской олимпиады по праву 
Мы поможем в написании ваших работ! ЗНАЕТЕ ЛИ ВЫ?
Влияние общества на человека
Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрации Практические работы по географии для 6 класса Организация работы процедурного кабинета Изменения в неживой природе осенью Уборка процедурного кабинета Сольфеджио. Все правила по сольфеджио Балочные системы. Определение реакций опор и моментов защемления |
Describe which mistakes were made by personnel in the following situationsСодержание книги
Поиск на нашем сайте
ACID TREATMENT
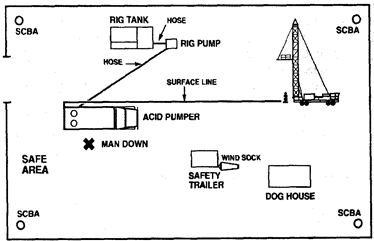
On a remote location, an acid pumper arrives on location to perform an acid wash and squeeze. The well is known to have a concentration of 20 000 ppm H2S. There is a service rig on location with a five man crew, an air trailer with a safety operator, one customer representative, one tank truck operator, and a three man acidizing crew. The pumper is spotted upwind of the wellhead, 25 metres from the rig tank. A kelly hose is run from the rig pump to the pumper unit. The pumper unit is rigged into a manifold to allow the pumping of fluid to either the tubing or casing. The safety operator has a portable H2S monitor on site with sensors located at the rig tank and wellhead. There are SCBA units located at the safe area.
Рисунок 27. Acid treatment. The day before the alarms had sounded at the rig tank when the well was being circulated. The safety operator checks over the rig with a personal monitor before the safety meeting and finds no H2S. He feels there is no need to supply the pumper operator with a SABA and air hose. During the safety meeting, the dangers of H2S are discussed and emergency procedures are reviewed. The pumper and rig pump operators ready their units to transfer fluid from the rig tank. The rest of the personnel meet at the rig shack for coffee. The rig pump operator starts to pump fluid from the rig tank to the pumper. The pumper operator looks in the tank to check the level and collapses on the far side of the truck. The rig pump operator does not see the operator fall and continues to pump. The supervisor comes out of the dog house and sees his operator down and runs toward the pumper. The supervisor goes down as he reaches the unit. The rig pump operator sees the supervisor go down and stops pumping. The portable monitor at the wellhead then goes off. Describe the mistakes made. WELL SERVICE
A rig crew and air trailer attendant arrive at a location at the same time to start the day. The air trailer attendant unlocks the trailer and proceeds to stretch out the air lines. The rig crew goes into the doghouse to change their clothes. One man, however, decides to check the shut-in tubing and casing pressure before changing his clothes. Once he records the pressure, he decides to bleed off pressure to an open tank. The return and kill lines had been drained the night before and not reconnected. The build-up pressure is released to the atmosphere.
Рисунок. Well service.
Approximately 2000 ppm of H2S is released into the atmosphere. It migrates downwind directly into the path of the air trailer attendant. He is instantly overcome and collapses near the end of the catwalk. A second crew man sees the air trailer attendant slump to the ground. He rushes over to assist and is also knocked down. The first crew member realizes what is happening and shuts the wellhead valve. Describe the mistakes made. DRILLING RIG
Рисунок. Drilling rig.
A rig crew was pulling a wet test. The crew members were all masked up. A safety supervisor, also masked up, was testing the floor area with a detector tube device. Several wet stands were pulled, and no H2S had been detected. The safety supervisor suggested the crew take off their masks, as they were tiring quickly. The situation was discussed with the rig manager and the wellsite representative. All agreed the crew should take off their masks. The safety supervisor would remain masked up and would continue testing. The crew went back onto the floor without masks. A stand was pulled and the tool joint broken. The mudcan was put on, and the crew left the floor. The driller picked up on the stand and the mud drained. The safety supervisor opened the mudcan and tested. No H2S was detected. The crew were called back on the floor to hoist another stand. As they were about to hook on the elevators, a small mud burp was observed. The safety supervisor told the crew to leave the floor, and he began to test.
Three of the crew members were going into the doghouse when the first one went down. Two more went down on top of him. The well was immediately shut in. The three crew members were revived shortly afterwords and taken to hospital. The safety supervisor detected 32% H2S. Describe the mistakes made.
|
|||||
|
Последнее изменение этой страницы: 2016-09-18; просмотров: 361; Нарушение авторского права страницы; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! infopedia.su Все материалы представленные на сайте исключительно с целью ознакомления читателями и не преследуют коммерческих целей или нарушение авторских прав. Обратная связь - 18.190.176.244 (0.009 с.) |