Заглавная страница Избранные статьи Случайная статья Познавательные статьи Новые добавления Обратная связь КАТЕГОРИИ: ТОП 10 на сайте Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрацииТехника нижней прямой подачи мяча. Франко-прусская война (причины и последствия) Организация работы процедурного кабинета Смысловое и механическое запоминание, их место и роль в усвоении знаний Коммуникативные барьеры и пути их преодоления Обработка изделий медицинского назначения многократного применения Образцы текста публицистического стиля Четыре типа изменения баланса Задачи с ответами для Всероссийской олимпиады по праву 
Мы поможем в написании ваших работ! ЗНАЕТЕ ЛИ ВЫ?
Влияние общества на человека
Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрации Практические работы по географии для 6 класса Организация работы процедурного кабинета Изменения в неживой природе осенью Уборка процедурного кабинета Сольфеджио. Все правила по сольфеджио Балочные системы. Определение реакций опор и моментов защемления |
Representation of CTS in the form of counts, matrixes and tables.
The structure of CTS is usually considered in terms of the theory of counts, i.e. in the form of the oriented count whose tops correspond to devices, and arches – to flows (for example as in Fig. 4.2). In Fig. 4.2 numbers of tops are designated in the big italics (on the right from above from top), and numbers of flows – a small direct font (under the line of the corresponding flow).
Fig. 4.2. Representation of CTS in the form of the oriented count The sequence of the linked arches allowing to pass from one top to another is called way. The way can be designated both through the sequence of arches, and through the sequence of tops. The way which initial top matches with final and each top, except for initial, is passed only once, is called a contour. For example, in Fig. 4.2 there are three contours (on tops): 2-3-4-2, 3-4-3 and 6-7-6. Complex, a part of the count whose tops have the following properties is called: • each of tops and arches of a complex enters one of the count's contours; • if the top of i is included into a complex, then this complex includes also all tops entering contours which contain i top. For example, on the count provided in Fig. 4.2 there are two complexes (on tops): 2-3-4 and 6-7. In the first complex two contours (2-3-4-2 and 3-4-3), and enter the second – one (6-7-6). The traffic pattern of material flows (columns) provided in Fig. 4.2 is rather simple, and therefore allows to carry out the analysis without use of any software products. In case of more difficult scheme, it becomes difficult to carry out the analysis since by search of an optimum set of the broken-off flows of complexes it is necessary to carry out the analysis of rather large number of information and speed. When using for the analysis of structure of CTS of special algorithms there is an input problem in the computer of the block diagram, i.e. its formalization in any numerical type. Depending on the chosen analysis method, the structure of CTS is usually formalized in the form of a matrix of contiguity or in the form of the list of contiguity. The matrix of contiguity represents the binary table, quantity of lines and which columns are equal to quantity of tops of the count. For accounting of entrance and output flows the matrix of contiguity is added in the zero line and a column, considering as zero top – the environment. If between two tops there is a communication, to a contiguity matrix element, being on crossing of a column and line with the corresponding numbers of tops, value "1", and in case of lack of communication – "0" is appropriated. For example, for the count provided in Fig. 4.2 it is possible to constitute the following matrix of contiguity:
Fig. 4.3. Contiguity matrix The list of contiguity for the count presented in Fig. 4.2 can be presented in the form: Fig. 4.4. List of contiguity
In this list, the first line of a matrix designates number of communication of the count. Number of top from where the specified communication comes out is specified in the second line, and in the third – into what top of the count communication is included. Except the list of contiguity, communication of the count it is possible to present in tables of communications. For example, for the count presented in Fig. 4.2 tables of communications will look as follows:
Fig. 4.5. Tables of communications
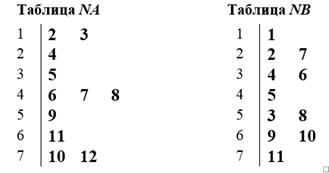
The table A is called the table of entrance communications, in the table B – the table of output communications. In the first column of the table A all tops of the count, and are specified in the subsequent – numbers of tops of the count where there are communications from the corresponding numbers of the tops specified in the first column of the table. Numbers of tops of the count from where there are communications to the corresponding numbers of tops specified in the first column of the table B are specified in the table B. Modification And yes In tables of communication are NA and NB tables of the communications differing from And yes In tables in the fact that numbers entering and leaving in the set top of communications are specified in them:
Fig. 4.6. The modified tables of communications
It is difficult to choose one since all ways equally well perform the functions from the specified ways of formalization of CTS and can be used without any restrictions for formalization and input in the computer of structure of CTS of any complexity. The main criterion of the choice of this or that way of formalization of CTS is the chosen algorithm of search of an optimum set of the broken links with the purpose of the translation of CTS from closed in the opened look.
|
||||
|
Последнее изменение этой страницы: 2017-02-07; просмотров: 258; Нарушение авторского права страницы; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! infopedia.su Все материалы представленные на сайте исключительно с целью ознакомления читателями и не преследуют коммерческих целей или нарушение авторских прав. Обратная связь - 18.223.106.232 (0.005 с.) |