
Заглавная страница Избранные статьи Случайная статья Познавательные статьи Новые добавления Обратная связь FAQ Написать работу КАТЕГОРИИ: ТОП 10 на сайте Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрацииТехника нижней прямой подачи мяча. Франко-прусская война (причины и последствия) Организация работы процедурного кабинета Смысловое и механическое запоминание, их место и роль в усвоении знаний Коммуникативные барьеры и пути их преодоления Обработка изделий медицинского назначения многократного применения Образцы текста публицистического стиля Четыре типа изменения баланса Задачи с ответами для Всероссийской олимпиады по праву 
Мы поможем в написании ваших работ! ЗНАЕТЕ ЛИ ВЫ?
Влияние общества на человека
Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрации Практические работы по географии для 6 класса Организация работы процедурного кабинета Изменения в неживой природе осенью Уборка процедурного кабинета Сольфеджио. Все правила по сольфеджио Балочные системы. Определение реакций опор и моментов защемления |
The States, Districts and Territories of the U.S.A.Содержание книги
Поиск на нашем сайте
Washington D.C. is a federal district under the authority of Congress. Puerto Rico is a commonwealth associated with the United States. Other dependent areas include American Samoa, Baker Island, Guam, Howland Island, Jarvis Island, Johnston Atoll, Kingman Reef, Midway Islands, Navassa Island, Palmyra Atoll, Virgin Islands, Wake Island.
CLIMATE Due to the United States' large size and wide range of geographic features, nearly every type of climate is represented. The climate is temperate in most areas, tropical in Hawaii and southern Florida, arctic in Alaska, semiarid in the Great Plains west of the Mississippi River, desert in the Southwest, mediterranean in coastal California, and arid in the Great Basin. Extreme weather is not uncommon—the states bordering the Gulf of Mexico are prone to hurricanes and most of the world's tornadoes occur within the continental United States. However, the predominantly temperate climate, infrequent severe drought in the major arable regions, and infrequent severe flooding have helped make the nation a world leader in agriculture. America's weather is affected markedly by the confrontation between polar continental air masses (usually cold, dry, and stable) and tropical maritime air masses (warm, moist, and unstable). Most parts оf America are subject to a generally westerly wind flow that tends to move weather systems eastward. The interaction of climatic controls creates a pattern of climatic regionalization. In the East, the principal element in climatic variation is temperature; in the West, it is precipitation. In the East, the divisions between the climate regions are based largely on the length of the growing season—the period from the average date of the last frost in spring to the first frost in fall—and on the average summer maximum temperature or winter minimum temperature. In the West, average annual precipitation is the key, although moderated temperatures are an important aspect of the marine West Coast climate. In the East, the more northerly areas are generally drier; in the West, they are colder. In the East, the major influence on climatic variation is latitude; in the West, it is topography.
Vocabulary notes Cropland- зерновые поля Pastureland- пастбища Urban- городской Coastline-побережье Vast- широкий, обширный Valley-долина Copper - медь Lead - свинец potash – углекислый калий tungsten - вольфрам timber - древесина hazard- опасность permafrost – вечная мерзлота impediment - преграда commonwealth - содружество Deciduous - лиственный Prevail - превалировать boreal - арктический altitude – высота над уровнем моря flat - плоский fertile - плодородный distinct - индивидуальный mediterranean - средиземноморский arid – сухой, засушливый drought - засуха arable - пахотный precipitation - осадки annual - ежегодный latitude - широта VEGETATION In most of the inhabited portions of America today the "natural" vegetation, if it ever existed, has been so substantially removed, rearranged, and replaced that it seldom is found now. In the Southeast, for example, the original mixed broadleaf and needle leaf forests were cut and replaced by the economically more important needle leaf forests. The grasses of the plains and prairies are mostly European imports. Their native American predecessors are gone either because they offered an inferior browse for farm animals or because they could not withstand the onslaught of modern humanity and its imported weeds. Most of what climax vegetation remains is in the West and North. The tundra of the far North is the result of a climate that is too cold and too dry for the growth of vegetation other than grasses, lichens, and mosses. Tundra exists in small areas far southward into the United States, where climatic conditions at high elevations are inhospitable to tree growth. Northward, the altitu-dinal tree line is found at lower elevations until, eventually, the latitudinal tree line is reached. With habitats ranging from tropical to Arctic, U.S. plant life is very diverse. The country has more than 17,000 identified species of native flora, including 5,000 just in California (which is home to the tallest, the most massive, and the oldest trees in the world). More than 400 species of mammal, 700 species of bird, 500 species of reptile and amphibian, and 90,000 species of insect have been documented. Wetlands such as the Florida Everglades are the base for much of this diversity. The country's many ecosystems include thousands of non-native exotic species that often adversely affect indigenous plant and animal communities. Vocabulary notes Inhabited - населенный Vegetation - растительность Broadleaf - широколиственный Needle leaf - хвойные Predecessor - предшественник Browse - бродить Withstand – устоять, выдержать Onslaught - нападение weeds - сорняк lichens - лишайник mosses - мох elevation - возвышение inhospitable - враждебный habitats – естественная среда species - виды mammal - млекопитающие indigenous - местный adversely - неблагоприятно diversity - разнообразие The Nation's Capital Washington, D.C.
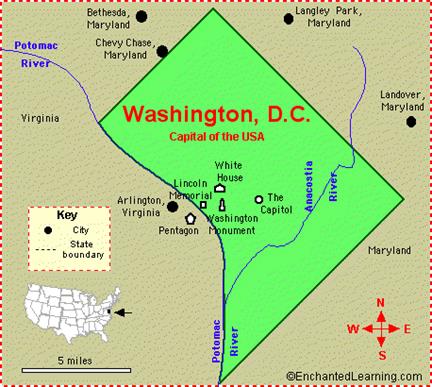
Facts from history New York City was the first capital of the United States once the Constitution was ratified. George Washington took the oath of office to become the first President of the United States from the balcony of the old City Hall. One of the issues the President had to deal with was a permanent location for the country’s seat of government. As part of a compromise, it was decided that the capital would move to Philadelphia, Pennsylvania in 1791 for ten years and then to a suitable permanent location on the Potomac River. Washington chose an area that included land from the states of Maryland and Virginia. At this time the area was primarily farm and marsh lands. Congress was scheduled to meet in the new capital on the first Monday in December 1800. Pierre Charles L’Enfant, the French architect, was hired to design the "Federal City." On June 11, 1800, the capital of the United States had a permanent home in Washington, D.C. The capital today
Postal Abbreviation – DC Area - 68.25 square miles (176.75 square km) Population - 572,059 Major Industry - government Major Rivers - Potomac River, Anacostia River Highest Point - Tenleytown - 410 feet (125 m) above sea level Bordering States - Virginia, Maryland Origin of the Name Washington, District of Columbia - The name Washington was to honor the first president of the USA, George Washington. The name Columbia is in reference to Christopher Columbus. Nickname - D.C. Official Motto - "Justia Omnibus" - Justice for All Official Song - The Star-Spangled Banner, words by Francis Scott Key
Official Bird - Wood thrush Official Flower - American beauty rose Official Tree - Scarlet Oak
District of Columbia (Washington, D.C.) is the capital city of the USA. The White House, the Capitol, the Supreme Court, and many other government buildings are located in Washington, D.C. The first President to live in Washington D.C. was John Adams; his family moved there in 1800. The city is commonly referred to as D.C., the District, or simply Washington. Historically, it was called the Federal City or Washington City. To avoid confusion with the state of Washington, located in the Pacific Northwest, the city is often called simply D.C.. The centers of all three branches of the U.S. federal government are in the District. It also serves as the headquarters for the World Bank, the International Monetary Fund, the Organization of American States, the Inter-American Development Bank, and other national and international institutions. Washington is the frequent location of political demonstrations and protests, large and small, particularly on the National Mall. Furthermore, Washington is a popular destination for tourists, the site of numerous national landmarks and monuments. It is a major American cultural center, with a number of important museums, galleries, performing arts centers and institutions, and native music scenes. The District has three major natural flowing streams: the Potomac River, the Anacostia River and Rock Creek. The Anacostia River and Rock Creek are tributaries of the Potomac River. Geographical features of Washington, D.C. include Theodore Roosevelt Island, Columbia Island, the Three Sisters Islands and Hains Point. Landmarks Among other attractive buildings are the embassies and legations of many foreign countries, many of them lining “Embassy Row” on Massachusetts Ave. The larger of the city’s fine parks are West Potomac Park, East Potomac Park, Rock Creek Park. Besides the Capitol and the White House, other important government buildings and places of historic interest include the Senate and House of Representatives office buildings, the Supreme Court Building, the Pentagon (in Virginia), the Federal Bureau of Investigation building, the Library of Congress, the National Archives Building, Constitution Hall, the Ronald Reagan Building, The Watergate apartment complex, the State Department (“Foggy Bottom”), and the headquarters of the World Bank. Ford’s Theatre, where Lincoln was shot, has been restored. In 1974 the Admiral’s House at the U.S. Naval Observatory became the official residence of the vice president. Of historic interest is Fort Washington (built 1809, destroyed 1814, rebuilt by 1824). Best known of the city’s many statues and monuments are the Washington Monument, the Lincoln Memorial, with its reflecting pool; the Franklin Delano Roosevelt Memorial; the Vietnam Veterans Memorial; the Korean War Veterans Memorial; the World War II Memorial; and the Thomas Jefferson Memorial. Among Washington’s famous churches are Washington National Cathedral (Episcopal), and the National Shrine of the Immaculate Conception, the largest Roman Catholic church in the United States. The city also contains Robert F. Kennedy Stadium, the home to major-league baseball and formerly to football. The Arlington Memorial Bridge across the Potomac connects the capital with Arlington National Cemetery. Also in Arlington is the U.S. Marine Corps War Memorial, one of the largest statues ever cast in bronze. In the Potomac itself lies Theodore Roosevelt Island, thickly wooded and with many foot trails.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Последнее изменение этой страницы: 2016-09-13; просмотров: 390; Нарушение авторского права страницы; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! infopedia.su Все материалы представленные на сайте исключительно с целью ознакомления читателями и не преследуют коммерческих целей или нарушение авторских прав. Обратная связь - 3.137.221.114 (0.007 с.) |

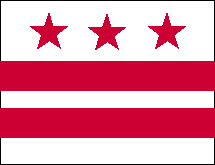 The flag of Washington, D.C., was adopted in 1938. Since Washington, D.C., had no official flag, a commission was formed in 1920 to find a design. Headed by A. E. Dubois, the final design was chosen on October 15, 1938. The design was based on the shield from George Washington's family's coat of arms.
The flag of Washington, D.C., was adopted in 1938. Since Washington, D.C., had no official flag, a commission was formed in 1920 to find a design. Headed by A. E. Dubois, the final design was chosen on October 15, 1938. The design was based on the shield from George Washington's family's coat of arms.



