Заглавная страница Избранные статьи Случайная статья Познавательные статьи Новые добавления Обратная связь КАТЕГОРИИ: ТОП 10 на сайте Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрацииТехника нижней прямой подачи мяча. Франко-прусская война (причины и последствия) Организация работы процедурного кабинета Смысловое и механическое запоминание, их место и роль в усвоении знаний Коммуникативные барьеры и пути их преодоления Обработка изделий медицинского назначения многократного применения Образцы текста публицистического стиля Четыре типа изменения баланса Задачи с ответами для Всероссийской олимпиады по праву 
Мы поможем в написании ваших работ! ЗНАЕТЕ ЛИ ВЫ?
Влияние общества на человека
Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрации Практические работы по географии для 6 класса Организация работы процедурного кабинета Изменения в неживой природе осенью Уборка процедурного кабинета Сольфеджио. Все правила по сольфеджио Балочные системы. Определение реакций опор и моментов защемления |
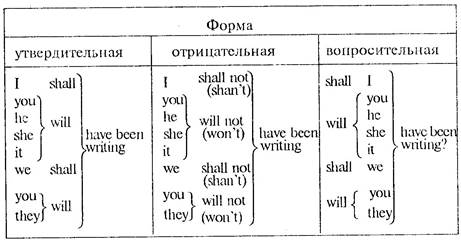
Будущее совершенное время длительного вида
The Future Perfect Continuous Tense образуется при помощи вспомогательного глагола to he b Future Perfect Tense и причастия I основного глагола.
Exercise 4. Make these sentences negative and interrogative. 1. In 85 minutes Father will have been working in the garden for three hours. 2. Next year Jim will have been studying history for 5 years. 3. In a mouth they will have been traveling abroadfor a year. 4. The workers will have been restoring the building for a year in autumn. 5. Next summer I'// have been teaching for 10 years in this school. 6. The children will have been sleeping for two hours by the time the parents come home. The Future Perfect Continuous обозначает действие, которое начнется до определенного момента в будущем и будет продолжаться до этого момента и в этот момент в будущем: In 15 minutes we shall have been writing the test for two hours. Через 15 минут будет дна часа, как мы пишем контрольную. Обратите внимание, что предложения с Future Perfect Continuous соответствуют сложноподчиненным предложениям в русском языке. Это время употребляется достаточно редко. Exercise 5. Supply the Future Perfect Continuous Tense of the verbs in brackets. 1. Next year we (study) English for three years. 2. In summer my brother (travel) in Siberia for a year. 3. In two years my friend's father (work) at the factory for 30 years. 4.It (snow) for a week tomorrow. 5. Next year she (give) music lessons for twenty years. 6. In a month he (play) football for seven years. 7. In ten minutes they (discuss) this question for three hours. 8. In September they (build) their country house for 2 years. 9. In two months she (work) at school for ten years. 10. In half an hour they (write) a test-paper for two hours. 11. The play (run) for a year in May. 12. In March 2000 she (dance) on this stage for fifteen years. 13. Tomorrow it (rain) heavily for almost a week.
Exercise 6. Supply the Future Perfect or the Future Perfect Continuous- 1. They (complete) the new bridge by the end of the year. 2. By the end of the week we (wait) seventeen weeks for our telephone to be repaired. 3. I hope you (finish) this report by the end of the day. 4. We (fly) non stop for fifteen hours before we get to Calcutta. 5. She (leave) for work before the children get home from school. 6. By this time next year he (write) his memories. 7. Do you know that your sister (work) for this company for ten years by next month, 8. They (be married) for twenty five years next year. 9. How long they (look) for a flat by next Monday? The Passive Voice Страдательный залог 1. В английском языке глагол имеет два залога: действительный (the Active Voice) и страдательный (the Passive Voice). Глагол употребляется в действительном залоге, если подлежащим в предложении является лицо или предмет, производящие действие; John cooked the dinner last night. Джон приготовил обед вчера. Глагол в страдательном залоге выражает действие, которое направлено на лицо или предмет, выраженное подлежащим: The dinner was cooked by John last night. Вчера обед был приготовлен Джоном. 2. Страдательный залог образуется при помощи глагола to be в соответствующем времени и причастия II смыслового глагола- В страдательном залоге употребляются следующие времена:
Exercise1. These are the passive forms of the Present, Past and Future Tenses. Study the sentences. Translate them into Russian. 1. Many accidents are caused by dangerous driving. 2. The problem will be discussed later. 3. My sister is being shown a new video. 4. The letter was given to him at once. 5. The director was being interviewed when I came in. 6. The boy has just been sent to bed. 7. A new park will have been laid out by summer. 8. He found out that the house had been sold to a rich American. 9. Have you heard the news? The Governor had been shot. 10. Jane didn't know about the change of plans. She hadn't been told. 1. The Passive Voice употребляется в тех случаях, когда лицо, совершающее действие, неизвестно или представляется несущественным; Rome wasn't built in a day. The matter will he discussed at the next meeting. 2. Если лицо, совершающее действие, упоминается в предложении, но не является подлежащим, то оно занимает позицию предложного дополнения, вводимого предлогом by: The music was composed by Beethoven. 3. Как правило, предложное дополнение употребляется и предложении, если в роли сказуемого пассивной конструкции употребляются глаголы: build, compose, damage, design, destroy, discover, invent, make, write. Who designed St. Paul's Cathedral? It was designed by Christopher Wren.
Exercise 2. Rewrite these sentences in the Passive using the Present Simple Tense. 1. Students write tests every month. 2. They make beautiful toys at this factory. 3. They export millions of cars from Japan every year. 4. Watchmakers repair watches. 5. People don't use this road very often. 6. The bill includes service. 7. They close the shop. at 8. 8. He translates articles every day, 9. She doesn't send telegrams before every holiday. Exercise 3. Supply the Passive forms of the verbs in the box, using the Past Indefinite Tense. invent, plant, kill, write, discover, design, paint, build, name 1. When... America...? 2. Five fruit-trees... in our garden last year. 3. The picture Mona Liza... by Leonardo da Vinci. 4. Marat... in his bath. 5. Radio... by A. Popov. 6. The first pyramid of Egypt... around 3000 BC. 7. The Winter Palace... by Rastrelli. 8. "War and Peace"... by L. Tolstoy. 9. Rossi street... after a famous Russian architect. Exercise 4. Complete the sentences using the Present Continuous Passive of these verbs; paint, feed, vacuum, milk, count, repair, cut, clean. Example: The grass is being cut. 1. The road... 2. The fence... 3. The cows... 4. The windows... 5. The cats... 6. The money... 7. The floor... 8. The carpet...
Exercise 5. Choose the correct form: Active or Passive. 1. The children taught / were taught Italian. 2. This problem will discuss / will be discussed at the conference. 3. The president interviewed / was interviewed on French TV. 4. Teachers have given / have been given a new pay rise by the government. 5. Walt Disney created / was created the cartoon character of Mickey Mouse. 6. The firm has been making / has been made dresses for twenty years, 7. He treats / is treated the girl very badly. 8. He said that he had taken / had been taken his watch to a watchmaker's.
9. Many new houses have been built / have built this year. Exercise 6. Complete the sentences using the Present Perfect Passive of these verbs: repair, paint, paper, take out, put up, clean, hang. Use some verbs more than once. Examples: The door has been repaired. Some new curtains have been put up. 1. The window... 2. The carpet... 3. The walls... 4. The light... 5. Some posters... 6. The old fireplace... 7. The picture... Exercise 7. Put the sentences into the Passive-Mind that the Perfect Continuous Tenses are not used in the Passive Voice. 1. His enemies have been following him all the time. 2. The students have been discussing the book for two hours. 3. This doctor has been treating my son for some weeks. 4. The mechanic has been repairing our TV set since morning. 5. He has been translating the book for two years. 6. She has been sending greetings cards to her teachers since 1981. 7. They have been visiting this museum since their childhood. 8. The children have been trying on their fancy dresses since morning. 9. We have been writing the test-paper for an hour and a half. Exercise 8. Rewrite the sentences in the Passive. 1. They are building a new ring road round the city. 2. They will read this book next term. 3. They cancelled all flights because of fog. 4. Somebody is cleaning the room at the moment. 5. I didn't realize that someone was recording our conversation. 6. They have changed the date of the meeting. 7. Dan told me that somebody had attacked him in the street. 8. She will have translated the article by the end of the day. 9. John had been courting Mary for a year before he proposed to her. 10. They have been discussing Ins proposal for hours.
Exercise 9. Supply the Passive form of the verbs in brackets in the required tense. 1. Lanny noticed that he... (watch) by three white men on the other side of the street. 2. I hope the letter... (send) tomorrow. 3. It... (decide) to say nothing to him until the answer... (receive). 4. You thought that the letter... (lose). 5. You don't know he was with me two hours before he... (find). 6. I don't want to hear another word, I never... (insult) so in my life. 7. The table... (lay) for his supper.
1. В силу специфики своего значения the Passive Voice употребляется преимущественно с переходными глаголами: Active: They built the house a few years ago. Passive: The house was built a few years ago. 2. В английском языке страдательный залог имеет более широкое применение, чем в русском, и существует ряд случаев употребления страдательного залога в английском языке, отличных от русского: а) ряд глаголов, имеющих в действительном залоге два дополнения, могут образовывать две пассивные конструкции, в которых подлежащим может быть как прямое, так и косвенное дополнение: Active: Someone gave Jimmy money. Passive: Jimmy was given money. Money was given to Jimmy. Как правило, подлежащим пассивной конструкции является лицо, а не предмет, поэтому первый вариант предпочтительнее. б) К числу глаголов, которые могут иметь два дополнения, относятся: give, send, offer, show, pay, teach, promise, tell m др. Exercise 10. Read these sentences. State the difference between the two passive constructions. Translate them into Russian. 1. They have read her an interesting story. a) An interesting story has been read to her. b) She has been read an interesting story. 2. The teacher gave each pupil a small map of England; a) A small map of England was given to each pupil. b) Each pupil was given a small map of England. 3. I have written a letter to my pen-friend. a) A letter has been written to my pen-friend. b) My pen-friend has been written a letter, 4. The hostess has made us some coffee. a) Some coffee has been made to us. b) We have been made some coffee. 5. The chief offered him a new job. a) A new job was offered to him. b) He was offered a new Job. 6. I shall send her some beautiful flowers. a) Some flowers will be sent to her. b) She will be sent some beautiful flowers. 7. The guide is showing a new exposition to the tourists. a) A new exposition is being shown to the tourists. b) The tourists are being shown a new exposition. Exercise 11. Give two Passive constructions of the following sentences. 1. They promised the children many new toys. 2. The librarian offered me a new novel. 3. I have already sent a telegram to my grandmother. 4. He wrote many letters to his wife. 5. They will give her a part in a new play. 6. My sister taught me cooking and.house-keeping. 7. The guide showed us many beautiful monuments. 8. Dick will give us some apples. 9. Mother has brought me many presents. 10. The teacher told many interesting things to her pupils. 11. The Browns have sold their house to a certain Mr. Miller. 12. My friend gave it to me. 13. She told me the whole story. 14. Father promised Nick a river-boat.
1. В английском языке the Passive Voice могут образовывать глаголы, управляющие предложным дополнением. В пассивной конструкции предлог сохраняется: Active: We looked for Mike everywhere.
Passive: Mike was looked for everywhere.
2. К числу глаголов, имеющих предложное дополнение, относятся: at, look for, look after, look through, send for, agree upon, rely on, touch upon, insist on, put up with, refer to, provide for, see to, talk of, arrive at и некоторые другие: The children will be well provided for. Exercise 12. Study the following sentences paying special attention to the passive forms. Translate them into Russian. for: 1. The doctor has Just been sent for. 2. The boys were being looked for everywhere but in vain. 3. The children were much cared for. 4. All his daughters were well provided for.
at: 1. After a long discussion the agreement was arrived at. 2. She felt that she was being looked at. 3. His jokes are so dull, that they are never laughed at.
upon (on): 1. The book is very popular because very important problems are touched upon in it. 2. I think your proof will be relied on (upon). 3. Summer was agreed upon as the best season for hiking. 4. He had been spied on for some time before he discovered it.
of: 1. The boys were well thought of at school. 2. He has never been heard of since. 3. Her behavior was greatly disapproved of. 4. His novel is already much spoken of.
to: 1. She will be spoken to the moment she conies. 2. The speech was being listened to with great attention. 3. His works are completely forgotten, they are never referred to.
with: 1. The situation was dealt with very delicately, 2. My old life was done away with. 3. His rudeness will never be put up with. В английском языке есть также ряд фразеологических единиц, которые могут употребляться в страдательном залоге: find fault with придираться, критиковать make fun of высмеивать make use of употреблять, использовать lose sight of терять из вида take notice of заметить, обратить внимание take care of заботиться, ухаживать pay attention to обратить внимание set fire to поджечь make a fool of высмеивать, одурачивать play a trick on сыграть шутку
The man was lost sight of long time ago.
Exercise 13. Read and translate these sentences. 1. I know that neither teachers nor pupils have been found fault with at tins school. 2. The ship leftthe harbour (гавань) and was lost sight of. 3. His advice will be paid much attention to. 4. Their love-affair was put an end to at last. 5. Such children are often made fun of. 6. His late arrival was not taken notice of. 7. Thechildren are taken good care of inthis boarding-house.8. His tools haven't been made use of for a long time. 9. English pronunciation is always paid much attention to. 10. He complains that he is always found fault with. 11. Her husband is often made a fool of. 12. She is soplain that she is seldom taken notice of.
Review of Tense and Voice Exercise 1. Complete the sentences using the Present Indefinite of the verbs in brackets. Example: Our boat (leave) Dover at 2.00 on Friday and (arrive) in Calais at 6.00. Our boat leaves Dover at 2.00 on Friday and arrives in Calais at 6.00. 1. The conference (start) on June 3rd and (finish) on June 10th. 2. We've got plenty of time. Our plane (not / take off) until 9 o'clock. 3. Tonight's concert (begin) at 8 o'clock and it (not / end) until 11.00. 4. When the next train (leave) for Bristol? 5. The expedition to the North Pole (start) in a few days. 6. The last train from N. (arrive) at 6.15. 7. The first term (end) before Christmas and the second (start) in the middle of January. 8. When the first train (leave)?
Exercise 2. Put one verb in each sentence into the Present Indefinite and the oilier verb into the will/won’t form. Example: If I (fail) the exam. I (take) it again. If I fail the exam, I' ll ta ke it again. 1. When I... (see) him I... (give) him your message. 2. I... (buy) a new car as soon as I... (have) enough money. 3. If the weather... (be) nice tomorrow, we... (go) sailing. 4. I... (look after) your cat while you... (be) on holiday. 5. He... (not / do) anything until lie... (hear) from us. 6. The door... (not / open) unless you... (push) it hard. 7. We.., (play) tennis this evening as long as it... (not / rain). 8. I... (lend) you the money provided you... (pay) me back tomorrow.
Exercise 3. Choose the right form (Active or Passive). 1. The book is being discussed/is discussing now. 2. The children are being played / are playing football in the yard. 3. This fact was mentioned/mentioned by many people. 4. Our car is usually repaired/repairs in Mike Anderson’s garage. 5. The children have been put to bed / will put to bed by their nurse. 6. All my questions were answered / will answer after classes.
Exercise 4. Choose the right form (Active or Passive). 1. The flowers will be watered / are watering in the evening. 2. My parents aren't approved of/ don ’t approve of heavily made up girls. 3. The suit-cases had been packed / had packed by 6 o'clock as the train started / was started at7 p.m. 4. The house didn't live in / was not lived in autumn and winter. 5. The garden looks after very well / is well looked after. 6. Doctors send for / are sent for when people feel unwell. Exercise 5. Give the corresponding active construction making the word in brackets the subject of this construction. 1. He was given to understand that he was wrong. (his wife) 2. The parcel was given to the addressee at once. (the postman) 3. I have been promised a pony. (Father) 4. A tape-recorder was promised to Alee. (Mother) 5. We have been told to stay where we are. (the policeman) 6. After all funny jokes and anecdotes had been told people felt dull again. (Mike) 7. I shall be told everything when I am older. (my parents) 8. Senior pupils are taught algebra and geometry. (Mr. Brown)
Exercise 6. Give the corresponding active construction making the word in brackets the subject of this construction 1. Foreign languages are taught at school, (good specialists) 2. Christmas presents are sent to them every year. (their friends) 3. She will be sent a special invitation. (I) 4. A very good reward was offered to him. (the man) 5. The boy was offered some books to his choice. (the teacher) 6. When we were in the forest I was shown beautiful flowers, (my friend) 7. You are deceived. A very good copy of this picture has been shown to you. (Mr. Smith)
Exercise7. Choose the correct answer. The National Security Bank in San Hutomo... (robbed / was robbed) last night. A safe... (blew open / was blown open) and around 800 000 dollars... (stole / were stolen). The robbery... (took / was taken) place between midnight and 1.00 a.m. Tlie police... (are looking / are being looked) for two men who... (saw / were seen) getting into a black car near the bank at about 1 o'clock last night. They... (also want / are also wanted) to hear from Mr. Jack Stillnian who... (worked / was worked) as a security guard at the bank. Mr. Stillman... (disappeared / was disappeared) just before the robbery and he... (has not seen / hasn't been seen) since then.
Exercise 8. Put into the Passive; mind the verbs with prepositions and post-verbal adverbs. Make the word in italics the subject of the passive construction. 1. They look after their children properly. 2. We are in a hurry, that's why we have sent for a taxi. 3. People will laugh at yon if you put on this hat. 4. I'm sure everybody will agree upon this plan. 5. He often refers to your words. 6. You can always rely on his word of honour. 1. She will never put up with poverty. 8. The policemen are looking for the man who has robbed the bank. 9. His teachers have always looked upon him as a very promising student. 10. I haven't seen much of him since his arrival. 11. My family didn't approve of my boy-friend. 12. I shall do away with my old life, I promise. 13. That day the family saw very little of her. 14. They have recently put up the fence between the two properties. Direct and Indirect Speech Прямая и косвенная речь PART I. Statements Утвердительные предложения При переводе утвердительных предложений в косвенную речь порядок слон не меняется. Меняется только форма подлежащего в зависимости от реальных участников ситуации и, соответственно, форма сказуемого. Косвенная речь вводится глаголами to say, to tell, to announce и to (в официальной речи). Глаголы to say и to announce не требуют обязательного адресата речи, а с глаголами to tell и to inform адресат обязателен. После глаголов to say, to announce адресат, если он указан, употребляется с предлогом to, глаголы to tell и to inform требуют беспредложного дополнения адресата.
Exercise 1. Put the following into Indirect Speech, 1. She says, "It is very cold here.” 2. Mary says, "My brother is a student." 3. Mother says, "We are four in the family." 4. The guide says, "The house is new." 5. The child says, "These apples are very sweet." 6. Jane says, "My grandmother is a pensioner." 7. Nick says, "Your garden is very beautiful, Mary." 8. The boy says, "There is no bread on the table, Mother". 9. The student says, "My friends are busy today." 10. Mother says, "It's too late to go out."
Exercise 2. Put the following into Indirect Speech
1. The girl says, "I am not married yet." 2. The children say, "We are happy to be here." 3. Frank says, "Dick's dog is very clever." 4. He says, "I'm a rich man now." 5. His wife says, "I'm going to tell you everything." 6. The librarian says, "The books are on the shelf." 7. The boy says, "It's still very early." 8. The policeman says, "There are no people in the street." 9. The students say, "It is not easy to study a foreign language." 10. Mary says, "I am very glad to see you here." 11. The man says. "These houses are very comfortable." 12. The boy says, "Our flat is on the second floor." 13. Jane says, "This girl is my cousin." 14. The teacher says, "Your English is very nice, Alice." Exercise 3. Put the following into Indirect Speech. Use the introductory verbs in brackets. 1. She says, "I have many friends at the University, Mother." (tell) 2. The teacher says, “You have an English test today, group 4.” (inform) 3. Ann says, "My brother has many English books." (announce) 4. The Dean says, "Dear colleagues. I have little spare time now. "(inform) 5. Nick says,"We usually have dinner at foul o'clock. Aunt Mary." (tell)
Exercise 4. Put the following into Indirect Speech. Use the introductory verbs in brackets
1. The manager says, "My staff has very much work today." (announce) 2. He says, "The Browns have a nice house in the country." (say) 3. The head teacher says, "First year student have no classes today." (announce) 4. She says, "Kelly, I have much to tell you."(say) 5. He says, "Mary, 1 have an appointment with my doctor." (inform) Imperative sentences Повелительные предложения При переводе в косвенную речь повелительных предложений глагол, выражающий просьбу или приказание, ставится в форме инфинитива. В качестве глаголов, вводящих косвенную речь, употребляются глаголы to ask, to order, to tell. Если в прямой речи было обращение, то оно становится адресатом глагола говорения. She says, "Ann, tell me everything." She asks Ann to tell her everything. Exercise1. Put the following into Indirect Speech. 1. She says, "Bill, open the window." 2. Mother says, "Ring me up at 6 o'clock." 3. John says, "Take these flowers, Mary." 4. The teacher says, "Do this exercise orally, pupils." 5. Mother says, "Sweep the floor and dust the furniture, Alice." 6. Dan says, "Make sandwiches for our party, Peter."
Exercise 2. Put the following into Indirect Speech 1. Father says. "Wash up dishes after supper, Liza." 2. The woman says, "Don't smoke here, boys."' 3. The librarian says. "Don't take this dictionary away." 4. The policeman says. "Don't cross the street under the red light, children." 5. Frank says, "Don't make so much noise, girls." 6. Jack says, "Stay where you are, Polly." Interrogative sentences Вопросительные предложения
|
|||||||||
|
Последнее изменение этой страницы: 2021-02-07; просмотров: 1147; Нарушение авторского права страницы; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! infopedia.su Все материалы представленные на сайте исключительно с целью ознакомления читателями и не преследуют коммерческих целей или нарушение авторских прав. Обратная связь - 3.142.195.204 (0.224 с.) |