
Заглавная страница Избранные статьи Случайная статья Познавательные статьи Новые добавления Обратная связь FAQ Написать работу КАТЕГОРИИ: ТОП 10 на сайте Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрацииТехника нижней прямой подачи мяча. Франко-прусская война (причины и последствия) Организация работы процедурного кабинета Смысловое и механическое запоминание, их место и роль в усвоении знаний Коммуникативные барьеры и пути их преодоления Обработка изделий медицинского назначения многократного применения Образцы текста публицистического стиля Четыре типа изменения баланса Задачи с ответами для Всероссийской олимпиады по праву 
Мы поможем в написании ваших работ! ЗНАЕТЕ ЛИ ВЫ?
Влияние общества на человека
Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрации Практические работы по географии для 6 класса Организация работы процедурного кабинета Изменения в неживой природе осенью Уборка процедурного кабинета Сольфеджио. Все правила по сольфеджио Балочные системы. Определение реакций опор и моментов защемления |
International monetary institutionsСодержание книги
Поиск на нашем сайте
There is little exaggeration in saying that international monetary developments affect all individuals as workers, consumers, travellers, businessmen producing goods for domestic or foreign markets, and investors at home or abroad. The channels which transmit the impact of monetary events to people in their various roles in society are numerous. Employment opportunities for some workers are improved when exports thrive and are weakened for other workers when foreign products compete effectively in price or quality with domestic output. A movement in the exchange rate may benefit an individual in one of his roles but leave him worse off in another. The individual as a consumer may have a different view of and a different interest in what happens in the international monetary sphere from that of the individual as a worker. Business activity is heavily influenced by international monetary conditions affecting prices, exchange rates, interest rates, imposition of controls on exports or imports or on capital movements. Interdependence among nations has intensified lately, thus there is great interest in the functioning of the international monetary system. The international monetary system is a set of arrangements, rules, practices, and institutions under which payments are made and received for transactions carried out across national boundaries. The international system is concerned not only with the supply of international money but with the relationships among the hundred or so currencies of individual countries and with the pattern of balance-of-payments relationships and the manner in which they are adjusted and settled. International monetary relations are governed by rules of the Articles of Agreement of the International Monetary Fund and also by agreements and consultations among nations through other international institutions: the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT), the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD), the Bank for International Settlements (BIS), the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD), the World Bank Group 2 and other organizations. The international monetary system is afflicted with problems. The main reason is that the nations that participate in it are politically independent but economically and financially interdependent. This discrepancy determines the functions of the international monetary system; at its best, the system acts to reconcile the conflicting economic policies of its politically independent members. In order to perform this reconciling function, the system is concerned, first, with how nations act to influence their balance-of-payments positions, with their policies that affect exchange rates. The system is concerned, second, with how nations settle their accounts with one another. Third, the system is concerned with the amount and form of international money. In broad terms, the international monetary system involves the management, in one way or another, of three processes: 1) the adjustment of balance-of-payments positions, including the establishment and alteration of exchange rates. 2) the financing of payments imbalances among countries by the use of credit or reserves; and 3) the provision of international money. B. DIALOGUE IMF'S SUPPORT FOR RUSSIAN REFORMS IMF official: In line with the IMF's desire for greater economic stability in the world, and for stronger, more sustained growth we made a decision to support Russia with an Extended Fund Facility (EFF)3 credit amounting to about $10 billion. Interviewer. Life has proved that4 Russia's strategy for adjustment and reform is strong, and Russian authorities are committed to the program. But isn't the program risky? Off.: All adjustment programs supported by the IMF entail risk, since only countries experiencing balance-of-payments difficulties borrow from the IMF. Int.: It is obvious the IMF can never eliminate all risks. But have you built any substantial safeguards into the Russian program?5 Off.: Certainly. They include the track record established by the authorities in the previous years, broader quarterly reviews, and continuation of monthly monitoring. I feel I must emphasize here that the Russian program is the only IMF-supported program subject to monthly monitoring. Int.: That's very reasonable, but some observers question the wisdom of negotiating a program that could be derailed by political developments in Russia and changes in the Government. Off.: In this connection I would like to stress that the IMF does not support individuals. It supports economic programs. As long as the duly constituted authorities continue to fulfil the requirements of the program agreed with the IMF, the IMF will continue to support that program. Int.: Is Russia receiving exceptionally favourable treatment from the IMF? The size of the loan is large, isn't it? Off.: Yes, the loan is large in absolute terms, but as a percentage of Russia's quota, the magnitude of the EFF arrangement is fully in line with the IMF's established lending limits. Int.: Is the program too demanding? Is there a danger that continued macroeconomic adjustment and sweeping structural changes can irreparably undermine domestic support for the reform? Off.: It's a very important question. The danger exists, and we must guard against it. This could be done by creating an adequate social safety net with enough budgetary resources to support it. Int.: And beyond this, I think, the government should be encouraged to do all that it can to ensure that the benefits of the reform emerge – and become evident to the Russian people – as soon as possible. Off.: Right. This should be uppermost on their minds.
Notes
1 International Monetary Fund – Международный Валютный Фонд (МВФ) 2 General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade – Генеральное соглашение о тарифах и торговле (ГАТТ) Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development – Организация экономического сотрудничества и развития Bank for International Settlements – Банк международных расчетов United Nations Conference on Trade and Development Конференция ООН по торговле и развитию (ЮНКТАД) World Bank Group – группа Мирового банка 3 Extended Fund Facility – система расширенного финансирования 4 Life has proved that – Жизнь доказала, что... 5 have you built any safeguards into the Russian program – предусмотрели ли вы гарантии в программе для России VOCABULARY LIST A. international monetary international monetary institutions международные финансовые организации exaggeration affect channel transmit impact employment opportunities thrive weaken v ослаблять, ослабевать movement in the exchange rate изменение валютного курса to leave smb worse off ставить кого-л. в более невыгодное положение imposition of controls введение контроля (ограничений) capital movements движение капитала interdependence set of arrangements national boundaries pattern adjust to be governed Articles of Agreement устав is afflicted interdependent discrepancy define reconcile conflicting balance-of-payments position состояние платежного баланса to settle in broad adjustment establishment and alteration payments imbalances B. in line with в соответствии с amount (to) v составлять (сумму), достигать, равняться strategy be committed adjustment program программа перестройки to entail experience track record monitoring question v (зд.) подвергать сомнению wisdom derail duly exceptionally favourable in absolute as a percentage quota magnitude EFF arrangement lending limit кредитный лимит, лимит кредитования одного заемщика degree imply irreparably undermine guard social safety net система социальной защиты evident EXERCISES Ex. 1. Answer these questions:
A. 1. In what ways are individuals affected by international monetary developments? 2. What is the international monetary system? 3. What is the international monetary system concerned with? 4. What are the international monetary relations governed by? 5. What are the major international monetary institutions? 6. Is the international monetary system afflicted with problems? B. 1. What facility has been granted to Russia? 2. What is characteristic of all adjustment programmes supported by the IMF? 3. What safeguards have been built into the Russian programme to eliminate its risks? 4. Does the IMF take into account political developments in the countries it supports? 5. Has the EFF been granted to Russia on exceptionally favourable terms? Ex. 2. Give derivatives of:
exaggeration n development n worker n investor n influence n dependence n participate v reconcile v maintain v establish v advise v provision n stability n authority n adjust v experience v support v treatment n addition n emerge v Ex. 3. Find English equivalents for the following Russian phrases:
A. не будет большим преувеличением сказать; сказываться на людях; пути, по которым передается это воздействие, различны; число вакансий увеличивается; экспорт процветает; конкурировать по ценам и по качеству; изменение валютного курса; введение экспортного контроля; международная валютная система – это совокупность договоренностей, правил, организаций и т.д.; характер взаимоотношений платежных балансов; взаимоотношения регулируются; быть зависимым экономически; определять функции; положение с платежным балансом; корректировка положения с платежным балансом; установление и изменение валютных курсов; B. в соответствии со стремлением достичь экономической стабильности; руководство привержено реформам; программа перестройки, поддерживаемая МВФ; страны, испытывающие трудности с платежным балансом; исключить риск; перечень достижений; пересматривать; подвергаться ежемесячному контролю; ставить под сомнение разумность; чрезвычайно выгодные условия; в абсолютном выражении; подорвать поддержку реформ; это можно сделать только при наличии системы социальной защиты; быть ощутимым (очевидным) для людей. Ex. 4. Say in a few words what the main text is about. Use the opening phrases from Ex. 4 (Unit 1).
|
||||
|
Последнее изменение этой страницы: 2016-04-19; просмотров: 1209; Нарушение авторского права страницы; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! infopedia.su Все материалы представленные на сайте исключительно с целью ознакомления читателями и не преследуют коммерческих целей или нарушение авторских прав. Обратная связь - 18.118.208.127 (0.007 с.) |

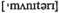 system международная валютная система
system международная валютная система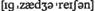 n преувеличение
n преувеличение v воздействовать, влиять
v воздействовать, влиять n канал, путь
n канал, путь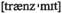 v передавать, отправлять, посылать
v передавать, отправлять, посылать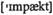 n влияние, воздействие
n влияние, воздействие вакансии
вакансии v процветать, преуспевать
v процветать, преуспевать n взаимозависимость
n взаимозависимость (зд.) совокупность договоренностей (мер, мероприятий)
(зд.) совокупность договоренностей (мер, мероприятий)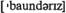 государственные границы
государственные границы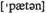 n структура, характер, паттерн
n структура, характер, паттерн v регулировать, корректировать
v регулировать, корректировать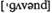 (by) регулироваться
(by) регулироваться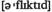 with problems (зд.) обременена проблемами
with problems (зд.) обременена проблемами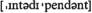 adj взаимозависимый
adj взаимозависимый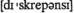 n расхождение, противоречие
n расхождение, противоречие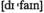 v определять
v определять v примирять
v примирять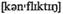 adj противоречивый
adj противоречивый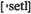 accounts урегулировать счета
accounts урегулировать счета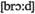 terms в широком смысле
terms в широком смысле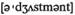 n корректировка, исправление
n корректировка, исправление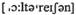 of exchange rates установление и изменение обменных курсов
of exchange rates установление и изменение обменных курсов неравновесие платежей
неравновесие платежей for adjustment стратегия перестройки
for adjustment стратегия перестройки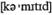 to быть приверженным чему-л.
to быть приверженным чему-л.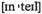 risk повлечь риск
risk повлечь риск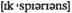 v испытывать
v испытывать (зд.) достижения, успехи
(зд.) достижения, успехи n мониторинг, контроль
n мониторинг, контроль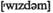 n (зд.) разумность
n (зд.) разумность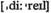 v (зд.) срывать выполнение (программы)
v (зд.) срывать выполнение (программы)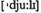 adv должным образом
adv должным образом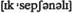 adv исключительно
adv исключительно treatment (зд.) благоприятные условия
treatment (зд.) благоприятные условия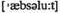 terms в абсолютном выражении
terms в абсолютном выражении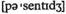 (of) в процентном выражении (от)...
(of) в процентном выражении (от)...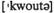 n квота
n квота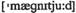 n величина
n величина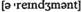 соглашение о предоставлении расширенного финансирования
соглашение о предоставлении расширенного финансирования n степень
n степень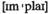 v подразумевать, означать
v подразумевать, означать adv непоправимо
adv непоправимо v подрывать основы
v подрывать основы (against) v защищать, стоять на страже
(against) v защищать, стоять на страже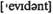 adj очевидный, явный
adj очевидный, явный


