
Заглавная страница Избранные статьи Случайная статья Познавательные статьи Новые добавления Обратная связь FAQ Написать работу КАТЕГОРИИ: ТОП 10 на сайте Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрацииТехника нижней прямой подачи мяча. Франко-прусская война (причины и последствия) Организация работы процедурного кабинета Смысловое и механическое запоминание, их место и роль в усвоении знаний Коммуникативные барьеры и пути их преодоления Обработка изделий медицинского назначения многократного применения Образцы текста публицистического стиля Четыре типа изменения баланса Задачи с ответами для Всероссийской олимпиады по праву 
Мы поможем в написании ваших работ! ЗНАЕТЕ ЛИ ВЫ?
Влияние общества на человека
Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрации Практические работы по географии для 6 класса Организация работы процедурного кабинета Изменения в неживой природе осенью Уборка процедурного кабинета Сольфеджио. Все правила по сольфеджио Балочные системы. Определение реакций опор и моментов защемления |
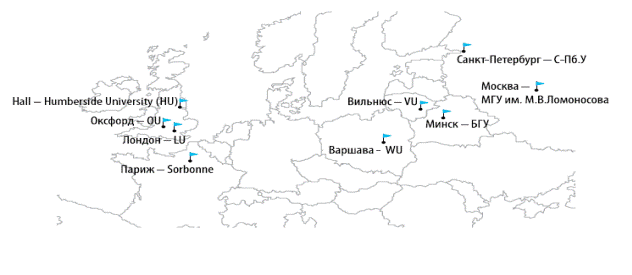
Look at the map of the Universities marked on the map of Europe. Do you know them? Pronounce their names in English. Sum up the ways universities are named.Содержание книги
Поиск на нашем сайте
Vilnius – VU, Minsk – the BSU, Moscow – MSU named after M.V. Lomonosov, St. Petersburg – SPbU, Warsaw – WU, London – LU, Oxford – ОU, Hall – Humberside University (HU), Paris – the Sorbonne. Look at the map again and name other European countries and their famous Universities. · Share what you know about the Universities you have named. · Mark the location of these Universities on the map. Below there is a list of criteria that can be of importance when one chooses a university to study at. Discuss these criteria and mark if they were considered by you when you made up your mind about the university to enter.
& 5 Read the text ‘ Types of Universities’ and find information on different types of universities and different types of teaching. While reading write out words and expressions that describe teaching and fill in the table below:
Types of Universities
There are several types of Universities that historically changed each other and were different in the way of study.
Industrial Shop Corporation First European Universities originated from Industrial Shop Corporations. Sorbonne and University of Prague featured shops of masters. Pupils gathered around the master (teacher) to get the mysteries of trade from hand to hand, by the teacher in person. The teacher had a small number of pupils. Such conditions of teaching formed Associative Pedagogy. Nowadays this form of teaching disappeared as a University type, but the importance of associative pedagogy still exists. This is the way Brahmanas and Daoists have been taught now. Orthodox Cloisters keep to this educational pattern as well. This type of university emphasises the role of a teacher as a model.
Classical Research University Gradually, with the development of sciences and education, scientific research and inquiries widely came into the university practice. The master`s figure was enriched with the figure of a researcher. As a result, in the beginning of XIX century Humboldt and Fichte established a new type of University that later became the model of German Classical Research University. Its fundamental practice consisted in science and art studies, as well as in classical knowledge transmission. The development of sciences was the basis* of this university type, for every new science led to the appearance of a new university discipline.
Factory University
Gradually by XX century, with its intensive industrial development, Factory University had come into demand. This type of University prepared a great number of specialists to satisfy the needs of the developing economy. This is the type of University where science takes the sidelines and, instead of assimilating the scientific basics, students assimilate different systems of knowledge, packed in academic subjects. Moreover, students learn a great number of subjects (about 80-100). This mass model resembles an educational conveyor that follows a certain curriculum. A new figure appears here – that of a teacher-specialist who, following the standard scheme, transfers estranged knowledge. His task is to prepare hundreds and thousands of specialists who know and can use a standard set of actions and procedures. This model is still followed by the majority of Russian Universities. Due to the rapidly developing economy, knowledge amplification, and the boost of professional requirements, this University type is losing its positions.
Supermarket University AfterWorld War II, due to democratization, education in developed countries was becoming more and more affordable. While it was seen as a service that was bringing high income, education became a separate branch of economy. It was profitable because of the fact that universities were treated as big supermarkets with a great number of services to be bough and the students, just like customers in these supermarkets, were given an opportunity to choose the services that they needed.
A new figure of educational manager appears with this type of universities. He doesn't treat students as individuals. His job is to ensure the process of students’ following educational schemes as well as to control the work of the educational mechanism in general. The amount of direct contact between the professors and students is minimized. Such a system requires students’ independent work that is why professors ask more than answer.
Project University
This type also originated in developed countries, in particular, in the advanced US universities and in the best Universities of the former USSR. This type does not presuppose teaching groups of students. It focuses on familiarizing students with early professional training by involving students into the work at places of their future professional activity (industrial companies, corporations and laboratories). There is a very slight difference between teachers and students in this type of universities. Team work is necessary here. Students and postgraduates, involved into a scientific project, form a project team. Team members specialize in different spheres and pursue their own goals in the project. Quite a concrete input into the project is required from everyone. Being in the process of carrying out projects, students get educated. It’s important that besides universal knowledge, students acquire creative thinking skills, communicative and business competence. This type is impossible on a massive scale, for such a university cannot be very big, with a high number of students. This type can be 'built-in' as separate educational modules (colleges, institutes and/or business schools) of big University Corporations. Network University By virtue of the contemporary tendency towards international relations expansion, world business and economy formation, global corporation and Universities competition growth, Universities (especially the strongest ones) started the so-called network model development. Network universities have affiliates in different regions and countries. All the subsidiaries work under common international programs, such as double diplomas programs, joint projects and research programs. Besides teaching future specialists, they produce strategies of a country/region/city development, development of economy, projects and programs for business companies and corporations. In such conditions a network university is not just an educational establishment, it`s a kind of a holding company, fulfilling different culture functions. This is the only type to survive in contemporary conditions. It`s impossible for a university to survive with a single educational function aiming at transmitting experience. (Smirnov, S.A. Russian higher school: on the way to new institutions. Retrieved from http://www.antropolog.ru/doc/persons/smirnov/smirnov17)
Using the Vocabulary that you have collected in this section discuss with your groupmates the type of the University you study at, the type of teaching that is being practiced there and the type of teaching you would like to experience.
Interpret – verb, [T] to explain; to translate; to construe; to give one’s own conception of, as in a play or musical composition. verb, [I] to serve, to translate as an interpreter for speakers of different languages. Interpretation is explanation; meaning; translation; exposition; the expression of a person’s conception of anything (text, piece of art, etc.). (Interpretation. (2009). In The Dictionary of the English Language. Retrieved from http://www.thefreedictionary.com/interpretation) 1 Read and compare texts and their interpretations. Answer the questions: · What is the difference between the original text and its interpretation? · What is the difference between interpretations given here and the renderings that you made in Section 2A?
Interpretation: As we see, knowledge is the interpretation of one’s experience. The conditions, whether we (1) obtain knowledge by living, or (2) take knowledge from teachers completely relying on them, we most evidently choose by ourselves. In any case, if one chooses the second approach to obtain knowledge (that is, completely relying on teachers), it is worth knowing that even having learnt a discipline, one needs to check it by their own experience; otherwise knowledge is nothing but the doctrines of the others.
Interpretation: Here we see the significance of interaction to obtain knowledge, as a person who studies and the one who teaches are forming a holistic set, a linkage: each element of the linkage is molding the other (each is the cortege [1] of the other).
Interpretation: Studying the meaning of Latin words we can discuss what ‘lectures’ or ‘classes’ at university are. Lecture is not aimed at giving knowledge. Its aim is to give opinions, attitudes, evaluation and choices (what is worth paying attention to and what is not, which definition to choose and which not). A lecture is the very beginning of knowledge: it is aimed at pushing you to reading, thinking, research, pushing you to real cognition. Listening to lectures is just a starting step to obtain knowledge.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Последнее изменение этой страницы: 2016-08-01; просмотров: 64; Нарушение авторского права страницы; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! infopedia.su Все материалы представленные на сайте исключительно с целью ознакомления читателями и не преследуют коммерческих целей или нарушение авторских прав. Обратная связь - 3.145.42.140 (0.009 с.) |

 1 4 Present the most significant criteria for choosing a university in the Vocabulary Map. You can include the criteria mentioned in Task 3 and/or add new ones.
1 4 Present the most significant criteria for choosing a university in the Vocabulary Map. You can include the criteria mentioned in Task 3 and/or add new ones. As the number of classical universities grew, a new type of teaching was formed. A professor was treated as a scientific knowledge holder and as a teacher whose duty was to familiarize students with the true science and art. The phenomenon of live contact still existed, but it gained universal character: a teacher shared not only his/her own experience, but also the universal experience of generations.
As the number of classical universities grew, a new type of teaching was formed. A professor was treated as a scientific knowledge holder and as a teacher whose duty was to familiarize students with the true science and art. The phenomenon of live contact still existed, but it gained universal character: a teacher shared not only his/her own experience, but also the universal experience of generations. This model, worked out in American universities, is associated with the credit* system of education. Students study academic disciplines the majority of which they choose out of the list proposed. Each course, when passed, gives a student definite number of credits. In this case credits serve as standard units necessary for control and for transferring students to their next year, another course or from one University to another.
This model, worked out in American universities, is associated with the credit* system of education. Students study academic disciplines the majority of which they choose out of the list proposed. Each course, when passed, gives a student definite number of credits. In this case credits serve as standard units necessary for control and for transferring students to their next year, another course or from one University to another. In the text there are a number of sentences where Passive Voice is used. Did you have any difficulties in recognizing such sentences and translating them into Russian? If ‘yes’, go to Grammar and Vocabulary File. Passive Voice, p. 151.
In the text there are a number of sentences where Passive Voice is used. Did you have any difficulties in recognizing such sentences and translating them into Russian? If ‘yes’, go to Grammar and Vocabulary File. Passive Voice, p. 151.


