Заглавная страница Избранные статьи Случайная статья Познавательные статьи Новые добавления Обратная связь FAQ Написать работу КАТЕГОРИИ: ТОП 10 на сайте Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрацииТехника нижней прямой подачи мяча. Франко-прусская война (причины и последствия) Организация работы процедурного кабинета Смысловое и механическое запоминание, их место и роль в усвоении знаний Коммуникативные барьеры и пути их преодоления Обработка изделий медицинского назначения многократного применения Образцы текста публицистического стиля Четыре типа изменения баланса Задачи с ответами для Всероссийской олимпиады по праву 
Мы поможем в написании ваших работ! ЗНАЕТЕ ЛИ ВЫ?
Влияние общества на человека
Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрации Практические работы по географии для 6 класса Организация работы процедурного кабинета Изменения в неживой природе осенью Уборка процедурного кабинета Сольфеджио. Все правила по сольфеджио Балочные системы. Определение реакций опор и моментов защемления |
Innovation orientation of the Ukrainian society and economyСодержание книги
Поиск на нашем сайте
The outcome of innovation is notoriously difficult to measure in Eastern European Countries, because they do not participate in the Community Innovation Survey (CIS), although Ukraine does conduct
189 Olena Koval, Vadym Yashenkov et al.: ”Overview of the internationalisation of Ukraine in RTDI including recent trends and developments”, Policy Brief in BILAT-UKR*AINA project, 2012
190 http://eacea.ec.europa.eu/erasmus_mundus/: accessed on 2 May 2016.
191 http://eacea.ec.europa.eu/tempus/: accessed on 2 May 2016.
192 Koval et al.: Overview of the internationalisation of Ukraine in RTDI including trends and developments, p.7
193 http://www.bilat-ukraina.eu/: accessed on 2 May 2016.
194 Koval et al.: Overview of the internationalisation of Ukraine in RTDI including trends and developments, p.6
195 UNESCO Science Report 2015, p.336
surveys itself every 2-3 years which are based on the CIS methodology196, despite difficulties in addressing the business community.
According to the most recent data from the World Economic Forum, Ukraine’s “innovation performance” improved compared to past years.197 Against the backdrop of the general economic environment and business situation of Ukraine today (see chapter 2. on the economic situation for more details), this is a positively surprising fact.
The following table 8 gives an overview on all indicators in the field of innovation as stipulated by the Global Competitiveness Index of the WEF.
Table 8: Ukraine's performance in the field of innovation, given by indicators stipulated for the field; source = WEF Global Competitiveness Reports 2012 to 2016
According to Table 8 Ukraine progressed mostly in the area of “capacities for innovation”. Compared to the ranking for 2014-2015, in which Ukraine occupied the 82nd position, the country ranks 52nd in the current statistics. Hence, Ukraine overtook 30 countries/positions just within a two years development.
The progress in “Governmental procurement of advanced technological products” (from 123rd to 98th position) is mainly the result of the on-going anti-corruption policies set in place by the government. However, the statistics of the WEF have to be treated with care, since they often depict great leaps, which are not always comprehensible.
196 Ibid., p.316
197 Schwab: The global competitiveness report 2015-2016. WEF, 2015, p.354
Figure 29: Ukraine's industry enterprises conducting innovative activities, share in % of total number of enterprises; source = Self-assessment report: SCIENTIFIC AND TECHNOLOGICAL SPHERE OF UKRAINE,
MESU
Based on the most recent data available from the Ukrainian Ministry of Education and Science, 1,609198 industrial enterprises were engaged in innovative activities in 2014. This represents a share of 16.10% of the number of industry enterprises, as depicted in Figure 29 above (see also footnote 198). Ukraine experienced a continuous increase in the share of innovative enterprises from 2009 until 2012. Since 2012, the share of innovative enterprises, however, decreased.199
Out of the 1,609 innovative enterprises in 2014, 1,208 (75.1%) were successful innovators, meaning they introduced innovative products and/or processes. Moreover, 137 of these companies introduced new products to the market, 504 introduced products new to the companies themselves and 164 launched new types of machinery, equipment, appliances, apparatus etc.200 The total spending on innovation activities by Ukrainian industrial enterprises in 2014 was 7,695,900,000 UAH or 0.5% of the GDP (in 2013 total spending was 9,562,630,000 UAH). The high-tech sector has a significantly higher spending on innovation activities (4.48%) than the mid-tech sector (1.59%).201
Table 9 below provides data on innovation spending in Ukraine from 2000 to 2014 (data are missing for 2001, 2002, 2003, 2004 and 2006). It gives an overview on the total spending on innovation distributed by sources. Furthermore, the relation to GDP is given.
198 According to information provided by Professor Igor Yegorov on 23 May 2016, these enterprises are selected from a sample of approximately 10,000 enterprises. The sample comprises all large and almost all medium-sized companies. The total number of industrial enterprises in Ukraine is aproximately 30,000.
199 Self-assessment report: Scientific and technological sphere of Ukraine, MESU, 2016, p.25
200 Ibid.
201 Ibid., p.27
Table 9: Spending on innovation in Ukraine, total numbers as % of GDP and per source; source = Self-assessment report: Scientific and technological sphere of Ukraine, MESU
According to the Ukrainian Ministry of Education and Science, the largest share of innovative activities seems to occur in the food production sector. This sector accounts for 17.1% of the total number of innovative enterprises. The machinery and machinery equipment production sector accounts for 9.6%, the sector for the fabrication of metal products accounts for 5.4% and the sector for manufacturing of chemicals and chemical products accounts for 4.7%.202
The share of innovation related activities in technology-producing enterprises is much higher than on average level. The share in the high-tech sector is 37.6%, and in the mid-tech sector 21.1%. The average level based on the overall industry sector is 16.10%, as previously shown in Figure 29. Within the technology-producing sector, the following industries show the highest innovation shares: aircraft, spacecraft and related equipment (56.7%), arms and ammunition (50.0%) and basic pharmaceutical products plus pharmaceutical drugs (38.2%).203
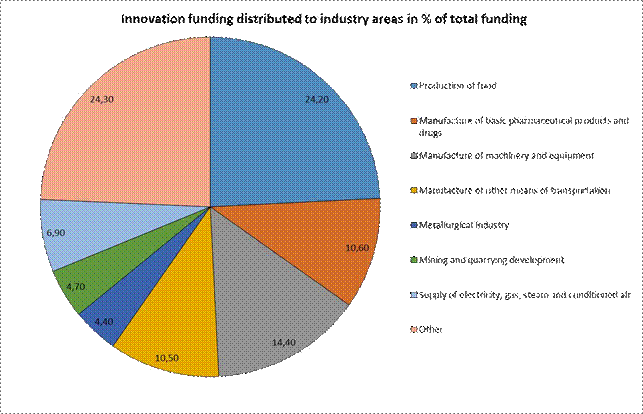
A similar picture is shown in terms of innovation funding received per industrial sector, as presented in Figure 30. Also in attaining money for innovation activities, the food production sector (as a single sector) ranks first in 2014. It received 24.20% of the total innovation funding spent on industries in Ukraine in this year. Second ranks the production of machinery and related equipment with 14.40% of total funding received in 2014. Least innovation funding went to the metallurgical industry (4.40%).204
202 Self-assessment report: Scientific and technological sphere of Ukraine, MESU, 2016, p.26
203 Ibid., p.27
204 Ibid., p.30
Figure 30: Innovation funding in Ukraine in 2014, distributed to industrial sectors and given in % share of total innovation funding; source = Self-assessment report: Scientific and technological sphere of Ukraine,
MESU
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Последнее изменение этой страницы: 2017-01-24; просмотров: 83; Нарушение авторского права страницы; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! infopedia.su Все материалы представленные на сайте исключительно с целью ознакомления читателями и не преследуют коммерческих целей или нарушение авторских прав. Обратная связь - 216.73.216.102 (0.007 с.) |