
Заглавная страница Избранные статьи Случайная статья Познавательные статьи Новые добавления Обратная связь FAQ Написать работу КАТЕГОРИИ: ТОП 10 на сайте Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрацииТехника нижней прямой подачи мяча. Франко-прусская война (причины и последствия) Организация работы процедурного кабинета Смысловое и механическое запоминание, их место и роль в усвоении знаний Коммуникативные барьеры и пути их преодоления Обработка изделий медицинского назначения многократного применения Образцы текста публицистического стиля Четыре типа изменения баланса Задачи с ответами для Всероссийской олимпиады по праву 
Мы поможем в написании ваших работ! ЗНАЕТЕ ЛИ ВЫ?
Влияние общества на человека
Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрации Практические работы по географии для 6 класса Организация работы процедурного кабинета Изменения в неживой природе осенью Уборка процедурного кабинета Сольфеджио. Все правила по сольфеджио Балочные системы. Определение реакций опор и моментов защемления |
Part 2. Jobs and responsibilitiesСодержание книги Поиск на нашем сайте
CONTENTS INTRODUCTION - 3 PART 1 SOCIALIZING - 4 Part 2 JOBS AND RESPONSIBILITIES -8 Part 3 SPEECH PRACTICE -12 Part 4 BUSINESS STRUCTURE - 13 Part 5 DEVELOPING SKILLS - 20 Part 6 GRAMMAR SECTION - 23 SUPPLEMENTARY I N T R O D U C T I O N The edition promotes you with the possibility to master your Business English skills independently. The Vocabulary, Grammar, Functions, Reading and Writing exercises and VIDEO are presented here in the corresponding sections and in the electronics version. You will find it easier to do the Developing Skills section after you have done the Grammar and Speech Practice ones. You should decide which of the exercises to do and which will be the most useful and interesting for you, bearing in mind what you have done in class for each unit. If necessary, ask your teacher for advice.
GOOD LUCK! Part 1. Socializing G R E E T I N G S
Commentary * 'How do you \ do?' is usually used while getting acquainted with other business people but not customary among people meeting every day. It's a general way of greeting people and requires the same phrase in reply corresponding to the Russian forms «Здравствуйте!» - «Здравствуйте!». But it is also often understood as "How are you getting \ on?" («Как дела?»). And there comes the reply: " \ Fine! \ Thanks! / And you?" ILLUSTRATIVE DIALOGUES: 1. - "How do you do, Mr. Smith? I am Frank Newman of Green Star LTD." -"How do you do, Mr. Newman?" 2. - "Morning, David! This is Edward Scott, our new sales representative." -"Oh, yes, Edward! Welcome to JCK Advertising! How do you do?" -"How do you do? Pleased to meet you." 3. -"Oh, hullo, Pete! How are you?" -"Hi, Bob! I am OK. Haven't seen you for ages!" SMALL TALK Small Talk - is a traditional beginning of any business contact. Before moving to the subject of the meeting, you should arrange a short conversation to build a bridge to mutual understanding. It's also called "socializing". It presents an exchange of some polite questions and answers, such as asking of one's affairs, flight or trip, if any, weather, hotel and replies to them. Usually, both the speaker and his companion is aware of the perspective reply to the question asked. Don't give detailed information! It's just Etiquette common in business communication. Phrases of " Welcoming " are preferable to compose a friendly atmosphere that promotes fruitful negotiating. NOTE: But not any questions are possible to ask. Keep in mind that it's better not to ask too personal questions at a first meeting. And never ask about money!
ILLUSTRATIVE SMALL TALK
N.: - Good morning, Mr. Smith! How are you? S.: - I'm fine, thank you. And how are you getting on with your business? N: - It's OK, thanks. Did you have a good trip? S: - Excellent! The weather is pleasant today, isn't it? N: - Yes. Good weather, good business. S: - Absolutely! N: - Would you like a cup of coffee? S: - Thanks. Let's get down to business now, if you don't mind?
N: - All right. Business before pleasure. S: - The British say: "Time and tide wait for no man." N: - I see. I N T R O D U C I N G P E O P L E Who are you? - the question is "What's your name?" and requires some information about the partner's fist name and family name. But you can initiate the procedure of introducing by yourself saying: "We haven't met before, have we?" or "Excuse me, have we met before? or "I don't think we've met, have we?" and get the answer: 'No, we haven't". In reply: - Let me intro\ duce myself, my name's Edward \ Green. - May I intro \ duce myself?" - Allow me to intro \ duce myself, I am Dr. Henry\Bendrix. Sometimes you need to introduce a stranger to other people. So you may say: - Have you met / Mr.Harvey? or - I'd like you to meet Doctor \ Stanley. - \Ms. Leeds, this is \Mr. Snow. - Unpretentious and yet formal enough for any occasion. NOTE: When introducing oneself the one addressed to is expected to say his name. Then follows the exchange of the phrases: - "How do you do?" - "How do you do?" from both being acquainted. In reply: - My \ pleasure. - It's nice \ meeting you - Pleased to \ meet you. - Glad to \ meet you. Only to the previous two phrases your counterpart can react saying: - "Me \ too." The other possible replies may be: - "The pleasure is \ mine /actually." - "Nice to meet you \ too." The replies mentioned above are rather formal. But in less official situations it's possible to say: -"Hal /lo!" or to give a usual answer - "How d'you do?" Examples - Good morning! Excuse me, have we met before? - Oh, I'm afraid, not! My name's John Brown. Pleased to meet you. - The pleasure is mine. And I am Robert Bean. What are you? - the question is "What do you do?" or "What's your job?" The speaker is interested in a person's job and responsibilities. Usually the answer provides some information about the legal name of the company, its activity and the position of the person in the group. It's customary accompanied by another question: "Where are you from?" and followed by an answer: "I'm from Bybery Systems." or "I'm from Orenburg", or "I'm from Russia." In reply: - I represent the THT Company. I work for* Transgas LTD. (or "I work with Transgas LTD) - I work in the office. - I work at the Research and Development department. I work in sales. - We are based in New York but have offices worldwide. We are active in gas transmitting. - We do business with many Asian and European countries.** - We engage a first class reputation. NOTES: * the verb "to work" can be followed by different prepositions as it is shown in the above sentences. ** the construction "to be based in..."varies in meaning depending on the subject 1. "We are based in..." means that the head office of the firm is located in some city or town and may have some branches or subsidiaries. 2. "I am based in Paris" means that the person is on the staff of a branch office or the head office but travels a lot. ILLUSTRATIVE DIALOGUES 1. - Excuse me, are you Mr. Briggs? - Yeah! - Hello! I am Mark Whites from JCK Co. - Hi! Nice to meet you! - And you. I am here to take you to the hotel. - Thank you. 2. - Hello! I am Robert Carlson. I don't think we've met, have we? - No. Glad to meet you. My name's Percy Alexander. - What are you, Mr. Alexander? - I represent Prodata Ltd. We are based in Geneva. - So you are not from Brighton then? - No. I am here temporarily. - I see. 3. - Good afternoon! Let me introduce myself. I am Carol Streep. - How do you do, Ms. Streep. - I am fine. But call me just Carol. - OK, Carol. And I'm Bob, Bob Russel.
- Where are you from, Bob? - I work for the Agrico Denmark. And what about you? What's your job? - I am a Sales Manager with Pepsico. - Really? That's interesting! Speech Practice Making contact A first meeting A. Peter Berger is a consultant with Prodata, a computer consultancy firm. He is normally based in Geneva but he's working in Bradford at the moment, setting up a new quality control system. On his first day there, he meets Jenny Carlson over lunch. PART 4. Business structure
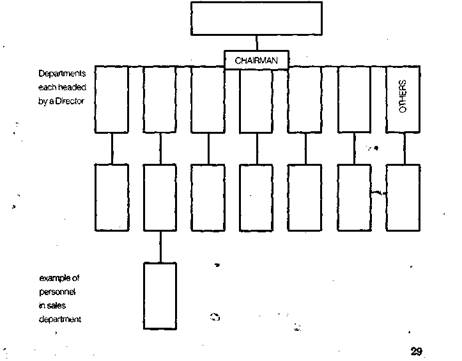
Complete the organization chart from the information provided. Two The Managing Director (sometimes called the Chief Executive, or President The company is run by a Board of Directors; each Director is in charge of a Most companies have Finance, Sales, Marketing (sometimes part of Sales), Most departments have a Manager, who is in charge of its day-to-day Various personnel in each department report to the Manager. One example,
ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE The Organizational Structure of the company depends on different matters, suchas: size of the company, type of ownership, availability of regional divisions,etc. But most of the companies have certain usual functions shown on the Organizational Chart. Job Descriptions are attached below.
• BOARD OF DIRECTORS is the highest level in the organizational structure
• MANAGING DIRECTOR is appointed by the Board of Directors for a certain period of time. He is responsible for managing the company, fulfilling the main strategy and developing business. He reports to the Board of Directors and shareholders.
• FINANCIAL CONTROLLER is responsible for Finance and Accounting
• PERSONNEL MANAGER is the Head of the Personnel Department. The Personnel Department is dealing with issues of personnel training, hiring policies, defining reward systems for people from different departments and divisions.
• MANUFACTURING MANAGER is responsible for managing production, quality control and research and development. Heads of workshops usually report to him. Information regarding new market trends comes from the Marketing Department to the Research and Development Division where they improve existing products or develop new ones. Quality Control Division is dealing not only with quality of products but • SALES AND MARKETING MANAGER is always a very hard and artistic job to do but I think that it gives you more satisfaction that any other works within the company. Sales and Marketing Department is responsible for sales of products, promotion and advertising, market research, developing product
• PURCHASING MANAGER is working closely with Manufacturing Function because the Purchasing Department is responsible for purchasing materials, low value items and all the assets for Production. They have to find the best quality materials at the lowest price. Company
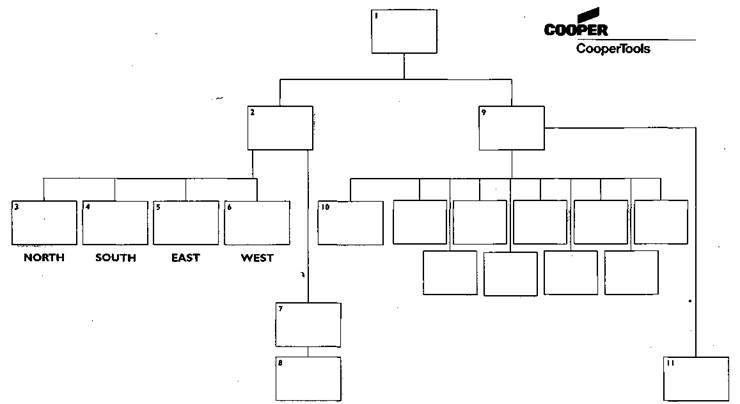
READING Look at the organization chart for Cooper France. Where should the following labels appear? Sales secretary agent Now read the passage and complete the chart to show the positions that Jean Lamadon and his
My name's Jean Lamadon, and I'm one of the two sales manager here at Cooper France. suppose that if I'm going to describe how things are organised here in France I'd better start As I said, there are two sales managers, because we sell two very different categories of product in
The way my department is organized is really quite simple. About 80% of our business is done VOCABULARY Ex.1 Circle the word that does not belong in each horizontal group. 1 business company society subsidiary 2 salary manager salesman employee 3 finance product research marketing 4 distributing selling assembling promoting 5 components tools hardware strategy 6 end user customer client distributor Ex.2 Which of the groups of three words that you identified above refer to the following definitions? b types of commercial organizations с different departments or functions d people who work inside a company e activities that involve meeting customers....................... f products that can be sold Ex.3 Match each of the words that you circled with the following: 1.......................... a monthly payment in exchange for work 2.......................... an item that has been made 3.......................... a plan of action 4.......................... a non-profit-making organization 5.......................... putting parts together 6.......................... a person or business which has an agreement to sell the goods of another firm PART 5. Developing Skills VIDEO Laboratory Work "COMPANY STRUCTURES AND BUSINESS PROFILE" NAMES OF THE STAFF: - Jenny Ross - Derek Jones - Don Bradley - Clive Harris - Edward Green - Geraldine Scott - Kate Mckenna - Bob and Pete - Sally Task 1. Show how many different job titles you can name ___________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ Task 2. Write down responsibilities of the following staff: 1. The head of the company ____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 2. The Director / Manager of the department ____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 3. The Customer Services Assistant ____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 4. The Sales Representative ____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ Task 3. Watch the VIDEO and give the answers to the questions a) Who arrives first? __________________________________ second? _____________________________________ third? ______________________________________ b) What day of the week is it? _________________________ c) What time of the day is it? __________________________ d) Who does Edward Green want to see? _________________________ e) Who does he meet first? _________________________ f) Where is she showing him to? _________________________ g) Name what you have seen there _________________________ Task 4. Give as full information about the company as possible - The official name of the company is___________________ - Its business profile is_______________________________ - The Product is____________________________________ - It is based in __________________________________ - _________________________ is everybody's Boss here. Task 5. Watch the VIDEO once again and fill in the gaps GREET A COLLEAGUE
INTRODUCE YOURSELF
INTRODUCE A NEW COLLEAGUE
Task 6. Match the names of the Bibury Systems staff with the jobs in the chart:


Part 6. Grammar Section A. Expressing Present UNIT 1 Present continuous (I am doing) a) Study this example situation:
We use the present continuous when we talk about something which is happening at the time of speaking: - Please don't make so much noise. I'm studying (not 'I study') - 'Where is Margaret?' 'She's having a bath.' (not 'she has') - Let's go out now. It isn't raining any more. - (at a party) Hello, Ann. Are you enjoying the party? (not 'do you enjoy') b) We also use the present continuous when we talk about something which is happening around, the time of speaking, but not necessarily exactly at the time of speaking.. Study this example situation: -Tom and Ann are talking and drinking in a cafe. Tom says: 'I'm reading an interesting book at the moment. I'll lend it to you when I've finished it.' Tom is not reading the book at the time of speaking. He means that he has begun the book and hasn't finished it yet. He is in the middle of reading it. Here are some more examples: - Silvia is learning English at the moment. (not 'learns') - Have you heard about Tom? He is building his own house. (not 'builds') But perhaps Silvia and Tom are not doing these things exactly at the time of speaking. c) We often use the present continuous when we talk about a period around the present. For example: today, this season etc.: - 'You're working hard today.' 'Yes, I have a lot to do.' - Tom isn't playing football this season. He wants to concentrate on his studies. d) We use the present continuous when we talk about changing situations: - The population of the world is rising very fast. (not 'rises') - Is your English getting better? (not 'does... get') Exercises 1.1 I n this exercise you have to put the verb into the correct form. Examples: Please don't make so much noise. I am studying (study). Let's go out now. It isn’t raining (not/rain) any more. Listen to those people. What language are they speaking. (they/speak)? 1. Please be quiet. I ………………… (try) to concentrate. 2. Look! It ……………………… (snow). 3. Why …………………… (you/look) at me like that? Have I said something wrong? 4. You ……………………. (make) a lot of noise. Can you be a bit quieter? 5. Excuse me, I …………………….. (look) for a phone box. Is there one near here? 6. (in the cinema) It's a good film, isn't it? ……………………… (you/enjoy) it? 7. Listen! Can you hear those people next door? They ……………………. (shout) at each other again. 8. Why …………………… (you/wear) your coat today? It's very warm. 9. I ………………………... (not/work) this week. I'm on holiday. 10. I want to lose weight. I ……………………... (not/eat) anything today. _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ 1.2 Complete these sentences using one of these verbs: Exercises 2.1 In this exercise you have to put the verb into the correct form. Examples: Water boils (boil) at 100 degrees centigrade. George doesn’t go (not/go) to the cinema very often. How many languages do you speak (you/speak)? 1. The swimming bath …………………. (open) at 9.00 and ………………… (close) at 18.30 every day. 2. What time ………………………… (the banks/close) in Britain? 3. I have a car but I ……………………… (not/use) it very often. 4. How many cigarettes ………………………… (you/smoke) a day? 5. 'What …………………........... (you/do)?' 'I'm an electrical engineer.' 6. 'Where ………………………... (your father/come) from?' 'He …………………… (come) from Scotland.' 7. If you need money, why ……………………………... (you / not / get) a job?
8. I ……………………… (play) the piano, but I …………………. (not/play) very well. 9. I don't understand the word 'deceive'. What …………………… ('deceive' / mean)? ________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 2.2 This time you have to read some sentences and correct them. The English is correct but the information is wrong. Write two correct sentences each time. Example: The sun goes round the earth. The sun doesn’t go round the earth. The earth goes round the sun. 1. The sun rises in the west. ………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. 2. Mice catch cats. …………………………………………………………………………………………...….. ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. 3. Carpenters make things from metal. …………………………………………………………...…..... ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. 4. The River Amazon flows into the Pacific Ocean. ………………………………….………….. ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. ________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 2.3 Now you have to use these sentences to make questions. Begin your question with the word(s) in brackets. Examples: Tom plays tennis. (How often?) How often does Tom play tennis? I get up in the morning. (What time/usually?) What time do you usually get up? 1. Ann watches television. (How often?) How often ………………………….………………………… 2. I write to my parents. (How often?) ……………………………………………………………………...…. 3. I have dinner in the evening? (What time /usually?) ………………………………………………… 4. Tom works. (Where?) …………………………………………………………………………………………..… 5. I go to the cinema. (How often?) …………………………………………………………………………….. 6. People do stupid things. (Why?) ………………………………………………………………………….….. 7. The car breaks down. (How often?) ……………………………………………………………………..….. UNIT 3 Present continuous (I am doing) or present simple (I do)?
a) Study this explanation and compare the examples:
b) Some verbs are used only in simple tenses. For example, you cannot say 'I am knowing'. You can only say I know. Here is a list of verbs which are not normally used in continuous tenses (but there are exceptions): Exercises
Exercises 4.1 In this exercise you have to read a sentence about the present and then write a sentence about the past. Example: Tom usually gets up at 7.30. Yesterday he got up at 7.30. 1. Tom usually wakes up early. Yesterday morning ………………………………….. 2. Torn usually walks to work. Yesterday …………………………………………….. 3. Tom is usually late for work. Yesterday ……………………………………………. 4. Tom usually has a sandwich for lunch. Yesterday ………………………………….. 5. Tom usually goes out in the evening. Yesterday evening …………………………... 6. Tom usually sleeps very well. Last night …………………………………………… ________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 4.2 This time you have to put one of these verbs in each sentence: hurt teach spend sell throw fall catch buy cos t Example: I was hungry, so I bought something to eat in the shop. 1. Tom's father ……………... him how to drive when he was 17. 2. Don ………...……. down the stairs this morning and ……………… his leg. 3. We needed some money so we ……….… our car. 4. Ann …………….….. a lot of money yesterday. She …………………. a dress which …………………………..……. £50. 5. Jim …………….…… the ball to Sue who ……………………..…. it. ________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 4.3 In this exercise you have to write questions. A friend has just come back from holiday and you are asking him about it. Examples: where /go? Where did you go?. food / good? Was the food good?. 1. how long / stay there? ………………………………………………………….……… 2. stay in a hotel? ……………………………………………………………..………….. 3. go alone? ……………………………………………………………..………………... 4. how / travel? ……………………………………………………………..…………….. 5. the weather/fine? …………………………………………………………….……….... 6. what / do in the evenings? ……………………………………………………………... 7. meet any interesting people? …………………………………………………………... ________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 4.4 This time you have to put the verb into the correct form. All the sentences are past. Example: I didn’t go (not/go) to work yesterday because I wasn’t (not/be) very well. 1. Tom ………………. (not/shave) this morning because he ………….. (not/have) time. 2. We …………………. (not/eat) anything because we ………………. (not/be) hungry. 3. I …………………. (not/rush) because I ……………. (not/be) in a hurry. 4. She ……………… (not/be) interested in the book because she ……………………….. (not/understand) it. UNIT 5 Past continuous (I was doing) a) Study this example situation:
We use the past continuous to say that someone was in the middle of doing something at a certain time. The action or situation had already started before this time but hadn't finished: - This time last year I was living in Brazil. - What were you doing at 10 o'clock last night? b) The past continuous does not tell us whether an action was finished or not. Perhaps it was finished, perhaps not. Compare: - Tom was cooking the dinner. (past continuous) = He was in the middle of cooking the dinner and we don't know whether he finished cooking it. - Tom cooked the dinner, (past simple) = He began and finished it. c) We often use the past continuous (I was doing) and the past simple (I did) together to say that something happened in the middle of something else: - Tom burnt his hand when he was cooking the dinner. - I saw Jim in the park. He was sitting on the grass and reading a book. - It was raining when I got up. - While I was working in the garden, I hurt my back.. But to say that one thing happened after another, use the past simple: - Yesterday evening Tom was having a bath when the phone rang. He got out of the bath and answered the phone. Compare: - When Tom arrived, we were having dinner. (past continuous) = We had already started dinner before Tom arrived. - When Tom arrived, we had dinner. (past simple) = Tom arrived and then we had dinner. Note: There are some verbs (for example know) which are not normally used in continuous tenses.
Exercises
5.1 Here is a list of some things that Ann did yesterday (and the times at which she did them):
Now write sentences saying what she was doing at these times:
________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 5.2 A group of people were staying in a hotel. One evening the fire alarm rang. Use the words in brackets to make sentences saying what each person was doing at the time. Example: (Don / have / a bath). Don was having a bath 1. (Ann / write / a letter in her room) Ann …………………………………………. 2. (George / get / ready to go out) George …………………………………………. 3. (Carol and Dennis / have / dinner) Carol and Dennis ………..………………….. 4. (Tom / make / a phone call) Tom ……………………………………………….. ________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 5.3 Make sentences from the words in brackets. Put the verbs into the correct form, past simple (I did) or past continuous (I was doing). Example: (I/fall/asleep when I/watch /television) I fell asleep when I was watching television. 1. (the phone / ring / when I / have / a shower) The phone …………………………...... 2. (it / begin / to rain when I / walk / home) …………………………………………..… 3. (we / see / an accident when we / wait / for the bus) ……………...………………..… ________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 5.4 Put the verb into the correct form, past continuous or past simple. Example: While Tom was cooking (cook) the dinner, the phone rang (ring). 1. George …………… (fall) off the ladder while he,………… (paint) the ceiling. 2. Last night I ………….. (read) in bed when suddenly I ………… (hear) a scream. 3. ……………. (you/watch) television when I phoned you? 4. Ann ………….. (wait) for me when I ………….. (arrive). 5. I ……………… (not/drive) very fast when the accident ……………… (happen). 6. I ……………… (break) a plate last night. I …………..….. (do) the washing-up when it ……………………………………… (slip) out of my hand. 7. Tom ……………. (take) a photograph of me while I ………………… (not/look). 8. We ……………… (not/go) out because it …………….. (rain). 9. What ………………. (you/do) at this time yesterday? UNIT 6 Present perfect (I have done)
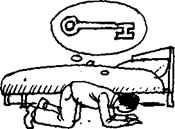
a) Study this example situation:
We form the present perfect with have/has + the past participle. The past participle often ends in - ed (open ed, decid ed) but many important verbs are irregular (lost, written, done etc.). b) When we use the present perfect there is a connection with the present: - I've lost my key. (= I haven't got it now.) - Jim has gone to Canada. (= He is in Canada or on his way there now.) - Oh dear, I've forgotten her name. (= I can't remember it now.) - Have you washed your hair? (= is it clean now?) c) We often use the present perfect to give new information or to announce a recent happening: - I've lost my key. Can you help me look for it? - Do you know about Jim? He's gone to Canada. - Ow! I've burnt myself. You can use the present perfect with just (= a short time ago): - 'Would you like something to eat?' 'No, thanks. I 've just had lunch.' - Hello, have you just arrived? You can use the present perfect with already to say that something has happened sooner than expected: - 'Don't forget to post the letter, will you?' 'I've already posted it. ' - 'When is Tom going to start his new job?' 'He has already started.' d) Study the difference between gone to and been to: - Ann is on holiday. She has gone to Italy. (= She is there now or she is on her way there.) - Tom is back in England now. He has been to Italy. (= He was there but now he has come back.) Exercises
6.1 You are writing a letter to a friend and giving news about people you both know. Use the words given to make sentences and put the verb into the correct form. Example: Phil / find a new job Phil has found a new job.. Dear Chris, Lots of things have happened since I last wrote to you. 1. Charles / go / Brazil Charles …………………………………………………………. 2. Jack and Jill / decide / to get married ………………………………………………….. 3. Suzanne / have / a baby ………………………………………………………………... 4. Monica / give up / smoking ……………………………………………………………. 5. George / pass / his driving-test ………………………………………………………… ________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 6.2 In this exercise you have to read the situation and then write a suitable sentence. Use the verb given. Example: Tom is looking for his key. He can't find it. (lose) He has lost his key.. 1. Ann's hair was dirty. Now it is clean. (wash) She ……..…………………………….. 2. Tom was 80 kilograms. Now he weighs 70. (lose weight) …...……………………... 3. The car has just stopped because there isn't any more petrol in the tank. (run out of petrol) ……………………………………………………………………………….…… 4. Yesterday Bill was playing football. Now he can't walk and his leg is in plaster. (break) …………….……………………………………………………………………... ________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 6.3 This time you have to use just. Answer the questions using the words given. Example: Would you like something to eat. (no thank you / I / just / have / dinner) No thank you. I’ve just had dinner.. 1. Have you seen John anywhere? (yes / I /just / see / him) Yes ………………………… 2. Has Ann phoned yet? (yes / she / just / phone) ………………………………………... 3. Would you like a cigarette? (no thanks / I / just / put / one out) ………………………. ________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 6.4 In this exercise you have to write sentences with already. Example: Don't forget to post that letter. 'I’ve already posted it.. 1. Don't forget to phone Tom. I …………………….…………………….… 2. Why don't you read the paper? ………………...……………………………. 3. Shall I pay the waiter? No, I ……………..…………………………. ________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 6.5 This time you have to put in been or gone. Example: 'Where's Ann?' 'She's on holiday. She has gone to Italy. ' 1. Hello! I've just ……………………. to the shops. Look! I've bought lots of things. 2. Jim isn't here at the moment. He's …………………………...... to the shops. 3. 'Are you going to the bank?' - 'No, I've already ………………………… to the bank.'
UNIT 7 Present perfect with how long and past simple with when Since and for a) Use the past simple (I did) to ask or say when something happened: - A: When did it start raining? B: It started raining at one o'clock / an hour ago. -A: When did Tom and Ann first meet? B: They first met when they were at school / a long time ago. Use the present perfect (I have done / I have been doing) to ask or say how long something has been happening (up to the present): - A: How long has it been raining? B: It' s been raining since one o'clock / for an hour. -A: How long have Tom and Ann known each other? B: They' ve known each other since they were at school / for a long time. b) Since and for We use both since and for to say how long something has been happening: - I've been waiting for you since 8 o'clock. - I've been waiting for you for two hours. We use since when we say the beginning of the period (8 o'clock). We use for when we say the period of time (two hours).
- She's been working here since April. (= from April until now) She's been working here for six months. (not 'since six months') - I haven't seen Tom since Monday. (= from Monday until now) I haven't seen Tom for three days. (not 'since three days') We do not use for in expressions with all (all day / all morning / all week / all my life etc.): - I've lived here all my life. (not 'for all my life') Exercises
7.1 In this exercise you have to write questions with how long and when. Example: It is raining. (how long /it / rain?) How long has it been raining?. (when / it / start / raining?) When did it start raining?. 1. Ann is learning Italian. (how long / she / learn / Italian?) …………………………………………………… (when / she / begin / learning Italian?) ……………………………………………… 2. I know Tom. (how long / you / know / Tom?) ……………………………………………………. (when / you / first / meet / Tom?) …………………………………………………... 3. Bob and Alice are married. (how long / they / be / married?) ……………………………………………………. (when / they / get / married?) ……………………………………….………………. ________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 7.2 In this exercise you have to put in since or for. Example: Tom and I have known each other for six months. 1. It's been raining............................................... I got up this morning. 2. Tom's father has been a policeman........................................ 20 years. 3. Have you been learning English....................................... a long time? 4........................................ Christmas, the weather has been quite mild. 5. Ann has been on holiday................................................... three days. 6. That's a very old car. I've had it.................................................. ages. ________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 7.3 This time you have to make a new sentence beginning in the way shown. Examples: I know Tom. I first met him six months ago. I have known him for six months. It's been raining since 2 o'clock. It started. raining at two o’clock.. 1. Tom's ill. He became ill three days ago. He has ………………...…………………. 2. We have been married for five years. We got ……………………………………… 3. Jim has a beard. He grew it ten years ago. He has …………………………………. 4. He has been in France for three weeks. He went …………………………………... 5. He has had his new car since February. He bought ……………………………….... ________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 7.4 In this exercise you have to imagine that two people are talking. You have to make sentences with It's... since... Example: A: Do you often go on holiday? (no / five years) B: No, it’s five years since I went on holiday.. 1. A: Do you often eat in restaurants? (no / six months) B: No, it …………………………………………………………………………… 2. A: Does it often snow here? (no / years) 3. B: No, ……….......................................................................................................... Exercises Present and past 1 Put the verb into the correct form, present simple (I do), present continuous (I am doing), past simple (I did) or past continuous (I was doing). 1. We can go out now. It is not raining (not/rain) any more. 2. Ann was waiting (wait) for me when I arrived (arrive). 3. I ………………. (get) hungry. Let's go and have something to eat. 4. What …………… (you do) in your spare time? Have you got any hobbies? ………… 5. What speed ……………. (the car/do) at the time of the accident? 6. Mary usually ………… (phone) me on Fridays but she … (not phone) last Friday. 7. A: - When I last saw you, you ……………………….. (think) of moving to a new flat В: - That's right, but in the end I (decide) to stay where I was. 8. What's that noise? What ……….. (happen)? 9. It's usually dry here at this time of the year. It (not rain) much. 10. ………………………………. Yesterday evening the phone (ring) three times while we ……………………………………… (have) dinner. 11. ………………………………... Linda was busy when we (go) to see her yesterday. She ………………………………….. (study) for an exam. We ………….. (not want) to disturb her, so we ……………… (not stay) very long. 12. ……………………………….. When I first ………………………. (tell) Tom the news, he ……………………………………………………………… (not believe) me. He ………………… (think) that I …………………….. (joke). FOCUS Present perfect With the present perfect we use How long …? for questions about duration and for or since for the answer: How long have you been a permanent resident? I’ve been a permanent resident since 1995. Past simple With the past simple we use When …? and How long …? To ask questions about the timing and duration of events in the past: When did you come to the States? (TIMING) How long did you live in Holland? (DURATION) We can answer the first question by giving the exact time in the past or by giving the total number of units of time that separate the event in from the present: I came in 1990 / I came 18 years ago. CONTENTS INTRODUCTION - 3 PART 1 SOCIALIZING - 4 Part 2 JOBS AND RESPONSIBILITIES -8 Part 3 SPEECH PRACTICE -12 Part 4 BUSINESS STRUCTURE - 13 Part 5 DEVELOPING SKILLS - 20 Part 6 GRAMMAR SECTION - 23 SUPPLEMENTARY I N T R O D U C T I O N The edition promotes you with the possibility to master your Business English skills independently. The Vocabulary, Grammar, Functions, Reading and Writing exercises and VIDEO are presented here in the corresponding sections and in the electronics version. You will find it easier to do the Developing Skills section after you have done the Grammar and Speech Practice ones. You should decide which of the exercises to do and which will be the most useful and interesting for you, bearing in mind what you have done in class for each unit. If necessary, ask your teacher for advice.
GOOD LUCK! Part 1. Socializing G R E E T I N G S
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Последнее изменение этой страницы: 2017-02-05; просмотров: 602; Нарушение авторского права страницы; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! infopedia.su Все материалы представленные на сайте исключительно с целью ознакомления читателями и не преследуют коммерческих целей или нарушение авторских прав. Обратная связь - 13.59.69.58 (0.016 с.) |

 Greets Jenny.
Greets Jenny.
 Makes small talk:
Makes small talk:
 Makes small talk:
Makes small talk:

 Greets Kate:
Greets Kate:
 Responds: 5. _______ ______ _________ _________________
Responds: 5. _______ ______ _________ _________________
 Gives Don's Name:
Gives Don's Name:
 2. to see Don Bradley
2. to see Don Bradley

 Are you Edward Green?
Are you Edward Green?
 Asks a polite question:
Asks a polite question:
 4. ______ _________ _______ ___________.
4. ______ _________ _______ ___________.
 Welсотes Edward:
5. _________ ________ __________
Welсотes Edward:
5. _________ ________ __________
 6. ________ __ __________Bibury Systems.
6. ________ __ __________Bibury Systems.

 Kate, _________ _____________
Kate, _________ _____________ Ah yes. Edward. Hello.
Ah yes. Edward. Hello.
 Sales and Marketing Director Financial Director Personnel Director
Sales and Marketing Director Financial Director Personnel Director





 I / he / she was
we / they / you were
I / he / she was
we / they / you were
 I/we/they/you have(= I've etc.)
he/she has (= he's etc.)
I/we/they/you have(= I've etc.)
he/she has (= he's etc.)
 I (etc.) haven't have you (etc.)
he/she hasn't has he/she
I (etc.) haven't have you (etc.)
he/she hasn't has he/she




