
Заглавная страница Избранные статьи Случайная статья Познавательные статьи Новые добавления Обратная связь FAQ Написать работу КАТЕГОРИИ: ТОП 10 на сайте Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрацииТехника нижней прямой подачи мяча. Франко-прусская война (причины и последствия) Организация работы процедурного кабинета Смысловое и механическое запоминание, их место и роль в усвоении знаний Коммуникативные барьеры и пути их преодоления Обработка изделий медицинского назначения многократного применения Образцы текста публицистического стиля Четыре типа изменения баланса Задачи с ответами для Всероссийской олимпиады по праву 
Мы поможем в написании ваших работ! ЗНАЕТЕ ЛИ ВЫ?
Влияние общества на человека
Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрации Практические работы по географии для 6 класса Организация работы процедурного кабинета Изменения в неживой природе осенью Уборка процедурного кабинета Сольфеджио. Все правила по сольфеджио Балочные системы. Определение реакций опор и моментов защемления |
II. Replace the words and word combinations with their synonyms.Содержание книги
Поиск на нашем сайте
To know, to be responsible for, to use skills, enhanced, to follow, official position, positive sides, negative sides, demands, to satisfy demands, to include, tiredness, to exclude, to check, to bear responsibility, to solve problems, flying skills, to provide safety, great importance, to work with, modern, to be equipped with, to make final decision, to operate the plane.
III. Use the necessary preposition. 1. to be responsible……….. 2. to be good ………..…….. 3. to be ……….charge …… 4. to be aware……………... 5. to cope..…..the problems 6. to be familiar……………. 7. to deal…………………… 8. to take ……….….account 9. to follow …...the footsteps 10. to be obliged…………….. 11. to bear responsibility…….. 12. to be fitted ………………. 13. to place the aircraft……….security 14. responsibility rests…………..pilots
IV. Make up sentences with the given phrases. · To assume responsibility/ indispensable · Official designation/ to follow one’s footsteps · To be familiar with/ to estimate the problem · To be aware of/ to cope with the problem · Advanced equipment/ to encompass · To master/ to ensure safety · To meet requirements/ airmanship · To assess the situation/ to adhere to · Jet lag/ to exclude · Pilot’s powers/ to be obliged to · To be of paramount importance/ to be at smb’s disposal
V. Answer the questions. Use the underlined phrase in your answer. 1. What is a first officer in charge of? 2. How is it possible to eliminate the problem with the jet-lag? 3. What documents do you have to adhere to? 4. Does the captain comply with first officer’s instructions if the latter is pilot flying? 5. What enhanced and advanced systems are there in your cockpit? 6. Who assumes responsibility for evacuation of the passengers? 7. How much time do the pilots have for evaluating the depressurization problem? 8. What requirements do the pilots have to meet? 9. Why is it necessary for pilot to master English? 10. Why do pilots have to be aware of the weather forecast? 11. What is of paramount importance for pilots in case of hijacking? 12. Can the first officer make a final decision if he is pilot flying?
VI. Answer the following questions. 1. Why have you given preference to pilot’s job? 2. What are the main purposes of the flight crew/cabin crew? 3. What is the captain in charge of? 4. What are the duties of the first officer? 5. How do you prepare for the flight? 6. How are the duties shared between the captain and the first officer during the flight? 7. What do you undertake after the flight? 8. What navigational devices and systems is your cockpit equipped with? 9. Speak about the functions of the major navigational systems. 10. What makes a good pilot? 11. What are the pros and corns of pilot’s profession? 12. What does your airline’s policy aimed at? 13. What trainings is it necessary to undergo in order to maintain professional skills? 14. What is better to fly passenger or cargo aircraft? 15. Give the examples when pilot’s mistake led to catastrophe.
VII. Read the text and discuss it. RESPONSIBILITIES OF A PILOT
Flight crew is responsible for: · ensuring the safety of all crew members and passengers on board · mastering flight technique and aircraft operation to complete safe flight
· readiness of the aircraft for the flight and its correct loading · correct assessing meteorological and aeronautical information as per take off, landing or during the flight Captain bears responsibility for: - all crew members preparation for the flight - correspondence of passengers number on the board and number in transportation documents - safety outcome of the flight, not depending whether he is pilot-flying or not - following assigned flight plan and observance of minimum heights - in time filling of log book First officer submits to the captain. His responsibilities encompass participation in flight operation to be ready to assume responsibility at any moment under captain’s order or in case captain is unable to execute his functions. Thus first officer is empowered - to operate the aircraft on all stages of the flight - to make ultimate decisions as per the flight if he is PF - to adopt pilot in command’s power in case of his incapacitation - to fill documentation
Before the flight Pilots typically report for work an hour before departure in order to meet with other crew members on pre-flight briefing which is conducted by the captain. Prior to briefing the captain confers with forecasters, obtains and verifies meteorological information related to the flight. On the briefing the captain selects alternative aerodromes, ultimately defines the necessary amount of fuel and discusses with other crew members the flight peculiarities. First officer is in charge of calculation of take-off and landing characteristics, loading and centering. Then crew proceeds to the aircraft and takes up other duties. Firstly first officer and following him the captain perform visual check of the plane for determining any dents, scratches, cut tires, consequences of maintenance work, for ensuring that outer surfaces are free from any deposits that may affect aircraft performance, that cargo is correctly loaded and fixed. First officer checks and reports to the captain on closing of cargo hatches and fillers. The first officer ensures that all radio and navigational equipment is operative, that fuel amount on the board equals to the calculated one, that proper type of fuel is used and also controls correct fuel distribution. Then he reports to the captain. So the captain has to be ensured that the aircraft is technically suitable, equipment and instruments are operative except the ones that are allowed by MEL. Then all necessary information should be inserted into FMS.
In flight. Pilots operate the flight in accordance with the Flight Plan. On modern aircraft pilots share their duties in accordance with being pilot-flying and pilot-non-flying. They steer the aircraft with assistance of autopilot and the flight management computer. PF operates the aircraft, PNF conducts communication with ATC, monitors and assesses the work of different systems, every 30 minutes checks the fuel supply which has to be efficient for reaching the destination. PNF duly reports to PF on all deviations and failures of airplane equipment. Pilots have to interact closely with the cabin crew to ensure friendly and effective passengers’ service. Most modern aircrafts have advanced computer systems that alert the pilot about any changes in weather or deviation from a scheduled flight After the flight. When on the ground first officer visually inspects the aircraft, fills the flight task and the captain certifies it with his signature. First officer arranges all manuals, maps and charts for another crew or returns them to Flight Dispatch Department. Captain conveys the aircraft to another crew or engineering personnel or properly parks and seals it and then places it under security.
Navigational equipment. Up- to- date aircraft possess a glass cockpit which is fitted with different navigational equipment and devices.
← Copilot's HUD of a C-130J
√ Waypoints √ Airways √ Radio navigational aids including DME, VOR and NDB √ Airports √ Runways √ Standard Instrument Departure (SID) √ Standard Terminal Arrival (STAR) √ Holding patterns
So, the DME system is composed of transmitter/receiver in the aircraft and a receiver/transmitter on the ground. They measure the distance in miles from aircraft to the RW threshold. It checks the distances from five different DME simultaneously in order to determine one position every 10 seconds.
Aircraft Description. One of the most sophisticated aircraft is A 320 at present time.
The A320's flight deck is equipped with: Ø Electronic Centralized Aircraft Monitor (ECAM) which supplies the flight crew with complete range of information about all the systems of the aircraft. It consists of - upper ECAM display (depicts engine parameters and issues warnings in case of engine malfunctions) - low ECAM display ( depicts conditions of aircraft systems and gives advice) Ø FMGS which is displayed by - Primary Flight Display which contains - Vertical Speed Indicator that measures rate of ascending or descending. - Attitude Indicator that gives pilots information about the aircraft’s pitch and roll characteristics and the orientation of the aircraft with respect to the horizon. - Airspeed Indicator that displays the speed of the aircraft in knots. - Altitude Indicator that displays the aircraft’s altitude above the sea level. - Heading Display that shows the pilot the magnetic heading of the aircraft. - Navigation display (depicts flight route, control points, constrains) Ø Automatic Directional Finding (ADF) is an onboard receiving instrument, with a needle that continuously indicates bearing to a selected radio beacon on the ground or commercial broadcast station. Ø Autopilot.
|
||||||
|
Последнее изменение этой страницы: 2021-03-10; просмотров: 127; Нарушение авторского права страницы; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! infopedia.su Все материалы представленные на сайте исключительно с целью ознакомления читателями и не преследуют коммерческих целей или нарушение авторских прав. Обратная связь - 3.149.29.190 (0.011 с.) |

 Up-to-date aircraft are operated by two pilots that create a crew. Despite subordination (captain- first officer) they are interdependent and both are of paramount importance for the safe outcome of the flight. One of them flies the aircraft and another handles communications and collision avoidance. This provides a sort of human redundancy as this team work allows them to cross check each other and thus minimize human factor mistakes.
Up-to-date aircraft are operated by two pilots that create a crew. Despite subordination (captain- first officer) they are interdependent and both are of paramount importance for the safe outcome of the flight. One of them flies the aircraft and another handles communications and collision avoidance. This provides a sort of human redundancy as this team work allows them to cross check each other and thus minimize human factor mistakes. A GLASS COCKPIT is a cockpit with electronic instrument displays. While on conventional aircraft there were mechanic gauges for displaying information, glass cockpits have electronic displays which are monitored by FMS. It simplifies the work of the pilots, allows to focus only on necessary information. This enhanced technology eliminates the necessity of flight engineer and navigator.
A GLASS COCKPIT is a cockpit with electronic instrument displays. While on conventional aircraft there were mechanic gauges for displaying information, glass cockpits have electronic displays which are monitored by FMS. It simplifies the work of the pilots, allows to focus only on necessary information. This enhanced technology eliminates the necessity of flight engineer and navigator. One more innovation that reduces workload on the crew is A HEAD-UP DISPLAY. It is transparent display on the glass of the cockpit that depicts necessary information which allows pilots to keep the heads up and not to be distracted by looking at the instruments.
One more innovation that reduces workload on the crew is A HEAD-UP DISPLAY. It is transparent display on the glass of the cockpit that depicts necessary information which allows pilots to keep the heads up and not to be distracted by looking at the instruments. A FLIGHT MANAGEMENT SYSTEM(FMS) is an advanced computer system that performs a great variety of in-flight tasks. It minimizes the workload on the flight crew and excludes the necessity to carry flight engineers or navigators. A primary function of it is in-flight management of the flight plan. The FMS makes use of different sensors to identify the position of the aircraft. The FMS guides the aircraft along the flight plan. The navigational data inserted into the FMS is usually updated every 28 hours. These include
A FLIGHT MANAGEMENT SYSTEM(FMS) is an advanced computer system that performs a great variety of in-flight tasks. It minimizes the workload on the flight crew and excludes the necessity to carry flight engineers or navigators. A primary function of it is in-flight management of the flight plan. The FMS makes use of different sensors to identify the position of the aircraft. The FMS guides the aircraft along the flight plan. The navigational data inserted into the FMS is usually updated every 28 hours. These include DISTANCE MEASURING EQUIPMENT (DME) is a transponder-based radio navigation technology that measures distance from aircraft to a land-based transponder by sending and receiving special impulses. The ground stations are typically co-located with VORs.
DISTANCE MEASURING EQUIPMENT (DME) is a transponder-based radio navigation technology that measures distance from aircraft to a land-based transponder by sending and receiving special impulses. The ground stations are typically co-located with VORs.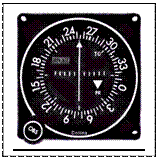 VOR - omnidirectional radio range, is a type of radio navigation system for aircraft. A VOR ground station broadcasts a signal including the station's identifier, voice (if equipped), and navigation signal. The identifier is morse code. The voice signal is usually station name, in-flight recorded advisories, or live flight service broadcasts. The navigation signal allows the airborne receiving equipment to determine a direction to the VOR station.
VOR - omnidirectional radio range, is a type of radio navigation system for aircraft. A VOR ground station broadcasts a signal including the station's identifier, voice (if equipped), and navigation signal. The identifier is morse code. The voice signal is usually station name, in-flight recorded advisories, or live flight service broadcasts. The navigation signal allows the airborne receiving equipment to determine a direction to the VOR station. GPS- Global Positioning System, precise navigation system using signals received from a fleet of low-orbiting satellites, allows pilots to determine their position. The aircraft unit finds the signals from the two nearest satellites and notifies the crew about their latitude and longitude.
GPS- Global Positioning System, precise navigation system using signals received from a fleet of low-orbiting satellites, allows pilots to determine their position. The aircraft unit finds the signals from the two nearest satellites and notifies the crew about their latitude and longitude. The A320 was the first civil airliner to include a full digital fly-by-wire flight control system, system which allows pilots to act as operators- to steer the aircraft by operating the computerized system.
The A320 was the first civil airliner to include a full digital fly-by-wire flight control system, system which allows pilots to act as operators- to steer the aircraft by operating the computerized system.


