
Заглавная страница Избранные статьи Случайная статья Познавательные статьи Новые добавления Обратная связь FAQ Написать работу КАТЕГОРИИ: ТОП 10 на сайте Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрацииТехника нижней прямой подачи мяча. Франко-прусская война (причины и последствия) Организация работы процедурного кабинета Смысловое и механическое запоминание, их место и роль в усвоении знаний Коммуникативные барьеры и пути их преодоления Обработка изделий медицинского назначения многократного применения Образцы текста публицистического стиля Четыре типа изменения баланса Задачи с ответами для Всероссийской олимпиады по праву 
Мы поможем в написании ваших работ! ЗНАЕТЕ ЛИ ВЫ?
Влияние общества на человека
Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрации Практические работы по географии для 6 класса Организация работы процедурного кабинета Изменения в неживой природе осенью Уборка процедурного кабинета Сольфеджио. Все правила по сольфеджио Балочные системы. Определение реакций опор и моментов защемления |
Krasnoyarsk team: Elena Glios, Margarita Mamontova, Nadezhda Silantyeva, Veronika Sychevskaya, Olga Fedoseenko.Содержание книги
Поиск на нашем сайте GREAT STARTS MAKE GREAT FINISHES Course Book for Aviation Personnel ICAO Level 3-4
INTRODUCTION
Great Starts Make Great Finishes is an aviation course book for air traffic controllers of ICAO levels 3-4. The established language syllabus is based on aviation topics that learners actually need at that stage in their language development. The Great Starts Make Great Finishes syllabus intergrates the learning of new vocabulary with speaking and listening skills development in delivering aviation English language. The coursecontents cover the main categories in language skills development and linguistic competence of learners that they need to achieve ICAO Level 4. The courseis designed to provide a series of skills-based challenging tasks that can help learners to measure their progress in terms of language competence according to ICAO testing system requirements. The coursecontents are fully compatible with ICAO testing system requirements and give learners regular opportunites to get prepared for it and then assessed. The Great Starts Make Great Finishes course is based on a guided discovery approach to learning: first learners check what they know and realize how much they know, then they are guided to make their passive knowledge active, together with a steady input of new language material. All new language material is regularly recycled and reviewed with a strong focus on speaking and listening throughout the course. The ultimate aim of most pre-operational learners is to achieve operational level (ICAO Level 4) through the aviation topics presented in course that motivate them to speak, so the key words and phrases necessary for extended speaking are given in fresh and stimulating contexts with numerous opportunites for communicative, personalised speaking practice. The course consists of Student's Book, Teacher's Book, CD-ROM and DVD-ROM. The Student's Book provides approximately 150 hours of teaching material for classroom activities, that can be extended with the photocopiable resources in the Teacher's Book. The Student's Book contains the material in the form of tasks for reading, listening, video activities providing and encouraging language skills development and linguistic competence they need to be able to communicate successfully on job-related topics. The Student's Book provides 10 thematically linked units, each with 2-5 lessons. Each lesson takes approximately 90 minutes depending on a group level competence. A teacher's creative initiative is highly appreciated. The CD-ROM contains all listening material for the Student's Book, including drill recordings, real radio exchange recordings. The DVD contains material for picture description activities and videos. The Teacher's Book includes Teaching Notes for 10 units, teaching tips for each lesson: listening scripts, answers for all the activities in the Student's Book and Photocopiable Materials. We believe that consolidated efforts of our team can help learners to expand their their knowledge of functional language, i.e. ablity to speak on job-related topics and improve their language competence in terms of ICAO testing system requirements. Krasnoyarsk team would like to thank the people who have contributed to making the course. In particular we would like to thank our co-authors: Marrianna Glagoleva, Elena Isaeva, Evgeniya Kocherova, Alla Nikolaenko for their support and ideas.
Answer the following questions given in the table below. We are going to watch a video Sky over Britain, what do you think these numbers refer to?
¸ Listening and Speaking Bank. Unit 1E. Exercise 9. How to describe a picture. Round-table talk. 1. What is the best / worst thing about your job? 2. What do you think is the most difficult in your job? 3. Can you give some examples of advantages and disadvantages of being an Air Traffic Controller? 4. Is there anything you dislike about your job? 5. 6. Do ATCOs in different countries have similar working conditions? 7. What would you change to improve working conditions of air traffic controllers? 8. What equipment do you use in your job? Are you satisfied with it? 9. What equipment would you like to have at your working place? 10. Would you like to work at a larger airport? 11. How do you think the job of an ATCO will change in the future? 12. Can you say a few words about ATCO’s training? 13. Does an ATCO need any special education? 14. What special knowledge and skills does the job of an ATCO require? 15. What qualities should you have to make a good air traffic controller? 16. Why is good health important for an ATCO? 17. Do you think it is possible that modern equipment might replace an air traffic controller? 18. Why are you learning English? 19. What is the secret of successful language learning? 20. What do you do to improve your English? 21. In what other areas of life can you use English? 22. How could good English make flights safer? 23. Is motivation important for English learning? 24. What do you find difficult in learning English? 25. What are the ICAO requirements in English language proficiency? 26. Would you learn English if you didn’t need it for your job?
VIDEO # 17
Unit 5A. Exercise 9-10. Read the instructions and do the task.
1. Look through the text and answer the following question: Q Why are wind speed and direction very important for flight?
3. Look at the table and check if you are right.
¸ VIDEO # 23
6.
Characteristics of a RW:
NB! Black ice – is very dangerous because it’s invisible but RW is slippery.
NB! Some specific information:
* But foreign pilots can also require braking coefficient in case of cross wind and poor braking action.
NB! Other characteristics of a RW: Rough / broken surface at the beginning of the RW. Snow banks / drifts on the RW edges. Snow removal / clearance at the stop-end of the RW. Snow removal / maintenance work / construction work in progress.
7. Can the runway covered with ice be perfect for landing?
¸ 8. Watch a short video. Have you changed your opinion? VIDEO # 24
9. Answer the following questions using your own experience: 1. 2. How does low temperature affect flights? 3. How does high temperature affect flights? 4. What are the controller’s actions, if a pilot reports low fuel temperature? Unit 5C. Exercise 12-13. Read the instructions and do the task.
Unit 5D. Exercise 3-4. Read the instructions and do the task. VIDEO # 26 1. A regular flight from Paris to Toronto takes 8 hours / 8 hours and a half. 2. An autopilot / a co-pilot does most of the work for the captain. 3. Overcast and rainy, with the chance of thunderstorm, temperature is below / in the low 20˚C. 4. The lightning has already forced the airport authorities to declare a Great / Red Alert. 5. The crew entered the holding pattern north-east / east-north of Toronto. |
| 6.The aircraft had 7500 kg of fuel in its tanks, more than / it wasn’t enough to get to the alternate. 7.After a short hold Air France 358 with 297 / 289 passengers on board began descent into the storm. 8.Ahead of Air France two aircraft / airbuses have touched down on the same RW that flight 358 was heading for. | 9.Facing unpredictable winds and a wet / bad RW the crew prepared for the landing. 10.Emergency workers were able to reach / search the burning jet just 52 seconds after the crash. 11.Remarkably, every single passenger and not all / all the members of the crew have managed to escape the burning plane. |
| 14. Answer the following questions using the information from the video you’ve watched and your own experience: | 1. What were the consequences of this aviation event? 2. Why did such an aviation event take place? 3. Was there any chance to prevent the aviation event with flight 358? 4. Who is to blame for this event in your opinion? |
 15. Round-talk table.
15. Round-talk table.
A B
| 1. to crack | a. to break or make smth. break suddenly into small parts |
| 2. to shatter | b. to take in |
| 3. to damage | c. to break (but not break apart/into pieces) |
| 4. to penetrate | d. animals living in natural habitat |
| 5. to ingest | e. combustion is lost |
| 6. wildlife | f. to terminate |
| 7. to abort | g. a group of birds flying together |
| 8. feathers | h. to make something move in different directions |
| 9. to disperse | i. to enter or move into |
| 10. flame out | j. to cause harm to something |
| 11. flock | k. to meet, usually unexpectedly |
| 12. to encounter | l. light soft things that cover a bird’s body |
| 13. to scare away | m. to frighten away |
| 14. to get sucked (into) | n. a metal covering for an engine |
| 15. to collide with | o. to hit |
| 16. cowl(ing) | p. to get ingested |
3. Complete the sentences with the words from the box. Make all necessary changes. Different variants are possible.
| 1. A bird can _______________ into an engine and cause an engine failure.
2. During the take-off roll, the aircraft _____________ sea gulls and the take-off __________________.
 3. The copilot was killed after a vulture ___________________ the windshield during cruise.
4. The explosion ________________ all the windows.
5. At most airports a special bird patrolis used _______________ flocks of birds _________ from the runways.
6. The pilot attempted to return to the airport but ___________________ trees just south of the airport.
7. One engine began to vibrate because it _____________________ a big bird. 3. The copilot was killed after a vulture ___________________ the windshield during cruise.
4. The explosion ________________ all the windows.
5. At most airports a special bird patrolis used _______________ flocks of birds _________ from the runways.
6. The pilot attempted to return to the airport but ___________________ trees just south of the airport.
7. One engine began to vibrate because it _____________________ a big bird.
|
AAR 541.
AUA 52.
AFR 112.
BAW 264.
DLH 710.
KAL 502.
KLM 865.

12.  Answer the following questions:
Answer the following questions:

¸
VIDEO # 29
| 1. Flight 4263, Boeing 767, departing from Manchester airport catches fire during take-off. 2. There are 225 passengers and 8 crew on board the aircraft. 3. The pilot declared Pan Pan due to engine malfunction. 4. There have been two large birds ingested into the left engine and which became the reason for engine failure. 5. The pilots decide to shut down the engine and to come back to Manchester airport. 6. Before landing they request clearance to dump fuel. 7. Thirty five minutes later they land successfully using only one engine. 8. There were only minor injuries to some passengers. 9. The plane is now being checked and the passengers are being boarded on another flight. | True / False True / False True / False True / False True / False True / False True / False True / False True / False |

Round-table talk.
1. Are controllers responsible for informing pilots about bird activities that might affect the flight?
2. What damage to aircraft can birds cause?
3. What might the results of bird strikes be?
4. What are pilots’ actions in case of bird strike?
5. What are controller’s actions in this emergency?
6. What birds scaring methods are used at your airport?
7. Have you ever handled or heard about traffic experiencing a bird strike?







 VIDEO # 30
VIDEO # 30
| Warm up. ¸ Watch a video and guess what we are going to discuss now. |
 Listening and Speaking Bank.
Listening and Speaking Bank.
A B
| 1. complicated | a) surroundings |
| 2. reverse | b) additional |
| 3. auxiliary | c) complex |
| 4. distribution | d) location |
| 5. to change | e) to alter |
| 6. purpose | f) to write down on a tape |
| 7. to record | g) dealing out |
| 8. variables | h) changeable quantities |
| 9. whereabouts | i) to hold something up |
| 10. aids | j) facilities |
| 11. to contain | k) with the purpose of |
| 12. to discover | l) to consist of, comprise |
| 13. in order to | m) action of changing direction |
| 14. deflection | n) to join or fix to smth |
| 15. mainly | o) function |
| 16. to attach | p) chiefly |
| 17. avionics | q) equipment |
| 18. device | r) to detect |
| 19. behaviour | s) aim |
| 20. to support | t) opposite |
| 21. environment | u) aviation electronics |
Round- table talk.
Where is the fin?
What do elevators control?
A B
| 1. rare | a) to make less, to shorten |
| 2. to determine | b) chance |
| 3. disaster | c) to happen |
| 4. opportunity | d) inappropriate |
| 5. probable | e) possible |
| 6. improper | f) catastrophe |
| 7. survey | g) analysis |
| 8. to minimize | h) to be |
| 9. shortly | i) not often |
| 10. consequence | j) result |
| 11. support | k) to find out |
| 12 to occur | l) soon |
| 13. to exist | m) help |
A B
| 1. mass | a) someone or something that can be trusted or depended on |
| 2. environment | b) a large amount |
| 3. to exclude | c) very great tiredness |
| 4. reliable | d) to trust someone or something |
| 5. to rely on | e) surroundings |
| 6. avionics | f) aviation radio electronic equipment |
| 7. considerably | g) to leave out, not to include something, especially a particular group of things |
| 8. fatigue | h) greatly |
| 3. Look at the numbers in the box and choose the number for each gap in the text. | 1950 / 1% / 1,843 / 80% / 11% / 53% / 6% / 2006 / 21% / 8% / |
Since the birth of flight, aircraft have crashed, often with serious consequences. This is because of the nature of flight, where air supports a mass of aircraft. As soon as this support fails, there is limited opportunity for a positive result. Because of this, aircraft design is aimed at minimizing the chance of failure. Despite this, accidents still occur, though statistically flying is the safest means of transportation. Approximately _________ of all aviation  accidents occur shortly before, after, or during takeoff or landing, and are often described as resulting from 'human error'; mid-flight disasters are rare. Among other things, the latter have been caused by bombs. An accident survey of ______ aircraft accidents from _______ through ________ determined the causes to be as follows:
accidents occur shortly before, after, or during takeoff or landing, and are often described as resulting from 'human error'; mid-flight disasters are rare. Among other things, the latter have been caused by bombs. An accident survey of ______ aircraft accidents from _______ through ________ determined the causes to be as follows:
Q _____: Pilot error,
Q _____: Mechanical failure,
Q _____: Weather,
Q _____: Sabotage (bombs, hijackings, shoot-downs),
Q _____: Other human error (air traffic controller error, improper loading of aircraft, improper maintenance, fuel contamination, language miscommunication etc.),
Q _____: Other causes.
The survey excluded military, private, and charter aircraft.
Unit 8A. Exercise 8-9
Read the instructions and do the task



 VIDEO # 32
VIDEO # 32
| Warm up. ¸ Watch a video and guess what we are going to discuss now. |
1. Match the words in column A to the words with the similar meaning in column B.
 2. Match the words in column A to their definitions in column B in the table given below.
2. Match the words in column A to their definitions in column B in the table given below.
| A | B |
| 1. probable | a) dangerous, important, serious | |
| 2. item | b) unfixed | |
| 3. strain | c) progress | |
| 4. cyclic | d) possible | |
| 5. swinging | e) to widen | |
| 6. advance | f) thing | |
| 7. to extend | g) different | |
| 8. numerous | h) many | |
| 9. various | i) repeated | |
| 10. critical | j) tension | |
| 11. to collapse | k) to fall down |
A B
| 1. tensile | a) to be likely affected to something |
| 2. term | b)able to be stretched |
| 3. to tend | c) a crack or broken part in hard substances |
| 4. to be subject to | d) to have a tendency |
| 5. fracture | e)faster than the speed of the sound |
| 6. supersonic speed | f) to make a small hole through which gases, smoke or liquid can escape from the enclosed space or a container |
| 7. debris | g)special word, often scientific |
| 8. to vent | h) remains, fragments |
| 9. to detect | i) to notice or discover something that is not easy to see or hear |
| 10. high-pitched | j) very high |
3. Read the text and choose a suitable heading for the paragraph from the list. 
| Q Metal Fatigue Q Metal Fatigue Events |
 Some structural failures are closely connected with metal fatigue. Metal fatigue is a term that we often hear, but seldom fully understand. What is it and when does it occur? Metal fatigue is a fracture mechanism. When things are broken due to metal fatigue, the fracture surface will have certain visible characteristics. Fatigue occurs when a metal or non-metal (plastic or composite) component is subject to swinging or cyclic stress and strain. Material fatigue can also result from pressurization and depressurization of an aircraft during takeoff and landing, or high winds causing the wings to move up and down.
Some structural failures are closely connected with metal fatigue. Metal fatigue is a term that we often hear, but seldom fully understand. What is it and when does it occur? Metal fatigue is a fracture mechanism. When things are broken due to metal fatigue, the fracture surface will have certain visible characteristics. Fatigue occurs when a metal or non-metal (plastic or composite) component is subject to swinging or cyclic stress and strain. Material fatigue can also result from pressurization and depressurization of an aircraft during takeoff and landing, or high winds causing the wings to move up and down.
 Technological advances and failure analysis have led to numerous ways to minimize the probability of starting fatigue cracks. Various inspection techniques are used looking for any fatigue cracks which might be growing. The idea here is to find and repair or replace the cracked component before the crack reaches a critical size. As with all serious emergencies the first option any crew will want is to get the aircraft safely onto the ground as soon as possible. This problem might also demand slow turns and descents. So the controller must provide immediate diversion to the nearest airfield available.
Technological advances and failure analysis have led to numerous ways to minimize the probability of starting fatigue cracks. Various inspection techniques are used looking for any fatigue cracks which might be growing. The idea here is to find and repair or replace the cracked component before the crack reaches a critical size. As with all serious emergencies the first option any crew will want is to get the aircraft safely onto the ground as soon as possible. This problem might also demand slow turns and descents. So the controller must provide immediate diversion to the nearest airfield available.
 Listening and Speaking Bank.
Listening and Speaking Bank.
Unit 8B. Exercise 4-5.
Read the instructions and do the task.
¸
✈ Watch a video and guess what we are going to discuss now.
VIDEO # 33
Unit 8C. Exercise 2-3.
Read the instructions and do the task.




 VIDEO # 35
VIDEO # 35
| Warm up. ¸ Watch a video and guess what we are going to discuss now. |
1.  Look through the text and think of a title. Then read the text and answer the questions.
Look through the text and think of a title. Then read the text and answer the questions.
……………………………………
 A review of accidents caused by fuel problems reveals that many power failures were due to use of improper fuel or careless servicing – fuelling aircraft from poorly filtered tanks.
A review of accidents caused by fuel problems reveals that many power failures were due to use of improper fuel or careless servicing – fuelling aircraft from poorly filtered tanks.
Fuel can be contaminated with water, rust, sand, dust, micro-organisms and certain additives that are not compatible with the fuel, fuel systems materials and engines. The presence of any contamination in aircraft fuel system is dangerous. During freezing temperatures, water may turn to ice, stopping fuel flow; freezing at high altitudes may plug fuel screens. Moreover, the fuel may be contaminated with dust and sand through openings in tanks and from the use of fuel handling equipment that is not clean. What is more, certain oil companies, in developing products to cope with aircraft fuel icing problems use some substances known as additives. Some additives may be harmful to other parts of the engine with which they come in contact. Fuel contamination is considered to be one of the most serious problems nowadays that might lead to engine vibration. In such a case a pilot has to shut down the engine, otherwise it can cause the engine destruction.
| additive / to reveal / specification / substances / harmful / to contaminate / compatible / |
A B
| harmful | a) chemicals |
| to contaminate | b) to make a place or substance dirty and dangerous by adding something to it |
| additive | c) causing damage |
| specification | d) substance which is added to something to improve it |
| compatible | e)well-matched |
| substances | f) to make something known which was previously hidden |
| to reveal | g) certain requirements |
A B
| 1. baggage handler | a) to try extremely hard to achieve smth, though it is very difficult |
| 2. to lock | b) to see smth happen |
| 3. to set to do smth | c) to find out |
| 4. to gain altitude | d) person who loads baggage |
| 5. huge | e) to start doing smth |
| 6. to shatter | f) extremely bad, frightening |
| 7. to bank | g) emergency |
| 8. to be behind schedule | h) to fasten something, usually with a key |
| 9. to struggle | i) event |
| 10. to pitch | j) to break suddenly into pieces |
| 11. to pick up speed | k) to go faster |
| 12. to witness | l) to get somewhere in time |
| 13. horrifying | m) to stop going up and down and continue at the same height |
| 14. to disappear | n) to move up and down in an uncontrolled way with the movement of the air |
| 15. hole | o) to reach height |
| 16. to level out/off | p) not to be ready to depart at the planned time |
| 17. crisis | q) to become impossible to find |
| 18. crippled | r) extremely large in size |
| 19. scene | s) damaged, disabled |
| 20. to discover | t) empty space |
| 21. to make it to | u) to slope to one side when turning |
7. Fill in the gaps with suitable phrases from the box given below.
|
VIDEO # 36
¸
VIDEO # 37
A B
| 1. layout | a) knowledge or understanding of a particular subject or a situation |
| 2. to be subject to | b) an official document which permits to do, own, or use smth. |
| 3. to fire | c) not suitable |
| 4. license | d) a type of lock for a door |
| 5. to revoke | e) to be likely to have, suffer or be affected by smth. |
| 6. to screen | f) when someone or something is very much dependant on someone or something else |
| 7. fitness | g) to become better |
| 8. to dive | h) to take medical test to see if someone has an illness |
| 9. latch | i) to force someone to leave their job, to dismiss someone from one’s job |
| 10 over-relianced | j) being very tired |
| 11 awareness | k) conditions, when you are healthy and strong enough to do hard work or sports |
| 12 to improve | l) to cancel a law, license |
| 13. fatigue | m) to make less forceful |
| 14. improper | n) the way in which the parts of something are arranged according to a plan |
| 15. to blunt | o) to go lower quickly |
| 16. manpower | p) the number of people working or available for work |
3. Fill in the gaps with appropriate words given in the box below. Make all necessary changes.
4. Look through the text below and find the answer to the following question: ✈ “Whose mistakes might lead to aviation events?” | 1. Special attention should be paid to wind flow when flights are made over hills or mountainous _______________. 2. The trainee’s flying skills ____________ ______________ a lot for recent time. 3. There are two ________________ cloud groups, stratus and cumulus. 4. Flights _____________________ to delays after the heavy snowfall. 5. The airline _______________ him for being drunk before the scheduled flight. 6. His license _________________ recently ______________. 7. The company is offering a free health _________________ to all air traffic controllers. 8. Being a pilot requires a high level of physical and psychological _________________. 9. The aircraft appeared to ________________ vertically towards the crowd. 10. Situational __________________ (having a picture) is central to the job of air traffic controller. |
Though the statistics approves that aviation is the safest mode of transport, a lot of people nowadays are afraid of flying. According to all available information, the reason for the majority of incidents and accidents is the human error.

 Indeed human factor is currently the most common factor of aviation crashes. It deals with all the human elements of people in man-machine systems. It covers not only the traditional design and layout of equipment and workplaces, but also all aspects of manpower, organization, management, distribution of responsibility, automation, communication, skills, training, health, safety, and the prevention of errors and accidents.
Indeed human factor is currently the most common factor of aviation crashes. It deals with all the human elements of people in man-machine systems. It covers not only the traditional design and layout of equipment and workplaces, but also all aspects of manpower, organization, management, distribution of responsibility, automation, communication, skills, training, health, safety, and the prevention of errors and accidents.
Pilots’ and controllers’ errors and improper communication are often reason for the collision of aircraft. Using inadequate phraseology can cause misunderstanding and result in a disaster, so the language aspect is also important. If pilots fail to monitor the flight instruments properly and if air traffic controllers fail to monitor aircraft tracks on radar screens and provide necessary separation between aircraft properly can have catastrophic consequences.
Rarely, flight crew members are arrested or subject to disciplinary action for being intoxicated on the job. In 2002 two America West pilots were arrested just before they were scheduled to fly from Miami, Florida, to Arizona, because they had been drinking alcohol. The pilots have been fired from America West and the FAA revoked their pilot’s licenses.
Although most air crews are screened for psychological fitness, some may take suicidal actions. In the case of Egypt Air Flight 990 in 1999, it appears that the first officer (co-pilot) deliberately dove his aircraft into the Atlantic Ocean.

 But human factors are not limited to errors made by the pilots and the air traffic controllers. The people concerned are those associated with the total system: designers, equipment suppliers, maintainers, support personnel, instructors and so on.
But human factors are not limited to errors made by the pilots and the air traffic controllers. The people concerned are those associated with the total system: designers, equipment suppliers, maintainers, support personnel, instructors and so on.
The failure to close a cargo door properly on Turkish Airlines Flight 981 in 1974 resulted in the loss of the aircraft – however, the design of the cargo door latch was also a major factor in the incident. In case of Japan Airlines Flight 123, improper maintenance resulted in the loss of the vertical stabilizer.
 Controlled flight into terrain (CFIT) is a class of accident in which an undamaged aircraft is flown, under control, into terrain. These accidents typically are a result of pilot error or navigational system error. Some pilots, over-relianced on advanced electronic navigational systems such as GPS, INS, Flight Management System computers, are partially responsible for these accidents. Crew awareness and careful monitoring of navigational systems can prevent CFIT accidents.
Controlled flight into terrain (CFIT) is a class of accident in which an undamaged aircraft is flown, under control, into terrain. These accidents typically are a result of pilot error or navigational system error. Some pilots, over-relianced on advanced electronic navigational systems such as GPS, INS, Flight Management System computers, are partially responsible for these accidents. Crew awareness and careful monitoring of navigational systems can prevent CFIT accidents.
Other technical aids can be used to help pilots maintain situational awareness. A ground-collision warning system is an on-board system that will alert a pilot if the aircraft is about to fly into the ground. Another on-board system, the TCAS computer, scans the airspace around the aircraft and in case an intruder aircraft is detected, it determines if evasive action is necessary, and if so what kind of evasive actions has to be taken.
 Flight incidents seldom happen because of deliberate non-observance of the established rules. Usually aviation events occur in circumstances which appear to be above opportunities of the person. Thus, while analyzing actions of the person during aviation incident or accident, his decision and acts it is necessary to take into account the level of working capacity of the person which depends on a limit of his physical and psychological opportunities, knowledge, qualification, skills, experience. The person is subject to such a big number of variable factors, various situations and circumstances that to predict all of them is very difficult. Therefore much attention should be given to all factors which can influence the particular person. In other words, it is necessary to analyze not only mistakes of a person, but also the reason for which they have occurred.
Flight incidents seldom happen because of deliberate non-observance of the established rules. Usually aviation events occur in circumstances which appear to be above opportunities of the person. Thus, while analyzing actions of the person during aviation incident or accident, his decision and acts it is necessary to take into account the level of working capacity of the person which depends on a limit of his physical and psychological opportunities, knowledge, qualification, skills, experience. The person is subject to such a big number of variable factors, various situations and circumstances that to predict all of them is very difficult. Therefore much attention should be given to all factors which can influence the particular person. In other words, it is necessary to analyze not only mistakes of a person, but also the reason for which they have occurred.
5. Read the text again. Find the information which could help prove the following statement:

Q “Self-calmness, self-assurance, absence of self-discipline can blunt feeling of danger and can lead to a bad end”
VIDEO # 39
Unit 9C. Exercise 5.
6. Report the situation using as many details as possible.
¸
VIDEO # 40
| Events | Reasons for events |
| Hanging by a thread | A few rivets caused a tail to blow away |
| Blow out | An aircraft appeared in the wrong place at the wrong time and was shot by mistake |
| Flying blind | Being in the cockpit a child pressed some buttons and caused aircraft to crash |
| Out of control | Piece of tape with glue covered static ports that had to provide data on altitude and speed (static ports should be covered during cleaning, but then any piece of tape should be removed) |
| Kid in the cockpit | Tiny fatigue crack caused a roof to blow away |
| Attack over Baghdad | Wrong sized bolts caused a windscreen to blow away and a pilot to suck out |
A B
| 1. fascinating | a) being controlled by computers and designed to react in a suitable way depending on the situation |
| 2. mystery | b) not happening very often; unusual |
| 3. smart | c) very interesting |
| 4. to be faced with smth | d) to deal with difficulties or a difficult situation |
| 5. rare | e) to do something, especially task/duty |
| 6. to perform | f) an event that people don’t understand or can’t explain |
| 7. useful | g) helpful, something that can help one do something |
VIDEO # 41
| Q Why is traveling by plane so popular nowadays ? | |
| Q What factors can affect safe flying? | |
| Q Are modern aircraft reliable enough? | |
| Q Have accidents reduced in number nowadays? Why? Why not? |
A B
| 1. mysteriously | a) district |
| 2. neighborhood | b) to find out |
| 3. to mobilise | c) combined material |
| 4. to determine | d) to be similar to |
| 5. to assume | e) discovery |
| 6. clue | f) to hurry when it is not necessary, to make false start |
| 7. obvious | g) hint, sign that helps to understand something |
| 8. to wallow | h) secretively |
| 9. composite material | i) understandable, evident |
| 10. to fracture | j) proof, facts, data |
| 11. evidence | k) to turn aside |
| 12. to swing | l) to organize oneself quickly |
| 13. to resemble | m) to move from side to side |
| 14. to deflect | n) to suppose |
| 15. revelation | o) to crack, to break |
| 16. to jump the gun | p) to move backward and forward back |
VIDEO # 42
| Q Co-pilots’ mistake Q Mechanical failure Q Terrorist’s attack Q Wake turbulence |
6. Report on the situation using the following words and phrases:
Q 12 November 2001
Q American 587
Q JFK Airport
Q 260 passengers and 5 people on the ground
Q To mobilise to determine a cause
Q To assume a terrorist act
Q No obvious evidence
Q Vital clue of a mechanical failure
Q Unique quality: composite material
Q Data recorder
Q Key pieces of evidence
Q To encounter wake turbulence
Q 5 miles separation
Q Pretty good speed
Q Competency of co-pilot
Q Shocking revelation
Q Abnormal manoeuvre
Q To jump the gun on responding
Q To deflect a rudder back and forth
Round-talk table.
Q Advanced equipment costs a lot of money. Which is more important, safety or cost?
Q Do you know any measures that are taken nowadays to improve flight safety?
Q What areas of air safety do you think require improvement?
Q What threatens flight safety nowadays? (Can you think of overcrowded skies over Europe, international terrorism …?)
Q How do you provide safety from the point of view of an aerodrome/approach/ en-route controller?
Q To what extent are modern equipment and machines reliable concerning flight safety?
Q Do you agree that flying is the safest way of traveling?
Q Do you think flying will be safer in the future? Why? Why not?



| Listening and Speaking Bank. | 
|
 Unit 1E, exercise 9.
Unit 1E, exercise 9.
Unit 2A, exercise 3. Domino collocation.
| to safeguard civil aviation |
| unlawful interference |
| to detect explosives |
| access area |
| false alarm |
| sniffer dog |
| biometric parameter |
| to carry out security |
| screening process |
| guard station |
| conveyor belt |
| body search |
| metal detector |
| attempted crime |
| terminal entrance |
| unattended baggage |
| suspicious items |
| explosive device |
Unit 4A, exercise 8-9.
9
Unit 4B, exercise 14-15.
9
Unit 5A, exercise 9-10.
9
Unit 5C, exercise 2-3.
9
|
| Поделиться: |



 Can you describe your working conditions? Are you satisfied with them?
Can you describe your working conditions? Are you satisfied with them?





 Explain the following words and phrases in English.
Explain the following words and phrases in English. 

 Listening and Speaking Bank.
Unit 4B. Exercise 14-15. Read the instructions and do the task.
16. Match the words and phrases to their definitions.
Listening and Speaking Bank.
Unit 4B. Exercise 14-15. Read the instructions and do the task.
16. Match the words and phrases to their definitions.




 A pilot needs to know wind direction and speed as wind might affect flight negatively. En route the headwind may delay the arrival of flights and is to be avoided if possible. The tailwind can be of a great advantage as it increases the ground speed and results in reduction of fuel consumption. As for the cross wind it is extremely dangerous for an aircraft, especially on landing. An aircraft loses speed and might not get on the RW. What is more, it can cause a crash of the aircraft. Winds vary with altitude and also from one place to another, so information about wind is very important.
A pilot needs to know wind direction and speed as wind might affect flight negatively. En route the headwind may delay the arrival of flights and is to be avoided if possible. The tailwind can be of a great advantage as it increases the ground speed and results in reduction of fuel consumption. As for the cross wind it is extremely dangerous for an aircraft, especially on landing. An aircraft loses speed and might not get on the RW. What is more, it can cause a crash of the aircraft. Winds vary with altitude and also from one place to another, so information about wind is very important.
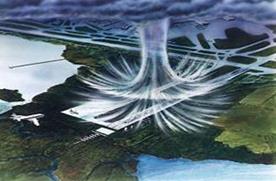
 Windshear is also a danger for an aircraft making steep turns near the ground. The different airspeed experienced by each wing tip can result in an aerodynamic stall on one wing, causing a loss of control.
Windshear is also a danger for an aircraft making steep turns near the ground. The different airspeed experienced by each wing tip can result in an aerodynamic stall on one wing, causing a loss of control.
 As the result of the accidents in the 1970s and 1980s, in 1988 the U.S. Federal Aviation Administration mandated that all commercial aircraft had to be equipped with on-board windshear detection systems. Since 1995, the number of major civil aircraft accidents caused by windshear has dropped to approximately one every ten years.
As the result of the accidents in the 1970s and 1980s, in 1988 the U.S. Federal Aviation Administration mandated that all commercial aircraft had to be equipped with on-board windshear detection systems. Since 1995, the number of major civil aircraft accidents caused by windshear has dropped to approximately one every ten years.
 Speak about any real situation when windshear caused a serious aviation event.
Speak about any real situation when windshear caused a serious aviation event.


 What weather phenomena influence visibility?
4. Under what weather conditions is landing prohibited?
What weather phenomena influence visibility?
4. Under what weather conditions is landing prohibited?


 What weather phenomena can influence RW condition?
2. What is bad RW condition?
3. Why is black ice dangerous for an aircraft?
4. Can you describe perfect RW condition?
5. Can you describe any real situation when bad RW condition resulted in a serious accident?
What weather phenomena can influence RW condition?
2. What is bad RW condition?
3. Why is black ice dangerous for an aircraft?
4. Can you describe perfect RW condition?
5. Can you describe any real situation when bad RW condition resulted in a serious accident?

 There are some hazardous weather phenomena which can seriously affect RW condition. They are heavy precipitation, such as snow, rain and freezing rain and sleet, changeable temperature, ice, etc. Ice and snow can make braking and taxing difficult or impossible if severe enough. Freezing rain might cause icing of an aircraft and RW surface. It reduces braking action and might be the reason for sliding off the RW or undercarriage problem which can lead to a serious incident or accident.
There are some hazardous weather phenomena which can seriously affect RW condition. They are heavy precipitation, such as snow, rain and freezing rain and sleet, changeable temperature, ice, etc. Ice and snow can make braking and taxing difficult or impossible if severe enough. Freezing rain might cause icing of an aircraft and RW surface. It reduces braking action and might be the reason for sliding off the RW or undercarriage problem which can lead to a serious incident or accident.
 Look through the 3 characteristics of a RW and cross the odd out.
Look through the 3 characteristics of a RW and cross the odd out.

 Does temperature influence flying?
Does temperature influence flying?


