Заглавная страница Избранные статьи Случайная статья Познавательные статьи Новые добавления Обратная связь FAQ Написать работу КАТЕГОРИИ: ТОП 10 на сайте Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрацииТехника нижней прямой подачи мяча. Франко-прусская война (причины и последствия) Организация работы процедурного кабинета Смысловое и механическое запоминание, их место и роль в усвоении знаний Коммуникативные барьеры и пути их преодоления Обработка изделий медицинского назначения многократного применения Образцы текста публицистического стиля Четыре типа изменения баланса Задачи с ответами для Всероссийской олимпиады по праву 
Мы поможем в написании ваших работ! ЗНАЕТЕ ЛИ ВЫ?
Влияние общества на человека
Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрации Практические работы по географии для 6 класса Организация работы процедурного кабинета Изменения в неживой природе осенью Уборка процедурного кабинета Сольфеджио. Все правила по сольфеджио Балочные системы. Определение реакций опор и моментов защемления |
XII. Write a letter to your tutor telling him or her which areas of Biology you would like to specialize in and why. Use these notes to help you.Содержание книги
Похожие статьи вашей тематики
Поиск на нашем сайте
Dear Mr / Mrs (tutor’s surname), Writing to tell you choices I have made Specialize in (one or two of the main areas) Reasons for choosing: interested in (plants / animals / latest ideas / laboratory work / your own ideas) Possible career choices: what I hope to do when I graduate (medicine / ecology / agriculture / your own idea) Offer to meet and discuss choices: I would like your advice and hope we can ……. Yours sincerely, (your full name: first name + surname) Write 100 – 140 words.
XIII. Prepare a short presentation to answer the question: ‘What is the scientific method?’ Talk about: · What is the essential aspect of a scientific experiment? · What is constantly changed in an experiment? · What is to be done at the end of an experiment?
Unit II. СELL Text 2.1 Cell Theory
■ Essential targets By the end of this text you should be able to: ● describe the main ideas of the cell theory ● compare the structures of animal and plant cells as seen with a light microscope.
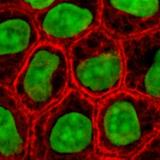
Pre-reading ■ With a partner consider the following questions and try to answer them. Then quickly scan the text to check your answers. 1. What is a cell? 2. Who discovered cells? 3. Do plant cells differ from animal cells? ■ Read the given text and make your essential assignments: Cells were discovered in 1665 by the English scientist and inventor Robert Hooke. Hooke designed his own compound light microscope to observe structures too small to be seen with the naked eye. Among the first structures he examined was a thin piece of cork (the outer surface of bark from a tree). Hooke described the cork as being made of hundreds of little boxes, giving it the appearance of a honeycomb. He called these little boxes cells. It soon became clear that virtually all living things are made of cells, and that these cells have certain features in common. The cell theory The concept that cells are the basic units of life became embodied in a theory called the cell theory, which embraces the following main ideas: ·cells form the building blocks of living organisms · cells arise only by the division of existing cells · cells contain inherited information which controls their activities · the cell is the functioning unit of life; metabolism (the chemical reactions of life) takes place in cells · given suitable conditions, cells are capable of independent existence. A typical animal cell The structure of a typical animal cell: · the cell has a cell surface membrane which encloses the cell contents · the contents consist of a central ball-shaped nucleussurrounded by material calledcytoplasm · the nucleus contains a fibrous material called chromatin · this condenses to form chromosomes during cell division · chromatin contains DNA, the material which controls the various activities inside the cell · scattered within the cytoplasm are mitochondria, small rod-like structures. They have been described as the “power-houses” of the cell because they supply energy. · smaller dots within the cytoplasm are particles of stored food. Many consist of glycogen, which is a food storage polysaccharide. A typical plant cell Like an animal cell, a typical plant cell has a cell surface membrane, cytoplasm, and a nucleus. However, plant cells differ from animal cells in several ways: · most plant cells have a large sap-filled cavity called the vacuole.Sap is a watery fluid containing salts and sugars. The vacuole surrounded by a membrane called the tonoplast. · the cytoplasm contains starch grains, the food storage products of plants · many plant cells have chloroplasts in the cytoplasm. These contain the pigments used in photosynthesis. Chlorophyll, which is green, is the main pigment. Chloroplasts occur only in the parts of plants exposed to light – the green parts. They are absent from underground structures such as roots. ■ Glossary of essential terms for you to know
■ Your Essential Assignments I. Quick check 1. Briefly state the main concept of the cell theory. 2. List the features: a) that only animal cells have b) that only plant cells have c) that both animal and plant cells have.
II. Fill in the missing words:
III. Use monolingual English dictionary and write down what could the words given below mean: surface, honeycomb, cavity, plant, sap. IV. Match these words with their definitions:
V. Find English equivalents to the following word combinations:
VI. Give Russian equivalents to the following English terms:
VII. Find synonyms among the pool of words:
VIII. Answer the following questions. Use all information given before: 1. When were cells discovered? 2. How did Robert Hooke discover cells? 3. What is called the cell theory? 4. What are the main ideas of the cell theory? 5. What is the structure of a typical animal cell? 6. How do plant cells differ from animal cells?
IX. Match the sentence halves. Make complete sentences:
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Последнее изменение этой страницы: 2017-01-19; просмотров: 609; Нарушение авторского права страницы; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! infopedia.su Все материалы представленные на сайте исключительно с целью ознакомления читателями и не преследуют коммерческих целей или нарушение авторских прав. Обратная связь - 18.221.52.77 (0.01 с.) |