Заглавная страница Избранные статьи Случайная статья Познавательные статьи Новые добавления Обратная связь FAQ Написать работу КАТЕГОРИИ: ТОП 10 на сайте Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрацииТехника нижней прямой подачи мяча. Франко-прусская война (причины и последствия) Организация работы процедурного кабинета Смысловое и механическое запоминание, их место и роль в усвоении знаний Коммуникативные барьеры и пути их преодоления Обработка изделий медицинского назначения многократного применения Образцы текста публицистического стиля Четыре типа изменения баланса Задачи с ответами для Всероссийской олимпиады по праву 
Мы поможем в написании ваших работ! ЗНАЕТЕ ЛИ ВЫ?
Влияние общества на человека
Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрации Практические работы по географии для 6 класса Организация работы процедурного кабинета Изменения в неживой природе осенью Уборка процедурного кабинета Сольфеджио. Все правила по сольфеджио Балочные системы. Определение реакций опор и моментов защемления |
Lecture purpose: Studying of the main methods of synthesis of CTSСодержание книги
Поиск на нашем сайте Plan of a lecture: 1. Purpose of a task of synthesis of CTS. 2. Synthesis methods. 3. Technological restrictions in case of the solution of a task.
When designing new or reconstruction of the existing production, one of the main tasks is synthesis of option of CTS allowing to reach high technical and economic rates. In a general view the task of synthesis of CTS is formulated as follows: It is known: structure and parameters of raw flows; structure and parameters of productional flows; indicator of an optimality criterion of functioning of CTS; restrictions for parameters of functioning of the CTS elements. It is necessary to determine: structure of CTS (the devices entering CTS); structure of CTS (communication between devices); design data of devices CTS; current technological parameters of work of CTS; the parameters of management of CTS satisfying to optimum parameters of functioning of CTS. In case of the solution of a task of synthesis of CTS, the way of carrying out process (chemism), and only shall be originally determined then becomes possible to make synthesis of structure of CTS, determination of parameters of work of its elements and parameters of the flows connecting these elements. Because the task of synthesis is a complex multiple challenge, its decision is possible only when using a certain methodology and the corresponding approaches. The method based on the principles of search of options of topology of CTS, parameters of functioning of elements, etc. can be the easiest way of synthesis. However, in connection with complexity of CTS and diversity of the solution of separate tasks of synthesis (mutual connection of reactors, heat exchangers, etc.) this method will require a large number of the additional information and time that can be insufficiently effective. For example, it is well known that spontaneously warmly to be transferred only from a hot flow to cold, therefore, the scheme assuming the return can be not considered. However, in case of simple search of various options, parameters of functioning of elements can be determined only after synthesis of topology of CTS and creation of its mathematical model necessary for calculation, and the calculation. Therefore, in this case, even impracticable options will require consideration, and, therefore, additional costs. For decrease in quantity of the considered options usually carry out decomposition of a task of synthesis of CTS on a number of subtasks or levels (a decompositional method of synthesis of CTS). The example of such decomposition on seven levels is provided in Fig. 3.1. When using simpler – two-level decomposition, at the top level will come synthesis of CTS from subsystems (chemical interaction, separation, mixture and so forth) and to be determined parameter values of the flows connecting these subsystems. At the lower level synthesis of subsystems will be made and to be determined parameter values of the flows connecting the devices entering these subsystems. In this case, if the version of any synthesized scheme in case of its calculation is impracticable, costs for synthesis, the analysis, modeling and calculation of option of CTS will be less. However even the task of synthesis of subsystems is rather difficult and requires additional decomposition or application of other methods of synthesis.
Fig. 3.1. Order multi-level decomposition of a task of synthesis of CTS
It is possible to refer the heuristic principle of synthesis of CTS which consists in mathematical formalization of the intuitive heuristic method which is widely used by designers to the principles allowing to solve more effectively a problem of synthesis of CTS a decomposition method, and, allowing highly qualified specialists to choose intuitively the most successful ways of solving the problem without complete search of all possible alternative options. When using this method decision making happens without reasons it by means of proofs. However this method of decision making doesn't reduce its value as it uses intuitive factors and rules, i.e. the generalizing knowledge and wide practical experience of highly qualified specialists. We will consider some heuristics, applied in case of development of technological schemes of a number of functional subsystems of chemical productions. For example, for the choice of the optimum technological scheme of separation of multicomponent mixes from a set of alternative options it is possible to use the heuristics following: a) the choice of option with consecutive allocation of target products in the form of easy products of elements of a subsystem; b) the choice of option, in which the relation of quantities of the upper and lower products in each element of a subsystem most close to 1; c) the choice of option in which separation of components is performed as reduction of distinctions in values of relative volatilities of the divided key components; d) the rectifying columns requiring the greatest costs for separation owing to close relative volatilities of key components or high requirements to purity of products shall be placed at the end of the scheme of separation; e) the choice of the option which is characterized by the minimum size of the given costs for implementation of this engineering procedure in a subsystem element, etc. In case of development of optimum technological schemes of thermal subsystems (systems of heat exchangers) the heuristics following can be used: a) couple of flows for which the amount of the transferred heat is maximum are chosen; b) couple of flows for which the set final temperatures of flows aren't reached are chosen, and the cost of use of auxiliary heat carriers for bringing temperature of these flows to the set final values is minimum; c) couple of flows which heating/chilling cost auxiliary warm / coolant is maximum are chosen; d) couple of flows for which the cost of heat exchange is minimum, etc. are chosen. In case of use of the heuristic principle of synthesis success in the basic depends on that, heuristic conditions are how close to conditions of achievement of an optimality of the considered CTS subsystem, and also from an order of application of heuristic conditions, type of a synthesizable subsystem, its complexity, parameters of flows and so forth. For determination of this order of application эвристик use weight functions separate эвристик. As an example, we will review/7/example of synthesis of the system of heat exchangers providing heating and chilling of technological flows to the set temperatures provided in literature. As well as for any technological scheme in an example the following restrictions are used: • the technological scheme shall use as much as possible energy of flows ("cold" flows shall heat up whenever possible "hot" flows); • technological flows can't be divided, however if separation of a technological flow is necessary, then the divided parts of a flow shall be considered as separate flows; • the synthesizable thermal scheme shall have the minimum costs for implementation of the set transaction of heat exchange between flows; • if for heating/chilling of flows it is impossible or unprofitable to use other flows, external heat carriers can be used: saturated steam with pressure of 31,6 kgfs/cm2 and the cooling water with a temperature of 38OC, and water it is impossible to heat higher than 82OC; • in case of heat exchange between technological flows, chilling their water and heating steam, respectively, reaches the following coefficients of a heat transfer: 852, 852, 1136 W / м2; • in case of heat exchange between technological flows, chilling by their water and heating steam, respectively, the minimum rapprochement of temperatures of the processed temperatures in the heat exchanger constitutes 11, 11 and 13OC. Initial parameters of technological flows are provided in Table 3.1. Table 3.1. Parameters of technological flows
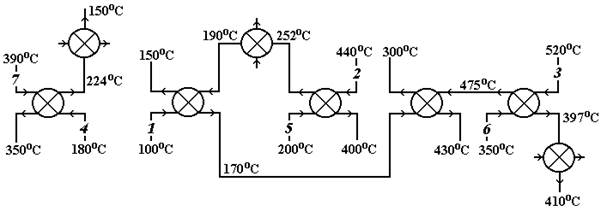
According to methodology of use of the heuristic principle, the order of synthesis of the thermal scheme (CTS) will be following: All set of flows is divided into subsets of the flows, which are subject to heating (a flow 1, 4, 5 and 6) and to chilling (a flow 2, 3 and 7). The weight coefficients different 0,5 are appropriated to all heuristics (will be used described above heuristics); Search of flows of both subsets determines a possibility of implementation of transactions of heat exchange (i.e. at first a flow 1 with flows 2, 3, 7, then a flow 4 with flows 2, 3, 7, etc.). Couples of flows for which heat exchange is possible are entered in the table of couples of processed flows; By means of the heuristics chosen taking into account weight coefficients one couple gets out of the table of couples of processed flows and for it calculation of the heat exchanger is made, i.e. final temperatures of flows are calculated; If the calculated final temperatures of flows correspond to the set final temperatures, then these flows are struck off lists. Otherwise, the flows having the calculated final temperatures are entered in tables as the remained raw flows; Points 2-5 repeat until all couples of processed flows are exhausted; The remained flows not reached final temperatures are exposed to heating/chilling by auxiliary flows. The given costs for implementation of the synthesized scheme are calculated; Calculated, by means of any technique, the size of the given costs is compared to the minimum value received earlier (the original cost of system of heat exchangers is calculated for system in which heating and chilling is carried out only by auxiliary water flows and couple). If the received decision turns out more economic, then the weight coefficients used эвристик increase, otherwise – decrease. If the weight coefficient of heuristics is equal to zero, then this heuristics isn't used further. Process of synthesis of CTS is conducted until present value of costs falls. In case of stabilization of present value of costs on some minimum value, calculations stop. The synthesized operator scheme of system of heat exchange (for this example) is provided in Fig. 3.2.
Fig. 3.2. The operator scheme of the synthesized system of heat exchange
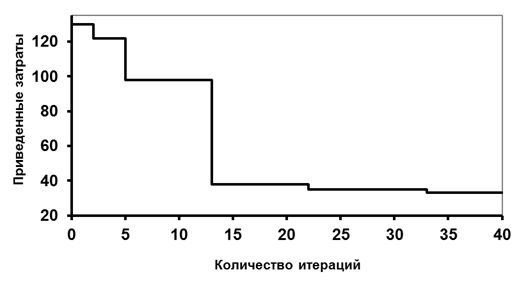
Decrease in the given costs in the course of synthesis of the thermal scheme is provided in Fig. 3.3.
Fig. 3.3. Change of the given costs in the course of synthesis of thermal schemes.
Apparently from drawings, the synthesized thermal scheme has the minimum given costs and consists of eight heat exchangers, five of which give warmth from the cooled flows to heating up, and only in three heat exchangers external coolant moves. The considered principles of synthesis of CTS rather widely are applied in case of synthesis of new productions, however in case of reconstruction of the existing productions, use of these principles will lead to consideration of excessive quantity of options and can be insufficiently effective. For the purposes of upgrade of the existing technological scheme, as well as for synthesis of new CTS the evolutionary principle of synthesis can be used. The methodological basis of the evolutionary principle of synthesis of CTS consists in consecutive modification of hardware registration and correction of structure of technological connections of some initial option of CTS with use of methods of heuristics and optimization. Otherwise, when using the evolutionary principle of synthesis of CTS, at first the initial option of technological topology of CTS, for example, by means of the heuristic principle of synthesis is created. By means of analysis methods for this option there is a "narrow" place of CTS, the optimality criterion is determined, and the corresponding modification of hardware registration and structure of technological communications is made. After the specified modification calculation of an optimality criterion and new search of the "narrow" place of CTS is made again. Process of modification of CTS is made until required value of an optimality criterion is reached. Thus, logically, this process consists of consecutive iterative alternation of stages of synthesis, the analysis, optimization and modification of some originally set technology solution of a task of synthesis of CTS or the existing technological scheme. Thus, practical implementation of the evolutionary principle of synthesis is connected with need of use of the following types эвристик: heuristics generalizing practical experience (the least effective elements or bottlenecks allowing to allocate in initial option of technological topology of CTS); intuitive heuristics (the possible options of modification or enhancement of bottlenecks of CTS allowing to determine); heuristics, based on knowledge of highly qualified specialists (the "joinings" of the modified CTS element with an unmodified part of CTS providing an opportunity). In conclusion, it should be noted that, unfortunately, use of the evolutionary principle of synthesis of CTS allows to receive local optimum results with the greatest efficiency that is caused by the fact that the result of the decision is considerably determined by the main concepts accepted at the first stage in case of development of initial option of technological topology of CTS.
Test questions 1. Formulate the purposes of a task of synthesis of CTS. 2. Synthesis methods. 3. The technological restrictions considered in case of the solution of a task of synthesis.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Последнее изменение этой страницы: 2017-02-07; просмотров: 287; Нарушение авторского права страницы; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! infopedia.su Все материалы представленные на сайте исключительно с целью ознакомления читателями и не преследуют коммерческих целей или нарушение авторских прав. Обратная связь - 216.73.216.41 (0.008 с.) |