
Заглавная страница Избранные статьи Случайная статья Познавательные статьи Новые добавления Обратная связь FAQ Написать работу КАТЕГОРИИ: ТОП 10 на сайте Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрацииТехника нижней прямой подачи мяча. Франко-прусская война (причины и последствия) Организация работы процедурного кабинета Смысловое и механическое запоминание, их место и роль в усвоении знаний Коммуникативные барьеры и пути их преодоления Обработка изделий медицинского назначения многократного применения Образцы текста публицистического стиля Четыре типа изменения баланса Задачи с ответами для Всероссийской олимпиады по праву 
Мы поможем в написании ваших работ! ЗНАЕТЕ ЛИ ВЫ?
Влияние общества на человека
Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрации Практические работы по географии для 6 класса Организация работы процедурного кабинета Изменения в неживой природе осенью Уборка процедурного кабинета Сольфеджио. Все правила по сольфеджио Балочные системы. Определение реакций опор и моментов защемления |
Part I. Anatomy. The Human BodyСодержание книги
Поиск на нашем сайте
Pharmacy and other Sciences Part I. Anatomy. The Human Body Lesson 1 I. Read the words according to the type of syllable
II. It is essential to know that: Слова в английском языке образуются несколькими способами: Аффиксацией Конверсией Словосложением Аффиксация – образование слов с помощью суффиксов и приставок.
! Remember Суффикс - al образует прилагательные от основ существительных: person – лицо, personal - личный Read and translate the following adjectives: Practical, biological, experimental, principal, social, special, formal, pharmaceutical, structural, analytical, internal.
! Remember Суффикс - y образует: а) существительные: body [bɔdi] - тело b) прилагательные: salt – соль, salty [sɔlti ] - соленый с) глаголы: [ i ] to study [stΛdi] – изучать [ai] to apply [әplai ] - применять Read and translate thefollowing Words; use dictionary if necessary
a) существительные (nouns) difficulty, anatomy, remedy, body, biopsy, autopsy, registry, expiry b) прилагательные (adjectives) watery, sleepy, wintry, sunny, windy, hairy, funny c) глаголы (verbs) [ai] occupy, multiply, supply, deny, rely
! Remember Конверсия – это совпадение форм многих слов, относящихся к разным частям речи: to help – помочь, помогать help – помощь
Form verbs by means of conversion: The study, a form, a group, an end, a part, a cut, a head, a work, a plan, a register, a name, an act ! Remember Существительное, стоящее перед другими существительными может выполнять роль определения и переводится на русский язык прилагательным и существительным в родительном падеже: winter session -зимняя сессия; human anatomy - анатомия человека Read and give Russian equivalents: coffee break, spring day; body temperature; square inch; rehabilitation period; Anatomy atlas; university laboratory; laboratory analyses; world standards; minimum qualification; instrument table
III. Memorize the following words: 1. head [hed] – n. голова 2. neck [nek] – n. шея 3. trunk [trʌŋk]- n. туловище, syn. torso 4. upper [ ′Λpә] extremity [ iks′tremiti ] – верхняя конечность lower [ louә] extremity [iks′tremiti ] – нижняя конечность 5. average [‘ævəridʒ] – adj. средний verb. в среднем составить on an average – в среднем 6. adult [ədʌlt] – n. взрослый (человек) – adj. взрослый 7. cell [sel] – n. клетка 8. bone [bɔun] – n. кость 9. muscle [mʌsl] – n. мышца 10. skin [skin] – n. кожа 11. thigh [θai] – n. бедро syn. hip 12. tiny [taini] – adj. крошечный 13. chest [tʃest] – n. грудная клетка, syn. thorax 14. abdomen [æbdoumən] – n. живот, брюшная полость 15. lung [lʌŋ] – n. лёгкое 16. heart [ha:t] – n. сердце 17. gullet [gʌlit] – n. пищевод, syn. esophagus [i:’sɔfəgəs ] iv. Read the text The Human Body Part I Human anatomy is the study of the biological systems. The principal parts of the human body are head, neck, trunk, two arms (upper extremities) and two legs (lower extremities). There are 11 systems in the human body. The upper part of the trunk is the chest and the lower part is the abdomen. The principal organs in the chest are the lungs, the heart and the gullet (esophagus). Our body has different special organs such as the eyes, the ears and the nose. Our largest bone is the thigh bone. Our smallest bone is a tiny bone inside the ear. The adult body has: 100 trillion cells, 206 bones, 600 muscles and 22 internal organs. The average height of an adult human is about 5 to 6 feet tall. Every square inch of the human body has about 19 million skin cells.
V. Find the word-combinations in the text and translate them into Russian: a) adjectives (ending in –al) + noun b) noun (as an attribute) + noun VI. Form the adjective ending in –y and give their Russian equivalents: heart, bone, skin, leg VII. Match the words close in meaning:
VIII. Render from Russian English: tiny: крошечная клетка, крошечная голова, очень маленькое туловище; крошечное сердце, крошечный нос; очень маленькая косточка average: средний (нормальный) взрослый; средний рост; средний вес (weight) сердца, в среднем; средний размер головы
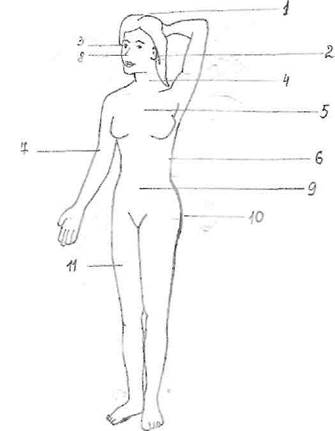
IX. Label the body parts in the picture:
X. Make the sentences complete: 1. The upper part of the trunk is … 2. The lower part of the trunk is … 3. The principal organs in the chest are… 4. The human body has 22… 5. The largest bone is… 6. The smallest bone in the human body is…
XI. Among the following numbers choose a correct one to answer the questions:
1. How many muscles has an adult body? 2. How many skin cells has a square inch of the human body? 3. How many internal organs are there in the body? 4. What is the average height of an adult human? 5. How many eyes has an average human? 6. How many systems are there in the human body? 7. How many bones has the adult body? 8. How many cells has the adult human body? Lesson 2 I. Read the words according to the type of syllable
II. It is essential to know that: Ударение в многосложных словах часто падает на третий от конца слова слог. Гласная в ударном слоге читается как в закрытом слоге, даже если этот слог открытый: an a tomy [ә′nætәmi] Ударение всегда ставится перед ударным слогом
Read the following words digestive, extremity, regimen, skeleton, medical, chemistry, intestine
! Remember Словосложение является одним из способов образования новых слов: head [hed] - голова + ache [eik] - боль = headache - головная боль. В составных существительных ударение обычно падает на первое слово: ′ schoolboy
Read and translate the following (use dictionary if necessary): · heartache; heartbeat; heartburn, heart-disease · headache; headquarters, head-nurse · cell-phone; chestnut; lungwort
! Remember a) Суффикс - ly образует наречия в английском языке: hour [auә], час – hourly [′auәli] – ежечасно
Read and translate the following adverbs: really; formally; badly; daily; monthly; yearly; normally; specially; weekly; partly; practically; b) суффиксы – ary (-ery, -ory) [әri] образуют прилагательные: pulmonary [′pΛlmәnәri] – легочный
Read and translate the following adjectives: elementary; ordinary; respiratory; primary; secondary; circulatory; coronary; c) суффикс – ar является суффиксом прилагательного: cellular [′seljulә] – клеточный Read and translate the following adjectives: regular; muscular; vascular; alveolar; d) суффикс -ic является суффиксом прилагательного образованного от основы существительного: diuretic [daijuә′retik] мочегонное средство Read and translate the following adjectives: plastic; basic; antibiotic; acidic; alcoholic; electric; dynamic; dystrophic; cosmetic; hypnotic; hygienic, glyceric; atmospheric; lymphatic; systemic; prophylactic; organic; inorganic III. Master the pronunciation of the words. Guess their meaning: cardiovascular [ֽka:di: әu′væskju:lә] musculoskeletal [ֽmΛskjulәu′skelitәl] immune [i′mju:n] endocrine [′endәukri:n] nervous [′nә:vәs] reproductive [ֽri:prә′dΛktiv] component [kәm′pәunәnt] function [fΛnk ∫(ә)n] mineral [′minәrәl] liter [′li:tә] phase [′feiz] portion [′pɔ:∫(ә)n] to circulate [′sә:kju:leit] to transport [træns′pɔ:t] IV. Memorize new words: 1. blood [blΛd] – n. кровь 2. vessel [′vesl] – n. сосуд 3. tissue [′tisju] – n. ткань 4. oxygen [′ɔksidƷәn] – n.кислород 5. vital [′vaitl] – adj. жизненный, жизнеспособный, витальный 6. by means of smth – при помощи чего-либо 7. distinct [dis′tiηkt] – adj. легко отличимый, ясный, отличный, определенный 8. rest [rest] – n. 1) отдых, покой, сон 2) остаток, остальные, другие v. отдыхать 9. back [bæk] – n. спина, хребет, тыл adv. назад, обратно backbone – n. позвоночник, позвоночный столб 10. major [′meidƷә] ] – adj. большой, старший, мед. серьезный 11. to pass [pa:s] – v. проходить, передаваться 12. supply [sә′plai] – v. питать, снабжать n. питание, запас, снабжение 13. digestive [di′dƷәstiv] – пищеварительный, способствующий пищеварению 14. integumentary [inֽtegju′mentәri] – покровный, кожный 15. urinary [′juәrinәri] –мочевой 16. through [θru:] – через, сквозь, по V. Give Russian equivalents the following word-combinations: · tissue culture; tissue juice; tissue reaction; tissue respiration; tissue change; tissue therapy · oxygen mask; oxygen therapy; oxygen exchange; · rest-home; to have a good rest; bed rest; at rest; rest oxygen; the rest of oxygen; the rest blood; day of rest; the rest of us · blood vessels; tiny vessels; heart vessels; vessel wall · vital minerals; vital organs; vital activity; vital function; · digestive system; digestive tract; digestive juice · urinary system; urinary organs; urinary pigment; urinary tract; urinary difficulty · through the blood; through the heart; through the tiny vessels; through the integumentary system, to supply through the digestive organs VI. Read and translate one-rooted words: · to circulate, circulatory, circulation · vessel, vascular · system, systemic · lymph, lymphatic · nerve, nervous · urine, urinary · to reproduce, reproductive
VII. Render from Russian into English: главные компоненты; жизненно-важные минералы; отчетливые части; в среднем; при помощи циркуляторной системы; переносить кровь; проходить через сердце; снабжать легкие; назад к сердцу. VIII. Read the text. Write out English equivalents to the following word-combinations: работает самостоятельно; общая циркуляторная система; кровообращение в системе воротной вены; почечная циркуляция; через тонкий кишечник; через почки; по определению. Human body systems The organ systems of the human body are the cardiovascular system, musculoskeletal system, digestive system, endocrine system, Integumentary system, urinary system, lymphatic system, immune system, respiratory system, nervous system and reproductive system. Cardiovascular system The main components of the human cardiovascular system are the heart and the blood vessels. The primary function of the heart is to circulate the blood and through the blood, oxygen and vital minerals to the tissues and organs of the body. On an average, the human body has about 5 liters of blood that is traveling through it by means of the circulatory system. The body’s circulatory system really has three distinct parts: pulmonary circulation, systemic circulation and coronary circulation or the lungs (pulmonary), the heart (coronary) and the rest of the system (systemic). Each part is working independently. The function of the pulmonary circulation is to transport blood away from the heart to the lungs and then back to the heart. The function of the systemic circulation is to transport blood away from the heart to the rest of the body and then back to the heart. Systemic circulation is a major part of the overall circulatory system. During systemic circulation, blood is passing through the kidneys. This phase of systemic circulation is renal circulation. Blood is also passing through the small intestine during systemic circulation. This phase is portal circulation. The function of the coronary system is to supply blood to the heart. This portion of the cardiovascular system is, by definition, a part of the systemic circulatory system.
IX. Find the word-combinations in the text and translate them into Russian: a) noun (as an attribute) + noun b) adjective (ending in –al) + noun c) adjective (ending in –ic) + noun d) adjective (ending in –ary/ory) + noun
X. Make the sentences complete: 1. The main components of the cardiovascular system are h … and b … v …. 2. Three distinct parts of the circulatory system are p … circulation, c … circulation and s … circulation. 3. The human body has 5 liters of blood traveling through the c … system. 4. The major part of the overall circulatory system is s … circulation.
XI. Make the spidergram complete:
LESSON 3 I. Read the words according to the syllable:
II. It is essential to know that: Существительные в английском языке, стоящие в общем падеже с предлогами of, to, by, with, выражают падежные отношения между существительными. Эти предлоги не переводятся на русский язык отдельными словами, т.к. в этом случае не имеют самостоятельного значения. 1. Существительное с предлогом of соответствуют русскому родительному падежу, отвечающему на вопрос кого? чего? В этом случае предлог of всегда стоит между двумя существительными. cтудент чего? группы (род.падеж) a student of the group 2. Существительные с предлогом to соответствует русскому дательному падежу, отвечающему на вопрос кому? чему? передать кому? студенту (дат. падеж) to pass to the student 3. Существительное с предлогом by соответствует русскому творительному падежу, отвечающему на вопрос кем? чем? Такие существительные обозначают лицо, объект, силу, которые задействованы в выполнении какой-то работы. Лекарства производятся кем? фармацевтическими компаниями. Drugs are manufactured by pharmaceutical companies. 4. Существительное с предлогом with соответствует русскому творительному падежу и обозначает предмет, при помощи которого выполняется действие. Писать чем? ручкой. To write with a pen резать чем? ножом to cut with a knife
Study the table:
Read and translate the following word-combinations; pay attention to the prepositions: · the study of the biological systems; the principal parts of the human body; the upper part of the trunk; every square inch of the human organism. · to give to the tissues and organs; to transport blood to the lungs; to the rest of the body; to supply oxygen to the systems. · by heart; with muscles; by pharmaceutist; by adult; with tiny cells; by the head-nurse.
! Remember Английские прилагательные не имеют ни рода, ни числа, ни падежа red face – красное лицо red nose – красный нос red skin – красная кожа red eyes – красные глаза Имена прилагательные могут изменяться только по степеням сравнения положительная – big – большой сравнительная – bigger – больше превосходная – the biggest – самый большой
Read and translate the adjectives: a) sharp; sharper; the sharpest deep; deeper; the deepest cold; colder; the coldest thin; thinner; the thinnest wet; wetter; the wettest hot; hotter; the hottest b) busy; busier; the busiest easy; easier; the easiest dirty; dirtier; the dirtiest tiny; tinier; the tiniest c) active; more active; the most active various; more various; the most various minute; more minute; the most minute; distinct; more distinct; the most distinct; vital; more vital; the most vital; difficult; more difficult; the most difficult; constant; more constant; the most constant; ! Remember Суффикс - er(or) является суффиксом существительного, который обозначает человека или предмет, выполняющий определенную работу; или человека, проживающего где-либо; или человека, изучающего какой-либо предмет (науку). Существительные с суффиксом - er(or) как правило образуются от глаголов
b) от названий местности
Read and translate the following words: helper; worker; teacher; visitor; runner; organizer; lecturer; operator; player; transporter; supplier; controller; master; mixer; pain-killer; director; inspector; producer ! Remember Суффикс – ure является суффиксом существительного. Этот суффикс имеет несколько вариантов: а) – ture читается [t∫ә] structure [′strΛkt∫ ә] – строение, структура в) – sure читается [Ʒә] measure [′meƷә] – мера, измерение N.B. Это слово может также употребляться как глагол to measure – измерять с) – ssure читается [∫ә] pressure [′pre∫ә] – давление
Read and translate the following words, mind the pronunciation of suffixes; use dictionary if necessary: · nature, lecture, picture, future, culture, mixture, temperature, structure; denture; tincture; departure; architecture; agriculture; · measure, treasure, pleasure, closure, exposure III. Master the pronunciation and guess the meaning of the words: arteriola [a:ֽtiәri′ oulә] artery [′a:tәri] vein [vein] capillary [kә′pilәri] aorta [ei′ɔ:tә] controller [kәn′troulә] vena cava [vi:nә keivә] (pl venae [′vi:ni:]) inferior [in′fiәriә] superior [sju′piәriә] diaphragm [′daiәfræm] systolic [sis′tɔlik] diastolic [ֽdai′æstәlik] venous [vi:nәs] chemical [′kemikәl] carotid [kærɔtid] subclavian [sәb′kleiviәn] millimeter [′miliֽmi:tә] venule [′venju:l]
IV. Memorize new words: to carry [′kæri] – v.нести, переносить to provide [prә′vaid] – v.обеспечивать, снабжать layer [leiә] – n.слой various [′veәriәs] – a.различный, разнообразный several [′sevrәl] – a.несколько branch [bra:nt∫] – n.ветвь, отрасль v.ветвиться to lead [li:d] – v.вести, приводиться flow [flou] – n.ток, течение, струя v.течь, циркулировать to receive [ri′si:v] – v.принимать, получать to drain [drein] – v.дренировать, стекать, высушивать minute [mai′nju:t] – a.тонкий, мелкий, маленький constant [′kɔnstәnt] – a.постоянный record [′rekɔ:d] – n. запись, протокол record [ri′kɔ:d] – v. записывать, отмечать, регистрировать exchange [iks′t∫ein(d)Ʒ] – n. обмен v. обмениваться
throughout [θru(:)′aut] 1. adv 1) повсюду, на всем протяжении 2) во всех отношениях 2. prep. по всему, в продолжение
V. Form the nouns using the suffix –er (-or):
VI. Read and translate the word-combinations incorporating new words: To provide exchange; throughout the body; exchange reaction; exchange of water; blood flow; branches of vessels; to drain blood from the head; to lead to the heart; various layers of tissue; to flow back to the lungs; to carry vital minerals; several organs; to record blood pressure; minute capillaries; to receive oxygen.
VII. Form adverbs and give their Russian equivalents: vital; various; distinct; constant; usual; inferior; superior; traditional; principal; minute
VIII. Read and translate one-rooted words: A. • to supply => supplier • to lead => leader • to transport => transporter • to carry => carrier • to receive => receiver • to record => recorder • to provide => provider • to control => controller B. • heart => hearty • bone => bony • skin => skinny • leg => leggy • blood => bloody
IX. Match the words close in meaning:
X. Render from Russian into English: various различные части; различные сосуды; различные кости; различные клетки; различные виды тканей several несколько органов; несколько записей; несколько отраслей; несколько мышц; несколько слоёв minute мельчайшие сосуды; в мельчайших деталях; мельчайшие клетки крови; микроскопическая анатомия
XI. Read the text: Blood vessel The blood vessels are the part of the circulatory system. They transport blood throughout the body. There are three major types of blood vessels: the arteries, the veins, the capillaries. Arteries carry the blood away from the heart. Veins carry blood from the capillaries back toward the heart. Capillaries are the smallest blood vessels. They provide the actual exchange of water and chemicals between the blood and the tissues. The arteries and veins have the same structure with three layers. There are various kinds of blood vessels. Aorta is the largest artery. It carries blood out of the heart. There are several branches of the aorta such as the carotid artery, the renal artery, the subclavian artery, etc. Arterioles are small branches of the artery. They lead into many smaller vessels – the capillaries. Arterioles are the principal controllers of blood flow and pressure. Vein is a large collecting vessel. The largest vein is vena cava. There are two of them: the inferior vena cava and the superior vena cava. The inferior vena cava receives blood from parts of the body below the diaphragm. The superior vena cava drains blood from the head, neck, thorax and arms. Both venae cavae carry blood into the heart. Venule is a minute vessel. It drains blood from the capillaries. Many venules unite to form a vein. The blood pressure in blood vessels is traditionally measured in millimeters of mercury (mm Hg). In the arterial system, this is usually around 120 mm Hg systolic and 80 mm Hg diastolic. These are recorded as 120 over 80. In contrast, pressures in the venous system are constantly 10 mm Hg.
XIII. Find the sentences in the text where the adjectives are used in the comparative or superlative degree. Render them from English into Russian. XIV. Fill in the gaps using the given numbers:
1. The arteries and veins have the structure with … layers. 2. The systolic pressure in the arterial system is … mm Hg. 3. The pressure in the venous system is … mm Hg. 4. There are … venae cavae in the human body. 5. In the arterial system diastolic pressure is … mm Hg.
XV. Translate the following words-combinations from Russian into English: часть системы; типы сосудов; обмен воды; ветви аорты; контролер давления; миллиметры ртутного столба; части тела
XVI. Substitute English words for the Russian ones:
1. There are two полая вена which are large вена. 2. Oxygen-poor blood from the body течет to the heart через the Vena Cava. 3. Верхняя Vena Cava returns blood from the верхние конечности. 4. Нижняя Vena Cava returns blood from the нижняя часть of the body. 5. The pulmonary артерия carries blood from the heart to the right and left легкое. 6. The coronary arteries снабжают blood to the heart itself. 7. Blood from the аорта passes into a branching system of arteries that ведут to различные parts of the body. 8. Then blood flows into a system of капилляры where its обменные функции take place.
XVII. Fill in the gaps with proper words in the right column:
XVIII. Make the sentences complete: 1. Three major of blood vessels are … 2. The vessels that carry blood away from the heart are … 3. The vessels that carry blood back toward the heart are … 4. The largest artery is … 5. The smaller branches of the artery are… 6. A large collecting vessel is … 7. The large vein is … 8. A minute vessel that drains blood from capillaries is …
XIX. Say what you can about the functions of the following vessels:
arteries veins capillaries aorta arterioles venules
дренировать, сердце, кровь, нести, обеспечивать, контролировать, ткани, вода, обмен, давление, химические вещества, кровоток
XX. Translate from Russian into English: 1. Кровеносные сосуды находятся повсюду в организме человека. 2. Они несут кровь от сердца ко всем частям тела. 3. Артерии несут кровь богатую кислородом от сердца. 4. Вены несут кровь назад к сердцу. 5. Артерии разветвляются и становятся меньше и меньше. 6. Они, в конце концов, становятся капиллярами. 7. Капилляры – это очень маленькие сосуды, которые дренируют в две коронарных вены 8. Кровеносные сосуды тела человека являются закрытой системой 9. Кровь течет в легочную артерию 10. Четыре легочных вены, которые дренируют каждое легкое, несут кровь богатую кислородом в левую часть сердца 11. Венулы дренируют капиллярное русло (bed) легких.
XXI. Listen to the text “Circulatory System” and give its summary in Russian. Look through the list of unknown words used in the text: nutrients [΄nju:triənt] – питательные вещества smooth [smu:ð] – гладкий waste [weist] – отходы carbon dioxide [΄ka:bən dai΄ɔksaid] – CO2, углекислый газ
Lesson 4
I. I II III v i rus l y mph f o rm n o de sm e ll o rgan sh a pe j o b int e rnal m a de f a t d a rk tr a ct f o r f u ngi w o rk m a rrow gl a nd t o nsil a ct f i lter
II. It is essential to know: К неопределенным местоимениям (indefinite pronouns) относятся местоимения some, any,no (и их производные), none, much, many, little, few, all, both, either, neither, each, every (и их производные), other, one.
! Remember Местоимения some, any, no.
a) some [sΛm] – несколько, некоторые, некоторое количество (употребляется в утвердительных предложениях). e.g. some vessels – несколько сосудов some blood – некоторое количество крови b) any [΄æni] – сколько-нибудь, какие-нибудь (употребляется в вопросительных и утвердительных предложениях). N.B. any cо значением любой, всякий может потребляться в утвердительных и вопросительных предложениях. e.g. You may buy this remedy at any chemist’s. – Вы можете купить это лекарство в любой аптеке.
c) no [nou] – ни один, никакой, нисколько. N.B. При наличии no глагол в предложении употребляется в утвердительной форме, т.к. в английском предложении может быть только одно отрицание. e.g. No information was received from our suppliers. – Никакой информации не было получено от поставщиков.
Read and translate the following sentences, pay attention to the translation of infinite pronouns: 1. There are some branches of the aorta. 2. Lymph has no color. 3. This vessel drains some blood from the capillaries. 4. These cells in the human body have no contact with the blood. 5. Some nutrients can pass from the blood into tissues. 6. Some veins, particularly veins in the legs, have valves (клапаны) them. 7. Some people with an inadequate blood supply have no pain at all. 8. Even serious heart disease may produce no symptoms. 9. Some knowledge of drug names can help in understanding drug product labels. 10. Any drug has there names: a chemical name, a generic name and trade name. ! Remember Суффикс –ion образует существительные от глагольных корней. Cочетания –tion и –ssion читаются [∫n], а сочетание –sion после гласной читается [ʒn]. e.g. to consult [kәn΄sΛlt] – консультировать consultation [kәnsΛl΄tei∫n] – консультация N.B. В большинстве случаев, если глагол, от которого образуется существительное, заканчивается на звук [d], то данное существительное приобретает суффикс –sion [ʒn]. e.g. to decide [di’said] – решать decision [di΄siʒn] – решение N.B. Многие существительные с данными суффиксами заимствованы в русский язык с суффиксами –ция, -сия. e.g. operation - операция session – сессия
Read and translate the following words: revolution, organization, demonstration, profession, commission, function, production, discussion, formation, variation, manipulation, regulation, radiation, fermentation;
! Remember Суффиксы -able [əbl], ible [ibl] образуют прилагательные от основы глаголов. Во многих случаях эти суффиксы придают прилагательному дополнительный смысл – «способный к…». e.g. to change – менять, меняться changeable – изменяемый
Read and translate the following words (use the dictionary if necessary): readable, eatable, absorbable, responsible, comfortable, considerable, dissoluble, comparable, convertible, suitable;
Master the pronunciation of the words and guess their meaning: gastrointestinal [ֽgæstroin΄testinl] virus [΄vaiərəs]; viruses [΄vaiərəsiz] bacterium [bæk΄tiəriəm]; bacteria [bæk΄tiəriə] fungus [΄fΛŋgəs]; fungi [΄fΛndʒai] gland [glænd] tonsil [΄tɔnsl] appendix [ə΄pendiks] filter [΄filtə] mass [mæs] lymph [limf] lymphoid [΄limfoid] lymphatic [lim΄fætik] absorbable [əb΄sɔ:bəbl]
Memorize new words: 1. channel [t∫ænl] – n. канал, путь, щель 2. multiple [΄mΛltipl] – a. множественный, многочисленный, многократный 3. to assist [ə΄sist] – v. помогать, содействовать 4. disease [di΄zi:z] – n. болезнь 5. to maintain [men΄tein] – v. поддерживать (в каком-либо состоянии) 6. similar [΄similə] – a. подобный, похожий, сходный 7. defense [di΄fens] – n. защита, оборона 8. invasion [in΄veiʒn] – n. 1) вторжение, внедрение паразита; 2) начало болезни 9. to consist [kən΄sist] – v. состоять из 10. marrow [΄mærou] – n. костный мозг 11. node [noud] – n. 1) узел; 2) нарост, утолщение 12. thymus [θaiməs] – n. зобная железа = thymus gland 13. stomach [΄stΛmək] – n. желудок 14. spleen [spli:n] – n. селезенка 15. both [bouθ] – pron. оба both … and (парный союз) – как …, так и ….; и …, и…. 16. fat [fæt] – n.жир, жировая клетчатка; adj. жирный, полный 17. nutrient [΄nju:triənt] – n.питательное вещество; adj. питательный
Read and translate one-rooted words: spleen, splenic to invade, invasion to assist, assistant to defend, defense to carry, carrier to provide, provider, provision various, variable, to vary cell, cellular muscle, muscular to circulate, circulatory, circulation
Read and give Russian equivalents to the following word-combinations: lymph nodes; lymphatic vessel; lymphatic system, lymph channels; lymph flow; lymph gland; lymphoid tissue; defense reaction; defense mechanism; assistant pharmacist; marrow cell; bone marrow; splenic artery; splenic vein; stomach-ache; stomach fermentation; stomach wall; virus disease; intracellular fat, fatly acids; fats under the skin; complex fats Find in the text English equivalents to the following Russian word-combinations: инородные тела; внутренние полости; яйцеобразный орган; основание шеи; миндалевидная структура
Read the text: The Lymphatic System Part 1 All tissues are made of cells, and, in between various cells, there are very tiny channels with fluid collection. This fluid is called lymph. Lymph has no color, no smell, and is easily absorbable. The lymphatic system has multiple jobs. It assists in the fight against foreign bodies and diseases in the blood flow and bodily tissues. It transports fats and nutrients from the gastrointestinal tract. It maintains fluids in the body tissue. The lymphatic system is both structurally and functionally similar to the body's circulatory system. The lymphatic system and the circulatory system often work together to form a defense against foreign invasion by viruses, bacteria, or fungi. The lymphatic system consists macroscopically of: the bone marrow, spleen, thymus gland, lymph nodes, tonsils, appendix, and some other organs. Tissue within the internal cavities of the bones is called bone marrow. Spleen is a dark-red ovoid organ situated on the left side of the body below and behind the stomach. Thymus is an organ situated in the root of the neck, above and in front of the heart. Lymph node is a small, almond-shaped structure, which acts as a filter for the lymph. Tonsil is a mass of lymphoid tissue on both sides of the back of the mouth.
IX. Give synonyms to the underlined words: 1. The lymphatic system helps in the fight against diseases. 2. The lymphatic system carries fats and nutrients. 3. The lymphatic system keeps up fluids in the body tissues.
X. Substitute English words for the Russian ones: Лимфатическая system collects the blood plasma lost from the циркуляторная system as лимфа and передает it назад to the circulatory system. The lymphatic system is a complex network of лимфоидных organs, lymph узлов, lymphatic тканей, lymph капилляров and lymph сосудов. The lymphatic system is a главный component of the immune system. It has three функции. Lymphatic system takes away the excess жидкости from body tissues. It absorbs жирные acids and транспортирует fat to the circulatory system. It produces immune клетки. There are несколько groups of lymph nodes по всему the human body.
XI. Render from Russian into English: 1. Лимфатическая система состоит из лимфатических капилляров, лимфатических сосудов, лимфатических узлов и протоков (duct). 2. Лимфатическая система имеет несколько функций. 3. Она дренирует жидкости, формирует защиту против вторжения инородных тел и т.д. 4. Лимфатические капилляры располагаются во всех органах за исключением кожи, глаз, хрящей (cartilage) и мозга. 5. Капилляры обеспечивают резорбцию (всасывание) из тканей различных веществ (воды, жиров). 6. Лимфатические сосуды нижней конечности ведут к паховым (groin [grɔin]) лимфатическим узлам. 7. Глубокие лимфатические сосуды несут лимфу в глубокие лимфатические узлы. 8. Миндалины – это скопление лимфоидной ткани. 9. Они помогают в защитной реакции организма. 10. Миндалины имеют продолговатую ([΄ɔblɔŋ]) форму; обычно они розового цвета. Они имеют много отверстий, которые ведут в узкие (narrow) щели.
XII. Speak about the functions of the lymphatic system using the scheme:
Lesson 5 I. Read the following words according to the syllable:
2. It is essential to know: Предлогами (prepositions) называются служебные слова, которые показывают отношение существительного (или местоимения) к другим словам в предложении. Предлоги выражают разнообразные отношения - пространственные, временные, причинные и т.д. В русском языке эти отношения выражаются предлогами + падежными окончаниями, а в английском языке – только предлогами. e.g. He studies in Moscow. – Он учится в Москв е. The door to the drugstore is under the drugstore sign. – Дверь в аптеку находится под вывеск ой. Многие предлоги имеют не одно, а несколько значений. Предлог about имеет значения: 1) - о, -об, относительно e.g. We spoke to her about this matter. – Мы поговорили с ней об этом деле. 2) - приблизительно, около e.g. This mixture costs about 30 roubles. – Эта микстура стоит примерно (приблизительно, около) тридцати рублей. 3) - вокруг, кругом, по e.g. The chemist looked about him. – Аптекарь посмотрел вокруг себя.
N.B. Предлоги также входят в состав многих сочетаний и выражений: e.g. in vain – напрасно at last – наконец for ever – навсегда on one (the other) hand – с одной (другой) стороны
N.B. Между английскими и русскими предлогами нет постоянного соответствия. Один и тот же английский предлог может переводиться различными русскими предлогами: e.g. The customer is standing at the counter. – Покупатель стоит у прилавка. The pharmacy usually opens at eight a.m. – Аптека обычно открывается в восемь утра. She works at the pharmaceutical factory. – Она работает на фармацевтическом заводе. All students laughed at him. – Все студенты смеялись над ним.
N.B. Один и тот же русский предлог может переводиться различными английскими предлогами: e.g. Аптечная посуда на столе. - Medicine bottles are on the table. Аптекарь посмотрел на меня. - The pharmacist looked at me. Она поедет на конференцию. - She’ll go to the conference. Она поедет туда на неделю. – She’ll go there for a week.
N.B. Некоторые глаголы английского языка употребляются с предлогами, а соответствующие им русские глаголы не требуют предлогов после себя. e.g. Wait for me. – Подождите меня. He asked for an ointment. – Он попросил мазь. Listen to the doctor. – Послушайте врача. И наоборот, английские глаголы употребляются без предлогов, а соответствующие им русские глаголы требуют предлога. e.g. She entered the drug-store. – Она вошла в аптеку. The customer addressed the chemist. – Покупатель обратился к аптекарю. The students watched the chemical reaction. – Студенты наблюдали за химической реакцией. He approached the medicine chest. – Он приблизился к ящику с лекарствами. We need this first-aid kit. – Мы нуждаемся в этой аптечке. N.B. По своей фо
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Последнее изменение этой страницы: 2016-12-12; просмотров: 323; Нарушение авторского права страницы; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! infopedia.su Все материалы представленные на сайте исключительно с целью ознакомления читателями и не преследуют коммерческих целей или нарушение авторских прав. Обратная связь - 3.149.244.92 (0.017 с.) |


 to dance – танцевать danc er –танцор
to dance – танцевать danc er –танцор to read – читать read er – читатель
to read – читать read er – читатель to write писать writ er – писатель
to write писать writ er – писатель Но иногда такие существительные могут быть образованы от других существительных: hat – шляпа hatter – шляпный мастер
Но иногда такие существительные могут быть образованы от других существительных: hat – шляпа hatter – шляпный мастер London – Лондон a Londoner – житель Лондона
London – Лондон a Londoner – житель Лондона village – деревня a villager – деревенский житель
village – деревня a villager – деревенский житель



