
Заглавная страница Избранные статьи Случайная статья Познавательные статьи Новые добавления Обратная связь FAQ Написать работу КАТЕГОРИИ: ТОП 10 на сайте Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрацииТехника нижней прямой подачи мяча. Франко-прусская война (причины и последствия) Организация работы процедурного кабинета Смысловое и механическое запоминание, их место и роль в усвоении знаний Коммуникативные барьеры и пути их преодоления Обработка изделий медицинского назначения многократного применения Образцы текста публицистического стиля Четыре типа изменения баланса Задачи с ответами для Всероссийской олимпиады по праву 
Мы поможем в написании ваших работ! ЗНАЕТЕ ЛИ ВЫ?
Влияние общества на человека
Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрации Практические работы по географии для 6 класса Организация работы процедурного кабинета Изменения в неживой природе осенью Уборка процедурного кабинета Сольфеджио. Все правила по сольфеджио Балочные системы. Определение реакций опор и моментов защемления |
How many litres of water must be added to 3.9 litres of NaОН solution with the titer 0.02034 to receive 0.05 M solution?Содержание книги
Поиск на нашем сайте
133. How many grams of KCl are necessary to be added to 450 g of 8 % solution of the same salt to receive 12 % solution?
134. How many kg of water is it necessary to add to 1 kg of 40 % solution of the sulfuric acid to receive 25 % solution?
135. How many mole of water should be added to 1.6 kg of 25 % NaOH solution to receive 16 % solution?
136. 300 g of 40 % solution of the sulfuric acid and 700 g of 10 % solution of the same acid are mixed; calculate the mass fraction (%) of the received solution.
137. How many grams of 32 % solution of nitric acid are necessary to be added to 600 g of 80 % solution of the same acid to receive 64 % solution?
138. 300 kg of water was evaporated from 750 kg of 48 % solution of the sulfuric acid, determine the mass fraction (%) of sulfuric acid in the received solution.
139. How many kg of water is it necessary to evaporate from 1 тon of 60 % sulfuric acid solution to receive 96 % solution?
140. It is necessary to prepare 1 М solution from 1 kg of 63 % nitric acid solution, determine the volume (litres) of the received solution.
141. It is necessary to prepare 1 M solution of HCI from 20 ml of 20 % HCl (density 1.1), determine the volume (ml) of the received solution.
142. It is necessary to prepare 1 M H3PO4 solution from 120 ml of 30 % H3PO4 (density 1.19), determine the volume (ml) of the received solution.
143. 800 ml of 3 M КОН solution and 1.2 litres of 12 % КОН solution (density 1.1) are mixed; calculate the molar concentration of the received solution.
144. 3 litres of 0.1 M H3PO4 solution and 2 litres of 9 % solution of the same acid (density 1.05) are mixed; calculate the normal concentration of the received solution.
145. How many ml of 20 % HCl solution (density 1.1) should be added to 4 litres of 0.6 M HCl solution to receive 1 M solution?
146. How many litres of 0.2 M NH3 solution are necessary to be added to 20 ml of 35 % NH3 solution (density 0.88) to receive 0.5 M solution?
147. How many litres of 0.1 n. solution of the sulfuric acid is it possible to prepare from 70 ml of 50 % solution of the same acid (density 1.4)?
148. How many litres of 8 M NaOH is it possible to prepare from 1 kg of 42 % NaOH solution?
149. How many litres of 8 M NaOH is it possible to prepare from 1 litre of 42 % NaOH solution (density 1.45)?
150. How many ml of 40 % solution of the phosphoric acid (density 1.25) are required for preparation of 400 ml of 0.25 M solution of the same acid?
151. How many ml of 40 % phosphoric acid solution (density 1.25) are required for preparation of 3 litres of 0.15 n. solution of the same acid?
152. Calculate the thermal effect of reaction (кJ) of methanol synthesis from hydrogen and carbon oxide on solid catalyst at 298К 2Н2 (г) +СО → СН3ОН (г), if A) –90,7 B) 311,7 C) 90,2 D) 60,9 E) –73,2
153. Determine thermal effect of reaction: СН º СН + СО + Н2О (ж) → СН2=СНСООН (ж) at standard pressure if warmth of formation is known
A) -214,78 B) 107,36 C) 1007,36 D) –623,09 E) –154,2
154. To calculate thermal effect of reaction (kJ) at Т=298К CuCl2 + Zn = ZnCl2 + Cu Values
A) -215,9 B) 740,5 C) –903,6 D) 904,2 E) 370,2
155. Calculate entropy change under standard conditions for reaction 2H2S + SO2 = 2 Н2О (ж) + 3S. Values S are given in the table.
A) –421,81 B) –102,50 C) 513,24 D) 350,72 E) 231,11
156. Calculate thermal effect of reaction (кJ) at Т=298К, Р=1,013×105 Па Cd (тв) + 2AgCl (тв) = 2Ag (тв) + CdCl2 (тв), if warmth of formation of substances are known
A) –135,4 B) –263,2 C) –515,8 D) 443,2 E) 344,8
157. Calculate standard change of energy of Gibbs (kJ) for reaction Cd (тв) + 2AgCl (тв) = 2Ag (тв) + CdCl2 (тв), if are known DН298 = –135,4 kJ; DS298 = –76,84 J/К. A) –112,5 B) 1393,55 C) –141,7 D) 24,61 E) 41,42
158. Calculate standard change of entropy for reaction H2(г)+
A) -163.155 J/к B) 144.39 J/к C) 450.59 J/к D) 370.25 J/к E) 265.67 J/к
159. Calculate standard thermal effect (kJ/mol) reactions of dissolution of zinc in the diluted water solution copper vitriol Zn(т)+CuSO4=Cu(т)+ZnSO4; DH ZnSO4=-978,2 kJ/mol; A) -207,1; B) -211,66; C) -316,1; D) 213,61; E) 166,19;
160. Calculate thermal effect of reaction (kJ/mol) synthesis methanol from hydrogen and carbon oxide on the solid catalyst at 298 K 2H2(г)+CO(г) → CH3OH(г), A) -90,7; B) -60,9; C) -90,2; D) -73,2; E) -86,1;
161. Define thermal effect of chemical reaction at 298 K CH3OH(г)+3/2 O2 → CO2+2H2O(г), if
A) -675,99 кJ/mol; B) 398,11 кJ/mol; C) 1764,2 кJ/mol; D) -575,25 кJ/mol; E) -834,78 кJ/mol;
162. Calculate thermal effect of reaction (kJ/mol) synthesis methanol from hydrogen and carbon oxide on the solid catalyst at 298 K 2H2(г)+CO2(г) → CH3OH(г), A) -90,7; B) -60,9; C) -90,2; D) -73,2; E) 86,1;
163. Define standard change of entropy for reaction: C2H2+2H2O(ж) → CH3COOH(ж)+H2,
A) -50,32 J/mol×К; B) -65,48 J/mol×К; C) -45,93 J/mol×К; D) -33,75 J/mol×К; E) -74,18 J/mol×К;
164. Calculate energy of Gibbs (J/mol) under standard conditions for reaction: C2H2+2H2O(ж) → CH3COOH(ж)+H2, A) -124,15×103; B) -113,61×103; C) -121,53×103; D) -135,93×103; E) -109,15×103;
165. Calculate thermal effect of reaction under standard conditions for reaction: C2H2+2H2O(ж) → CH3COOH(ж)+H2,
A) -139,97×103 J/mol; B) -145,32×103 J/mol; C) -151,64×103 J/mol; D) 125,86×103 J/mol; E) 108,52×103 J/mol;
166. Calculate ΔU under standard conditions for reaction: C2H2+2H2O(ж) → CH3COOH(ж)+H2 at 298,2 К and A) 139,97 ×103 J/mol; B) 145,32 ×103 J/mol; C) 151,64 ×103 J/mol; D) 125,86×103 J/mol; E) 108,52×103 J/mol;
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Последнее изменение этой страницы: 2016-12-30; просмотров: 111; Нарушение авторского права страницы; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! infopedia.su Все материалы представленные на сайте исключительно с целью ознакомления читателями и не преследуют коммерческих целей или нарушение авторских прав. Обратная связь - 216.73.216.169 (0.007 с.) |

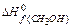 = – 201,2 кJ/mol; DН0f(CO ) = – 110,5 кJ/mol;
= – 201,2 кJ/mol; DН0f(CO ) = – 110,5 кJ/mol; 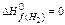
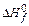 [kJ/mol ]
[kJ/mol ]
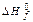 are resulted in the table:
are resulted in the table: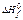
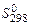 [J/mol×К]
[J/mol×К]
 298 [kJ/mol ]
298 [kJ/mol ]
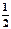 O2(г)
O2(г)  H2Oж under standard conditions:
H2Oж under standard conditions: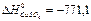 kJ/mol.
kJ/mol.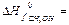 =- 201,2 kJ/mol;
=- 201,2 kJ/mol; 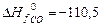 kJ/mol.
kJ/mol.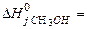 -201,2 кJ/mol,
-201,2 кJ/mol, 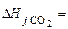 -393,51 кJ/mol,
-393,51 кJ/mol, 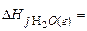 -241,84 кJ/mol:
-241,84 кJ/mol: -201,2 кJ/mol,
-201,2 кJ/mol,  -110.5 кJ/mol:
-110.5 кJ/mol: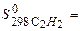 200,8 J/mol×К,
200,8 J/mol×К, 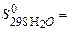 69,96 J/mol×К,
69,96 J/mol×К, 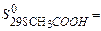 159,8 J/mol×К,
159,8 J/mol×К, 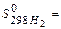 130,6 J/mol×К:
130,6 J/mol×К: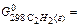 209,25 ×103 J/mol,
209,25 ×103 J/mol, 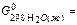 -237,23103 J/mol,
-237,23103 J/mol, 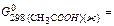 -389,36×103 J/mol,
-389,36×103 J/mol, 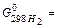 0
0  226,75 ×103 J/mol,
226,75 ×103 J/mol, 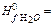 -285,84×103 J/mol,
-285,84×103 J/mol, 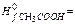 -484,9×103 J/mol,
-484,9×103 J/mol, 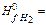 0:
0: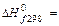 139,97 ×103 J/mol:
139,97 ×103 J/mol:


