Заглавная страница Избранные статьи Случайная статья Познавательные статьи Новые добавления Обратная связь FAQ Написать работу КАТЕГОРИИ: ТОП 10 на сайте Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрацииТехника нижней прямой подачи мяча. Франко-прусская война (причины и последствия) Организация работы процедурного кабинета Смысловое и механическое запоминание, их место и роль в усвоении знаний Коммуникативные барьеры и пути их преодоления Обработка изделий медицинского назначения многократного применения Образцы текста публицистического стиля Четыре типа изменения баланса Задачи с ответами для Всероссийской олимпиады по праву 
Мы поможем в написании ваших работ! ЗНАЕТЕ ЛИ ВЫ?
Влияние общества на человека
Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрации Практические работы по географии для 6 класса Организация работы процедурного кабинета Изменения в неживой природе осенью Уборка процедурного кабинета Сольфеджио. Все правила по сольфеджио Балочные системы. Определение реакций опор и моментов защемления |
Methods of animal cloning, reproductive and therapeutic cloningСодержание книги
Поиск на нашем сайте
A clone is an organism that is descended from — and is genetically identical to — a single common ancestor. Cloning involves making genetically identical copies of an organism, using asexual reproduction. Animals can be cloned by two different methods: ü mechanical embryo splitting ü nuclear transfer --mechanical embryo splitting Embryo splitting involves bisecting the multi-cellular embryo at an early stage of development to generate clones or “twins.” A 32-cell embryo, for example, might be bisected into two 16-cell twins. This type of cloning occurs naturally (human identical twins result from this process, but fraternal twins do not), but it can also be performed in a laboratory where it has been successfully used to produce clones from a number of different animal species., in that a maximum of four clones can be produced from each embryo. -- nuclear transfer Cloning can also be done by nuclear transfer, where the genetic material from one cell is placed into a “recipient” unfertilized egg that has had its genetic material removed by a process called enucleation. In order to begin the development process, the donor nucleus must be fused with the egg through the administration of a brief electrical pulse or a chemical fusion process, after which the embryo starts to divide as if it had been fertilized. In the case of mammals, the embryo is then placed into a surrogate mother where it will develop until birth, where it will be delivered just as with any newborn.
Microorganisms in water and wastewater treatment The sludges accumulated in a wastewater treatment process must be treated and disposed of in a safe and effective manner. The purpose of digestion is to reduce the amount of organic matterand the number of disease-causing microorganisms present in the solids. The most common treatment options include anaerobic digestion, aerobic digestion, and composting. Incineration is also used, albeit to a much lesser degree. Sludge treatment depends on the amount of solids generated and other site-specific conditions. Composting is most often applied to small-scale plants with aerobic digestion for mid sized operations, and anaerobic digestion for the larger-scale operations. The sludge is sometimes passed through a so-called pre-thickener which de-waters the sludge. Types of pre-thickeners include centrifugal sludge thickeners[25] rotary drum sludge thickeners and belt filter presses. Anaerobic digestion Anaerobic digestion is a bacterial process that is carried out in the absence of oxygen. The process can either be thermophilic digestion, in which sludge is fermented in tanks at a temperature of 55 °C, or mesophilic, at a temperature of around 36 °C. Though allowing shorter retention time (and thus smaller tanks), thermophilic digestion is more expensive in terms of energy consumption for heating the sludge. Anaerobic digestion is the most common (mesophilic) treatment of domestic sewage in septic tanks, which normally retain the sewage from one day to two days, reducing the biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) by about 35 to 40 percent. This reduction can be increased with a combination of anaerobic and aerobic treatment by installing Aerobic Treatment Units (ATUs) in the septic tank. Mesophilic anaerobic digestion (MAD) is also a common method for treating sludge produced at sewage treatment plants. The sludge is fed into large tanks and held for a minimum of 12 days to allow the digestion process to perform the four stages necessary to digest the sludge. These are hydrolysis, acidogenesis, acetogenesis and methanogenesis. In this process the complex proteins and sugars are broken down to form more simple compounds such as water, carbon dioxide and methane.[28] One major feature of anaerobic digestion is the production of biogas (with the most useful component being methane), which can be used in generators for electricity production and/or in boilers for heating purposes. Many larger sites utilize the biogas for combined heat and power, using the cooling water from the generators to maintain the temperature of the digestion plant at the required 35 ± 3 °C. Aerobic digestion Aerobic digestion is a bacterial process occurring in the presence of oxygen. Under aerobic conditions, bacteria rapidly consume organic matter and convert it into carbon dioxide. The operating costs used to be characteristically much greater for aerobic digestion because of the energy used by the blowers, pumps and motors needed to add oxygen to the process. However, recent technological advances include non-electric aerated filter systems that use natural air currents for the aeration instead of electrically operated machinery. Aerobic digestion can also be achieved by using diffuser systems or jet aerators to oxidize the sludge. Fine bubble diffusers are typically the more cost-efficient diffusion method, however, plugging is typically a problem due to sediment settling into the smaller air holes. Coarse bubble diffusers are more commonly used in activated sludge tanks (generally a side process in waste water management) or in the flocculation stages. A key component for selecting diffuser type is to ensure it will produce the required oxygen transfer rate. Composting Composting is also an aerobic process that involves mixing the sludge with sources of carbon such as sawdust, straw or wood chips. In the presence of oxygen, bacteria digest both the wastewater solids and the added carbon source and, in doing so, produce a large amount of heat.
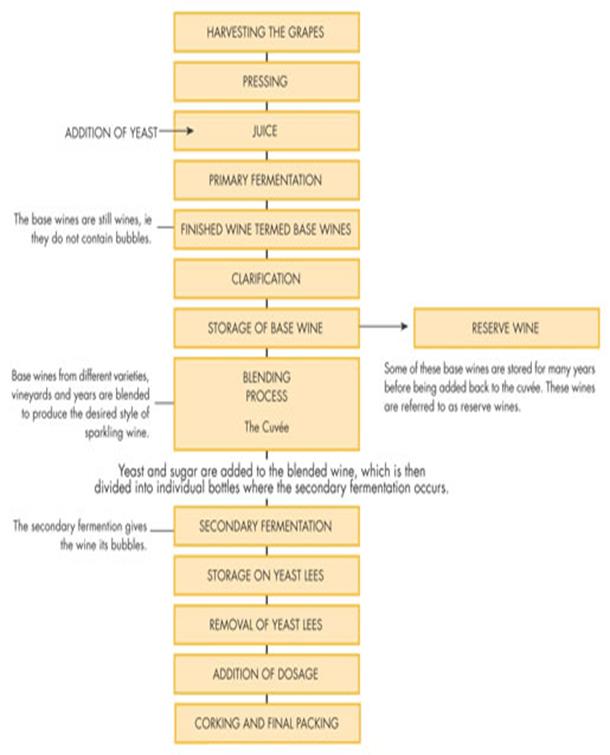
Brewing is the production of beer through steeping a starch source (commonly cereal grains) in water and then fermenting with yeast. Brewing hastaken place since around the 6th millennium BC, and archaeological evidence suggests that this technique was used in ancient Egypt. Descriptions of various beer recipes can be found in Sumerian writings, some of the oldest known writing of any sort.[1][2][3] Brewing is done in a brewery by a brewer, and the brewing industry is part of most western economies. The basic ingredients of beer are water; a starch source, such as malted barley, which is able to be fermented (converted into alcohol); a brewer's yeastto produce the fermentation; and a flavouring, such as hops. A secondary starch source (an adjunct) may be used, such as maize (corn), rice or sugar. There are several steps in the brewing process, which include malting, milling, mashing, lautering, boiling, fermenting, conditioning, filtering, andpackaging. There are three main fermentation methods, warm, cool and wild or spontaneous. Fermentation may take place in open or closed vessels. There may be a secondary fermentation that can take place in the brewery, in the cask, or in the bottle. Brewing specifically includes the process of steeping, such as with making tea, sake, and soy sauce. Wine production
85 The microorganisms used in industry The use of microorganism in large scale production of food and industrial products is being done worldwide.The sources of food production in such cases may be animals or plants but the processing is done by enzymatic activities by microorganism only. Microorganism contains various enzymes which are capable of degradation of substrates. This is also known as fermentation process in which the degradations is not completed and results in useful by products. These by products include, beverages, antibiotics, milk by products etc which are used by humans as nutritive foods. With the development of technology like genetic engineering, many mutants are developed which are capable of performing extra with respect to production quality and quantity as compared to their wild types. Today pharmaceutical agents like antibiotics and other drugs are manufactured at large scale which utilizes microorganism. The history of microbiology has given us very broad spectrum antibiotics like Penicillin and Streptomycin which are still in use at large throughout the globe. Foods which are originated from animals are enzymatic ally processed by specific microorganisms resulting in increase in their nutritive value. These foods are fermented foods like Yogurt, milk by products like cheese, sweet chocolates and silage. Many algae are today used as source of protein. Fungus like mushroom is today being used as source of nutrition as well as medicine. Bacteria like Lactic acid bacteria are used in production of pure curd and other milk products. Bacteria like Bifidobacteria are being used in food industry as probiotics which helps in curing of diseases of digestive systems and intestinal disorders. Polysaccharides, polyamides, polyesters and many other varieties of biopolymers are produced by many microorganisms. These are ranging from plastics to viscous solutions. Today many researches in drug delivery and tissue engineering are being successfully done with the help of genetically manipulated microorganisms which are producing biopolymers which are having medical applications. Many wild as well as genetically mutated strains are used in industries for biosynthesis of cellulose, levan, hyaluronic acids, polysaccharides and organic acids, etc. Today many pollutants are degraded with the help of saprophytes (specific type of bacteria/fungi capable of surviving in waste organic material their by metabolism) this process is also known as biodegradation. Today bioremediation and other methods like biotransformation are used for cleaning of the environments. Today even heavy metals like mercury which is toxic and results in biomagnifications. The degradation of this is very costly by chemical and other standards technologies. Therefore the alternative method is bioremediation. Today in modern societies, lot of waste is being generated from domestic wastes. These are accumulating every day and are very harmful to not only the society but also the environment (Our mother earth). The processing of such waste using living organisms is known as biotreatment. These methods are helping society and saving earth from accumulation of hazardous wastes. This method of using microorganisms in degradation of hazardous waste is not only useful but also simple, cost effective and eco friendly. The systematic method of biotreatment is done with the help of bioreactors having aeration system, baffles which suitable for microbial enzymatic reaction. Apart from waste treatments, microorganisms are used in production of biological like insulin, serum antibodies, and essential hormones. Today with the development of technology and science, new ways of diagnosis of diseases are being used for early detection using microorganism’s e.g. rapid microbial test, enzyme employed detection, etc. One of the microbe known as Clostridium is useful in treatment of malignant cells like cancers. These organisms have the ability to selectively target cancerous cells. Streptomyces genus is used worldwide in the production of medicines and agriculture. These microorganisms process many secondary metabolites like antibiotics and plant growth hormones like Gibberilla (Microorganism used is Gibberella fujikuroi).
|
||||||
|
Последнее изменение этой страницы: 2016-08-14; просмотров: 330; Нарушение авторского права страницы; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! infopedia.su Все материалы представленные на сайте исключительно с целью ознакомления читателями и не преследуют коммерческих целей или нарушение авторских прав. Обратная связь - 18.216.208.243 (0.007 с.) |