
Заглавная страница Избранные статьи Случайная статья Познавательные статьи Новые добавления Обратная связь FAQ Написать работу КАТЕГОРИИ: ТОП 10 на сайте Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрацииТехника нижней прямой подачи мяча. Франко-прусская война (причины и последствия) Организация работы процедурного кабинета Смысловое и механическое запоминание, их место и роль в усвоении знаний Коммуникативные барьеры и пути их преодоления Обработка изделий медицинского назначения многократного применения Образцы текста публицистического стиля Четыре типа изменения баланса Задачи с ответами для Всероссийской олимпиады по праву 
Мы поможем в написании ваших работ! ЗНАЕТЕ ЛИ ВЫ?
Влияние общества на человека
Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрации Практические работы по географии для 6 класса Организация работы процедурного кабинета Изменения в неживой природе осенью Уборка процедурного кабинета Сольфеджио. Все правила по сольфеджио Балочные системы. Определение реакций опор и моментов защемления |
Factors That Influence Human Population GrowthСодержание книги
Поиск на нашем сайте
- Humans (unlike other species) are influenced by biological, social, political, economic, and ethical factors. • Able to make conscious decisions and adjust lives accordingly. Biological Factors Main factor of population growth rate: # of women with children & # of children each woman has. T otal fertility rate - # of children a woman has during her lifetime: rate of 2.1 = replacement fertility level; Zero population growth: birth rate = death rate
Social Factors Education level of women: If level of education increases, fertility rates fall. Why? a) Financial independence leads to later marriage. b) Educated women are more likely use birth control. In some cultures women desire large families: Where infant mortality is high, it is traditional to have large families since not all children may survive. Parents feel secure when there are many children to look after them in old age. Economic Factors: In less developed countries, the economic benefits of children are extremely important. Even young children can be given jobs that contribute to the family economy, such as protecting livestock, gathering firewood, or carrying water. - In the developed world, large numbers of children are an economic drain. - They are prevented from working. - They must be sent to school at great expense. - They consume large amounts of the family income.
Political Factors Governments can reward or punish high fertility rates. European countries are concerned about low birth rates à policies to encourage having more children: Paid maternity leave & guaranteed job fo a mother. Childcare facilities. Child tax deductions. Most developing countries are concerned about fast population growth à programs to limit growth: Education of population: family planning, maternal & child health. Free or low-cost contraceptives. One-child policy in China
Factors usually included in an analysis of standard of living: Economic well-being Health conditions Social status and mobility Economic measure of standard of living is average purchasing power per person. Gross national income (GNI) is an index of purchasing power measuring total goods and services generated by citizens of a country. Human populations can increase in size only if other plant and animal populations decrease in size
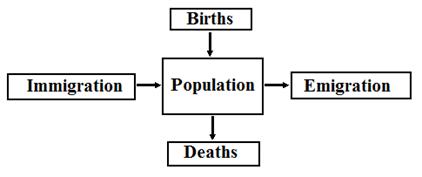
3. Basic demographic processes: v Births = Natality v Deaths = Mortality Note: mortality ≠ morbidity! v Migration
Demographic balancing equation: Population change = (Births – Deaths) + (Immigrants – Emigrants) or ∆P = Pt – P0 = (B – D) + (I – E) (1) where P0 is the initial population and Pt is the population after time t.
Demographic balancing equation (1) can be split into 2 basic components: Natural increase = Births (B) – Deaths (D) Net Migration = Immigration (I) – Emigration (E) Natural increase is the most important component of the overall population change.
Population Growth Rates Each component of population change (births, deaths, migration) can be expressed as an absolute number (pop change) – crude values or more commonly, as annual rates expressed in %. Demographic rates are ordinarily calculated per 1000 persons per year. • Birth Rate = Humans born per 1000 individuals per year. • Death Rate = Humans died per 1,000 individuals per year. Since population is changing throughout the year, we use for calculations mid-year population, which is the population in the middle of the particular year. Crude Birth Rate (СBR) = total number of live births per year per thousand mid-year population. Crude Death Rate (СDR) = total number of deaths per year per thousand mid-year population. CBR =
CDR =
Crude (Natural) Growth Rate (CGR) = natural (population) growth per year per thousand mid-year population: CGR = CBR – CDR This is a natural growth rate. The total growth rate is different, since it includes immigration, emigration. Crude (Natural) Growth Rate, or just Crude Growth Rate may be also calculated this way: CGR = Note: CGR as well as other crude rates, may be expressed in %. Example 1: suppose that CGR = 15. How many percent was population growth? It means that natural increase in population is equal to 15 persons per 1000 population per year. To convert it to %, use the following proportion: 15 people à per 1000 population X people à per 100 population Solving proportion, find X:
You may have noticed that 1.5% can be obtained from 15 by just dividing by 10! 1.5% represents annual rate of population growth.
The average rate of population growth over some extended time period can be calculated if the population size at two points in time is known. Exponential growth formulas: Population growth is described by exponential function: Pt = P0 × (1+r)t (1) where Po is the initial population, Pt is population at the end of t years, r is annual growth rate expressed as a decimal. For t = 1 year, that is for annual population growth the formula (1) will look simple: Pt = P0×(1+r) (2) Example 2. Annual population growth rate is 6%. Assuming that the initial population of certain country at the beginning of the year was 10 mln, find its population by the end of the year. P0 = 10 mln r = 0.06 (6%) Pt =? Using formula (2), we get: Pt = 10 mln *(1+0.06) = 10.6 mln people Applying fundamental limit rule to formula(1) at high t values (more accurately, at
where Pt - population in t years from 0 time; P0 - population in time 0; t represents number of yrs and r is annual rate of growth (decimal). Formula (3) is convenient for calculations and even at relatively small t gives good approximation. Population doubling time = the number of years until the population will double if the annual rate of growth remains constant. Rule of 70 for calculating doubling time: T2 = 5. Urban problems in developing & developed countries In developing contries: · Dense traffic, smoky factories, use of wood or coal fires cause excessive air pollution. · Lenient pollution laws, corrupt officials and ignorance cause even more pollution. · Only 35% of urban residents in developing countries have satisfactory sanitation services. In developed countries • The rapid growth of central cities in Europe and North America has now slowed or even reversed. • The good news is better air and water quality, safer working conditions, fewer communicable diseases. • The bad news is urban decay and sprawl and transportation issues have worsened Urban Sprawl - is a Current Developed World Problem In most American metropolitan areas, the bulk of new housing is in large, tract developments that leapfrog beyond city edges in search of inexpensive land. Urban sprawl consumes about 200,000 ha of US agricultural land annually. Planning authorities are often divided among many small local jurisdictions. Most American cities devote ~1/3 of their land area to cars. Freeways have reshaped our lives. Public transportation is expensive and difficult to establish.
6. Ways to achieve urban sustainability
|
|||||
|
Последнее изменение этой страницы: 2016-12-12; просмотров: 203; Нарушение авторского права страницы; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! infopedia.su Все материалы представленные на сайте исключительно с целью ознакомления читателями и не преследуют коммерческих целей или нарушение авторских прав. Обратная связь - 18.226.159.94 (0.01 с.) |

 100 0, where # births is number of births during one year,
100 0, where # births is number of births during one year,  is mid-year population. Mid-year population can be calculated as average number between two population values: at the beginning and at the end of the year.
is mid-year population. Mid-year population can be calculated as average number between two population values: at the beginning and at the end of the year. 1000, where # deaths is number of deaths during one year,
1000, where # deaths is number of deaths during one year, 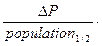 1000, where
1000, where  - population change during one year.
- population change during one year.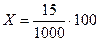 = 1.5%
= 1.5% ), we get:
), we get: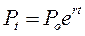 (3)
(3)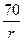 , where r is annual growth rate in %.
, where r is annual growth rate in %.


