
Заглавная страница Избранные статьи Случайная статья Познавательные статьи Новые добавления Обратная связь FAQ Написать работу КАТЕГОРИИ: ТОП 10 на сайте Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрацииТехника нижней прямой подачи мяча. Франко-прусская война (причины и последствия) Организация работы процедурного кабинета Смысловое и механическое запоминание, их место и роль в усвоении знаний Коммуникативные барьеры и пути их преодоления Обработка изделий медицинского назначения многократного применения Образцы текста публицистического стиля Четыре типа изменения баланса Задачи с ответами для Всероссийской олимпиады по праву 
Мы поможем в написании ваших работ! ЗНАЕТЕ ЛИ ВЫ?
Влияние общества на человека
Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрации Практические работы по географии для 6 класса Организация работы процедурного кабинета Изменения в неживой природе осенью Уборка процедурного кабинета Сольфеджио. Все правила по сольфеджио Балочные системы. Определение реакций опор и моментов защемления |
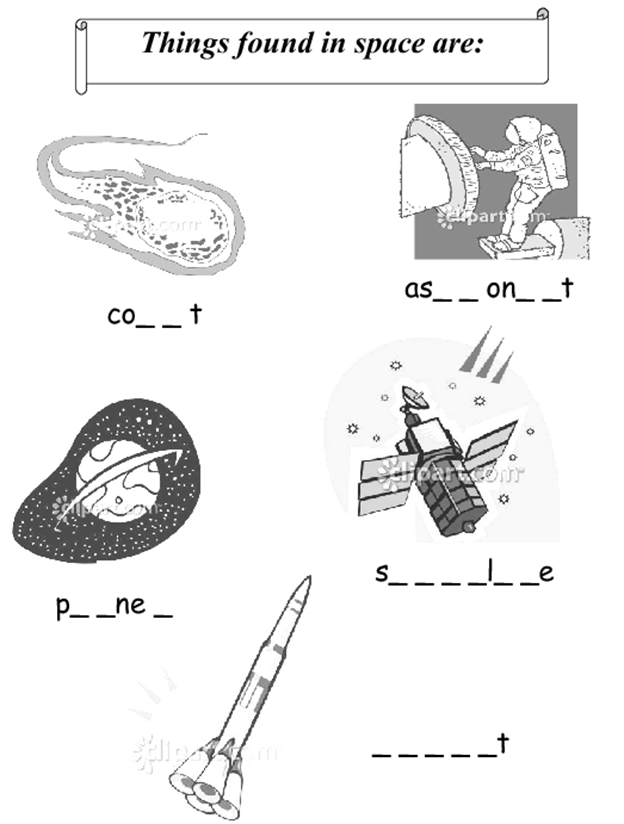
Check your answers: planet, comet, satellite, rocket, astronaut.Содержание книги
Поиск на нашем сайте
MODULE 12 Space Exploration Guess the words in the picture:
Check your answers: planet, comet, satellite, rocket, astronaut. Part I Text 12A Before you read, discuss the following: · What comes into your mind when someone says “Space exploration“? · What is the greatest achievement in space exploration in your opinion? · Can you remember the names of people who contributed greatly into space research? · Do you believe that there is life on other planets? Do you think that humans will ever go and live on other planets? «The Earth is the cradle of the mind-but Read the words and mind their pronunciation reconnaissance [rɪˈkɒnɪs(ə)ns], Saturn [ˈsætən], Uranus [jʊˈreɪnəs], Neptune [ˈnɛptjuːn], Earth [ɜːθ], Mars [mɑːz], Venus [ˈviːnəs], Mercury [ˈmɜːkjʊrɪ], habitable [ˈhæbɪtəb(ə)l], species [ˈspiːʃiːz], Copernicus [koʊˈpɜːrnɪkəs], Galileo Galilei [ɡaliˈlɛːo ɡaliˈlɛi] Do you know the order of the planets in the Solar System? If not, the following mnemonic rule might help you to remember it: «M y V ery E ducated M other J ust S erved U s N achos » Learn the following words and phrases cradle (n) - колыбель eternally (adv) - постоянно reconnaissance (n) – разведка, расследование habitable (adj) – пригодный для жилья essential (adj) – необходимый, непременный extraterrestrial (adj) - внеземной, находящийся за пределами Земли to suit (v) – подходить, соответствовать, быть пригодным rather than - скорее чем; не столько... сколько prominent (adj) – выдающийся to result in/from (v) – приводить к, иметь результатом/ являться результатом to figure out (v) – вычислять, понимать, постигать to manage to do (v) – суметь сделать что-либо to overweigh (v) – перевесить, оказывать большее значение profound (adj) – основательный, глубокий replenish (v) – пополнять to commit oneself to (v) – посвящать себя чему-либо Reading Grammar: do ex-s 8, 9, 10 p.238-239, and then look through the text once again and define the functions of the underlined words and phrases Ex. 1 Read the following statements about space exploration (based on the text above). Say whether they are true (T), false (F) or the information is not given (Not Mentioned – NM) 1. Space exploration means investigation of interplanetary or interstellar space, its properties, biology and the bodies that exist within it. 2. Space research is carried out by astronauts during their missions. 3. Space travel without science is tourism. 4. Outer planets like Venus and Jupiter could be reached with current crewed space flight technology. 5. Tsiolkovsky was the first to launch a rocket into space. 6. The ISS is an international endeavor (попытка, стремление) of global collaboration, with more than 220 astronauts from 17 countries visiting the ISS since 2000. 7. The ISS was designed for testing space craft systems and equipment for missions to the Moon and Mars. 8. The possible benefits from exploring space outweigh the risks and money spent on this industry.
Ex. 2 Answer the questions: 1. How is the space exploration carried out? 2. Why are many space missions suited to telerobotic? 3. What are the most important reasons for space exploration? 4. What do you know about Konstantin Tsiolkovsky? 5. Why is the ISS one of the most ambitious and successful projects? 6. What was the ISS designed for? 7. How could future space exploration benefit people? Ex 3. Practice chain questions. Ask a group-mate a question about information provided in Text 12. The student who has answered the question asks another student a question, who answers it and so on. Ex. Question: What does the term “space exploration” refer to? Answer: It refers to… What Which How Why Who Ex. 4 Find terms/words in Text 12A corresponding to the following definitions: 1. a person who studies the physical world (n) 2. man-manned device put in orbit round a planet (n) 3. travel into or through an area in order to learn about it (v) 4. to do a task as required (v) 5. a test done in order to learn smth. (v) 6. the area beyond the earth around the planet and stars (n) 7. to understand or solve smth. (v) 8. the branch of science that deals with rockets and rocket propulsion (n) 9. necessary, most important (adj) 10. favourable time, occasion (n) 11. lasting for a long time or forever (adj) 12. profit, gain (n) 13. sort, type (n) (pl unchanged)
Ex. 5 Fill in the gaps in the text below with the words from the box in their correct form:
(1) ______ have already (2) ______ (3) ______ (4) ______ the surface of Mars, and (5) ______ (6) ______ to see if they can (7) ______ any signs of life. So far, they (8) ______ any, but the (9) ______ of rocks from Mars that they (10) ______ by the (11) ______ of water and wind. In other words, life (12) ______ in the past.
Ex. 6 Learn some more words related to space exploration The Universe and Space Exploration English Vocabulary An orbit - the path an object in space takes while it moves. Generally, objects in space such as planets and comets take elliptical orbits around larger objects, such as a star. An asteroid - a combination of rocks and iron that is too small to form a planet. There are many asteroids that orbit the sun between the orbits of Jupiter and Mars. A comet - a small body of gas and ice orbiting around the solar system. We can see the tail of the comet because it is the sun heating and melting the ice. The most famous comet is Halley's Comet which is visible from Earth every 75-76 years. A star - made up of clouds of gas and dust. Many people love to go outside at night and count the stars, but there are so many that it is impossible for one person to count them all. A constellation - a group of bright stars that form shapes or 'pictures' in the sky. The Southern Cross is a constellation in the Southern hemisphere that points towards the South Pole. The Big Dipper is a constellation in the Northern hemisphere that is in the shape of a ladle or a large spoon. The sun - the star in the middle of our solar system. The eight planets in our solar system all orbit around the sun. The closest planet to the sun is Mercury and then comes Venus. The planet that we live on is called Earth. It is the third closest planet to the sun in our solar system. Mars is the fourth planet from the sun. It is a small red planet, named after the roman god of war. Jupiter is the largest of all the planets in the solar system. The next planet is Saturn which has thin rings around it. Uranus and Neptune are the next two planets after Saturn. Pluto used to be considered a planet, but now is called a dwarf planet because it is so small. Its orbit is further away from the sun than any of the other planets. A solar eclipse - moment when the moon's orbit comes between the earth and the sun and it looks like the sun is blacked out. We can only see the edge of the sun around the moon. A lunar eclipse is when the earth prevents sunlight from reaching the moon. Because the moon orbits the Earth and the Earth orbits the sun we can only see parts of the moon at a time. This cycle happens every month. A new moon is when we can not see any of it. This shows the beginning of the cycle. Half way through the month we can see the full moon. A full moon makes the sky bright at night because it reflects the light of the sun. The galaxy we live in is called the Milky Way. It is made up of billions of stars. A telescope - an instrument which has reflective lenses that allows us to see the objects in the sky closer and clearer. It magnifies objects that normally cannot be seen unaided. Some telescopes are very powerful and can be used to see thousands of light years away. There are many large powerful telescopes in the north of Chile. An astronaut - a person who leaves Earth and goes into space. Many of them work in the international space station and do scientific experiments. Astronauts need to wear space suits because it is very cold in space and they do not have oxygen to breath. A spacecraft (plural – spacecraft) - any type of vehicle used for travelling in space. There are many different types of spacecrafts. A space shuttle is a spacecraft used for repeated use in between earth and a space station and contains astronauts. A rocket - the type of plane that astronauts used to use to fly into space. Now they are used to leave satellites in orbit around the Earth. It has a special cylindrical shape so that it can go very fast for a long distance. A space probe - a type of space craft that does not have a person inside. Space probes can be sent to far away distances for long periods of time to gather information about different areas in space. A lunar module - a small craft used for travelling between the moon and the larger space craft orbiting the moon. When the first men walked on the moon they came out of the lunar module. The first man to walk on the moon said "One small step for man, one giant leap for mankind." UFOs - unidentified flying objects Ex. 7 Guess the words associated with the topic and circle the correct answer. 1. A ___ group of bright stars that form shapes or pictures in the sky. a. moon b. constellation c. satellite d. meteor 2. A ___ is a small body of gas and ice orbiting around the Solar system. Sometimes it appears to have a tail from the Sun heating and melting the ice. a. star b. space probe c. constellation d. comet 3. An ___ is a combination of rocks and iron that is too small to form a planet. There are many between the orbit of Jupiter and Mars. a. asteroid b. astronaut c. orbit d. eclipse 4. The Sun is a ___ in the middle of our Solar System. a. rock b. star c. constellation d. comet 5. ___ is the planet that is closest to the Sun. a. Venus b. Mercury c. Mars d. Uranus 6. The largest planet of our Solar System is ___. a. Venus b. Uranus c. Neptune d. Jupiter 7. The planet that doesn’t have rings around is ___ a. Neptune b. Mercury c. Earth d. Jupiter 8. ___ is when the Moon’s orbit comes between the Earth and the Sun and it looks like the Sun is blacked out. We can only see the edge of the Sun around the Moon. a. Solar eclipse b. Lunar eclipse c. Black night d. Solar storm 9. The galaxy that we live in is called the ___. a. Moonwalk b. Astro System c. Milky Way d. Slimy Way 10. An ___ is a person who leaves the Earth and goes into space. a. asteroid b. astronaut c. astronomer d. asterix 11. A ___ is sent to very far for a long period of time to gather information about different areas in space. a. space station b. space shuttle c. space probe d. space bar 12. A ___ is an instrument that allows us to see distant objects in the sky closer and clearer. a. magnifying glass b. satellite c. telescope d. comet 13. The constellation in the Southern Hemisphere that points towards the South Pole is the ___. a. Big Dipper b. Skinny Finger c. Southern Point d. Southern Cross e. 14. The ___ is a constellation in the Northern Hemisphere that is in the shape of a ladle or a large spoon. a. Big Dipper b. Southern Cross c. Kitchen Spoon d. Great Scoop 15. The most famous comet is _____. It is visible from the Earth every 75-76 years. a. Harold’s b. Harriet’s c. Henry’s d. Halley’s 16. A ___ is made up of billions of stars. a. constellation b. galaxy c. Solar System d. Hollywood movie 17. Rockets are used to leave ____ in orbit around the Earth. a. rocks b. astronauts c. satellites d. space suits 18. A ___ was a small craft used for travelling between the Moon and a larger spacecraft orbiting the Moon. a. moon b. full moon c. lunar module d. lunar eclipse 19. The first words of the astronaut who stood on the Moon for the first time were: ___. a. “I am glad I can stretch my legs now; that lunar module is cramped” b. “There is much dust here, they need sweep a bit more often” c. “One small step for man, one giant leap for mankind” d. “Can you turn the lights down? They are still a bit too bright” 20. UFO means ___. a. Unique Friends Only b. Uniform Fighting Officer c. Unidentified Flying Object d. Unusual Floating Obstacle Ex. 8 Combine the two parts from the table to make one sentence:
Ex. 9 Highlight all the benefits of space exploration mentioned in Text 12. Start to fill in the table, giving reasons for and against space research. Add some more after watching the movie and listening to audio files
Ex. 10 Match the numbers given below with the information in the pictures
· 22 · 34 · 930000 · 6 (x2) · 29 · 7 · 1760 · 26500 · 1200 · 83 · 13
Ex. 11 Solve the crossword Space Exploration Crossword Puzzle
Across
l. An is someone who travels in space. 3. is our closest neighboring planet. 4. A is a hug ball of burning gas, held together by its own gravity. 5. is used to describe anything of or relating to the Moon. 7. The orbits the Earth once every 28 days. 9. power helps power the International Space Station (ISS). ll. Our galaxy is called the. l5. is the eighth planet from the Sun. l9. The International orbits the Earth l6 times a day. 20. is our home planet. 2l. is the second planet from the Sun. 24. The Earth takes 365 days to the Sun. 26. is the power of certain forces of nature to do work. 30. NASA’s Human and Development of Space (HEDS) Enterprise helps bring space technology down to Earth. 32. Astronauts on the ISS like in space. 33. The is the center of our solar system. 34. Each Shuttle mission has a specially trained of astronauts. 37. is near weightlessness, almost zero gravity. 39. To __is to study and observe something to learn more about it. 4l. The __is everything that exists anywhere on Earth or in space. 42. The Space Shuttle lifts off from the pad.
Down
2. Our contains the Sun and all the planets that orbit the Sun. 3. is the planet closest to the Sun. 4., the sixth planet from the Sun, is known for its rings. 6. NASA wants to have more astronauts living and in space. 8. A is a region where people live near an uncharted or unexplored area where there are no people. l0. There are nine _____ in our solar system. l2. To is to search or travel to discover new things. l3. is the planet that is farthest from the Sun. l4. The Space transports astronauts and cargo into space. l6. is science as it is put to use in the work of everyday life. l7. Scientists send on the ISS to test the effects of microgravity. l8. refers to any type of vehicle that travels in space. 22. is everything beyond the Earth’s atmosphere, where the Sun, stars and other planets are. 23. is the largest of the planets. 25. The Space Station is NASA’s laboratory in space. 27. Stars and solar systems grouped together form a. 28. is the seventh planet from the Sun. 29. A Russian astronaut is called a. 3l. A is a place where scientists can work and do experiments. 35. HEDS stands for the Human Exploration and of Space. 36., known as space rocks, are found especially between the orbit of Mars and Jupiter 38. are designed to do things that are too dangerous for astronauts to do. 40. means belonging to the group that includes all people.
Text 12B Before you read A) Discuss these questions with a partner. a. Are you interested in space travel? Do you have any desire to travel to another planet? Why of why not? b. Do you think space exploration is important? What can scientists learn from studying other planets? c. Do you think there is life anywhere else in the universe? Explain your answer. B) Skim the article. Circle the correct answer. a. What is the article mainly about? i. the benefits of space research ii. new research about the planet Mars iii. the possibility of life on Mars b. What is the aim of the article? i. to get the reader exited about the new research ii. to dissuade the reader from going to Mars iii. to teach the reader how to measure gravity on Mars c. What is the tone of the article? i. humorous ii. depressing iii. enthusiastic C) Learn the meanings of the following words and phrases before you read the article. mission – полёт iron out – улаживать, справляться с трудностями gravity - гравитация collaborator – соратник automated – автоматизированный shelter – укрытие boost – ускорять composition – состав Destination Mars If you’re lucky, you might someday walk on the surface of Mars. For some scientists, the question is no longer WHETHER people will ever get to Mars. It’s a question of WHEN people will travel there. The most cautious of the bunch say it may take many decades to overcome the obstacles standing in the way of such an expedition. Others are more optimistic. “I’d like to think that missions will be going there as early as 15 years from now”, says Paul Wooster. He’s director of the Mars Gravity Biosatellite Program at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). Whether or not you want to go to Mars yourself, the Red Planet is exciting. Two radio-controlled robots, or rovers, named Spirit and Opportunity, are now exploring the planet. The rovers are sending back amazing images and information about places that scientists had never before studied in such detail. Before any of us can vacation on Mars, though, there are still plenty of complications to iron out. Some of the biggest questions have to do with the human body. We are fine-tuned to deal with conditions here on Earth. No one knows how our bodies might react to living on another planet. Gravity, in particular, is a big concern. Because Mars is smaller and less massive than Earth, its gravity is weaker then Earth’s. A person weighing 100 pounds on Earth would weigh just 38 pounds on Mars. What’s more, astronauts would experience zero gravity during the year or more of travel time going to and from Mars. When astronauts spend time in zero gravity, their muscles and bones break down. It’s as if they had been lying motionless in bed for a long time. If astronauts don’t do weigh-bearing exercises while they’re in orbit aboard the space shuttle or space station, it can be difficult for them to walk when they get back. The longer astronauts spend in space, the longer it takes them to recover. A mission to Mars would last at least two and a half years, including travel time. That’s much longer than anyone has previously spent in outer space. Mice in Space To find out how mammals might get along on Mars, Wooster is planning to send 15 mice into outer space. Each mouse will have its own cage. For five weeks, the spacecraft will spin just enough for the mice to experience the gravitational pull found on Mars. Over the course of the mission, Wooster and his collaborators (which include more than 100 college students around the world) will monitor the health and activity levels of the mice. Each cage will be built to collect urine samples on cloth pads underneath a mesh barrier at the bottom of the cage. Every few days, an automated system will roll up and store the urine-soaked pads. When the mission return to Earth, the scientists will look at chemical markers in the urine to measure how quickly muscles and bones break down. “This is going to be the longest partial-gravity study on mammals in space”, says Wooster, who hopes to launch the mission next year. What happens to mice could also happen to people. The data that researches collect will help determine how much exercise and what types of activity Mars travellers might need to stay healthy and strong for the entire trip. Travel to Mars presents other complications. Mars doesn’t have any grocery stores or fast-food restaurants. Plants don’t even grow there. And the rovers still haven’t found pools of liquid water on the planet. So, astronauts will have to bring all their food and water with them – enough to last several years. Also, it will be impossible for people to breathe Martian air, which is 95 percent carbon dioxide. Earth’s atmosphere is 78 percent nitrogen, 21 percent oxygen, and about 0.035 percent carbon dioxide. Therefore, astronauts will need reliable spacesuits, pressurized vehicles, and airtight shelters to survive on Mars. Heavily insulated clothes will also be essential. Because Mars is father from the sun than Earth, it gets extremely cold in winter, with temperatures as low as -111 degrees Celsius. And a Martian year lasts 687 Earth days, so that’s a lot of cold days. Planetary Research Putting people on Mars would be a huge boost for planetary research, Wooster says. “In a couple of hours at most, an astronaut can do pretty much everything the rovers are doing currently”, he says. “And an astronaut can do it much better and more comprehensively”. Already, Spirit and Opportunity have turned up some interesting findings about the rocks dirt and landscape of Mars. Opportunity, for instance, dug a trench with its front wheel. Analyses showed that the soil composition changes with the depth. The way the soil is packed together suggests the presence of small amounts of water in the past. On the other side of the planet, Spirit found the top layer of soil to be stickier than expected. One possibility is that liquid water that was once present in the soil combined with salts to produce the stickiness. Finding water on Mars would be an enormous triumph. Water makes life possible here on Earth. So, finding signs of water on Mars would indicate that life might have existed there in the past and could still be there today. Today, mobile robots are exploring Mars. In a few years, mice may experience Mars in their own way. Looking father ahead, people like you might get to walk across the Red Planet’s dusty surface one day. · fine-tune – to make small changes in something to make it the best it can be · mesh – material made of threads or wires that have been woven together like a net · pressurized – refers to an aircraft in which the air pressure inside is similar to the air pressure on the ground · airtight – not allowing air to get in or out · pound = 453,6 grams Comprehension check A) Answer these questions with the information from the article. a. Who is Paul Wooster? b. What are Spirit and Opportunity? c. What are they doing? d. What problems do scientists have to resolve so that astronauts can survive on Mars? e. Why is Wooster sending mice into space? f. Why would finding water on Mars be such an important discovery? B) Decide if each statement is a fact or an opinion. Check the correct box.
Vocabulary practice A) Match each word of phrase with the correct definition.
B) Complete each sentence with the correct word or phrase from Exercise A. Be sure to use the correct form of the words. 1. There is less _________ on the Moon than on Earth. 2. We are living in a temporary _________ because our house was destroyed in the hurricane. 3. We _________ a few problems, and now the plan is working well. 4. A _________ to Mars would take about two and a half years. 5. Dr. Johnson and his _________ are developing a new device to measure the blood pressure of astronauts. 6. The new shopping center was a _________ to the economy of our city. 7. When we studied the _________ of the rock, we found it contained quartz. 8. ATM stands for _________ teller machine.
Talk it over - Discuss these questions as a class. 1. Would you like to visit Mars in the future? Why or why not? 2. In addition to the physical difficulties of living on Mars, what other problems might astronauts on the planet face? 3. Why do think Mars is a good place to study to find out whether there is the life anywhere else in the universe?
Research a Planet – Use the Internet or library to do some research about one of the planets in our solar system. Use the list below as a guide. Share your information with your classmates. · name of the planet · how the planet got its name · size and diameter of the planet · description of the planet’s rotation around the sun · moons · your weight on the planet · distance from Earth and from the Sun · the planet’s average temperature
Text 12C Before you read: A – Discuss these questions with a partner: After watching With your partner take turns asking and answering the questions. 1. Why are asteroids dangerous for our planet? 2. Why does space exploration matter? (Give 5 reasons based on the movie) 3. What reasons against space exploration are mentioned in the movie?
Note: nitinol - нитинол
Ex.3 Listening I Discuss the following questions: 1) How does Moon look like if you look at it from Earth? 2) Do you believe that life on Mars is possible? 3) Have you seen/read the movie/book “The Martian”? Do you think the events described will be a reality soon? Vocabulary: to be fascinated – быть очарованным, заворожённым weird – таинственный, фантастический, странный with the naked eye – невооружённым глазом tantalizing – волнующий, провоцирующий pretty cold – довольно холодный arid – сухой, безводный harsh – агрессивный, суровый collision – столкновение disrupt – прерывать, разрушать extremophiles – экстремофилы (совокупное название для живых существ, в том числе бактерий и микроорганизмов, способных жить и размножаться в экстремальных условиях окружающей среды, т.е. в низких/высоких температурах, чрезвычайном давлении и радиации) meteorite – метеорит evolved – развиваться, эволюционировать 1. Why do people get excited about the possibility of life on Mars? 2. What have you learned about the conditions (temperature, atmosphere) on the planet? 3. In what form does water exist on Mars? 4. Why doesn’t solar radiation kill human beings? 5. How might life on Mars have evolved? Listening 2 Before you listen, could you guess what topic is going to be discussed? Is there a wide range of opinions about the true value of space flight? Suggest one of your own and after listening compare them to the narrator’s view. Try to suggest the true reasons why we should explore the space. Vocabulary: tangible – вещественный, материальный; ощутимый, заметный consciousness – осознание, понимание cost effective – экономически выгодный controversial – спорный, сомнительный to stir up somebody with – побуждать, возбуждать, всколыхнуть, взволновать, активизировать to embed – вкладывать, заключаться capabilities – возможности machinery – механизмы, машины, оборудование descendants – потомки
I wonder if Don’t you think Are you suggesting Do you know How does… What would you do…in case It can be helpful to explain the background to your question before asking it. It is known as a lead-in to the question. Example You mentioned that the costs of privately run space vehicles will be much lower than those for government space flight programmes. Do you have any data or evidence to support this? 1. It takes a while for your body to adjust. I spent about three days being sick at first. Some people feel OK very quickly, but others clan be sick for up to a week. 2. Sleeping is the hardest part. It’s actually very comfortable, but really, really noisy, because of fans and other equipment running all the time. And of course you’re excited, so feel pretty sleep-deprived after a while. 3. From space, looking down on the Earth, you realize just how thin the atmosphere is. There’s this huge planet and just this tiny, thin atmosphere. 4. I think there’s great opportunity for private enterprise in space, whether it’s for tourism or commercial industry, or even exploration. I think private companies, over the next few decades, are going to achieve amazing thing in space. 5. There’s a great sense of community among the crew, even though we’re all from different countries. Most people either speak Russian or English, because we all have language courses during our training, and we communicate just fine.
B. A professional astronaut has just given a lecture; at the end they are asked some questions. Complete the lead-ins and questions below with the phrases in the box.
1. You ________ go back into space. Why is that? 2. You ________ looked from space. Do ________ changed since global warming started? 3. You mentioned plans by Space Agencies to return to the Moon. ________ expensive in this time of economic crisis? 4. You suggested humans would live on Mars one day. ________ within our lifetime? 5. There have been many discoveries in space, ________? Which do you think has been the most important? 6. Many people in this hall believe in UFOs and extraterrestrials. ________ already be here if there were any? 7. You mentioned not being afraid of going into space. Was ________ you were worried about? 8. You touched upon retirement. Is ________ remembered for?
C. Work in groups. Comment on the following statement: Space exploration ought to be abandoned (отказываться от чего-либо, прекращать что-либо/делать что-либо) until more important problems of mankind have been solved. One point of view: Space exploration is very expensive; food production is far more important than Mars studies or Moon walks; it is immoral to spend huge sums of money on space exploration while millions of people suffer hunger (голод); space exploration is useless anyway because we can’t colonize other planets; it would be much better to colonize, for example, the Sahara before trying to colonize the Moon or Mars; mankind must not waste its resources. A contrary point of view: Space exploration is of great significance for scientific and technological development; space exploration gives new knowledge that could be used for other purposes; we might find 10000 things to do on the ISS that nobody has thought of or even imagined. Words and word combinations to help you:
Ex. 1. Look at the writing assignment. What should the article be about? What ideas do you think might be mentioned?
The editor of Popular science magazine has invited readers to think about the value of space research. She has claimed: “The huge quantities of money that governments spend on space exploration should be used to solve problems on Earth”. Do you agree?
Ex. 2. Now read the article a student has written in an answer to this task and choose a more eye-catching and suitable title. A. Space research is really important for everyone B. Exploring space is a waste of scientists’ time and tax-payers’ money C. Space - the final frontier for scientific research? D. Space exploration - money well spent? Article: Space exploration I strongly agree that the amount of money spent on space exploration should be reduced. There are many scientific areas that don’t have enough government interest. In fact, I firmly believe money spent on space exploration should be spent on Earth. Most of us agree that governments are only interested in spending money on space, arms and defense. I suggest this money could be better spent on exploring our seas. Did you know that 70% of the Earth is covered by water? I’m absolutely certain we could learn much more from our oceans than planets that are millions of kilometers away. There are so many problems on Earth: famine and drought in Africa, poverty and unemployment in many parts of the world, not to mention global warming and the fact that we are destroying our precious planet. Why do our best scientists research outer space instead of investigating, for instance, renewable energies? To conclude, I think politicians should solve problems on Earth instead of spending valuable time, money and resources on space. Ex. 3. Match these ideas 1-7 to the correct paragraph in the article. Two of the ideas are not mentioned. 1. Space exploration is necessary in order to find out more about other planets. 2. The money spent on space exploration should be spent on solving problems on Earth. 3. People think too much money is spent on space. 4. Exploring the World Ocean would tell us more about our planet than exploring space. 5. Examples of problems on Earth that need to be solved. 6. It is difficult to say whether we should spend less on space exploration. 7. Politicians should do more about solving problems on Earth.
Ex. 4. Which expressions does the writer use to express a strong opinion? Ex. 5. Complete these sentences about writing an article using the words on the box.
1. It has an _____________title. 2. It uses questions to engage and_____________. 3. It gives_____________ to help illustrate the main points. 4. It is divided into different paragraphs, each with a ____________. 5. It uses _____________ language. 6. It gives a conclusion or _____________ at the end of the article.
Ex. 6. Which of the statements in Exercise 5 are true about the article on space exploration? You have been asked to contribute to a science blog that includes articles on topics such as new technologies, space research, discoveries and inventions. Ex. 7. Look at the task and write an article (using between 120-180 words) on the topic: Space exploration is essential.
Writing skills Remember to · Brainstorm your ideas before you write; · Plan your paragraphs; · Give specific examples, where appropriate; · Use a more formal writing style · Use varied and interesting language (e.g. Questions, adjectives and adverbs) to interest the reader; · Include a conclusion and final comment; · Think of a short, eye-catching title; · Check your writing for basic grammar and spelling mistakes.
Student Research Projects Students can deal with research projects at many different levels of sophistication, the following list presents only some potential research topics. They cover a wide range of topics; obviously, science is the focus, but there are also links to other subjects including family studies, nutrition, environmental studies and geography. The list of topics has the potential to be endless. The list was developed using "the availability of resources" as one of the key criteria. It should be viewed simply as a starting point for ideas related to student research.
Suggested Topics 1. How does the climate of Mars compare to that of Earth? 2. What technologies should be implemented to allow the growing crops on Mars? 3. Review several space-related films and identify "errors" in how life in space is depicted. 4. Is there microbial life in the surface layers of Mars? 5. The Moon will play an important role in the future space travel. Research to find out what the plans are for the future Moon expeditions. 6. How will travel to, and working on the Moon assist in the plans for space travel to Mars? 7. Is there any true Paleobiological evidence of life on Mars? 8. How can research related to farming on Mars be applied to practices here on Earth? 9. What is the relationship between science fiction and space travel reality? 10. Sputnik went up in 1957. Then, the United States became more active in the space program. What countries are now in the "space race" and what are their major areas of focus? 11. You have an idea for space exploration. Research how you could find out if it is practical. 12. Should human space travel be replaced with robots? 13. Compare the exploration of space to the exploration of a new area in the history of the Earth - the Americas, Africa, or the expedition to the top of Mount Everest. 14. Should the exploration of space be controlled/financed by countries or should the process be privatized? 15. Research Newton's laws of motion and design a demonstration of Newton's first or third law. The demonstration must be applicable to space travel. A possible extension might involve students' study of the relationships among force, mass and acceleration [Newton's 2nd law] and the design of an experiment to test the variables. 16. Although many young people would like to be astronauts, it is statistically more difficult than becoming a major league athlete. However, there are many alternative occupations related to the space program that will demand scientific and technological expertise. Research one area of interest related to space and/or space agriculture, and outline the educational path it would take to work in this area. 17. On Earth we may have to deal with sunburn as a consequence of working outdoors in summer. Research the effect of radiation on astronauts and, in particular, on astronauts who may be spacewalking during the construction of the International Space Station. 18. Research the effect of radiation on the development of plant life for space travel. 19. Research one of the following aspects of life support in space - food, water, waste disposal, atmosphere control, or fire protection. 20. Is it possible to use solar rays in space to make a space "sailing ship" move through space, thus creating an energy efficient space craft? 21. Research the earth's magnetosphere - how it works, its components, the benefits for us on earth, how it is detected from a spacecraft. 22. Research how food will be produced within closed life-support systems as a means of enhancing self-sufficiency and crew health during long space missions. 23. Tomatoes are the focus for this study; research to determine the role of other potential food sources that have been studied for long-term space travel. Outline the advantages and disadvantages of each. Rank order a list of potential foods for long-term space travels. 24. Research the topic of "space medicine". 25. Design a habitat for living on Mars for 6 astronauts for a period of six months; the habitat would include bedrooms, bathrooms, exercise area, kitchen, laboratory and medical station. 26. Design a kitchen appliance that could be used on the surface of Mars. 27. Research the nutrition issues facing astronauts when travelling to and from Mars. 28. Design a greenhouse for implementation on the surface of Mars. Consider Mars' weather conditions – temperature level and moisture availability, chemistry, radiation and gravity. 29. Investigate the climate and physiography of Devon Island to determine the rationale for choosing this site for the CSA Mars simulation studies. 30. Research the time-line from now until a trip to Mars takes place. Identify one major obstacle to overcome in the time-line and suggest solutions to eliminate the obstacle. 31. Research areas of the Earth that might be used for simulations of the Mars environment. Prioritize your choices and provide a rationale for the ranking. 32. Identify an environmental problem on Earth that may be solved by the application of space-based research on Earth; correlate the potential findings from space to the Earth-based environmental problem.
Part III (Grammar) Ex 3. Subjunctive test 1. Mr. A acted that way as if he _______ a foreigner. a. should be b. is c. were d. had been 2. It was suggested that each traveler _______ enough clothes on the trip. a. brought b. bring c. had better bring d. would bring 3. The writer _______ her job well, but she _______ so careless. a. could do, was b. had done, had been c. hadn’t done, had been d. could have done, was 4. He may even request that such an evil law __________. a. not be passed b. will be passed c. mustn’t be passed d. would be passed 5. If my car _______ out of gas, I would have arrived here. a. shouldn’t run b. didn’t run c. hadn’t run d. haven’t run 6. The Chairperson demanded the survey _______ by the end of the next week. a. should complete b. be completed c. would be completed d. was completed 7. Jack didn’t come yesterday, or you _______ him. a. were to see him b. would see c. had seen d. might have seen 8. Doris’s father insisted Doris _______ a rich man. a. be engaged to b. would be engaged to c. must be engaged to d. should engage to 9. _______ it rain tomorrow, we would have to put off the visit to the farm. a. Should b. Were c. Will d. Would 10. The president of the country gave the order that the whole nation _______ to go out at night. a. should not be allowed b. shouldn’t allow c. mustn’t be allowed d. not be allowed
Passive constructions with the verbs which can be followed by prepositions:
Mind the place of the preposition in Russian and English:
Some of the verbs are listed below: to send for – посылать за, to follow by -следовать за, to depend on – зависетьот, to deal with – иметь дело с, рассматривать, to refer to – ссылаться на, to rely on – полагаться на, to influence by – влиять на, to work at/on – работатьнад, to speak of/about – говорить о, to object to - возражать против, etc. Ex. 4 Translate into Russian: 1. The invention of an internal combustion engine was followed by the appearance of a motor car as we know it today. 2. The improvement of our working conditions and life is influenced by the achievements of scientific and technological progress. 3. International cooperation, especially in the field of space and science, may be spoken of as a long-standing tradition. 4. Lead is very slightly acted upon by the oxygen of the air. 5. In mechanics the study of kinematics is followed by the study of dynamics. 6. It is quite evident that not every experiment can be relied upon. Ex. 5 Translate into English: 1. На развитие физики значительно повлияло открытие радиоактивности. 2. На любой летательный аппарат действуют аэродинамические силы. 3. Против этих условий будут возражать другие ученые. 4. О новых разработках в области сверхпроводимости много пишут. 5. В механике за изучением кинематики следует изучение динамики. 6. За работами Циолковского последовал целый ряд очень важных работ в области космонавтики. MODULE 12 Space Exploration Guess the words in the picture:
Check your answers: planet, comet, satellite, rocket, astronaut. Part I Text 12A Before you read, discuss the following: · What comes into your mind when someone says “Space exploration“? · What is the greatest achievement in space exploration in your opinion? · Can you remember the names of people who contributed greatly into space research? · Do you believe that there is life on other planets? Do you think that humans will ever go and live on other planets? «The Earth is the cradle of the mind-but
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Последнее изменение этой страницы: 2016-04-26; просмотров: 1619; Нарушение авторского права страницы; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! infopedia.su Все материалы представленные на сайте исключительно с целью ознакомления читателями и не преследуют коммерческих целей или нарушение авторских прав. Обратная связь - 18.116.24.148 (0.015 с.) |



 Ex. 4. Listen to the text “Life on Mars” and say what you have learned about Mars. Answer the following questions.
Ex. 4. Listen to the text “Life on Mars” and say what you have learned about Mars. Answer the following questions.


