Заглавная страница Избранные статьи Случайная статья Познавательные статьи Новые добавления Обратная связь FAQ Написать работу КАТЕГОРИИ: ТОП 10 на сайте Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрацииТехника нижней прямой подачи мяча. Франко-прусская война (причины и последствия) Организация работы процедурного кабинета Смысловое и механическое запоминание, их место и роль в усвоении знаний Коммуникативные барьеры и пути их преодоления Обработка изделий медицинского назначения многократного применения Образцы текста публицистического стиля Четыре типа изменения баланса Задачи с ответами для Всероссийской олимпиады по праву 
Мы поможем в написании ваших работ! ЗНАЕТЕ ЛИ ВЫ?
Влияние общества на человека
Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрации Практические работы по географии для 6 класса Организация работы процедурного кабинета Изменения в неживой природе осенью Уборка процедурного кабинета Сольфеджио. Все правила по сольфеджио Балочные системы. Определение реакций опор и моментов защемления |
Main characteristics of inflationСодержание книги Поиск на нашем сайте
Introduction
The aim of this research is to clarify the relationship between unemployment and inflation in Kazakhstan. Time series data shall be used for the phase 2000-2015. Unemployment rate is taken as dependent variable whereas inflation rate is taken as independent variable. The link between them would be finding by Simple Linear Regression. This research will conduct by using the method of Regression. The key reason of this work is to examine ways of extending the theory of inflation and unemployment. This research is about time series analysis and forecasting Kazakhstan’s inflation and unemployment. The most important purpose for selecting this topic is to get the knowledge and identify the different time series models. The idea of this report is to know the logic of inflation and unemployment strategy of Kazakhstan’s government and fluctuation of both in different years. To forecast Kazakhstan inflation by exercising models of econometric and to describe the term of inflation and unemployment broadly by studying historical data. Kazakhstan has practiced extreme and insistent inflation for more than twenty years. Inflation is one of the most important concepts in economics. In the basic level inflation is a rise in prices. When there is raise in the price of goods and services, than the value of dollar shall go down, as we will not be able to buy as enough with the dollar as we could have last time or last period. Mostly people thinks that inflation is the increase in price but according to economist inflation is the decreasing power of dollar. [1] Later on, the anti-inflationary policy of Kazakhstan will be covered in this report. The international experience of such countries, as: Russia and Belorussia.
Main characteristics of inflation
The essence of inflation In modern conditions in many countries, great importance has become a phenomenon of inflation. Inflation (from the Latin Inflation - swelling) - is the process of depreciation of money, reflected in the overall increase in prices. Inflation has been associated with the emergence in ancient times devalued money - coins spoiled, loss of purchasing power which often led to riots. In the XVII century Europe there was impairment of gold money, known as "price revolution". It was caused by pouring into Europe from the New World the flow of precious metals. In subsequent periods, the inflation depreciation of paper money were exposed. Since the mid 60-ies of XX century, inflation has become one of the central macroeconomic problem for many countries, both developing and industrialized. [2] The impact of macroeconomic factors on the development of inflation in many countries has been extensively studied in the economic literature, especially in the framework of the monetary approach. Inflation as a process is a devaluation (depreciation) of paper money, which leads to higher prices for goods and services and resources. The theoretical aspect of communication with the release rates of the money supply, a mismatch in the mechanisms of supply and demand, a surplus of the consumer, the budget deficit, outpacing wage growth. The most commonly used indicators are price index. Indirect indicators of inflation, which may serve as indicators of its appearance, are the high growth of the money supply as a percentage increase in nominal interest rates, the availability and size of gold and currency reserves, the ratio of foreign exchange reserves and the money supply. The process of the opposite of inflation, which is manifested in a general fall in prices is called deflation (from the Latin deflatio -. Deflation). Under the disinflation understand slowdown in price growth. [3] Types of inflation. The problems and the effects of inflation Depending on the pace of the following types of inflation: • Creeping (moderate) inflation, which is characterized by relatively low rate of price growth to around 10% or slightly more per cent a year. Such inflation is inherent in most countries with developed market economies, and it is not something unusual. Data for the 70 th, 80 th and early 90-ies. the US, Japan and Western European countries, and just talk about the presence of creeping inflation [5, p. 280]. Average inflation for the countries of the European Community has made in recent years about 1.3-2%. • Galloping inflation (rising prices by 10-200% per year). Such high rates in the 80-ies. observed, for example, in many countries of Latin America, some countries of South Asia. Table 1.1.1. given indices of consumer prices, and the growth rate of nominal money income in the CIS countries (1992 to 1991, the number of times) • Hyperinflation - prices are rising astronomically, the discrepancy in prices and wages becomes catastrophic collapses welfare of even the most affluent societies, non-profit and unprofitable become the largest enterprises.tak, in Argentina in April 1990 recorded a rise in prices in 200 times (growth rate inflation - 2,000%). Saved by the Argentines is that they dominated subsistence agriculture without market relations can live for some time. The recent record belongs to Nicaragua during the period of civil war, the average annual increase in prices reached 33,000%. Indicative examples of hyperinflation as in Hungary (1946.), Russia and Yugoslavia (in the early 90-ies. In the XX-th.). In Ukraine, there was hyperinflation in 1992-1993. when inflation was 10 256%. [4] In terms of expected and predictable inflation is isolated: the expected and unexpected inflation. Expected inflation can be predicted in advance and predicted with a reasonable degree of reliability; suddenly - occur spontaneously, can not be forecast. Impact of inflation on real income level is contradictory. Inflation has a different effect on the redistribution of income, depending on whether it is expected or unexpected. If the recipient of income expected inflation may take measures to prevent or reduce the negative effects of inflation, which, otherwise, will affect the value of its real income. From the viewpoint of the criterion of correlation of growth in the various commodity groups the prices are distinguished: balanced and unbalanced inflation inflation. When balanced inflation price increases moderate and simultaneously on most goods and services. In this case, according to the annual increase in prices increases the interest rate, which is equivalent to the economic situation with stable prices. And when unbalanced inflation rates for various goods and services are constantly changing in relation to each other, and in different proportions. [5] The inflation in Kazakhstan
A characteristic feature of inflation in Kazakhstan is stable, fairly high rate of inflation, despite the efforts of the authorities. This reflects, first, the presence of certain permanent factors affecting the nature of monetary relations and secondly about the limitations and inefficiencies of operating these relations management. The main reason for the ineffectiveness of methods of regulation of inflation is the imbalance of the economy. [ 8]
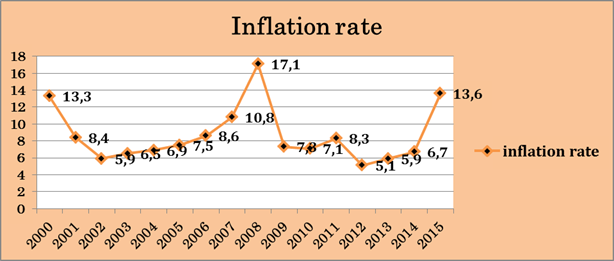
Figure 2. The dynamics of inflation 2000-2015 (source: Trading economics)
Inflation in annual terms from 2001 to 2004 remained relatively stable in the range of 6-7-8%. However, since 2002, there has been a strengthening of inflationary processes in the economy of Kazakhstan. In 2005 the inflation was at 7.5% [9] The actual inflation rate in Kazakhstan for three years more than the official forecast of the National Bank and the government. 2005 was no exception. According to the Kazakh Statistics Agency, inflation in December 2005 compared to December 2004 was 6.9 %, while National Bank of the Republic predicted annual inflation of 5.2-6.9%, and the Ministry of Economy and Budget planning in the corridor of 5-7%. [10] The main reasons for exit of inflation over the forecast level of featured external factors - high oil and metal prices (the basis of Kazakhstan's exports), as well as internal - social payments from the budget, aimed at increasing the salaries, pensions, stipends, allowances, price growth energy, services and fruit and vegetables. However, 2005 was marked by high levels of socio-economic development. According to preliminary data of the Statistics Agency, GDP growth amounted to 9.2% in 2005, investment in fixed capital increased by almost a quarter, the positive balance of foreign trade turnover exceeded $ 9 billion. The measures taken by the National Bank to tighten monetary policy in early 2006 had a dampening impact on inflation, which in annual terms fell from 9.0% in May 2007 to 8.6% in September 2007 Among the main factors affecting inflation in 2007 should be allocated to the increase in aggregate demand, inflow of foreign currency, a significant increase in wages, the growth of budget expenditures, the growth of production costs, as well as the low level of competition in some markets of goods and services. [11]
In early 2008, National Bank of Kazakhstan has promised to keep inflation at around 10%, despite the fact that at the end of 2007, annual inflation stood at 17.1%, while the Prime Minister Karim Masimov has promised that the government will strengthen the monitoring of inflationary processes. In 2008, inflationary processes were multidirectional nature. In January-August, the situation on the consumer market was characterized by a high degree of inflationary pressures, the main factor which served as the influence of external factors. Since September 2008 the inflation was decreasing. This was due to a decline in prices on world commodity markets, a slowdown in economic growth, limited consumer demand, stagnation of credit activity of the banking sector, low growth of money supply in the economy. As a result, annual inflation slowed more than 2 times from August to December 2008. (picture above) 2014-2015 Annual inflation at the end of December 2014 was 6.7 %. Gain compared with 2013 year (4.8%) contributed to inflation increase in prices for non-food and food products due to seasonal factors, as well as rising prices of imported goods in the domestic market. The rate of growth of tariffs for paid services continued zamedlenie. Inflow of money, the main indicator of the money supply in the economy decreased by 4.8% for October-December 2014. Overall, the annualized money supply corresponds to the needs of the economy and the current economic conditions, its volume is sufficient to maintain the business. At the same time, real GDP growth in 2014, according to preliminary data of the Committee on Statistics of the Ministry of National Economy of the Republic of Kazakhstan, was 4.3%. Within the framework of the implementation of monetary policy in the 4th quarter of 2014 the National Bank continued to conduct operations aimed at regulating short-term tenge liquidity in the money market. [12]
Since the beginning of 2015 there was a slowdown of inflationary processes in Kazakhstan. Since the second quarter of 2015, annual inflation is below the target range of 6-8% for 2015 year. One of the factors reducing the rate of inflation in 2015 was the low business activity, accompanied by a slowdown in output growth in the main sectors of the economy of Kazakhstan. Against the background of low economic activity and limited consumer demand is observed decline in domestic lending and money supply growth remains low. The influence of external factors also contributed to the reduction of inflationary background in the economy. In particular, the drop in world prices for oil, metals and food were the main factors slowing inflation. In early 2015 a deterrent inflation in Kazakhstan was the imbalance between the Russian ruble and Kazakh tenge, when the ruble has weakened significantly in late 2014. The weakening of the ruble against the tenge has led to cheaper Russian goods to the Kazakh market. Relatively cheap goods from Russia increased price competition in the market of Kazakhstan. This has had an impact on the growth in demand among domestic consumers for products produced in Russia, Kazakhstan producers were forced to reduce the prices of their products, which influenced the decline in inflation. In September 2015, annual inflation was 4.4%, an increase compared to August (3.8%). The main factor accelerating inflation is the effect of the transfer of weakening exchange rate of KZT. [13] At the end of 2015 the inflation was 13.6 %, because of the weakening exchange rate of KZT. Regression analysis To discover the relationship between inflation and unemployment rate, we have used regression. For the purpose of sample, annual data is collected from the economic survey of Kazakhstan and World Bank website for the period of 2000 to 2015. Unemployment is used as dependent variable, whereas Inflation rate and GDP growth rate as independent (explanatory) variable. [15] Based on the theoretical work and empirical literature, we have developed a model to investigate the relationship/impact of macroeconomic variables on the unemployment. UE =β0+β1 INF+ β2 GDP rate +U Where: UE is unemployment of total labor force of a country in percentage β0 representing the coefficient intercept term as constant β1 INF representing inflation (annual percentages of consumer prices) β2 GDP rate representing GDP growth rate U representing the error term of the study The regression analysis is used because it helps to test on the relationship and the significant of relationship of two phenomena the dependent variable and independent variable. The following table tells about statistic of dependent and independent variables. Significance value shows the relationship between dependent and each independent variable. In accordance with Figure 2 it is concluded that unemployment have a significant effect on Inflation. Figure 5. Regression Linear Model between inflation rate and unemployment (source: excel file)
If the β (coefficient) value is positive means that there is positive relationship between independent and dependent variable and the negative value of β means there is negative relationship between independent and dependent variable. It shows there is positive relationship exists between Unemployment, GDP growth rate and Inflation rate. The coefficient of inflation rate (β1), is quite a small positive number. This indicates a positive relationship between unemployment, inflation and GDP growth rates. The equation is:
For a one % increase in inflation rate, unemployment rate increases by approximately 0.228 %. Each additional per cent in GDP growth rate will increase unemployment rate by 0.49 %. Moreover, R- square is 0.59685, it must be conclude, that the explanatory variables “explains” 59.68 % of the variance of unemployment rate. A more exact measure of goodness of fit, which takes into account the number of explanatory variables, is the adjusted R – square. Adjusted R square shows an adequacy of model with 0.53483 that shows independent variables (Inflation and GDP growth rates) can predict 53.48% of variance in dependent variable (Unemployment). [16] The F statistic shows overall effects of independent variable on our target variable. The F – statistic, which tests the overall significance of the sample regression, is 9.62304. Regression model is significant because, because P = 0.00273<0.05.The outcome of simple linear regression verifies the reality of positive relationship between unemployment and inflation. It can be saying easily that Phillips curve does not exist in Kazakhstan. Findings show that inflation and unemployment were much related variables. But there is a positive relationship between them. As we know from the literature of Economics, higher inflation causes lower unemployment and lower inflation causes higher inflation. Thus, findings of this research do not support the same relation. Research Hypothesis Testing the hypothesis: Inflation rate and GDP growth rate considerably influence unemployment rate = 0 H0: β 2 < 0 H1: β 2 ≥0 As it is seen from the hypothesis, we have taken 15 years as the degree of freedom, therefore we have used Student distribution, where T- test value was found as 1.1852. Using α=0.05 level of significant the two tail test t-test with 15 degrees of freedom has critical ± 2.16037. Because t-statistic 1.1852 < 2.16037, then, H0 is accepted, therefore it can be concluded that the first order parameter of the regressive model is insignificant and should not remain in the model. Therefore, according to the hypothesis, inflation rate and GDP growth rate does not have an influence on unemployment rate, because H0 has been accepted. [17]
Russia Comparative analysis of Russian data with that of other countries shows that Russia is in an extreme condition. Inflationary policy of Russia is special. The main regulatory tool is monetary policy today. Subject to certain adjustments and rounding tenths per month for a year, then we can talk about the level of inflation in Russia in 2013 - 6.5% and in 2012 - 6.6%, the index fell slightly in 2012. by 0.1%. Measures of monetary policy adopted by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation, to coordinate the inflationary processes in Russia were the following: a) improvement of the mechanism of lending under the pledge of non-marketable assets or guarantees of credit institutions; Belorussia The Belarusian economy had extremely high rates of inflation for the 1992-1994., When the consumer price index stood at 1070% in 1992, 1290 in% 1993 2321% in 1994. And until 1993, the inflation rate in demand was observed in the country. payments crisis originated in the country. Another factor was the huge uncontrolled public spending. Since 1993 - cost inflation. The reasons: higher prices for Russian raw materials and energy to the world level, a significant increase in production costs. In 1996, hyperinflation was halted. In 1997-1999 -a new round of unwinding of inflation and its surge in 1999, mainly demand-pull inflation. Since 2000 he held a moderately tight monetary policy and a decrease in the rate of inflation. In 2006 the economic situation was characterized by a slowdown in inflation and devaluation processes. The anti-inflationary policies occupy an important place administrative measures to curb rising prices (despite liberalization, specific regulation exists). The decline in inflation should be carried out at the same time improving the efficiency and competitiveness of enterprises in the real sector of the economy. Such an approach would minimize costs while maintaining a high level of employment, capacity utilization, and social protection. In the first stage (until 2010) the pricing policy will be aimed at achieving the rational from the point of view of an efficient economic structure of relative prices. The price mechanism should encourage the restructuring and modernization of the real sector of the economy, the transition to technologies with higher productivity, reorientation from labor-intensive to capital-intensive technology. In the foreign trade pricing provided to ensure increase in average export prices on the basis of the manufacturer's reorientation on complex high-tech products and improve the quality of exported products. Second stage (2011-2020) In the second stage the priority areas of pricing policy should be: restriction and suppression of monopolistic activity of economic entities, promoting competition, improving the regulation of natural monopolies. In the field of regulated pricing work will be aimed at phased reduction of cross-subsidies and budget in some sectors of the economy, such as housing and communal services, passenger transport. Reducing subsidies to be carried out by carrying out a series of measures to reduce the cost of providing these types of services, reducing the number of privileged categories of citizens. [21]
4. Anti-inflationary policy of the Republic of Kazakhstan Conclusion
In this study we tried to examine Kazakhstan’s inflation and unemployment by using time series analysis. At the beginning of report, we have explained the brief theory of inflation and the relationship between inflation rate and unemployment rate. At the end of this study, we forecasted inflation and unemployment through Regressive Time Series model separately. We found that this model fits to forecast inflation and unemployment. An effort was made to find the relationship between unemployment and inflation to confirm the reality of Phillips curve in Kazakhstan by the help of time series data for phase of 2000-2015. Unemployment rate is taken as dependent variable whereas inflation rate and GDP growth rate are taken as independent (explanatory) variables. Moreover, R- square is 0.59685, it must be conclude, that the explanatory variables “explains” 59.68 % of the variance of unemployment rate. A more exact measure of goodness of fit, which takes into account the number of explanatory variables, is the adjusted R – square. Adjusted R square shows an adequacy of model with 0.53483 that shows independent variables (Inflation and GDP growth rates) can predict 53.48% of variance in dependent variable (Unemployment). The F statistic shows overall effects of independent variable on our target variable. The F – statistic, which tests the overall significance of the sample regression, is 9.62304. Regression model is significant because, because P = 0.00273<0.05.The outcome of simple linear regression verifies the reality of positive relationship between unemployment and inflation. It can be saying easily that Phillips curve does not exist in Kazakhstan. Findings show that inflation and unemployment were much related variables. But there is a positive relationship between them. As we know from the literature of Economics, higher inflation causes lower unemployment and lower inflation causes higher inflation. Thus, findings of this research do not support the same relation. Likewise, in this report we have covered such popular topic as Anti-inflationary policy of the Republic of Kazakhstan. We have looked at the Action of National Bank, which was taken in 2014, the nature of anti-inflationary policy. List of Literature
1. KazReferatInfo. (2007, February 15). Retrieved March 9, 2016, from KazReferatInfo - Казахстанские рефераты: http://www.kazreferat.info/read/inflyaciya-i-krivaya-fillipsa-inflyaciya-v-kazahstane-MTE3MDcw 2. Aup.ru административно-управленческий портал. (1999, November 16). Retrieved March 20, 2016, from Тема 4. ЭКОНОМИЧЕСКИЕ ЦИКЛЫ, БЕЗРАБОТИЦА И ИНФЛЯЦИЯ: http://www.aup.ru/books/m202/13_8.htm 3. KazReferatInfo. (2007, February 15). Retrieved March 10, 2016, from KazReferatInfo - Казахстанские рефераты: http://www.kazreferat.info/ 4. Инфляция в Казахстане. (2008, April 6). Retrieved March 16, 2016, from Библиофонд: http://bibliofond.ru/download_list.aspx?id=702559 5. история Казахстана. (2012, July 12). RetrievedMarch 13, 2016, from Инфляция в Казахстане: http://e-history.kz/ru 6. Концепция развития финансового сектора 2007 – 2009// Официальный сайт законодательных актов РеспубликиКазахстан https://ru.wikipedia.org/wiki/%D0%9A%D1%80%D0%B8%D0%B2%D0%B0%D1%8F_%D0%A4%D0%B8%D0%BB%D0%BB%D0%B8%D0%BF%D1%81%D0%B0 7. О самых значимых делах. (2013, May 21). Retrieved March 9, 2016, from Экономика БГЭУ — Блог: http://www.econlib.org/library/Enc/PhillipsCurve.html 8. Инфляция в Республике Казахстан. (2014). Retrieved 2016, from baza-referat.ru: http://baza-referat.ru/%D0%98%D0%BD%D1%84%D0%BB%D1%8F%D1%86%D0%B8%D1%8F_%D0%B2_%D0%A0%D0%B5%D1%81%D0%BF%D1%83%D0%B1%D0%BB%D0%B8%D0%BA%D0%B5_%D0%9A%D0%B0%D0%B7%D0%B0%D1%85%D1%81%D1%82%D0%B0%D0%BD 9. СТРАТЕГИЧЕСКИЙ ПЛАН. (2014). Retrieved 2016, from NATIONAL BANK: http://www.nationalbank.kz/cont/publish469989_25924.pdf 10.СТРАТЕГИЧЕСКИЙ ПЛАН Национального Банка Республики Казахстан. (2014). Retrieved 2016, from national bank: http://www.nationalbank.kz/cont/publish469989_25924.pdf 11.Инфляция в Казахстане в 2014 году составила 7,4% – МНЭ РК. (n.d.). Retrievedfrom Казахстанская правда: http://www.kazpravda.kz/rubric/ekonomika/inflyatsiya-v-kazahstane-v-2014-godu-sostavila-74--mne-rk/ 12. Основные итоги реализации Концепции развития финансового сектора 2003 – 2006 // Официальный сайт в Интернете www.souz-atameken.kz. 13. Концепция развития финансового сектора 2007 – 2009// Официальный сайт законодательных актов Республики Казахстан www.zakon.kz. 14, Анализ инфляционных процессов Республики Казахстан. (2013, Апрель 23). Retrieved Март 14, 2016, fromВестник КАСУ Online Версия журнала: http://abmyod.aydin.edu.tr/makaleler/sayi37_38_39_40/time-series-analysis-a-case-study-on-forecasting-turkey 15. Стратегии индустриально-инновационного развития Республики Казахстан на 2003-2015 годы, Указ Президента Республики Казахстан от 17 мая 2003 года. - N 1096.- С.32; https://www.tcd.ie/Economics/assets/pdf/SER/2002/An%20Econometric%20Analysis%20of%20Information%20and%20Unemployment%20in%20Ireland%20By%20Orson%20Francescone.pdf 16. Анализ инфляционных процессов Республики Казахстан. (2013, Апрель 23). Retrieved Март 14, 2016, fromВестник КАСУ Online Версия журнала http://irmbrjournal.com/papers/1371452025.pdf 17. Основные направления денежно-кредитной политики Национального Банка Республики Казахстан на 2008-2009 годы, Правления Национального Банка Республики Казахстан от 24 декабря 2007 года №146; О методах сдерживания инфляции в Казахстане.- Жеты кун / "Хабар". - Номад, Казахстан.- Официальный Сайт в Интернете https://www.tcd.ie/Economics/assets/pdf/SER/2002/An%20Econometric%20Analysis%20of%20Information%20and%20Unemployment%20in%20Ireland%20By%20Orson%20Francescone.pdf
18. Р. Даукенов Инфляция: причины, сущность и методы борьбы// Қаржы-Қаражат.-2009г.-№12.- С.61. 19. Основные направления денежно-кредитной политики Национального Банка Республики Казахстан на 2008-2009 годы, Правления Национального Банка Республики Казахстан от 24 декабря 2007 года №146;
Introduction
The aim of this research is to clarify the relationship between unemployment and inflation in Kazakhstan. Time series data shall be used for the phase 2000-2015. Unemployment rate is taken as dependent variable whereas inflation rate is taken as independent variable. The link between them would be finding by Simple Linear Regression. This research will conduct by using the method of Regression. The key reason of this work is to examine ways of extending the theory of inflation and unemployment. This research is about time series analysis and forecasting Kazakhstan’s inflation and unemployment. The most important purpose for selecting this topic is to get the knowledge and identify the different time series models. The idea of this report is to know the logic of inflation and unemployment strategy of Kazakhstan’s government and fluctuation of both in different years. To forecast Kazakhstan inflation by exercising models of econometric and to describe the term of inflation and unemployment broadly by studying historical data. Kazakhstan has practiced extreme and insistent inflation for more than twenty years. Inflation is one of the most important concepts in economics. In the basic level inflation is a rise in prices. When there is raise in the price of goods and services, than the value of dollar shall go down, as we will not be able to buy as enough with the dollar as we could have last time or last period. Mostly people thinks that inflation is the increase in price but according to economist inflation is the decreasing power of dollar. [1] Later on, the anti-inflationary policy of Kazakhstan will be covered in this report. The international experience of such countries, as: Russia and Belorussia.
Main characteristics of inflation
The essence of inflation In modern conditions in many countries, great importance has become a phenomenon of inflation. Inflation (from the Latin Inflation - swelling) - is the process of depreciation of money, reflected in the overall increase in prices. Inflation has been associated with the emergence in ancient times devalued money - coins spoiled, loss of purchasing power which often led to riots. In the XVII century Europe there was impairment of gold money, known as "price revolution". It was caused by pouring into Europe from the New World the flow of precious metals. In subsequent periods, the inflation depreciation of paper money were exposed. Since the mid 60-ies of XX century, inflation has become one of the central macroeconomic problem for many countries, both developing and industrialized. [2] The impact of macroeconomic factors on the development of inflation in many countries has been extensively studied in the economic literature, especially in the framework of the monetary approach. Inflation as a process is a devaluation (depreciation) of paper money, which leads to higher prices for goods and services and resources. The theoretical aspect of communication with the release rates of the money supply, a mismatch in the mechanisms of supply and demand, a surplus of the consumer, the budget deficit, outpacing wage growth. The most commonly used indicators are price index. Indirect indicators of inflation, which may serve as indicators of its appearance, are the high growth of the money supply as a percentage increase in nominal interest rates, the availability and size of gold and currency reserves, the ratio of foreign exchange reserves and the money supply. The process of the opposite of inflation, which is manifested in a general fall in prices is called deflation (from the Latin deflatio -. Deflation). Under the disinflation understand slowdown in price growth. [3]
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Последнее изменение этой страницы: 2016-08-06; просмотров: 836; Нарушение авторского права страницы; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! infopedia.su Все материалы представленные на сайте исключительно с целью ознакомления читателями и не преследуют коммерческих целей или нарушение авторских прав. Обратная связь - 3.145.108.87 (0.023 с.) |