
Заглавная страница Избранные статьи Случайная статья Познавательные статьи Новые добавления Обратная связь FAQ Написать работу КАТЕГОРИИ: ТОП 10 на сайте Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрацииТехника нижней прямой подачи мяча. Франко-прусская война (причины и последствия) Организация работы процедурного кабинета Смысловое и механическое запоминание, их место и роль в усвоении знаний Коммуникативные барьеры и пути их преодоления Обработка изделий медицинского назначения многократного применения Образцы текста публицистического стиля Четыре типа изменения баланса Задачи с ответами для Всероссийской олимпиады по праву 
Мы поможем в написании ваших работ! ЗНАЕТЕ ЛИ ВЫ?
Влияние общества на человека
Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрации Практические работы по географии для 6 класса Организация работы процедурного кабинета Изменения в неживой природе осенью Уборка процедурного кабинета Сольфеджио. Все правила по сольфеджио Балочные системы. Определение реакций опор и моментов защемления |
Unit 1 Our Home – Planet EarthСодержание книги
Поиск на нашем сайте
1. Work in teams. Brainstorm all the words and phrases you know related to the word environment. Present your mind map to the rest of the class and explain how the ideas are connected.
2. Work in small groups. Which of the environmental problems listed below are the most serious? Put them in order, 1-7 (1 = the most serious, 7 = the least serious). Give reasons for your choice. § global warming/climate change § air/water/soil pollution § shrinking habitats and loss of bio-diversity § acid rain § ozone layer depletion § deforestation § natural disasters: floods, heavy rainfalls, violent storms, droughts, etc.
3. Match the environmental problems with the factors that cause them. Some factors may go with more than one problem. Choose to write about three problems and their factors.
1. Look at the definition. Which environmental problem does it refer to?
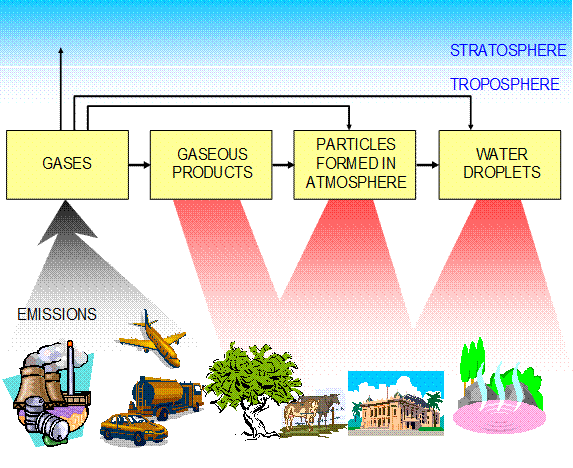
2. Look at the picture below. With a partner brainstorm your ideas about acid rain. What causes acid rain? How can it harm the environment?
3. Look through the text about the acid rain problem and check your predictions. Acid rain is strongly acidic rain that absorbs microscopic particles of nitric acid or sulfuric acid as it falls towards the ground. But why do we have acid
rain? The reason lies in atmospheric pollution. As human beings developed their economic behavior, they began to use huge amounts of fossil fuels such as coal and oil. When fossil fuel is burned, sulfur and nitrogen oxides are released into the atmosphere. These pollutants are affected by ultraviolet rays and combine with atmospheric water vapor to form tiny particles of nitric acid and sulfuric acid that float in the atmosphere. When these particles dissolve into rain, it falls to the ground as acid rain. This process is called "wet deposition". At other times these pollutants are absorbed into fog or mist in a gas or particle form, are deposited on
forests, and eventually return to the soil; this is called "dry deposition." Chemical substances released from chemical plant chimneys are a major factor in the contamination of the atmosphere and lead to the formation of acid rain. Many of us have our own “private factories” for producing modern acid rain - cars. Vehicle exhausts contain NOx (nitrogen oxides), hydrocarbons and other chemicals. The damage caused by acid rain first appears in rivers, lakes and marshes. When the water of a lake or marsh declines to pH5 or so, at first the plankton and aquatic vegetation disappear. Needless to say, the fish that feed on these living things also decline in number and even die out. Then, as the acidity level of soil increases, aluminum and other harmful metals contained in the soil begin to dissolve, which also contributes to the death of aquatic life. Eventually the lakes cannot support life at all. Acid rain makes soil highly acidic, which leads to the drying and death of forests. Soil naturally contains many metallic ions such as calcium and magnesium, and these help to neutralize acid to a certain extent, even in the case of acid rain. However, when this neutralization power is exhausted, the acidity of the soil increases, killing microorganisms and worms. There are also cases when acid rain enters directly into the leaves, trunks, and branches of plants and damages trees. The damage created by acid rain in Europe and North America is truly grave. It is reported that in many European countries about one half of the total area of forests has been damaged. Countries like Sweden, Norway, and other Scandinavian countries do not contribute much to atmospheric pollution, but they are suffering extensive damage from atmospheric pollutants carried there from other countries. For example, it has been reported that fish have disappeared from one-third of the lakes and marshes of Norway. In Asia, acid rain is having truly serious consequences in China, which is the second largest producer of coal in the world. Furthermore, with the expansion of industry and the spread of the automobile, acid rain is becoming a serious issue even in developing countries. Historical sites and buildings are also damaged by acid rain, especially in Europe with its many historical buildings made of marble and copper. The chemical reaction between marble and sulfuric acid changes the marble into plaster. Therefore, ancient sculptural works made of marble often crumble after contact with acid rain. Copper items also break down in contact with acid rain. For example, the copper plates of the United States' Statue of Liberty were eaten away to a dangerous degree by acid rain, and needed large-scale reconstruction. Historical structures and buildings, which have been handed down as cultural heritage for centuries, have been in danger of being lost in the past several decades simply because of acid rain. Acid rain is no longer someone else’s problem: it’s happening here. (Adapted from http://www.virtualglobe.org/en/info/env/)
4. Read the text again and complete the cause and result chart for acid rain.
Comprehension check 1. Look back in the text and find words that have similar meaning to
2. In the text find and translate into your native language the words that: a) refer to a means of transport b) can be used to describe the movement up and down c) are the names of chemical elements and compounds
Focus on language 1. Complete the table. Turn the words given in the table into verbs, nouns and adjectives. Use a dictionary if necessary.
2. Fill in the gaps with the right form of the words in capitals.
3. Read these sentences. What grammar rule do they follow? § Acid rain is strongly acidic rain which/that absorbs microscopic particles of nitric acid or sulfuric acid as it falls towards the ground. § In Asia, acid rain is having truly serious consequences in China, which is the second largest producer of coal in the world. § As the acidity level of soil increases, aluminum and other harmful metals contained in the soil begin to dissolve, which also contributes to the death of aquatic life.
4. Put in which, what or that. Put comma if necessary. a) She cycles to work every day, which makes her healthy. b) Everything ………… he told us about water pollution made me upset. c) Graffiti is vandalism. This is ……… we need to understand. d) The world’s population is growing very fast ……… makes the world critically short for food and water. e) Even with just an A-level in Biology I could understand ……… they were doing. f) Planting trees is a great thing ……… also makes us feel better and encourage less littering. g) I did everything ……… I could to save an entangled seal. h) She joined a Girl Scout team ………… surprised us all. i) Our modern lifestyle is destroying the fragile environment ………leads to the environmental catastrophe.
Search the environmental websites or specialized magazines to get information about the ways to solve the acid rain problem. Make notes on what you have found and report back to the class.
1.
2. You are going to listen to an environmentalist talking to the students about the pollution of the environment. The words below are all to do with different types of litter. Explain the difference in their meaning. Use a dictionary if necessary.
What sources of pollution can you name? Which of them are the most/least harmful?
3. Listen to the talk and answer the questions. a) What kind of pollution is the main focus of the talk? b) Why aquatic pollution is such a serious environmental problem? c) What types of pollution does the environmentalist mention? d) What are the main sources of water pollution? e) Why plastic litter is so harmful? f) Why entanglement and indigestion are the two major problems for the wildlife in waterways? g) How does debris contaminate water? h) What is the purpose of the talk?
Discuss Ø Litter is ugly, dangerous and expensive. Moreover it multiplies and travels. Why is it so? Ø Who do you think is responsible for solving the problem of litter in cities? Ø Have you ever participated in a cleaning up activity or any other civic improvement programs in your city? Do you think such programs can help to improve your community? How would you feel walking along a street after you had helped to clean it of litter?
Interview ten of your fellow students about the most serious environmental problems in your hometown.
How different are their opinions? Discuss your findings as a class. Use the phrases in the Functional language box.
Complete the bar chart below marking each bar with the results of your interviews. Summarize your findings in a paragraph.
1. Look through the texts on various green initiatives that are introduced worldwide and take notes on a particular green initiative and its benefits described in each text.
B
Search the Internet, specialized magazines or talk to the experts who work in your university to get comprehensive and reliable information about one of the environmental problems in your country or the region you live in. Summarize the information you have collected and report back to the class. Follow the guidelines: § State the problem briefly but clearly § Describe the problem in detail (the causes and effects) § Give examples of green initiatives aimed at solving the problem.
Work in groups of 3-4 and discuss what actions as individuals you can take to help to solve the environmental problems listed below. Brainstorm solutions to some national or local problems. Use the phrases from the Functional language box. Share your solutions with the rest of the class. What can be done … a) to control the cutting down of forests? b) to clean up the beaches? c) to reduce air pollution? d) to save rare animals and plants? e) to slow down global warming? f) to stop the spread of droughts? g) to reduce floods?
A big petroleum company has announced that it wishes to build a plant for refining petroleum products in an area of countryside near your city. The plans have divided the community into three groups: Greens: You regard the chosen site as an area of outstanding natural beauty which should not be harmed in any way. You oppose any construction on the site. Enthusiasts: You welcome the economic benefits that the new plant will bring and aim to provide technological and financial support which will help the refinery to reduce its impact on the environment. Regulators: You would like to strengthen the rules on pollution and increase the fines on companies that release pollutants.
1. Which group do you associate yourself with?
2. Write a letter to the local authorities of your own city giving your opinion on this problem and saying which suggestions you agree or disagree with. Follow the model.
3. Work in pairs. Exchange your letters and read them. Is the language, used by your fellow student, appropriate for a formal letter? Are his/her ideas and viewpoints clear? Make any suggestions for improvements.
All of you are at the meeting which is held to discuss the most urgent environmental problems in your city. Each student plays one of the roles described below. Read the situation and the role descriptions and decide who will play each role. Divide into 5 groups (group A – environmentalists, B – bank representatives, C – city residents, D – city council members, E – project managers). Prepare for ten minutes before you begin the meeting. Make use of the functional language in the Functional language box. The situation The World Bank has decided to fund the “Eco-friendly city” programme. As the representatives of different local organizations and the community you have to discuss the most urgent environmental problems in your city, the ways to solve them and to work out projects that will allow to cope with the most urgent problems in your neighborhood. As a result the World Bank will choose the most attractive project.
Roles: project manager You live in this city and work in the local branch of the World Bank. The Board of trustees appointed you to be the person in charge for the successful realization of the eco-programme in your city. You introduce the programme of the World Bank, briefly describe the situation and conduct the meeting. Roles: environmentalists You are a member of the local Green Peace organization. You are concerned with the high level of industrial waste, soil and water contamination in your city. Present your project and suggest the ways for its realization. Roles: city residents You are worried about the shrinking of green spaces and increasing of air pollution in your city. Present your project and suggest ways and terms of its realization.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Последнее изменение этой страницы: 2016-09-18; просмотров: 748; Нарушение авторского права страницы; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! infopedia.su Все материалы представленные на сайте исключительно с целью ознакомления читателями и не преследуют коммерческих целей или нарушение авторских прав. Обратная связь - 216.73.216.214 (0.009 с.) |






 Work with a partner. Brainstorm as many environmental problems typical for big cities as you can. Compare your ideas as a class.
Work with a partner. Brainstorm as many environmental problems typical for big cities as you can. Compare your ideas as a class.



 A
A
 C
C D
D E
E Your address
and the date
Your address
and the date
 Name and address of the company/person you are writing to
Name and address of the company/person you are writing to



