Заглавная страница Избранные статьи Случайная статья Познавательные статьи Новые добавления Обратная связь FAQ Написать работу КАТЕГОРИИ: ТОП 10 на сайте Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрацииТехника нижней прямой подачи мяча. Франко-прусская война (причины и последствия) Организация работы процедурного кабинета Смысловое и механическое запоминание, их место и роль в усвоении знаний Коммуникативные барьеры и пути их преодоления Обработка изделий медицинского назначения многократного применения Образцы текста публицистического стиля Четыре типа изменения баланса Задачи с ответами для Всероссийской олимпиады по праву 
Мы поможем в написании ваших работ! ЗНАЕТЕ ЛИ ВЫ?
Влияние общества на человека
Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрации Практические работы по географии для 6 класса Организация работы процедурного кабинета Изменения в неживой природе осенью Уборка процедурного кабинета Сольфеджио. Все правила по сольфеджио Балочные системы. Определение реакций опор и моментов защемления |
Contents. Dedication. Elon’s world. Africa. Canada. Elon’s first start-up. Paypal Mafia boss. Mice in space. Photographic insert. All electric. Pain, suffering, and survivalСодержание книги
Поиск на нашем сайте
CONTENTS
DEDICATION 1 ELON’S WORLD 2 AFRICA 3 CANADA 4 ELON’S FIRST START-UP 5 PAYPAL MAFIA BOSS 6 MICE IN SPACE PHOTOGRAPHIC INSERT 7 ALL ELECTRIC 8 PAIN, SUFFERING, AND SURVIVAL 9 LIFTOFF 10 THE REVENGE OF THE ELECTRIC CAR 11 THE UNIFIED FIELD THEORY OF ELON MUSK EPILOGUE APPENDIX 1 APPENDIX 2 APPENDIX 3 ACKNOWLEDGMENTS ABOUT THE AUTHOR ALSO BY ASHLEE VANCE CREDITS COPYRIGHT ABOUT THE PUBLISHER
DEDICATION
For Mum and Dad. Thanks for Everything.
ELON’S WORLD DO YOU THINK I’M INSANE?” This question came from Elon Musk near the very end of a long dinner we shared at a high-end seafood restaurant in Silicon Valley. I’d gotten to the restaurant first and settled down with a gin and tonic, knowing Musk would—as ever—be late. After about fifteen minutes, Musk showed up wearing leather shoes, designer jeans, and a plaid dress shirt. Musk stands six foot one but ask anyone who knows him and they’ll confirm that he seems much bigger than that. He’s absurdly broad-shouldered, sturdy, and thick. You’d figure he would use this frame to his advantage and perform an alpha-male strut when entering a room. Instead, he tends to be almost sheepish. It’s head tilted slightly down while walking, a quick handshake hello after reaching the table, and then butt in seat. From there, Musk needs a few minutes before he warms up and looks at ease. Musk asked me to dinner for a negotiation of sorts. Eighteen months earlier, I’d informed him of my plans to write a book about him, and he’d informed me of his plans not to cooperate. His rejection stung but thrust me into dogged reporter mode. If I had to do this book without him, so be it. Plenty of people had left Musk’s companies, Tesla Motors and SpaceX, and would talk, and I already knew a lot of his friends. The interviews followed one after another, month after month, and two hundred or so people into the process, I heard from Musk once again. He called me at home and declared that things could go one of two ways: he could make my life very difficult or he could help with the project after all. He’d be willing to cooperate if he could read the book before it went to publication, and could add footnotes throughout it. He would not meddle with my text, but he wanted the chance to set the record straight in spots that he deemed factually inaccurate. I understood where this was coming from. Musk wanted a measure of control over his life’s story. He’s also wired like a scientist and suffers mental anguish at the sight of a factual error. A mistake on a printed page would gnaw at his soul—forever. While I could understand his perspective, I could not let him read the book, for professional, personal, and practical reasons. Musk has his version of the truth, and it’s not always the version of the truth that the rest of the world shares. He’s prone to verbose answers to even the simplest of questions as well, and the thought of thirty-page footnotes seemed all too real. Still, we agreed to have dinner, chat all this out, and see where it left us. Our conversation began with a discussion of public-relations people. Musk burns through PR staffers notoriously fast, and Tesla was in the process of hunting for a new communications chief. “Who is the best PR person in the world?” he asked in a very Muskian fashion. Then we talked about mutual acquaintances, Howard Hughes, and the Tesla factory. When the waiter stopped by to take our order, Musk asked for suggestions that would work with his low-carb diet. He settled on chunks of fried lobster soaked in black squid ink. The negotiation hadn’t begun, and Musk was already dishing. He opened up about the major fear keeping him up at night: namely that Google’s cofounder and CEO Larry Page might well have been building a fleet of artificial-intelligence-enhanced robots capable of destroying mankind. “I’m really worried about this,” Musk said. It didn’t make Musk feel any better that he and Page were very close friends and that he felt Page was fundamentally a well-intentioned person and not Dr. Evil. In fact, that was sort of the problem. Page’s nice-guy nature left him assuming that the machines would forever do our bidding. “I’m not as optimistic,” Musk said. “He could produce something evil by accident.” As the food arrived, Musk consumed it. That is, he didn’t eat it as much as he made it disappear rapidly with a few gargantuan bites. Desperate to keep Musk happy and chatting, I handed him a big chunk of steak from my plate. The plan worked . . . for all of ninety seconds. Meat. Hunk. Gone.
It took awhile to get Musk off the artificial intelligence doom-and-gloom talk and to the subject at hand. Then, as we drifted toward the book, Musk started to feel me out, probing exactly why it was that I wanted to write about him and calculating my intentions. When the moment presented itself, I moved in and seized the conversation. Some adrenaline released and mixed with the gin, and I launched into what was meant to be a forty-five-minute sermon about all the reasons Musk should let me burrow deep into his life and do so while getting exactly none of the controls he wanted in return. The speech revolved around the inherent limitations of footnotes, Musk coming off like a control freak and my journalistic integrity being compromised. To my great surprise, Musk cut me off after a couple of minutes and simply said, “Okay.” One thing that Musk holds in the highest regard is resolve, and he respects people who continue on after being told no. Dozens of other journalists had asked him to help with a book before, but I’d been the only annoying asshole who continued on after Musk’s initial rejection, and he seemed to like that. The dinner wound down with pleasant conversation and Musk laying waste to the low-carb diet. A waiter showed up with a giant yellow cotton candy desert sculpture, and Musk dug into it, ripping off handfuls of the sugary fluff. It was settled. Musk granted me access to the executives at his companies, his friends, and his family. He would meet me for dinner once a month for as long as it took. For the first time, Musk would let a reporter see the inner workings of his world. Two and a half hours after we started, Musk put his hands on the table, made a move to get up, and then paused, locked eyes with me, and busted out that incredible question: “Do you think I’m insane?” The oddity of the moment left me speechless for a beat, while my every synapse fired trying to figure out if this was some sort of riddle, and, if so, how it should be answered artfully. It was only after I’d spent lots of time with Musk that I realized the question was more for him than me. Nothing I said would have mattered. Musk was stopping one last time and wondering aloud if I could be trusted and then looking into my eyes to make his judgment. A split second later, we shook hands and Musk drove off in a red Tesla Model S sedan. ANY STUDY OF ELON MUSK must begin at the headquarters of SpaceX, in Hawthorne, California—a suburb of Los Angeles located a few miles from Los Angeles International Airport. It’s there that visitors will find two giant posters of Mars hanging side by side on the wall leading up to Musk’s cubicle. The poster to the left depicts Mars as it is today—a cold, barren red orb. The poster on the right shows a Mars with a humongous green landmass surrounded by oceans. The planet has been heated up and transformed to suit humans. Musk fully intends to try and make this happen. Turning humans into space colonizers is his stated life’s purpose. “I would like to die thinking that humanity has a bright future,” he said. “If we can solve sustainable energy and be well on our way to becoming a multiplanetary species with a self-sustaining civilization on another planet—to cope with a worst-case scenario happening and extinguishing human consciousness—then,” and here he paused for a moment, “I think that would be really good.”
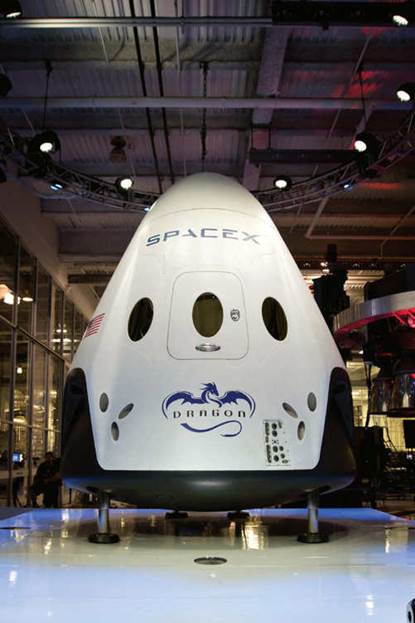
If some of the things that Musk says and does sound absurd, that’s because on one level they very much are. On this occasion, for example, Musk’s assistant had just handed him some cookies-and-cream ice cream with sprinkles on top, and he then talked earnestly about saving humanity while a blotch of the dessert hung from his lower lip. Musk’s ready willingness to tackle impossible things has turned him into a deity in Silicon Valley, where fellow CEOs like Page speak of him in reverential awe, and budding entrepreneurs strive “to be like Elon” just as they had been striving in years past to mimic Steve Jobs. Silicon Valley, though, operates within a warped version of reality, and outside the confines of its shared fantasy, Musk often comes off as a much more polarizing figure. He’s the guy with the electric cars, solar panels, and rockets peddling false hope. Forget Steve Jobs. Musk is a sci-fi version of P. T. Barnum who has gotten extraordinarily rich by preying on people’s fear and self-hatred. Buy a Tesla. Forget about the mess you’ve made of the planet for a while. I’d long been a subscriber to this latter camp. Musk had struck me as a well-intentioned dreamer—a card-carrying member of Silicon Valley’s techno-utopian club. This group tends to be a mix of Ayn Rand devotees and engineer absolutists who see their hyperlogical worldviews as the Answer for everyone. If we’d just get out of their way, they’d fix all our problems. One day, soon enough, we’ll be able to download our brains to a computer, relax, and let their algorithms take care of everything. Much of their ambition proves inspiring and their works helpful. But the techno-utopians do get tiresome with their platitudes and their ability to prattle on for hours without saying much of substance. More disconcerting is their underlying message that humans are flawed and our humanity is an annoying burden that needs to be dealt with in due course. When I’d caught Musk at Silicon Valley events, his highfalutin talk often sounded straight out of the techno-utopian playbook. And, most annoyingly, his world-saving companies didn’t even seem to be doing all that well. Yet, in the early part of 2012, the cynics like me had to take notice of what Musk was actually accomplishing. His once-beleaguered companies were succeeding at unprecedented things. SpaceX flew a supply capsule to the International Space Station and brought it safely back to Earth. Tesla Motors delivered the Model S, a beautiful, all-electric sedan that took the automotive industry’s breath away and slapped Detroit sober. These two feats elevated Musk to the rarest heights among business titans. Only Steve Jobs could claim similar achievements in two such different industries, sometimes putting out a new Apple product and a blockbuster Pixar movie in the same year. And yet, Musk was not done. He was also the chairman and largest shareholder of SolarCity, a booming solar energy company poised to file for an initial public offering. Musk had somehow delivered the biggest advances the space, automotive, and energy industries had seen in decades in what felt like one fell swoop. It was in 2012 that I decided to see what Musk was like firsthand and to write a cover story about him for Bloomberg Businessweek. At this point in Musk’s life, everything ran through his assistant/loyal appendage Mary Beth Brown. She invited me to visit what I’ve come to refer to as Musk Land. Anyone arriving at Musk Land for the first time will have the same head-scratching experience. You’re told to park at One Rocket Road in Hawthorne, where SpaceX has its HQ. It seems impossible that anything good could call Hawthorne home. It’s a bleak part of Los Angeles County in which groupings of rundown houses, run-down shops, and run-down eateries surround huge, industrial complexes that appear to have been built during some kind of architectural Boring Rectangle movement. Did Elon Musk really stick his company in the middle of this dreck? Then, okay, things start to make more sense when you see one 550,000-square-foot rectangle painted an ostentatious hue of “Unity of Body, Soul, and Mind” white. This is the main SpaceX building. It was only after going through the front doors of SpaceX that the grandeur of what this man had done became apparent. Musk had built an honest-to-God rocket factory in the middle of Los Angeles. And this factory was not making one rocket at a time. No. It was making many rockets—from scratch. The factory was a giant, shared work area. Near the back were massive delivery bays that allowed for the arrival of hunks of metal, which were transported to two-story-high welding machines. Over to one side were technicians in white coats making motherboards, radios, and other electronics. Other people were in a special, airtight glass chamber, building the capsules that rockets would take to the Space Station. Tattooed men in bandanas were blasting Van Halen and threading wires around rocket engines. There were completed bodies of rockets lined up one after the other ready to be placed on trucks. Still more rockets, in another part of the building, awaited coats of white paint. It was difficult to take in the entire factory at once. There were hundreds of bodies in constant motion whirring around a variety of bizarre machines. This is just building number one of Musk Land. SpaceX had acquired several buildings that used to be part of a Boeing factory, which made the fuselages for 747s. One of these buildings has a curved roof and looks like an airplane hangar. It serves as the research, development, and design studio for Tesla. This is where the company came up with the look for the Model S sedan and its follow-on, the Model X SUV. In the parking lot outside the studio, Tesla has built one of its recharging stations where Los Angeles drivers can top up with electricity for free. The charging center is easy enough to spot because Musk has installed a white and red obelisk branded with the Tesla logo that sits in the middle of an infinity pool.
It was in my first interview with Musk, which took place at the design studio, that I began to get a sense of how he talked and operated. He’s a confident guy, but does not always do a good job of displaying this. On initial encounter, Musk can come off as shy and borderline awkward. His South African accent remains present but fading, and the charm of it is not enough to offset the halting nature of Musk’s speech pattern. Like many an engineer or physicist, Musk will pause while fishing around for exact phrasing, and he’ll often go rumbling down an esoteric, scientific rabbit hole without providing any helping hands or simplified explanations along the way. Musk expects you to keep up. None of this is off-putting. Musk, in fact, will toss out plenty of jokes and can be downright charming. It’s just that there’s a sense of purpose and pressure hanging over any conversation with the man. Musk doesn’t really shoot the shit. (It would end up taking about thirty hours of interviews for Musk to really loosen up and let me into a different, deeper level of his psyche and personality.) Most high-profile CEOs have handlers all around them. Musk mostly moves about Musk Land on his own. This is not the guy who slinks into the restaurant. It’s the guy who owns the joint and strides about with authority. Musk and I talked, as he made his way around the design studio’s main floor, inspecting prototype parts and vehicles. At each station, employees rushed up to Musk and disgorged information. He listened intently, processed it, and nodded when satisfied. The people moved away and Musk moved to the next information dump. At one point, Tesla’s design chief, Franz von Holzhausen, wanted Musk’s take on some new tires and rims that had come in for the Model S and on the seating arrangements for the Model X. They spoke, and then they went into a back room where executives from a seller of high-end graphics software had prepared a presentation for Musk. They wanted to show off new 3-D rendering technology that would allow Tesla to tweak the finish of a virtual Model S and see in great detail how things like shadows and streetlights played off the car’s body. Tesla’s engineers really wanted the computing systems and needed Musk’s sign-off. The men did their best to sell Musk on the idea while the sound of drills and giant industrial fans drowned out their shtick. Musk, wearing leather shoes, designer jeans, and a black T-shirt, which is essentially his work uniform, had to don 3-D goggles for the demonstration and seemed unmoved. He told them he’d think about it and then walked toward the source of the loudest noise—a workshop deep in the design studio where Tesla engineers were building the scaffolding for the thirty-foot decorative towers that go outside the charging stations. “That thing looks like it could survive a Category Five hurricane,” Musk said. “Let’s thin it up a bit.” Musk and I eventually hop into his car—a black Model S—and zip back to the main SpaceX building. “I think there are probably too many smart people pursuing Internet stuff, finance, and law,” Musk said on the way. “That is part of the reason why we haven’t seen as much innovation.” MUSK LAND WAS A REVELATION. I’d come to Silicon Valley in 2000 and ended up living in the Tenderloin neighborhood of San Francisco. It’s the one part of the city that locals will implore you to avoid. Without trying very hard, you can find someone pulling down his pants and pooping in between parked cars or encounter some deranged sort bashing his head into the side of a bus stop. At dive bars near the local strip clubs, transvestites hit on curious businessmen and drunks fall asleep on couches and soil themselves as part of their lazy Sunday ritual. It’s the gritty, knife-stabby part of San Francisco and turned out to be a great place to watch the dotcom dream die. San Francisco has an enduring history with greed. It became a city on the back of the gold rush, and not even a catastrophic earthquake could slow San Francisco’s economic lust for long. Don’t let the granola vibes fool you. Booms and busts are the rhythm of this place. And, in 2000, San Francisco had been overtaken by the boom of all booms and consumed by avarice. It was a wonderful time to be alive with just about the entire populace giving in to a fantasy—a get-rich-quick, Internet madness. The pulses of energy from this shared delusion were palpable, producing a constant buzz that vibrated across the city. And here I was in the center of the most depraved part of San Francisco, watching just how high and low people get when consumed by excess.
Stories tracking the insanity of business in these times are well-known. You no longer had to make something that other people wanted to buy in order to start a booming company. You just had to have an idea for some sort of Internet thing and announce it to the world in order for eager investors to fund your thought experiment. The whole goal was to make as much money as possible in the shortest amount of time because everyone knew on at least a subconscious level that reality had to set in eventually. Valley denizens took very literally the cliché of working as hard as you play. People in their twenties, thirties, forties, and fifties were expected to pull all-nighters. Cubicles were turned into temporary homes, and personal hygiene was abandoned. Oddly enough, making Nothing appear to be Something took a lot of work. But when the time to decompress arrived, there were plenty of options for total debauchery. The hot companies and media powers of the time seemed locked in a struggle to outdo each other with ever-fancier parties. Old-line companies trying to look “with it” would regularly buy space at a concert venue and then order up some dancers, acrobats, open bars, and the Barenaked Ladies. Young technologists would show up to pound their free Jack and Cokes and snort their cocaine in porta-potties. Greed and self-interest were the only things that made any sense back then. While the good times have been well chronicled, the subsequent bad times have been—unsurprisingly—ignored. It’s more fun to reminiscence on irrational exuberance than the mess that gets left behind. Let it be said for the record, then, that the implosion of the get-rich-quick Internet fantasy left San Francisco and Silicon Valley in a deep depression. The endless parties ended. The prostitutes no longer roamed the streets of the Tenderloin at 6 A.M. offering pre-commute love. (“Come on, honey. It’s better than coffee!”) Instead of the Barenaked Ladies, you got the occasional Neil Diamond tribute band at a trade show, some free T-shirts, and a lump of shame. The technology industry had no idea what to do with itself. The dumb venture capitalists who had been taken during the bubble didn’t want to look any dumber, so they stopped funding new ventures altogether. Entrepreneurs’ big ideas were replaced by the smallest of notions. It was as if Silicon Valley had entered rehab en masse. It sounds melodramatic, but it’s true. A populace of millions of clever people came to believe that they were inventing the future. Then . . . poof! Playing it safe suddenly became the fashionable thing to do. The evidence of this malaise is in the companies and ideas formed during this period. Google had appeared and really started to thrive around 2002, but it was an outlier. Between Google and Apple’s introduction of the iPhone in 2007, there’s a wasteland of ho-hum companies. And the hot new things that were just starting out—Facebook and Twitter—certainly did not look like their predecessors—Hewlett-Packard, Intel, Sun Microsystems—that made physical products and employed tens of thousands of people in the process. In the years that followed, the goal went from taking huge risks to create new industries and grand new ideas, to chasing easier money by entertaining consumers and pumping out simple apps and advertisements. “The best minds of my generation are thinking about how to make people click ads,” Jeff Hammerbacher, an early Facebook engineer, told me. “That sucks.” Silicon Valley began to look an awful lot like Hollywood. Meanwhile, the consumers it served had turned inward, obsessed with their virtual lives. One of the first people to suggest that this lull in innovation could signal a much larger problem was Jonathan Huebner, a physicist who works at the Pentagon’s Naval Air Warfare Center in China Lake, California. Huebner is the Leave It to Beaver version of a merchant of death. Middle-aged, thin, and balding, he likes to wear a dirt-inspired ensemble of khaki pants, a brown-striped shirt, and a canvas khaki jacket. He has designed weapons systems since 1985, gaining direct insight into the latest and greatest technology around materials, energy, and software. Following the dot-com bust, he became miffed at the ho-hum nature of the supposed innovations crossing his desk. In 2005, Huebner delivered a paper, “A Possible Declining Trend in Worldwide Innovation,” which was either an indictment of Silicon Valley or at least an ominous warning. Huebner opted to use a tree metaphor to describe what he saw as the state of innovation. Man has already climbed past the trunk of the tree and gone out on its major limbs, mining most of the really big, game-changing ideas—the wheel, electricity, the airplane, the telephone, the transistor. Now we’re left dangling near the end of the branches at the top of the tree and mostly just refining past inventions. To back up his point in the paper, Huebner showed that the frequency of life-changing inventions had started to slow. He also used data to prove that the number of patents filed per person had declined over time. “I think the probability of us discovering another top-one-hundred-type invention gets smaller and smaller,” Huebner told me in an interview. “Innovation is a finite resource.”
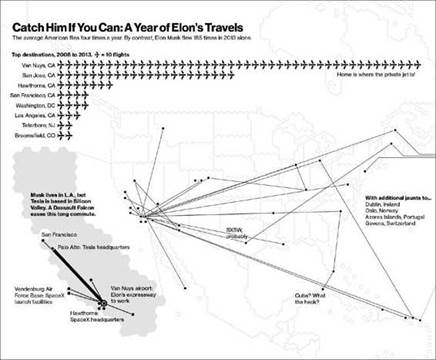
Huebner predicted that it would take people about five years to catch on to his thinking, and this forecast proved almost exactly right. Around 2010, Peter Thiel, the PayPal cofounder and early Facebook investor, began promoting the idea that the technology industry had let people down. “We wanted flying cars, instead we got 140 characters” became the tagline of his venture capital firm Founders Fund. In an essay called “What Happened to the Future,” Thiel and his cohorts described how Twitter, its 140-character messages, and similar inventions have let the public down. He argued that science fiction, which once celebrated the future, has turned dystopian because people no longer have an optimistic view of technology’s ability to change the world. I’d subscribed to a lot of this type of thinking until that first visit to Musk Land. While Musk had been anything but shy about what he was up to, few people outside of his companies got to see the factories, the R&D centers, the machine shops, and to witness the scope of what he was doing firsthand. Here was a guy who had taken much of the Silicon Valley ethic behind moving quickly and running organizations free of bureaucratic hierarchies and applied it to improving big, fantastic machines and chasing things that had the potential to be the real breakthroughs we’d been missing. By rights, Musk should have been part of the malaise. He jumped right into dot-com mania in 1995, when, fresh out of college, he founded a company called Zip2—a primitive Google Maps meets Yelp. That first venture ended up a big, quick hit. Compaq bought Zip2 in 1999 for $307 million. Musk made $22 million from the deal and poured almost all of it into his next venture, a start-up that would morph into PayPal. As the largest shareholder in PayPal, Musk became fantastically well-to-do when eBay acquired the company for $1.5 billion in 2002. Instead of hanging around Silicon Valley and falling into the same funk as his peers, however, Musk decamped to Los Angeles. The conventional wisdom of the time said to take a deep breath and wait for the next big thing to arrive in due course. Musk rejected that logic by throwing $100 million into SpaceX, $70 million into Tesla, and $10 million into SolarCity. Short of building an actual money-crushing machine, Musk could not have picked a faster way to destroy his fortune. He became a one-man, ultra-risk-taking venture capital shop and doubled down on making super-complex physical goods in two of the most expensive places in the world, Los Angeles and Silicon Valley. Whenever possible, Musk’s companies would make things from scratch and try to rethink much that the aerospace, automotive, and solar industries had accepted as convention. With SpaceX, Musk is battling the giants of the U.S. military-industrial complex, including Lockheed Martin and Boeing. He’s also battling nations—most notably Russia and China. SpaceX has made a name for itself as the low-cost supplier in the industry. But that, in and of itself, is not really good enough to win. The space business requires dealing with a mess of politics, back-scratching, and protectionism that undermines the fundamentals of capitalism. Steve Jobs faced similar forces when he went up against the recording industry to bring the iPod and iTunes to market. The crotchety Luddites in the music industry were a pleasure to deal with compared to Musk’s foes who build weapons and countries for a living. SpaceX has been testing reusable rockets that can carry payloads to space and land back on Earth, on their launchpads, with precision. If the company can perfect this technology, it will deal a devastating blow to all of its competitors and almost assuredly push some mainstays of the rocket industry out of business while establishing the United States as the world leader for taking cargo and humans to space. It’s a threat that Musk figures has earned him plenty of fierce enemies. “The list of people that would not mind if I was gone is growing,” Musk said. “My family fears that the Russians will assassinate me.” With Tesla Motors, Musk has tried to revamp the way cars are manufactured and sold, while building out a worldwide fuel distribution network at the same time. Instead of hybrids, which in Musk lingo are suboptimal compromises, Tesla strives to make all-electric cars that people lust after and that push the limits of technology. Tesla does not sell these cars through dealers; it sells them on the Web and in Apple-like galleries located in high-end shopping centers. Tesla also does not anticipate making lots of money from servicing its vehicles, since electric cars do not require the oil changes and other maintenance procedures of traditional cars. The direct sales model embraced by Tesla stands as a major affront to car dealers used to haggling with their customers and making their profits from exorbitant maintenance fees. Tesla’s recharging stations now run alongside many of the major highways in the United States, Europe, and Asia and can add hundreds of miles of oomph back to a car in about twenty minutes. These so-called supercharging stations are solar-powered, and Tesla owners pay nothing to refuel. While much of America’s infrastructure decays, Musk is building a futuristic end-to-end transportation system that would allow the United States to leapfrog the rest of the world. Musk’s vision, and, of late, execution seem to combine the best of Henry Ford and John D. Rockefeller. With SolarCity, Musk has funded the largest installer and financer of solar panels for consumers and businesses. Musk helped come up with the idea for SolarCity and serves as its chairman, while his cousins Lyndon and Peter Rive run the company. SolarCity has managed to undercut dozens of utilities and become a large utility in its own right. During a time in which clean-tech businesses have gone bankrupt with alarming regularity, Musk has built two of the most successful clean-tech companies in the world. The Musk Co. empire of factories, tens of thousands of workers, and industrial might has incumbents on the run and has turned Musk into one of the richest men in the world, with a net worth around $10 billion. The visit to Musk Land started to make a few things clear about how Musk had pulled all this off. While the “putting man on Mars” talk can strike some people as loopy, it gave Musk a unique rallying cry for his companies. It’s the sweeping goal that forms a unifying principle over everything he does. Employees at all three companies are well aware of this and well aware that they’re trying to achieve the impossible day in and day out. When Musk sets unrealistic goals, verbally abuses employees, and works them to the bone, it’s understood to be—on some level—part of the Mars agenda. Some employees love him for this. Others loathe him but remain oddly loyal out of respect for his drive and mission. What Musk has developed that so many of the entrepreneurs in Silicon Valley lack is a meaningful worldview. He’s the possessed genius on the grandest quest anyone has ever concocted. He’s less a CEO chasing riches than a general marshaling troops to secure victory. Where Mark Zuckerberg wants to help you share baby photos, Musk wants to . . . well . . . save the human race from self-imposed or accidental annihilation. The life that Musk has created to manage all of these endeavors is preposterous. A typical week starts at his mansion in Bel Air. On Monday, he works the entire day at SpaceX. On Tuesday, he begins at SpaceX, then hops onto his jet and flies to Silicon Valley. He spends a couple of days working at Tesla, which has its offices in Palo Alto and factory in Fremont. Musk does not own a home in Northern California and ends up staying at the luxe Rosewood hotel or at friends’ houses. To arrange the stays with friends, Musk’s assistant will send an e-mail asking, “Room for one?” and if the friend says, “Yes,” Musk turns up at the door late at night. Most often he stays in a guest room, but he’s also been known to crash on the couch after winding down with some video games. Then it’s back to Los Angeles and SpaceX on Thursday. He shares custody of his five young boys—twins and triplets—with his ex-wife, Justine, and has them four days a week. Each year, Musk tabulates the amount of flight time he endures per week to help him get a sense of just how out of hand things are getting. Asked how he survives this schedule, Musk said, “I had a tough childhood, so maybe that was helpful.” During one visit to Musk Land, he had to squeeze our interview in before heading off for a camping trip at Crater Lake National Park in Oregon. It was almost 8 P.M. on a Friday, so Musk would soon be piling his boys and nannies into his private jet and then meeting drivers who would take him to his friends at the campsite; the friends would then help the Musk clan unpack and complete their pitch-black arrival. There would be a bit of hiking over the weekend. Then the relaxation would end. Musk would fly with the boys back to Los Angeles on Sunday afternoon. Then, he would take off on his own that evening for New York. Sleep. Hit the morning talk shows on Monday. Meetings. E-mail. Sleep. Fly back to Los Angeles Tuesday morning. Work at SpaceX. Fly to San Jose Tuesday afternoon to visit the Tesla Motors factory. Fly to Washington, D.C., that night and see President Obama. Fly back to Los Angeles Wednesday night. Spend a couple of days working at SpaceX. Then go to a weekend conference held by Google’s chairman, Eric Schmidt, in Yellowstone. At this time, Musk had just split from his second wife, the actress Talulah Riley, and was trying to calculate if he could mix a personal life into all of this. “I think the time allocated to the businesses and the kids is going fine,” Musk said. “I would like to allocate more time to dating, though. I need to find a girlfriend. That’s why I need to carve out just a little more time. I think maybe even another five to ten—how much time does a woman want a week? Maybe ten hours? That’s kind of the minimum? I don’t know.” Musk rarely finds time to decompress, but when he does, the festivities are just as dramatic as the rest of his life. On his thirtieth birthday, Musk rented out a castle in England for about twenty people. From 2 A.M. until 6 A.M., they played a variation of hide-and-seek called sardines in which one person runs off and hides and everyone else looks for him. Another party occurred in Paris. Musk, his brother, and cousins found themselves awake at midnight and decided to bicycle through the city until 6 A.M. They slept all day and then boarded the Orient Express in the evening. Once again, they stayed up all night. The Lucent Dossier Experience—an avant-garde group of performers—were on the luxurious train, performing palm readings and acrobatics. When the train arrived in Venice the next day, Musk’s family had dinner and then hung out on the patio of their hotel overlooking the Grand Canal until 9 A.M. Musk loves costume parties as well, and turned up at one dressed like a knight and using a parasol to duel a midget wearing a Darth Vader costume. For one of his most recent birthdays, Musk invited fifty people to a castle—or at least the United States’ best approximation of a castle—in Tarrytown, New York. This party had a Japanese steampunk theme, which is sort of like a sci-fi lover’s wet dream—a mix of corsets, leather, and machine worship. Musk dressed as a samurai. The festivities included a performance of The Mikado, a Victorian comic opera by Gilbert and Sullivan set in Japan, at a small theater in the heart of town. “I am not sure the Americans got it,” said Riley, whom Musk remarried after his ten-hour-a-week dating plan failed. The Americans and everyone else did enjoy what followed. Back at the castle, Musk donned a blindfold, got pushed up against a wall, and held balloons in each hand and another between his legs. The knife thrower then went to work. “I’d seen him before, but did worry that maybe he could have an off day,” Musk said. “Still, I thought, he would maybe hit one gonad but not both.” The onlookers were stunned and frightened for Musk’s safety. “That was bizarre,” said Bill Lee, a technology investor and one of Musk’s good friends. “But Elon believes in the science of things.” One of the world’s top sumo wrestlers showed up at the party along with some of his compatriots. A ring had been set up at the castle, and Musk faced off against the champion. “He was three hundred and fifty pounds, and they were not jiggly pounds,” Musk said. “I went full adrenaline rush and managed to lift the guy off the ground. He let me win that first round and then beat me. I think my back is still screwed up.” Riley turned planning these types of parties for Musk into an art. She met Musk back in 2008, when his companies were collapsing. She watched him lose his entire fortune and get ridiculed by the press. She knows that the sting of these years remains and has combined with the other traumas in Musk’s life—the tragic loss of an infant son and a brutal upbringing in South Africa—to create a tortured soul. Riley has gone to great lengths to make sure Musk’s escapes from work and this past leave him feeling refreshed if not healed. “I try to think of fun things he has not done before where he can relax,” Riley said. “We’re trying to make up for his miserable childhood now.” Genuine as Riley’s efforts might have been, they were not entirely effective. Not long after the Sumo party, I found Musk back at work at the Tesla headquarters in Palo Alto. It was a Saturday, and the parking lot was full of cars. Inside of the Tesla offices, hundreds of young men were at work—some of them designing car parts on computers and others conducting experiments with electronics equipment on their desks. Musk’s uproarious laugh would erupt every few minutes and carry through the entire floor. When Musk came into the meeting room where I’d been waiting, I noted how impressive it was for so many people to turn up on a Saturday. Musk saw the situation in a different light, complaining that fewer and fewer people had been working weekends of late. “We’ve grown fucking soft,” Musk replied. “I was just going to send out an e-mail. We’re fucking soft.” (A word of warning: There’s going to be a lot of “fuck” in this book. Musk adores the word, and so do most of the people in his inner circle.) This kind of declaration seems to fit with our impressions of other visionaries. It’s not hard to imagine Howard Hughes or Steve Jobs chastising their workforce in a similar way. Building things—especially big things—is a messy business. In the two decades Musk has spent creating companies, he’s left behind a trail of people who either adore or despise him. During the course of my reporting, these people lined up to give me their take on Musk and the gory details of how he and his businesses operate. My dinners with Musk and periodic trips to Musk Land revealed a different set of possible truths about the man. He’s set about building something that has the potential to be much grander than anything Hughes or Jobs produced. Musk has taken industries like aerospace and automotive that America seemed to have given up on and recast them as something new and fantastic. At the heart of this transformation are Musk’s skills as a software maker and his ability to apply them to machines. He’s merged atoms and bits in ways that few people thought possible, and the results have been spectacular. It’s true enough that Musk has yet to have a consumer hit on the order of the iPhone or to touch more than one billion people like Facebook. For the moment, he’s still making rich people’s toys, and his budding empire could be an exploded rocket or massive Tesla recall away from collapse. On the other hand, Musk’s companies have already accomplished far more than his loudest detractors thought possible, and the promise of what’s to come has to leave hardened types feeling optimistic during their weaker moments. “To me, Elon is the shining example of how Silicon Valley might be able to reinvent itself and be more relevant than chasing these quick IPOs and focusing on getting incremental products out,” said Edward Jung, a famed software engineer and inventor. “Those things are important, but they are not enough. We need to look at different models of how to do things that are longer term in nature and where the technology is more integrated.” The integration mentioned by Jung—the harmonious melding of software, electronics, advanced materials, and computing horsepower—appears to be Musk’s gift. Squint ever so slightly, and it looks like Musk could be using his skills to pave the way toward an age of astonishing machines and science fiction dreams made manifest. In that sense, Musk comes off much more like Thomas Edison than Howard Hughes. He’s an inventor, celebrity businessman, and industrialist able to take big ideas and turn them into big products. He’s employing thousands of people to forge metal in American factories at a time when this was thought to be impossible. Born in South Africa, Musk now looks like America’s most innovative industrialist and outlandish thinker and the person most likely to set Silicon Valley on a more ambitious course. Because of Musk, Americans could wake up in ten years with the most modern highway in the world: a transit system run by thousands of solar-powered charging stations and traversed by electric cars. By that time, SpaceX may well be sending up rockets every day, taking people and things to dozens of habitats and making preparations for longer treks to Mars. These advances are simultaneously difficult to fathom and seemingly inevitable if Musk can simply buy enough time to make them work. As his ex-wife, Justine, put it, “He does what he wants, and he is relentless about it. It’s Elon’s world, and the rest of us live in it.”
AFRICA THE PUBLIC FIRST MET ELON REEVE MUSK IN 1984. The South African trade publication PC and Office Technology published the source code to a video game Musk had designed. Called Blastar, the science-fiction-inspired space game required 167 lines of instructions to run. This was back in the day when early computer users were required to type out commands to make their machines do much of anything. In that context, Musk’s game did not shine as a marvel of computer science but it certainly surpassed what most twelve-year-olds were kicking out at the time. Its coverage in the magazine netted Musk five hundred dollars and provided some early hints about his character. The Blastar spread on page 69 of the magazine shows that the young man wanted to go by the sci-fi-author-sounding name E. R. Musk and that he already had visions of grand conquests dancing in his head. The brief explainer states, “In this game you have to destroy an alien space freighter, which is carrying deadly Hydrogen Bombs and Status Beam Machines. This game makes good use of sprites and animation, and in this sense makes the listing worth reading.” (As of this writing, not even the Internet knows what “status beam machines” are.) A boy fantasizing about space and battles between good and evil is anything but amazing. A boy who takes these fantasies seriously is more remarkable. Such was the case with the young Elon Musk. By the middle of his teenage years, Musk had blended fantasy and reality to the point that they were hard to separate in his mind. Musk came to see man’s fate in the universe as a personal obligation. If that meant pursuing cleaner energy technology or building spaceships to extend the human species’s reach, then so be it. Musk would find a way to make these things happen. “Maybe I read too many comics as a kid,” Musk said. “In the comics, it always seems like they are trying to save the world. It seemed like one should try to make the world a better place because the inverse makes no sense.” At around age fourteen, Musk had a full-on existential crisis. He tried to deal with it like many gifted adolescents do, turning to religious and philosophical texts. Musk sampled a handful of ideologies and then ended up more or less back where he had started, embracing the sci-fi lessons found in one of the most influential books in his life: The Hitchhiker’s Guide to the Galaxy, by Douglas Adams. “He points out that one of the really tough things is figuring out what questions to ask,” Musk said. “Once you figure out the question, then the answer is relatively easy. I came to the conclusion that really we should aspire to increase the scope and scale of human consciousness in order to better understand what questions to ask.” The teenage Musk then arrived at his ultralogical mission statement. “The only thing that makes sense to do is strive for greater collective enlightenment,” he said. It’s easy enough to spot some of the underpinnings of Musk’s search for purpose. Born in 1971, he grew up in Pretoria, a large city in the northeastern part of South Africa, just an hour’s drive from Johannesburg. The specter of apartheid was present throughout his childhood, as South Africa frequently boiled over with tension and violence. Blacks and whites clashed, as did blacks of different tribes. Musk turned four years old just days after the Soweto Uprising, in which hundreds of black students died while protesting decrees of the white government. For years South Africa faced sanctions imposed by other nations due to its racist policies. Musk had the luxury of traveling abroad during his childhood and would have gotten a flavor for how outsiders viewed South Africa. But what had even more of an impact on Musk’s personality was the white Afrikaner culture so prevalent in Pretoria and the surrounding areas. Hypermasculine behavior was celebrated and tough jocks were revered. While Musk enjoyed a level of privilege, he lived as an outsider whose reserved personality and geeky inclinations ran against the prevailing attitudes of the time. His notion that something about the world had gone awry received constant reinforcement, and Musk, almost from his earliest days, plotted an escape from his surroundings and dreamed of a place that would allow his personality and dreams to flourish. He saw America in its most clichéd form, as the land of opportunity and the most likely stage for making the realization of his dreams possible. This is how it came to pass that a lonesome, gawky South African boy who talked with the utmost sincerity about pursuing “collective enlightenment” ended up as America’s most adventurous industrialist. When Musk did finally reach the United States in his twenties, it marked a return to his ancestral roots. Family trees suggest that ancestors bearing the Swiss German surname of Haldeman on the maternal side of Musk’s family left Europe for New York during the Revolutionary War. From New York, they spread out to the prairies of the Midwest—Illinois and Minnesota, in particular. “We had people that fought on both sides of the Civil War apparently and were a family of farmers,” said Scott Haldeman, Musk’s uncle and the unofficial family historian. Throughout his childhood, boys teased Musk because of his unusual name. He earned the first part of it from his great-grandfather John Elon Haldeman, who was born in 1872 [Journal of the Canadian Chiropractic Association, 1995.] and grew up in Illinois before heading to Minnesota. There he would meet his wife, Almeda Jane Norman, who was five years younger. By 1902, the couple had settled down in a log cabin in the central Minnesota town of Pequot and given birth to their son Joshua Norman Haldeman, Musk’s grandfather. He would grow up to become an eccentric and exceptional man and a model for Musk. /Two years after the birth of his son, John Elon began to show signs of diabetes. The condition amounted to a death sentence at the time and, despite being only thirty-two, John Elon learned that he would likely have six months or so to live. With a bit of nursing experience behind her, Almeda took it upon herself to discover an elixir or treatment that would extend John Elon’s life. According to family lore, she hit on chiropractic procedures as an effective remedy, and John Elon lived for five years following the original diabetes diagnosis. The life-giving procedures established what would become an oddly rich chiropractic tradition in the Haldeman family. Almeda studied at a chiropractic school in Minneapolis and earned her doctor of chiropractic, or, D.C., degree in 1905. Musk’s great-grandmother went on to set up her own clinic and, as far as anyone can tell, became the first chiropractor to practice in Canada./ Joshua Norman Haldeman is described as an athletic, self-reliant boy. In 1907, his family moved to the prairies of Saskatchewan, and his father died shortly thereafter when Joshua was just seven, leaving the boy to help run the house. He took to the wide-open land and picked up bronco horseback riding, boxing, and wrestling. Haldeman would break in horses for local farmers, often hurting himself in the process, and he organized one of Canada’s first rodeos. Family pictures show Joshua dressed in a decorative pair of chaps demonstrating his rope-spinning skills. As a teenager, Haldeman left home to get a degree from the Palmer School of Chiropractic in Iowa and then returned to Saskatchewan to become a farmer. When the depression hit in the 1930s, Haldeman fell into a financial crisis. He could not afford to keep up with bank loans on his equipment and had five thousand acres of land seized. “From then on, Dad didn’t believe in banks or holding on to money,” said Scott Haldeman, who would go on to receive his chiropractic degree from the same school as his father and become one of the world’s top spinal pain experts. After losing the farm around 1934, Haldeman lived something of a nomadic existence that his grandson would replicate in Canada decades later. Standing six feet, three inches, he did odd jobs as a construction worker and rodeo performer before settling down as a chiropractor. /Haldeman also entered politics, trying to start his own political party in Saskatchewan, publishing a newsletter, and espousing conservative, antisocialist ideas. He would later make an unsuccessful run for Parliament and chair the Social Credit Party./ By 1948, Haldeman had married a Canadian dance studio instructor, Winnifred Josephine Fletcher, or Wyn, and built a booming chiropractic practice. That year, the family, which already included a son and a daughter, welcomed twin daughters Kaye and Maye, Musk’s mother. The children lived in a three-story, twenty-room house that included a dance studio to let Wyn keep teaching students. Ever in search of something new to do, Haldeman had picked up flying and bought his own plane. The family gained some measure of notoriety as people heard about Haldeman and his wife packing their kids into the back of the single-engine craft and heading off on excursions all around North America. Haldeman would often show up at political and chiropractic meetings in the plane and later wrote a book with his wife called The Flying Haldemans: Pity the Poor Private Pilot. Haldeman seemed to have everything going for him when, in 1950, he decided to give it all away. The doctor-cum-politician had long railed against government interference in the lives of individuals and had come to see the Canadian bureaucracy as too meddlesome. A man who forbade swearing, smoking, Coca-Cola, and refined flour at his house, Haldeman contended that the moral character of Canada had started to decline. Haldeman also possessed an enduring lust for adventure. And so, over the course of a few months, the family sold their house and dance and chiropractic practices and decided to move to South Africa—a place Haldeman had never been. Scott Haldeman remembers helping his father disassemble the family’s Bellanca Cruisair (1948) airplane and put it into crates before shipping it to Africa. Once in South Africa, the family rebuilt the plane and used it to scour the country for a nice place to live, ultimately settling on Pretoria, where Haldeman set up a new chiropractic practice. The family’s spirit for adventure seemed to know no bounds. In 1952, Joshua and Wyn made a 22,000-mile round-trip journey in their plane, flying up through Africa to Scotland and Norway. Wyn served as the navigator and, though not a licensed pilot, would sometimes take over the flying duties. The couple topped this effort in 1954, flying 30,000 miles to Australia and back. Newspapers reported on the couple’s trip, and they’re believed to be the only private pilots to get from Africa to Australia in a single-engine plane. /The journey took them up the African coast, across the Arabian Peninsula, all the way through Iran, India, and Malaysia and then down the Timor Sea to Australia. It required one year of preparation just to secure all of the necessary visas and paperwork, and they suffered from constant stomach bugs and an erratic schedule along the way. “Dad passed out crossing the Timor Sea, and mum had to take over until they hit Australia. He woke up right before they landed,” said Scott Haldeman. “It was fatigue.”/ When not up in the air, the Haldemans were out in the bush going on great, monthlong expeditions to find the Lost City of the Kalahari Desert, a supposed abandoned city in southern Africa. A family photo from one of these excursions shows the five children in the middle of the African bush. They have gathered around a large metal pot being warmed by the embers of a campfire. The children look relaxed as they sit in folding chairs, legs crossed and reading books. Behind them is the ruby-red Bellanca plane, a tent, and a car. The tranquility of the scene belies how dangerous these trips were. During one incident, the family’s truck hit a tree stump and forced the bumper through the radiator. Stuck in the middle of nowhere with no means of communication, Joshua worked for three days to fix the truck, while the family hunted for food. At other times, hyenas and leopards would circle the campfire at night, and, one morning, the family woke to find a lion three feet away from their main table. Joshua grabbed the first object he could find—a lamp—waved it, and told the lion to go away. And it did. /Both Joshua and Wyn were accomplished marksmen and won national shooting competitions. In the mid-1950s, they also tied for first place in the eight-thousand-mile Cape Town to Algiers Motor Rally, beating pros in their Ford station wagon./ The Haldemans had a laissez-faire approach to raising their children, which would extend over the generations to Musk. Their kids were never punished, as Joshua believed they would intuit their way to proper behavior. When mom and dad went off on their tremendous flights, the kids were left at home. Scott Haldeman can’t remember his father setting foot at his school a single time even though his son was captain of the rugby team and a prefect. “To him, that was all just anticipated,” said Scott Haldeman. “We were left with the impression that we were capable of anything. You just have to make a decision and do it. In that sense, my father would be very proud of Elon.” Haldeman died in 1974 at the age of seventy-two. He’d been doing practice landings in his plane and didn’t see a wire attached to a pair of poles. The wire caught the plane’s wheels and flipped the craft, and Haldeman broke his neck. Elon was a toddler at the time. But throughout his childhood, Elon heard many stories about his grandfather’s exploits and sat through countless slide shows that documented his travels and trips through the bush. “My grandmother told these tales of how they almost died several times along their journeys,” Musk said. “They were flying in a plane with literally no instruments—not even a radio, and they had road maps instead of aerial maps, and some of those weren’t even correct. My grandfather had this desire for adventure, exploration doing crazy things.” Elon buys into the idea that his unusual tolerance for risk may well have been inherited directly from his grandfather. Many years after the last slide show, Elon tried to find and purchase the red Bellanca plane but could not locate it. Maye Musk, Elon’s mother, grew up idolizing her parents. In her youth, she was considered a nerd. She liked math and science and did well at the coursework. By the age of fifteen, however, people had taken notice of some of her other attributes. Maye was gorgeous. Tall with ash-blond hair, Maye had the high cheekbones and angular features that would make her stand out anywhere. A friend of the family ran a modeling school, and Maye took some courses. On the weekends, she did runway shows, magazine shoots, occasionally showed up at a senator’s or ambassador’s home for an event, and ended up as a finalist for Miss South Africa. (Maye has continued to model into her sixties, appearing on the covers of magazines like New York and Elle and in Beyoncé’s music videos.) Maye and Elon’s father, Errol Musk, grew up in the same neighborhood. They met for the first time when Maye, born in 1948, was about eleven. Errol was the cool kid to Maye’s nerd but had a crush on her for years. “He fell in love with me because of my legs and my teeth,” said Maye. The two would date on and off throughout their time at university. And, according to Maye, Errol spent about seven years as a relentless suitor seeking her hand in marriage and eventually breaking her will. “He just never stopped proposing,” she said. Their marriage was complicated from the start. Maye became pregnant during the couple’s honeymoon and gave birth to Elon on June 28, 1971, nine months and two days after her wedding day. While they may not have enjoyed marital bliss, the couple carved out a decent life for themselves in Pretoria. Errol worked as a mechanical and electrical engineer and handled large projects such as office buildings, retail complexes, residential subdivisions, and an air force base, while Maye set up a practice as a dietician. A bit more than a year after Elon’s birth came his brother Kimbal, and soon thereafter came their sister Tosca. Elon exhibited all the traits of a curious, energetic tot. He picked things up easily, and Maye, like many mothers do, pegged her son as brilliant and precocious. “He seemed to understand things quicker than the other kids,” she said. The perplexing thing was that Elon seemed to drift off into a trance at times. People spoke to him, but nothing got through when he had a certain, distant look in his eyes. This happened so often that Elon’s parents and doctors thought he might be deaf. “Sometimes, he just didn’t hear you,” said Maye. Doctors ran a series of tests on Elon, and elected to remove his adenoid glands, which can improve hearing in children. “Well, it didn’t change,” said Maye. Elon’s condition had far more to do with the wiring of his mind than how his auditory system functioned. “He goes into his brain, and then you just see he is in another world,” Maye said. “He still does that. Now I just leave him be because I know he is designing a new rocket or something.” Other children did not respond well to these dreamlike states. You could do jumping jacks right beside Musk or yell at him, and he would not even notice. He kept right on thinking, and those around him judged that he was either rude or really weird. “I do think Elon was always a little different but in a nerdy way,” Maye said. “It didn’t endear him to his peers.” For Musk, these pensive moments were wonderful. At five and six, he had found a way to block out the world and dedicate all of his concentration to a single task. Part of this ability stemmed from the very visual way in which Musk’s mind worked. He could see images in his mind’s eye with a clarity and detail that we might associate today with an engineering drawing produced by computer software. “It seems as though the part of the brain that’s usually reserved for visual processing—the part that is used to process images coming in from my eyes—gets taken over by internal thought processes,” Musk said. “I can’t do this as much now because there are so many things demanding my attention but, as a kid, it happened a lot. That large part of your brain that’s used to handle incoming images gets used for internal thinking.” Computers split their hardest jobs between two types of chips. There are graphics chips that deal with processing the images produced by a television show stream or video game and computational chips that handle general purpose tasks and mathematical operations. Over time, Musk has ended up thinking that his brain has the equivalent of a graphics chip. It allows him to see things out in the world, replicate them in his mind, and imagine how they might change or behave when interacting with other objects. “For images and numbers, I can process their interrelationships and algorithmic relationships,” Musk said. “Acceleration, momentum, kinetic energy—how those sorts of things will be affected by objects comes through very vividly.” The most striking part of Elon’s character as a young boy was his compulsion to read. From a very young age, he seemed to have a book in his hands at all times. “It was not unusual for him to read ten hours a day,” said Kimbal. “If it was the weekend, he could go through two books in a day.” The family went on numerous shopping excursions in which they realized mid-trip that Elon had gone missing. Maye or Kimbal would pop into the nearest bookstore and find Elon somewhere near the back sitting on the floor and reading in one of his trancelike states. As Elon got older, he would take himself to the bookstore when school ended at 2 P.M. and stay there until about 6 P.M., when his parents returned home from work. He plowed through fiction books and then comics and then nonfiction titles. “Sometimes they kicked me out of the store, but usually not,” Elon said. He listed The Lord of the Rings, Isaac Asimov’s Foundation series, and Robert Heinlein’s The Moon Is a Harsh Mistress as some of his favorites, alongside The Hitchhiker’s Guide to the Galaxy. “At one point, I ran out of books to read at the school library and the neighborhood library,” Musk said. “This is maybe the third or fourth grade. I tried to convince the librarian to order books for me. So then, I started to read the Encyclopaedia Britannica. That was so helpful. You don’t know what you don’t know. You realize there are all these things out there.” Elon, in fact, churned through two sets of encyclopedias—a feat that did little to help him make friends. The boy had a photographic memory, and the encyclopedias turned him into a fact factory. He came off as a classic know-it-all. At the dinner table, Tosca would wonder aloud about the distance from Earth to the Moon. Elon would spit out the exact measurement at perigee and apogee. “If we had a question, Tosca would always say, ‘Just ask genius boy,’” Maye said. “We could ask him about anything. He just remembered it.” Elon cemented his bookworm reputation through his clumsy ways. “He’s not very sporty,” said Maye. Maye tells the story of Elon playing outside one night with his siblings and cousins. When one of them complained of being frightened by the dark, Elon pointed out that “dark is merely the absence of light,” which did little to reassure the scared child. As a youngster, Elon’s constant yearning to correct people and his abrasive manner put off other kids and added to his feelings of isolation. Elon genuinely thought that people would be happy to hear about the flaws in their thinking. “Kids don’t like answers like that,” said Maye. “They would say, ‘Elon, we are not playing with you anymore.’ I felt very sad as a mother because I think he wanted friends. Kimbal and Tosca would bring home friends, and Elon wouldn’t, and he would want to play with them. But he was awkward, you know.” Maye urged Kimbal and Tosca to include Elon. They responded as kids will. “But Mom, he’s not fun.” As he got older, however, Elon would have strong, affectionate attachments to his siblings and cousins—his mother’s sister’s sons. Though he kept to himself at school, Elon had an outgoing nature with members of his family and eventually took on the role of elder and chief instigator among them. For a while, life inside the Musk household was quite good. The family owned one of the biggest houses in Pretoria thanks to the success of Errol’s engineering business. There’s a portrait of the three Musk children taken when Elon was about eight years old that shows three blond, fit children sitting next to each other on a brick porch with Pretoria’s famous purple jacaranda trees in the background. Elon has large, rounded cheeks and a broad smile. Then, not long after the photo was taken, the family fell apart. His parents separated and divorced within the year. Maye moved with the kids to the family’s holiday home in Durban, on South Africa’s eastern coast. After a couple of years of this arrangement, Elon decided he wanted to live with his father. “My father seemed sort of sad and lonely, and my mom had three kids, and he didn’t have any,” Musk said. “It seemed unfair.” Some members of Musk’s family have bought into this idea that Elon’s logical nature propelled him, while others claim that his father’s mother, Cora, exerted a lot of pressure on the boy. “I could not understand why he would leave this happy home I made for him—this really happy home,” said Maye. “But Elon is his own person.” Justine Musk, Elon’s ex-wife and the mother of his five boys, theorized that Elon identified more with the alpha male of the house and wasn’t bothered by the emotional aspect of the decision. “I don’t think he was particularly close with either parent,” Justine said, while describing the Musk clan overall as being cool and the opposite of doting. Kimbal later opted to live with Errol as well, saying simply that by nature a son wants to live with his father. Whenever the topic of Errol arrives, members of Elon’s family clam up. They’re in agreement that he is not a pleasant man to be around but have declined to elaborate. Errol has since been remarried, and Elon has two, younger half sisters of whom he’s quite protective. Elon and his siblings seem determined not to bad-mouth Errol publicly, so as not to upset the sisters. The basics are as follows: Errol’s side of the family has deep South African roots. The Musk clan can trace its presence in the country back about two hundred years and claim an entry in Pretoria’s first phone book. Errol’s father, Walter Henry James Musk, was an army sergeant. “I remember him almost never talking,” Elon said. “He would just drink whiskey and be grumpy and was very good at doing crossword puzzles.” Cora Amelia Musk, Errol’s mother, was born in England to a family famed for its intellectual genes. She embraced both the spotlight and her grandchildren. “Our grandmother had this very dominant personality and was quite an enterprising woman,” said Kimbal. “She was a very big influence in our lives.” Elon considered his relationship with Cora—or Nana, as he called her—particularly tight. “After the divorce, she took care of me quite a lot,” he said. “She would pick me up from school, and I would hang out with her playing Scrabble and that type of thing.” On the surface, life at Errol’s house seemed grand. He had plenty of books for Elon to read from cover to cover and money to buy a computer and other objects that Elon desired. Errol took his children on numerous trips overseas. “It was an amazingly fun time,” said Kimbal. “I have a lot of fun memories from that.” Errol also impressed the kids with his intellect and dealt out some practical lessons. “He was a talented engineer,” Elon said. “He knew how every physical object worked.” Both Elon and Kimbal were required to go to the sites of Errol’s engineering jobs and learn how to lay bricks, install plumbing, fit windows, and put in electrical wiring. “There were fun moments,” Elon said. Errol was what Kimbal described as “ultra-present and very intense.” He would sit Elon and Kimbal down and lecture at them for three to four hours without the boys being able to respond. He seemed to delight in being hard on the boys and sucked the fun out of common childhood diversions. From time to time, Elon tried to convince his dad to move to America and often talked about his intentions to live in the United States later in life. Errol countered such dreams by trying to teach Elon a lesson. He sent the housekeepers away and had Elon do all the chores to let him know what it was like “to play American.” While Elon and Kimbal declined to provide an exact recounting, they clearly experienced something awful and profound during those years with their father. They both talk about having to endure some form of psychological torture. “He definitely has serious chemical stuff,” said Kimbal. “Which I am sure Elon and I have inherited. It was a very emotionally challenging upbringing, but it made us who we are today.” Maye bristled when the subject of Errol came up. “Nobody gets along with him,” she said. “He is not nice to anyone. I don’t want to tell stories because they are horrendous. You know, you just don’t talk about it. There are kids and grandkids involved.” When asked to chat about Elon, Errol responded via e-mail: “Elon was a very independent and focused child at home with me. He loved computer science before anyone even knew what it was in South Africa and his ability was widely recognized by the time he was 12 years old. Elon and his brother Kimbal’s activities as children and young men were so many and varied that it’s difficult to name just one, as they travelled together with me extensively in S. Africa and the world at large, visiting all the continents regularly from the age of six onwards. Elon and his brother and sister were and continue to be exemplary, in every way a father could want. I’m very proud of what Elon’s accomplished.” Errol copied Elon on this e-mail, and Elon warned me off corresponding with his father, insisting that his father’s take on past events could not be trusted. “He is an odd duck,” Musk said. But, when pressed for more information, Musk dodged. “It would certainly be accurate to say that I did not have a good childhood,” he said. “It may sound good. It was not absent of good, but it was not a happy childhood. It was like misery. He’s good at making life miserable—that’s for sure. He can take any situation no matter how good it is and make it bad. He’s not a happy man. I don’t know . . . fuck . . . I don’t know how someone becomes like he is. It would just cause too much trouble to tell you any more.” Elon and Justine have vowed that their children will not be allowed to meet Errol. When Elon was nearly ten years old, he saw a computer for the first time, at the Sandton City Mall in Johannesburg. “There was an electronics store that mostly did hi-fi-type stuff, but then, in one corner, they started stocking a few computers,” Musk said. He felt awed right away—“It was like, ‘Whoa. Holy shit!’”—by this machine that could be programmed to do a person’s bidding. “I had to have that and then hounded my father to get the computer,” Musk said. Soon he owned a Commodore VIC-20, a popular home machine that went on sale in 1980. Elon’s computer arrived with five kilobytes of memory and a workbook on the BASIC programming language. “It was supposed to take like six months to get through all the lessons,” Elon said. “I just got super OCD on it and stayed up for three days with no sleep and did the entire thing. It seemed like the most super-compelling thing I had ever seen.” Despite being an engineer, Musk’s father was something of a Luddite and dismissive of the machine. Elon recounted that “he said it was just for games and that you’d never be able to do real engineering on it. I just said, ‘Whatever.’” While bookish and into his new computer, Elon quite often led Kimbal and his cousins (Kaye’s children) Russ, Lyndon, and Peter Rive on adventures. They dabbled one year in selling Easter eggs door-to-door in the neighborhood. The eggs were not well decorated, but the boys still marked them up a few hundred percent for their wealthy neighbors. Elon also spearheaded their work with homemade explosives and rockets. South Africa did not have the Estes rocket kits popular among hobbyists, so Elon would create his own chemical compounds and put them inside of canisters. “It is remarkable how many things you can get to explode,” Elon said. “Saltpeter, sulfur, and charcoal are the basic ingredients for gunpowder, and then if you combine a strong acid with a strong alkaline, that will generally release a lot of energy. Granulated chlorine with brake fluid—that’s quite impressive. I’m lucky I have all my fingers.” When not handling explosives, the boys put on layers of clothing and goggles and shot each other with pellet guns. Elon and Kimbal raced dirt bikes against each other in sandlots until Kimbal flew off his bike one day and hurtled into a barbed wire fence. As the years went on, the cousins took their entrepreneurial pursuits more seriously, even attempting at one point to start a video arcade. Without any parents knowing, the boys picked out a spot for their arcade, got a lease, and started navigating the permit process for their business. Eventually, they had to get someone over eighteen to sign a legal document, and neither the Rives’ father nor Errol would oblige. It would take a couple of decades, but Elon and the Rives would eventually go into business together. The boys’ most audacious exploits may have been their trips between Pretoria and Johannesburg. During the 1980s, South Africa could be a terribly violent place, and the thirty-five-mile train trip linking Pretoria and Johannesburg stood out as one of the world’s more dangerous rides. Kimbal counted the train journeys as formative experiences for him and Elon. “South Africa was not a happy-go-lucky place, and that has an impact on you. We saw some really rough stuff. It was part of an atypical upbringing—just this insane set of experiences that changes how you view risk. You don’t grow up thinking getting a job is the hard part. That’s not interesting enough.” The boys ranged in age from about thirteen to sixteen and chased a mix of parties and geeky exploits in Johannesburg. During one jaunt, they went to a Dungeons & Dragons tournament. “That was us being nerd master supremes,” Musk said. All of the boys were into the role-playing game, which requires someone to help set the mood for a contest by imagining and then describing a scene. “You have entered a room, and there is a chest in the corner. What will you do? . . . You open the chest. You’ve sprung a trap. Dozens of goblins are on the loose.” Elon excelled at this Dungeon Master role and had memorized the texts detailing the powers of monsters and other characters. “Under Elon’s leadership, we played the role so well and won the tournament,” said Peter Rive. “Winning requires this incredible imagination, and Elon really set the tone for keeping people captivated and inspired.” The Elon that his peers encountered at school was far less inspirational. Throughout middle and high school, Elon bounced around a couple of institutions. He spent the equivalent of eighth and ninth grades at Bryanston High School. One afternoon Elon and Kimbal were sitting at the top of a flight of concrete stairs eating when a boy decided to go after Elon. “I was basically hiding from this gang that was fucking hunting me down for God knows fucking why. I think I accidentally bumped this guy at assembly that morning and he’d taken some huge offense at that.” The boy crept up behind Musk, kicked him in the head, and then shoved him down the stairs. Musk tumbled down the entire flight, and a handful of boys pounced on him, some of them kicking Musk in the side and the ringleader bashing his head against the ground. “They were a bunch of fucking psychos,” Musk said. “I blacked out.” Kimbal watched in horror and feared for Elon’s life. He rushed down the stairs to find Elon’s face bloodied and swollen. “He looked like someone who had just been in the boxing ring,” Kimbal said. Elon then went to the hospital. “It was about a week before I could get back to school,” Musk said. (During a news conference in 2013, Elon disclosed that he’d had a nose job to deal with the lingering effects of this beating.) For three or four years, Musk endured relentless hounding at the hands of these bullies. They went so far as to beat up a boy that Musk considered his best friend until the child agreed to stop hanging out with Musk. “Moreover, they got him—they got my best fucking friend—to lure me out of hiding so they could beat me up,” Musk said. “And that fucking hurt.” While telling this part of the story, Musk’s eyes welled up and his voice quivered. “For some reason, they decided that I was it, and they were going to go after me nonstop. That’s what made growing up difficult. For a number of years, there was no respite. You get chased around by gangs at school who tried to beat the shit out of me, and then I’d come home, and it would just be awful there as well. It was just like nonstop horrible.” Musk spent the latter stages of his high school career at Pretoria Boys High School, where a growth spurt and the generally better behavior of the students made life more bearable. While a public school by definition, Pretoria Boys has functioned more like a private school for the last hundred years. It’s the place you send a young man to get him ready to attend Oxford or Cambridge. The boys from Musk’s class remember him as a likable, quiet, unspectacular student. “There were four or five boys that were considered the very brightest,” said Deon Prinsloo, who sat behind Elon in some classes. “Elon was not one of them.” Such comments were echoed by a half dozen boys who also noted that Musk’s lack of interest in sports left him isolated in the midst of an athletics-obsessed culture. “Honestly, there were just no signs that he was going to be a billionaire,” said Gideon Fourie, another classmate. “He was never in a leadership position at school. I was rather surprised to see what has happened to him.” While Musk didn’t have any close friends at school, his eccentric interests did leave an impression. One boy—Ted Wood—remembered Musk bringing model rockets to school and blasting them off during breaks. This was not the only hint of his aspirations. During a science-class debate, Elon gained attention for railing against fossil fuels in favor of solar power—an almost sacrilegious stance in a country devoted to mining the earth’s natural resources. “He always had firm views on things,” said Wood. Terency Beney, a classmate who stayed in touch with Elon over the years, claimed that Musk had started fantasizing about colonizing other planets in high school as well. In another nod to the future, Elon and Kimbal were chatting during a class break outdoors when Wood interrupted them and asked what they were going on about. “They said, ‘We are talking about whether there is a need for branch banking in the financial industry and whether we will move to paperless banking.’ I remember thinking that was such an absurd comment to make. I said, ‘Yeah, that’s great.’” /Musk couldn’t remember this particular conversation. “I think they might be having creative recollection,” he said. “It’s possible. I had lots of esoteric conversations the last couple years of high school, but I was more concerned about general technology than banking.”/ While Musk might not have been among the academic elite in his class, he was among a handful of students with the grades and self-professed interest to be selected for an experimental computer program. Students were plucked out of a number of schools and brought together to learn the BASIC, COBOL, and Pascal programming languages. Musk continued to augment these technological leanings with his love of science fiction and fantasy and tried his hand at writing stories that involved dragons and supernatural beings. “I wanted to write something like Lord of the Rings,” he said. Maye viewed these high school years through a mother’s eyes and recounted plenty of tales of Musk performing spectacular academic feats. The video game he wrote, she said, impressed much older, more experienced techies. He aced math exams well beyond his years. And he had that incredible memory. The only reason he did not outrank the other boys was a lack of interest in the work prescribed by the school. As Musk saw it, “I just look at it as ‘What grades do I need to get where I want to go?’ There were compulsory subjects like Afrikaans, and I just didn’t see the point of learning that. It seemed ridiculous. I’d get a passing grade and that was fine. Things like physics and computers—I got the highest grade you can get in those. There needs to be a reason for a grade. I’d rather play video games, write software, and read books than try and get an A if there’s no point in getting an A. I can remember failing subjects in like fourth and fifth grade. Then, my mother’s boyfriend told me I’d be held back if I didn’t pass. I didn’t actually know you had to pass the subjects to move to the next grade. I got the best grades in class after that.” At seventeen, Musk left South Africa for Canada. He has recounted this journey quite often in the press and typically leans on two descriptions of the motivation for his flight. The short version is that Musk wanted to get to the United States as quickly as possible and could use Canada as a pit stop via his Canadian ancestry. The second go-to story that Musk relies on has more of a social conscience. South Africa required military service at the time. Musk wanted to avoid joining the military, he has said, because it would have forced him to participate in the apartheid regime. What rarely gets mentioned is that Musk attended the University of Pretoria for five months before heading off on his grand adventure. He began pursuing physics and engineering but put lackluster effort into the work and soon dropped out of school. Musk characterized the time at university as just something to do while he awaited his Canadian documentation. In addition to being an inconsequential part of his life, Musk lazing through school to avoid South Africa’s required military service rather undermines the tale of a brooding, adventurous youth that he likes to tell, which is likely why the stint at the University of Pretoria never seems to come up. There’s no question, though, that Musk had been pining to get to the United States on a visceral level for a long time. Musk’s early inclination toward computers and technology had fostered an intense interest in Silicon Valley, and his trips overseas had reinforced the idea that America was the place to get things done. South Africa, by contrast, presented far less opportunity for an entrepreneurial soul. As Kimbal put it, “South Africa was like a prison for someone like Elon.” Musk’s opportunity to flee arrived with a change in the law that allowed Maye to pass her Canadian citizenship to her children. Musk immediately began researching how to complete the paperwork for this process. It took about a year to receive the approvals from the Canadian government and to secure a Canadian passport. “That’s when Elon said, ‘I’m leaving for Canada,’” Maye said. In these pre-Internet days, Musk had to wait three agonizing weeks to get a plane ticket. Once it arrived, and without flinching, he left home for good.
CANADA MUSK’S GREAT ESCAPE TO CANADA WAS NOT WELL THOUGHT OUT. He knew of a great-uncle in Montreal, hopped on a flight and hoped for the best. Upon landing in June 1988, Musk found a pay phone and tried to use directory assistance to find his uncle. When that didn’t work, he called his mother collect. She had bad news. Maye had sent a letter to the uncle before Musk left and received a reply while her son was in transit. The uncle had gone to Minnesota, meaning Musk had nowhere to stay. Bags in hand, Musk headed for a youth hostel. After spending a few days in Montreal exploring the city, Musk tried to come up with a long-term plan. Maye had family scattered all across Canada, and Musk began reaching out to them. He bought a countrywide bus ticket that let him hop on and off as he pleased for one hundred dollars, and opted to head to Saskatchewan, the former home of his grandfather. After a 1,900-mile bus ride, he ended up in Swift Current, a town of fifteen thousand people. Musk called a second cousin out of the blue from the bus station and hitched a ride to his house. Musk spent the next year working a series of odd jobs around Canada. He tended vegetables and shoveled out grain bins at a cousin’s farm located in the tiny town of Waldeck. Musk celebrated his eighteenth birthday there, sharing a cake with the family he’d just met and a few strangers from the neighborhood. After that, he learned to cut logs with a chain saw in Vancouver, British Columbia. The hardest job Musk took came after a visit to the unemployment office. He inquired about the job with the best wage, which turned out to be a gig cleaning the boiler room of a lumber mill for eighteen dollars an hour. “You have to put on this hazmat suit and then shimmy through this little tunnel that you can barely fit in,” Musk said. “Then, you have a shovel and you take the sand and goop and other residue, which is still steaming hot, and you have to shovel it through the same hole you came through. There is no escape. Someone else on the other side has to shovel it into a wheelbarrow. If you stay in there for more than thirty minutes, you get too hot and die.” Thirty people started out at the beginning of the week. By the third day, five people were left. At the end of the week, it was just Musk and two other men doing the work. As Musk made his way around Canada, his brother, sister, and mother were figuring out how to get there as well. /When Maye went to Canada to check out places to live, a fourteen-year-old Tosca seized the moment and put the family house in South Africa up for sale. “She had sold my car as well and was in the midst of putting our furniture up for sale, too,” Maye said. “When I got back, I asked her why. She said, ‘There is no need to delay. We are getting out of here.’”/ When Kimbal and Elon eventually reunited in Canada, their headstrong, playful natures bloomed. Elon ended up enrolling at Queen’s University in Kingston, Ontario, in 1989. (He picked Queen’s over the University of Waterloo because he felt there were more good-looking women at Queen’s.) [http://queensu.ca/news/alumnireview/rocket-man] Outside of his studies, Elon would read the newspaper alongside Kimbal, and the two of them would identify interesting people they would like to meet. They then took turns cold-calling these people to ask if they were available to have lunch. Among the harassed was the head of marketing for the Toronto Blue Jays baseball team, a business writer for the Globe and Mail, and a top executive at the Bank of Nova Scotia, Peter Nicholson. Nicholson remembered the boys’ call well. “I was not in the habit of getting out-of-the-blue requests,” he said. “I was perfectly prepared to have lunch with a couple of kids that had that kind of gumption.” It took six months to get on Nicholson’s calendar, but, sure enough, the Musk brothers made a three-hour train ride and showed up on time. Nicholson’s first exposure to the Musk brothers left him with an impression many would share. Both presented themselves well and were polite. Elon, though, clearly came off as the geekier, more awkward counterpoint to the charismatic, personable Kimbal. “I became more impressed and fascinated as I talked to them,” Nicholson said. “They were so determined.” Nicholson ended up offering Elon a summer internship at the bank and became his trusted advisor. Not long after their initial meeting, Elon invited Peter Nicholson’s daughter Christie to his birthday party. Christie showed up at Maye’s Toronto apartment with a jar of homemade lemon curd in hand and was greeted by Elon and about fifteen other people. Elon had never met Christie before, but he went right up to her and led her to a couch. “Then, I believe the second sentence out of his mouth was ‘I think a lot about electric cars,’” Christie said. “And then he turned to me and said, ‘Do you think about electric cars?’” The conversation left Christie, who is now a science writer, with the distinct impression that Musk was handsome, affable, and a tremendous nerd. “For whatever reason, I was so struck by that moment on the sofa,” she said. “You could tell that this person was very different. He captivated me in that way.” With her angular features and blond hair, Christie fit Musk’s type, and the two stayed in touch during Musk’s time in Canada. They never really dated, but Christie found Musk interesting enough to have lengthy conversations with him on the phone. “One night he told me, ‘If there was a way that I could not eat, so I could work more, I would not eat. I wish there was a way to get nutrients without sitting down for a meal.’ The enormity of his work ethic at that age and his intensity jumped out. It seemed like one of the more unusual things I had ever heard.” A deeper relationship during this stint in Canada arose between Musk and Justine Wilson, a fellow student at Queen’s. Leggy with long, brown hair, Wilson radiated romance and sexual energy. Justine had already fallen in love with an older man and then ditched him to go to college. Her next conquest was meant to wear a leather jacket and be a damaged, James Dean sort. As fortune would have it, however, the clean-cut, posh-sounding Musk spotted Wilson on campus and went right to work trying to date her. “She looked pretty great,” Musk said. “She was also smart and this intellectual with sort of an edge. She had a black belt in tae kwon do and was semi-bohemian and, you know, like the hot chick on campus.” He made his first move just outside of her dorm, where he pretended to have bumped into her by accident and then reminded her that they had met previously at a party. Justine, only one week into school, agreed to Musk’s proposal of an ice cream date. When he arrived to pick up Wilson, Musk found a note on the dorm room door, notifying him that he’d been stood up. “It said that she had to go study for an exam and couldn’t make it and that she was sorry,” Musk said. Musk then hunted down Justine’s best friend and did some research, asking where Justine usually studied and what her favorite flavor of ice cream was. Later, as Justine hid in the student center studying Spanish, Musk appeared behind her with a couple of melting chocolate chip ice cream cones in hand. Wilson had dreamed of having a torrid romance with a writer. “I wanted to be Sylvia and Ted,” she said. What she fell for instead was a relentless, ambitious geek. The pair attended the same abnormal-psychology class and compared their grades following an exam. Justine notched a 97, Musk a 98. “He went back to the professor, and talked his way into the two points he lost and got a hundred,” Justine said. “It felt like we were always competing.” Musk had a romantic side as well. One time he sent Wilson a dozen roses, each with its own note, and he also gifted Wilson a copy of The Prophet filled with handwritten romantic musings. “He can sweep you off your feet,” Justine said. During their university years, the two youngsters were off and on, with Musk having to work hard to keep the relationship going. “She was hip and dated the coolest guys and wasn’t interested in Elon at all,” Maye said. “So that was hard on him.” Musk pursued a couple of other girls, but kept returning to Justine. Any time she acted cool toward him, Musk responded with his usual show of force. “He would call very insistently,” she said. “You always knew it was Elon because the phone would never stop ringing. The man does not take no for an answer. You can’t blow him off. I do think of him as the Terminator. He locks his gaze on to something and says, ‘It shall be mine.’ Bit by bit, he won me over.” College suited Musk. He worked on being less of a know-it-all, while also finding a group of people who respected his intellectual abilities. The university students were less inclined to laugh off or deride his opinionated takes on energy, space, and whatever else was captivating him at the moment. Musk had found people who responded to his ambition rather than mocking it, and he fed on this environment. Navaid Farooq, a Canadian who grew up in Geneva, ended up in Musk’s freshman-year dormitory in the fall of 1990. Both men were placed in the international section where a Canadian student would get paired with a student from overseas. Musk sort of broke the system, since he technically counted as a Canadian but knew almost nothing about his surroundings. “I had a roommate from Hong Kong, and he was a really nice guy,” Musk said. “He religiously attended every lecture, which was helpful, since I went to the least number of classes possible.” For a time, Musk sold computer parts and full PCs in the dorm to make some extra cash. “I could build something to suit their needs like a tricked-out gaming machine or a simple word processor that cost less than what they could get in a store,” Musk said. “Or if their computer didn’t boot properly or had a virus, I’d fix it. I could pretty much solve any problem.” Farooq and Musk bonded over their backgrounds living abroad and a shared interest in strategy board games. “I don’t think he makes friends easily, but he is very loyal to those he has,” Farooq said. When the video game Civilization was released, the college chums spent hours building their empire, much to the dismay of Farooq’s girlfriend, who was forgotten in another room. “Elon could lose himself for hours on end,” Farooq said. The students also relished their loner lifestyles. “We are the kinds of people that can be by ourselves at a party and not feel awkward,” Farooq said. “We can think to ourselves and not feel socially weird about it.” Musk was more ambitious in college than he’d been in high school. He studied business, competed in public speaking contests, and began to display the brand of intensity and competitiveness that marks his behavior today. After one economics exam, Musk, Farooq, and some other students in class came back to the dorms and began comparing notes to try to ascertain how well they did on the test. It soon became clear that Musk had a firmer grasp on the material than anyone else. “This was a group of fairly high achievers, and Elon stood way outside of the bell curve,” Farooq said. Musk’s intensity has continued to be a constant in their long relationship. “When Elon gets into something, he develops just this different level of interest in it than other people. That is what differentiates Elon from the rest of humanity.” In 1992, having spent two years at Queen’s, Musk transferred to the University of Pennsylvania on a scholarship. Musk saw the Ivy League school as possibly opening some additional doors and went off in pursuit of dual degrees—first an economics degree from the Wharton School and then a bachelor’s degree in physics. Justine stayed at Queen’s, pursuing her dream of becoming a writer, and maintained a long-distance relationship with Musk. Now and again, she would visit him, and the two would sometimes head off to New York for a romantic weekend. Musk blossomed even more at Penn, and really started to feel comfortable while hanging out with his fellow physics students. “At Penn, he met people that thought like him,” Maye said. “There were some nerds there. He so enjoyed them. I remember going for lunch with them, and they were talking physics things. They were saying, ‘A plus B equals pi squared’ or whatever. They would laugh out loud. It was cool to see him so happy.” Once again, however, Musk did not make many friends among the broader school body. It’s difficult to find former students who remember him being there at all. But he did make one very close friend named Adeo Ressi, who would go on to be a Silicon Valley entrepreneur in his own right and is to this day as tight with Elon as anyone. Ressi is a lanky guy well over six feet tall and possesses an eccentric air. He was the artistic, colorful foil to the studious, more buttoned-up Musk. Both of the young men were transfer students and ended up being placed in the funky freshman dorm. The lackluster social scene did not live up to Ressi’s expectations, and he talked Musk into renting a large house off campus. They got the ten-bedroom home relatively cheap, since it was a frat house that had gone unrented. During the week, Musk and Ressi would study, but as the weekend approached, Ressi, in particular, would transform the house into a nightclub. He covered the windows with trash bags to make it pitch black inside and decorated the walls with bright paints and whatever objects he could find. “It was a full-out, unlicensed speakeasy,” Ressi said. “We would have as many as five hundred people. We would charge five dollars, and it would be pretty much all you could drink—beer and Jell-O shots and other things.” Come Friday night, the ground around the house would shake from the intensity of the bass being pumped out by Ressi’s speakers. Maye visited one of the parties and discovered that Ressi had hammered objects into the walls and lacquered them with glow-in-the-dark paint. She ended up working the door as the coat check/money taker and grabbed a pair of scissors for protection as the cash piled up in a shoe box. A second house had fourteen rooms. Musk, Ressi, and one other person lived there. They fashioned tables by laying plywood on top of used kegs and came up with other makeshift furniture ideas. Musk returned home one day to find that Ressi had nailed his desk to the wall and then painted it in Day-Glo colors. Musk retaliated by pulling his desk down, painting it black, and studying. “I’m like, ‘Dude, that’s installation art in our party house,’” said Ressi. Remind Musk of this incident and he’ll respond matter-of-factly, “It was a desk.” Musk will have the occasional vodka and Diet Coke, but he’s not a big drinker and does not really care for the taste of alcohol. “Somebody had to stay sober during these parties,” Musk said. “I was paying my own way through college and could make an entire month’s rent in one night. Adeo was in charge of doing cool shit around the house, and I would run the party.” As Ressi put it, “Elon was the most straight-laced dude you have ever met. He never drank. He never did anything. Zero. Literally nothing.” The only time Ressi had to step in and moderate Musk’s behavior came during video game binges that could go on for days. Musk’s longtime interest in solar power and in finding other new ways to harness energy expanded at Penn. In December 1994, he had to come up with a business plan for one of his classes and ended up writing a paper titled “The Importance of Being Solar.” The document started with a bit of Musk’s wry sense of humor. At the top of the page, he wrote: “The sun will come out tomorrow. . . .”—Little Orphan Annie on the subject of renewable energy. The paper went on to predict a rise in solar power technology based on materials improvements and the construction of large-scale solar plants. Musk delved deeply into how solar cells work and the various compounds that can make them more efficient. He concluded the paper with a drawing of the “power station of the future.” It depicted a pair of giant solar arrays in space—each four kilometers in width—sending their juice down to Earth via microwave beams to a receiving antenna with a seven-kilometer diameter. Musk received a 98 on what his professor deemed a “very interesting and well written paper.” A second paper talked about taking research documents and books and electronically scanning them, performing optical character recognition, and putting all of the information in a single database—much like a mix between today’s Google Books and Google Scholar. And a third paper dwelled on another of Musk’s favorite topics—ultracapacitors. In the forty-four-page document, Musk is plainly jubilant over the idea of a new form of energy storage that would suit his future pursuits with cars, planes, and rockets. Pointing to the latest research coming out of a lab in Silicon Valley, he wrote: “The end result represents the first new means of storing significant amounts of electrical energy since the development of the battery and fuel cell. Furthermore, because the Ultracapacitor retains the basic properties of a capacitor, it can deliver its energy over one hundred times faster than a battery of equivalent weight, and be recharged just as quickly.” Musk received a 97 for this effort and praise for “a very thorough analysis” with “excellent financials!” The remarks from the professor were spot-on. Musk’s clear, concise writing is the work of a logician, moving from one point to the next with precision. What truly stood out, though, was Musk’s ability to master difficult physics concepts in the midst of actual business plans. Even then, he showed an unusual knack for being able to perceive a path from a scientific advance to a for-profit enterprise. As Musk began to think more seriously about what he would do after college, he briefly considered getting into the videogame business. He’d been obsessed with video games since his childhood and had held a gaming internship. But he came to see them as not quite grand enough a pursuit. “I really like computer games, but then if I made really great computer games, how much effect would that have on the world,” he said. “It wouldn’t have a big effect. Even though I have an intrinsic love of video games, I couldn’t bring myself to do that as a career.” In interviews, Musk often makes sure that people know he had some truly big ideas on his mind during this period of his life. As he tells it, he would daydream at Queen’s and Penn and usually end up with the same conclusion: he viewed the Internet, renewable energy, and space as the three areas that would undergo significant change in the years to come and as the markets where he could make a big impact. He vowed to pursue projects in all three. “I told all my ex-girlfriends and my ex-wife about these ideas,” he said. “It probably sounded like super-crazy talk.” Musk’s insistence on explaining the early origins of his passion for electric cars, solar energy, and rockets can come off as insecure. It feels as if Musk is trying to shape his life story in a forced way. But for Musk, the distinction between stumbling into something and having intent is important. Musk has long wanted the world to know that he’s different from the run-of-the-mill entrepreneur in Silicon Valley. He wasn’t just sniffing out trends, and he wasn’t consumed by the idea of getting rich. He’s been in pursuit of a master plan all along. “I really was thinking about this stuff in college,” he said. “It is not some invented story after the fact. I don’t want to seem like a Johnny-come-lately or that I’m chasing a fad or just being opportunistic. I’m not an investor. I like to make technologies real that I think are important for the future and useful in some sort of way.”
ELON’S FIRST START-UP IN THE SUMMER OF 1994, Musk and his brother, Kimbal, took their first steps toward becoming honest-to-God Americans. They set off on a road trip across the country. Kimbal had been working as a franchisee for College Pro Painters and done well for himself, running what amounted to a small business. He sold off his part of the franchise and pooled the money with what Musk had on hand to buy a beat-up 1970s BMW 320i. The brothers began their trip near San Francisco in August, as temperatures in California soared. The first part of the drive took them down to Needles, a city in the Mojave Desert. There they experienced the sweaty thrill of 120-degree weather in a car with no air-conditioning and learned to love pit stops at Carl’s Jr. burger joints, where they spent hours recuperating in the cold. The trip provided plenty of time for your typical twenty-something hijinks and raging capitalist daydreaming. The Web had just started to become accessible to the public thanks to the rise of directory sites like Yahoo! and tools like Netscape’s browser. The brothers were tuned in to the Internet and thought they might like to start a company together doing something on the Web. From California to Colorado, Wyoming, South Dakota, and Illinois, they took turns driving, brainstorming, and talking shit before heading back east to get Musk to school that fall. The best idea to arise from the journey was an online network for doctors. This wasn’t meant to be something as ambitious as electronic health records but more of a system for physicians to exchange information and collaborate. “It seemed like the medical industry was one that could be disrupted,” Kimbal said. “I went to work on a business plan and the sales and marketing side of it later, but it didn’t fly. We didn’t love it.” Musk had spent the earlier part of that summer in Silicon Valley, holding down a pair of internships. By day, he worked at Pinnacle Research Institute. Based in Los Gatos, Pinnacle was a much-ballyhooed start-up with a team of scientists exploring ways in which ultracapacitors could be used as a revolutionary fuel source in electric and hybrid vehicles. The work also veered—at least conceptually—into more bizarre territory. Musk could talk at length about how ultracapacitors might be used to build laser-based sidearms in the tradition of Star Wars and just about any other futuristic film. The laser guns would release rounds of enormous energy, and then the shooter would replace an ultracapacitor at the base of the gun, much like swapping out a clip of bullets, and start blasting away again. Ultracapacitors also looked promising as the power supplies for missiles. They were more resilient than batteries under the mechanical stresses of a launch and would hold a more consistent charge over long periods of time. Musk fell in love with the work at Pinnacle and began using it as the basis for some of his business plan experiments at Penn and for his industrialist fantasies. In the evenings, Musk headed to Rocket Science Games, a start-up based in Palo Alto that wanted to create the most advanced video games ever made by moving them off cartridges and onto CDs that could hold more information. The CDs would in theory allow them to bring Hollywood-style storytelling and production quality to the games. A team of budding all-stars who were a mix of engineers and film people was assembled to pull off the work. Tony Fadell, who would later drive much of the development of both the iPod and iPhone at Apple, worked at Rocket Science, as did the guys who developed the QuickTime multimedia software for Apple. They also had people who worked on the original Star Wars effects at Industrial Light & Magic and some who did games at LucasArts Entertainment. Rocket Science gave Musk a flavor for what Silicon Valley had to offer both from a talent and culture perspective. There were people working at the office twenty-four hours a day, and they didn’t think it at all odd that Musk would turn up around 5 P.M. every evening to start his second job. “We brought him in to write some very menial low-level code,” said Peter Barrett, an Australian engineer who helped start the company. “He was completely unflappable. After a short while, I don’t think anyone was giving him any direction, and he ended up making what he wanted to make.” Specifically, Musk had been asked to write the drivers that would let joysticks and mice communicate with various computers and games. Drivers are the same types of annoying files that you have to install to get a printer or camera working with a home computer—true grunt work. A self-taught programmer, Musk fancied himself quite good at coding and assigned himself to more ambitious jobs. “I was basically trying to figure out how you could multitask stuff, so you could read video from a CD, while running a game at the same time,” Musk said. “At the time, you could do one or the other. It was this complicated bit of assembly programming.” Complicated indeed. Musk had to issue commands that spoke directly to a computer’s main microprocessor and fiddled with the most basic functions that made the machine work. Bruce Leak, the former lead engineer behind Apple’s QuickTime, had overseen the hiring of Musk and marveled at his ability to pull all-nighters. “He had boundless energy,” Leak said. “Kids these days have no idea about hardware or how stuff works, but he had a PC hacker background and was not afraid to just go figure things out.” Musk found in Silicon Valley a wealth of the opportunity he’d been seeking and a place equal to his ambitions. He would return two summers in a row and then bolt west permanently after graduating with dual degrees from Penn. He initially intended to pursue a doctorate in materials science and physics at Stanford and to advance the work he’d done at Pinnacle on ultracapacitors. As the story goes, Musk dropped out of Stanford after two days, finding the Internet’s call irresistible. He talked Kimbal into moving to Silicon Valley as well, so they could conquer the Web together. The first inklings of a viable Internet business had come to Musk during his internships. A salesperson from the Yellow Pages had come into one of the start-up offices. He tried to sell the idea of an online listing to complement the regular listing a company would have in the big, fat Yellow Pages book. The salesman struggled with his pitch and clearly had little grasp of what the Internet actually was or how someone would find a business on it. The flimsy pitch got Musk thinking, and he reached out to Kimbal, talking up the idea of helping businesses get online for the first time. “Elon said, ‘These guys don’t know what they are talking about. Maybe this is something we can do,’” Kimbal said. This was 1995, and the brothers were about to form Global Link Information Network, a start-up that would eventually be renamed Zip2. (For details on the controversy surrounding Zip2’s founding and Musk’s academic record, see Appendix 1.) The Zip2 idea was ingenious. Few small businesses in 1995 understood the ramifications of the Internet. They had little idea how to get on it and didn’t really see the value in creating a website for their business or even in having a Yellow Pages–like listing online. Musk and his brother hoped to convince restaurants, clothing shops, hairdressers, and the like that the time had come for them to make their presence known to the Web-surfing public. Zip2 would create a searchable directory of businesses and tie this into maps. Musk often explained the concept through pizza, saying that everyone deserved the right to know the location of their closest pizza parlor and the turn-by-turn directions to get there. This may seem obvious today—think Yelp meets Google Maps—but back then, not even stoners had dreamed up such a service. The Musk brothers brought Zip2 to life at 430 Sherman Avenue in Palo Alto. They rented a studio-apartment-sized office—twenty feet by thirty feet—and acquired some basic furniture. The three-story building had its quirks. There were no elevators, and the toilets often backed up. “It was literally a shitty place to work,” said an early employee. To get a fast Internet connection, Musk struck a deal with Ray Girouard, an entrepreneur who ran an Internet service provider operation from the floor below the Zip2 offices. According to Girouard, Musk drilled a hole in the drywall near the Zip2 door and then strung an Ethernet cable down the stairwell to the ISP. “They were slow to pay a couple of times but never stiffed me on the bill,” Girouard said. Musk did all of the original coding behind the service himself, while the more amiable Kimbal looked to ramp up the door-to-door sales operation. Musk had acquired a cheap license to a database of business listings in the Bay Area that would give a business’s name and its address. He then contacted Navteq, a company that had spent hundreds of millions of dollars to create digital maps and directions that could be used in early GPS navigation-style devices, and struck a masterful bargain. “We called them up, and they gave us the technology for free,” said Kimbal. Musk merged the two databases together to get a rudimentary system up and running. Over time, Zip2’s engineers had to augment this initial data haul with more maps to cover areas outside of major metropolitan areas and to build custom turn-by-turn directions that would look good and work well on a home computer. Errol Musk gave his sons $28,000 to help them through this period, but they were more or less broke after getting the office space, licensing software, and buying some equipment. For the first three months of Zip2’s life, Musk and his brother lived at the office. They had a small closet where they kept their clothes and would shower at the YMCA. “Sometimes we ate four meals a day at Jack in the Box,” Kimbal said. “It was open twenty-four hours, which suited our work schedule. I got a smoothie one time, and there was something in it. I just pulled it out and kept drinking. I haven’t been able to eat there since, but I can still recite their menu.” Next, the brothers rented a two-bedroom apartment. They didn’t have the money or the inclination to get furniture. So there were just a couple of mattresses on the floor. Musk somehow managed to convince a young South Korean engineer to come work at Zip2 as an intern in exchange for room and board. “This poor kid thought he was coming over for a job at a big company,” Kimbal said. “He ended up living with us and had no idea what he was getting into.” One day, the intern drove the Musks’ battered BMW 320i to work, and a wheel came off en route. The axle dug into the street at the intersection of Page Mill Road and El Camino Real, and the groove it carved out remained visible for years. Zip2 may have been a go-go Internet enterprise aimed at the Information Age, but getting it off the ground required old-fashioned door-to-door salesmanship. Businesses needed to be persuaded of the Web’s benefits and charmed into paying for the unknown. In late 1995, the Musk brothers began making their first hires and assembling a motley sales team. Jeff Heilman, a free-spirited twenty-year-old trying to figure out what to do with his life, arrived as one of Zip2’s first recruits. He’d been watching TV late one night with his dad and seen a Web address printed at the bottom of the screen during a commercial. “It was for something dot-com,” Heilman said. “I remember sitting there and asking my dad what we were looking at. He said he didn’t know, either. That’s when I realized I had to go find me some Internet.” Heilman spent a couple of weeks trying to chat up people who could explain the Internet to him and then stumbled on a two-by-two-inch Zip2 job listing in the San Jose Mercury News. “Internet Sales Apply Here!” it read, and Heilman got the gig. A handful of other salespeople joined him and worked for commissions. Musk never seemed to leave the office. He slept, not unlike a dog, on a beanbag next to his desk. “Almost every day, I’d come in at seven thirty or eight A.M., and he’d be asleep right there on that bag,” Heilman said. “Maybe he showered on the weekends. I don’t know.” Musk asked those first employees of Zip2 to give him a kick when they arrived, and he’d wake up and get back to work. While Musk did his possessed coder thing, Kimbal became the rah-rah sales leader. “Kimbal was the eternal optimist, and he was very, very uplifting,” Heilman said. “I had never met anyone quite like him.” Kimbal sent Heilman to the high-end Stanford shopping mall and to University Avenue, the main drag in Palo Alto, to coax retailers into signing up with Zip2, explaining that a sponsored listing would send a company to the top of search results. The big problem, of course, was that no one was buying. Week after week, Heilman knocked on doors and returned to the office with very little to report in the way of good news. The nicest responses came from the people who told Heilman that advertising on the Internet sounded like the dumbest thing they had ever heard of. Most often, the shop owners just told Heilman to leave and stop bothering them. When lunchtime came around, the Musks would reach into a cigar box where they kept some cash, take Heilman out, and get the depressing status reports on the sales. Craig Mohr, another early employee, gave up his job selling real estate to hawk Zip2’s service. He decided to court auto dealerships because they usually spent lots of money on advertising. He told them about Zip2’s main website—www.totalinfo.com—and tried to convince them that demand was high to get a listing like www.totalinfo.com/toyotaofsiliconvalley. The service did not always work when Mohr demonstrated it or it would load very slowly, as was common back then. This forced him to talk the customers into imagining Zip2’s potential. “One day I came back with about nine hundred dollars in checks,” Mohr said. “I walked into the office and asked the guys what they wanted me to do with the money. Elon stopped pounding his keyboard, leaned out from behind his monitor, and said, ‘No way, you’ve got money.’” What kept the employees’ spirits up were the continuous improvements Musk made with the Zip2 software. The service had morphed from a proof-of-concept to an actual product that could be used and demoed. Ever marketing savvy, the Musk brothers tried to make their Web service seem more important by giving it an imposing physical body. Musk built a huge case around a standard PC and lugged the unit onto a base with wheels. When prospective investors would come by, Musk would put on a show and roll this massive machine out so that it appeared like Zip2 ran inside of a mini-supercomputer. “The investors thought that was impressive,” Kimbal said. Heilman also noticed that the investors bought into Musk’s slavish devotion to the company. “Even then, as essentially a college kid with zits, Elon had this drive that this thing—whatever it was—had to get done and that if he didn’t do it, he’d miss his shot,” Heilman said. “I think that’s what the VCs saw—that he was willing to stake his existence on building out this platform.” Musk actually said as much to one venture capitalist, informing him, “My mentality is that of a samurai. I would rather commit seppuku than fail.” Early on in the Zip2 venture, Musk acquired an important confidant, who tempered some of these more dramatic impulses. Greg Kouri, a Canadian businessman in his mid-thirties, had met the Musks in Toronto and bought into the early Zip2 brainstorming. The boys had showed up at his door one morning to inform Kouri that they intended to head to California to give the business a shot. Still in his red bathrobe, Kouri went back into the house, dug around for a couple of minutes, and came back with a wad of $6,000. In early 1996, he moved to California and joined Zip2 as a cofounder. Kouri, who had done a number of real estate deals in the past and had actual business experience and skills at reading people, served as the adult supervision at Zip2. The Canadian had a knack for calming Musk and ended up becoming something of a mentor. “Really smart people sometimes don’t understand that not everyone can keep up with them or go as fast,” said Derek Proudian, a venture capitalist who would become Zip2’s chief executive officer. “Greg is one of the few people that Elon would listen to and had a way of putting things in context for him.” Kouri also used to referee fistfights between Elon and Kimbal, in the middle of the office. “I don’t get in fights with anyone else, but Elon and I don’t have the ability to reconcile a vision other than our own,” Kimbal said. During a particularly nasty scrap over a business decision, Elon ripped some skin off his fist and had to go get a tetanus shot. Kouri put an end to the fights after that. (Kouri died of a heart attack in 2012 at the age of fifty-one, having made a fortune investing in Musk’s companies. Musk attended his funeral. “We owe him a lot,” said Kimbal.) In early 1996, Zip2 underwent a massive change. The venture capital firm Mohr Davidow Ventures had caught wind of a couple of South African boys trying to make a Yellow Pages for the Internet and met with the brothers. Musk, while raw in his presentation skills, pitched the company well enough, and the investors came away impressed with his energy. Mohr Davidow invested $3 million into the company. /The Musk brothers were not the most aggressive businessmen at this point. “I remember from their business plan that they were originally asking for a ten-thousand-dollar investment for twenty-five percent of their company,” said Steve Jurvetson, the venture capitalist. “That is a cheap deal! When I heard about the three-million-dollar investment, I wondered if Mohr Davidow had actually read the business plan. Somehow, the brothers ended up raising a normal venture round.”/ With these funds in hand, the company officially changed its name from Global Link to Zip2—the idea being zip to here, zip to there—moved to a larger office at 390 Cambridge Avenue in Palo Alto, and began hiring talented engineers. Zip2 also shifted its business strategy. At the time, the company had built one of the best direction systems on the Web. Zip2 would advance this technology and take it from focusing just on the Bay Area to having a national scope. The company’s main focus, however, would be an altogether new play. Instead of selling its service door-to-door, Zip2 would create a software package that could be sold to newspapers, which would in turn build their own directories for real estate, auto dealers, and classifieds. The newspapers were late understanding how the Internet would impact their businesses, and Zip2’s software would give them a quick way of getting online without needing to develop all their own technology from scratch. For its part, Zip2 could chase bigger prey and get a cut of a nationwide network of listings. This transition of the business model and the company’s makeup would be a seminal moment in Musk’s life. The venture capitalists pushed Musk into the role of chief technology officer and hired Rich Sorkin as the company’s CEO. Sorkin had worked at Creative Labs, a maker of audio equipment, and run the business development group at the company, where he steered a number of investments in Internet start-ups. Zip2’s investors saw him as experienced and clued in to the Web. While Musk agreed to the arrangement, he came to resent giving up control of Zip2. “Probably the biggest regret the whole time I worked with him was that he had made a deal with the devil with Mohr Davidow,” said Jim Ambras, the vice president of engineering at Zip2. “Elon didn’t have any operational responsibilities, and he wanted to be CEO.” Ambras had worked at Hewlett-Packard Labs and Silicon Graphics Inc. and exemplified the high-caliber talent Zip2 brought on after the first wave of money arrived. Silicon Graphics, a maker of high-end computers beloved by Hollywood, was the flashiest company of its day and had hoarded the elite geeks of Silicon Valley. And yet Ambras used the promise of Internet riches to poach a team of SGI’s smartest engineers over to Zip2. “Our attorneys got a letter from SGI saying that we were cherry-picking the very best guys,” Ambras said. “Elon thought that was fantastic.” While Musk had exceled as a self-taught coder, his skills weren’t nearly as polished as those of the new hires. They took one look at Zip2’s code and began rewriting the vast majority of the software. Musk bristled at some of their changes, but the computer scientists needed just a fraction of the lines of code that Musk used to get their jobs done. They had a knack for dividing software projects into chunks that could be altered and refined whereas Musk fell into the classic self-taught coder trap of writing what developers call hairballs—big, monolithic hunks of code that could go berserk for mysterious reasons. The engineers also brought a more refined working structure and realistic deadlines to the engineering group. This was a welcome change from Musk’s approach, which had been to set overly optimistic deadlines and then try to get engineers to work nonstop for days on end to meet the goals. “If you asked Elon how long it would take to do something, there was never anything in his mind that would take more than an hour,” Ambras said. “We came to interpret an hour as really taking a day or two and if Elon ever did say something would take a day, we allowed for a week or two weeks.” Starting Zip2 and watching it grow imbued Musk with self-confidence. Terence Beney, one of Musk’s high school friends, came to California for a visit and noticed the change in Musk’s character right away. He watched Musk confront a nasty landlord who had been giving his mother, who was renting an apartment in town, a hard time. “He said, ‘If you’re going to bully someone, bully me.’ It was startling to see him take over the situation. The last time I had seen him he was this geeky, awkward kid who would sometimes lose his temper. He was the kid you would pick on to get a response. Now he was confident and in control.” Musk also began consciously trying to manage his criticism of others. “Elon is not someone who would say, ‘I feel you. I see your point of view,’” said Justine. “Because he doesn’t have that ‘I feel you’ dimension there were things that seemed obvious to other people that weren’t that obvious to him. He had to learn that a twenty-something-year-old shouldn’t really shoot down the plans of older, senior people and point out everything wrong with them. He learned to modify his behavior in certain ways. I just think he comes at the world through strategy and intellect.” The personality tweaks worked with varying degrees of success. Musk still tended to drive the young engineers mad with his work demands and blunt criticism. “I remember being in a meeting once brainstorming about a new product—a new-car site,” said Doris Downes, the creative director at Zip2. “Someone complained about a technical change that we wanted being impossible. Elon turned and said, ‘I don’t really give a damn what you think,’ and walked out of the meeting. For Elon, the word no does not exist, and he expects that attitude from everyone around him.” Periodically, Musk let loose on the more senior executives as well. “You would see people come out of the meetings with this disgusted look on their face,” Mohr, the salesman, said. “You don’t get to where Elon is now by always being a nice guy, and he was just so driven and sure of himself.” As Musk tried to come to terms with the changes the investors had inflicted on Zip2, he did enjoy some of the perks of having big-money backing. The financiers helped the Musk brothers with their visas. They also gave them $30,000 each to buy cars. Musk and Kimbal had traded in their dilapidated BMW for a dilapidated sedan that they spray-painted with polka dots. Kimbal upgraded from that to a BMW 3 Series, and Musk bought a Jaguar E-Type. “It kept breaking down, and would arrive at the office on a flatbed,” Kimbal said. “But Elon always thought big.” /Musk also got to show off the new office to his mother, Maye, and Justine. Maye sometimes sat in on meetings and came up with the idea of adding a “reverse directions” button on the Zip2 maps, which let people flip around their journeys and ended up becoming a popular feature on all mapping services./ As a bonding exercise one weekend, Musk, Ambras, a few other employees and friends took off for a bike ride through the Saratoga Gap trail in the Santa Cruz Mountains. Most of the riders had been training and were accustomed to strenuous sessions and the summer’s heat. They set up the mountains at a furious pace. After an hour, Russ Rive, Musk’s cousin, reached the top and proceeded to vomit. Right behind him were the rest of the cyclists. Then, fifteen minutes later, Musk became visible to the group. His face had turned purple, and sweat poured out of him, and he made it to the top. “I always think back to that ride. He wasn’t close to being in the condition needed for it,” Ambras said. “Anyone else would have quit or walked up their bike. As I watched him climb that final hundred feet with suffering all over his face, I thought, That’s Elon. Do or die but don’t give up.” Musk continued to be a ball of energy around the office as well. Ahead of visits by venture capitalists and other investors, Musk would rally the troops and instruct them all to get on the phone to create a buzzy atmosphere. He also formed a video-game team to participate in competitions around Quake, a first-person-shooter game. “We competed in one of the first nationwide tournaments,” Musk said. “We came in second, and we would have come in first, but one of our top players’ machine crashed because he had pushed his graphics card too hard. We won a few thousand dollars.” Zip2 had remarkable success courting newspapers. The New York Times, Knight Ridder, Hearst Corporation, and other media properties signed up to its service. Some of these companies contributed $50 million in additional funding for Zip2. Services like Craigslist with its free online classifieds had just started to appear, and the newspapers needed some course of action. “The newspapers knew they were in trouble with the Internet, and the idea was to sign up as many of them as possible,” Ambras said. “They wanted classifieds and listings for real estate, automotive, and entertainment and could use us as a platform for all these online services.” Zip2 acquired a trademark for its “We Power the Press” slogan and the influx of cash kept Zip2 growing fast. Company headquarters were soon so crowded that one desk ended up directly in front of the women’s bathroom. In 1997, Zip2 moved into flashier, more spacious digs at 444 Castro Street in Mountain View. It irritated Musk that Zip2 had become a behind-the-scenes player to the newspapers. He believed the company could offer interesting services directly to consumers and encouraged the purchase of the domain name city.com with the hopes of turning it into a consumer destination. But the lure of the media companies’ money kept Sorkin and the board on a conservative path, and they decided to worry about a consumer push down the road. In April 1998, Zip2 announced a blockbuster move to double down on its strategy. It would merge with its main competitor CitySearch in a deal valued at around $300 million. The new company would retain the CitySearch name, while Sorkin would head up the venture. On paper, the union looked very much like a merger of equals. CitySearch had built up an extensive set of directories for cities around the country. It also appeared to have strong sales and marketing teams that would complement the talented engineers at Zip2. The merger had been announced in the press and seemed inevitable. The opinions on what happened next vary greatly. The logistics of the situation required the two companies to go over each other’s books and to figure out which employees would be fired to avoid a duplication of roles. This process raised some questions about how frank CitySearch had been with its financials and rankled some executives at Zip2 who could see their positions being diminished or erased altogether at the new company. One faction inside Zip2 argued that the deal should be abandoned, while Sorkin demanded that it go through. Musk, who had been an early advocate of the deal, turned against it. In May 1998, the two companies canceled the merger, and the press pounced, making a big deal of the chaotic bust-up. Musk urged Zip2’s board to oust Sorkin and reinstate him as CEO of Zip2. The board declined. Instead, Musk lost his chairman title, and Sorkin was replaced by Derek Proudian, a venture capitalist with Mohr Davidow. Sorkin considered Musk’s behavior through the whole affair atrocious and later pointed to the board’s reaction and Musk’s demotion as evidence that they felt the same way. “There was a lot of backlash and finger-pointing,” Proudian said. “Elon wanted to be CEO, but I said, ‘This is your first company. Let’s find an acquirer and make some money, so you can do your second, third, and fourth company.’” With the deal busted, Zip2 found itself in a predicament. It was losing money. Musk still wanted to go the consumer route, but Proudian feared that would take too much capital. Microsoft had mounted a charge into the same market, and start-ups with mapping, real estate, and automotive ideas multiplied. The Zip2 engineers were deflated and worried that they might not be able to outrun the competition. Then, in February 1999, the PC maker Compaq Computer suddenly offered to pay $307 million in cash for Zip2. “It was like pennies from heaven,” said Ed Ho, a former Zip2 executive. Zip2’s board accepted the offer, and the company rented out a restaurant in Palo Alto and threw a huge party. Mohr Davidow had made back twenty times its original investment, and Musk and Kimbal had come away with $22 million and $15 million, respectively. Musk never entertained the idea of sticking around at Compaq. “As soon as it was clear the company would be sold, Elon was on to his next project,” Proudian said. From that point on, Musk would fight to maintain control of his companies and stay CEO. “We were overwhelmed and just thought these guys must know what they’re doing,” Kimbal said. “But they’ didn’t. There was no vision once they took over. They were investors, and we got on well with them, but the vision had just disappeared from the company.” Years later, after he had time to reflect on the Zip2 situation, Musk realized that he could have handled some of the situations with employees better. “I had never really run a team of any sort before,” Musk said. “I’d never been a sports captain or a captain of anything or managed a single person. I had to think, Okay, what are the things that affect how a team functions. The first obvious assumption would be that other people will behave like you. But that’s not true. Even if they would like to behave like you, they don’t necessarily have all the assumptions or information that you have in your mind. So, if I know a certain set of things, and I talk to a replica of myself but only communicate half the information, you can’t expect that the replica would come to the same conclusion. You have to put yourself in a position where you say, ‘Well, how would this sound to them, knowing what they know?’” Employees at Zip2 would go home at night, come back, and find that Musk had changed their work without talking to them, and Musk’s confrontational style did more harm than good. “Yeah, we had some very good software engineers at Zip2, but I mean, I could code way better than them. And I’d just go in and fix their fucking code,” Musk said. “I would be frustrated waiting for their stuff, so I’m going to go and fix your code and now it runs five times faster, you idiot. There was one guy who wrote a quantum mechanics equation, a quantum probability on the board, and he got it wrong. I’m like, ‘How can you write that?’ Then I corrected it for him. He hated me after that. Eventually, I realized, Okay, I might have fixed that thing but now I’ve made the person unproductive. It just wasn’t a good way to go about things.” Musk, the dot-com striver, had been both lucky and good. He had a decent idea, turned it into a real service, and came out of the dot-com tumult with cash in his pockets, which was better than what many of his compatriots could say. The process had been painful. Musk had yearned to be a leader, but the people around him struggled to see how Musk as the CEO could work. As far as Musk was concerned, they were all wrong, and he set out to prove his point with what would end up being even more dramatic results.
PAYPAL MAFIA BOSS THE SALE OF ZIP2 INFUSED ELON MUSK WITH A NEW BRAND OF CONFIDENCE. Much like the video-game characters he adored, Musk had leveled up. He had solved Silicon Valley and become what everyone at the time wanted to be—a dot-com millionaire. His next venture would need to live up to his rapidly inflating ambition. This left Musk searching for an industry that had tons of money and inefficiencies that he and the Internet could exploit. Musk began thinking back to his time as an intern at the Bank of Nova Scotia. His big takeaway from that job, that bankers are rich and dumb, now had the feel of a massive opportunity. During his time working for the head of strategy at the bank in the early 1990s, Musk had been asked to take a look at the company’s third-world debt portfolio. This pool of money went by the depressing name of “less-developed country debt,” and Bank of Nova Scotia had billions of dollars of it. Countries throughout South America and elsewhere had defaulted in the years prior, forcing the bank to write down some of its debt value. Musk’s boss wanted him to dig into the bank’s holdings as a learning experiment and try to determine how much the debt was actually worth. While pursuing this project, Musk stumbled upon what seemed like an obvious business opportunity. The United States had tried to help reduce the debt burden of a number of developing countries through so-called Brady bonds, in which the U.S. government basically backstopped the debt of countries like Brazil and Argentina. Musk noticed an arbitrage play. “I calculated the backstop value, and it was something like fifty cents on the dollar, while the actual debt was trading at twenty-five cents,” Musk said. “This was like the biggest opportunity ever, and nobody seemed to realize it.” Musk tried to remain cool and calm as he rang Goldman Sachs, one of the main traders in this market, and probed around about what he had seen. He inquired as to how much Brazilian debt might be available at the 25-cents price. “The guy said, ‘How much do you want?’ and I came up with some ridiculous number like ten billion dollars,” Musk said. When the trader confirmed that was doable, Musk hung up the phone. “I was thinking that they had to be fucking crazy because you could double your money. Everything was backed by Uncle Sam. It was a no-brainer.” Musk had spent the summer earning about fourteen dollars an hour and getting chewed out for using the executive coffee machine, among other status infractions, and figured his moment to shine and make a big bonus had arrived. He sprinted up to his boss’s office and pitched the opportunity of a lifetime. “You can make billions of dollars for free,” he said. His boss told Musk to write up a report, which soon got passed up to the bank’s CEO, who promptly rejected the proposal, saying the bank had been burned on Brazilian and Argentinian debt before and didn’t want to mess with it again. “I tried to tell them that’s not the point,” Musk said. “The point is that it’s fucking backed by Uncle Sam. It doesn’t matter what the South Americans do. You cannot lose unless you think the U.S. Treasury is going to default. But they still didn’t do it, and I was stunned. Later in life, as I competed against the banks, I would think back to this moment, and it gave me confidence. All the bankers did was copy what everyone else did. If everyone else ran off a bloody cliff, they’d run right off a cliff with them. If there was a giant pile of gold sitting in the middle of the room and nobody was picking it up, they wouldn’t pick it up, either.” In the years that followed, Musk considered starting an Internet bank and discussed it openly during his internship at Pinnacle Research in 1995. The youthful Musk lectured the scientists about the inevitable transition coming in finance toward online systems, but they tried to talk him down, saying that it would takes ages for Web security to be good enough to win over consumers. Musk, though, remained convinced that the finance industry could do with a major upgrade and that he could have a big influence on banking with a relatively small investment. “Money is low bandwidth,” he said, during a speech at Stanford University in 2003, to describe his thinking. “You don’t need some sort of big infrastructure improvement to do things with it. It’s really just an entry in a database.” The actual plan that Musk concocted was beyond grandiose. As the researchers at Pinnacle had pointed out, people were barely comfortable buying books online. They might take their chances entering a credit card number but exposing just their bank accounts to the Web was out of the question to many. Pah. So what? Musk wanted to build a full-service financial institution online: a company that would have savings and checking accounts as well as brokerage services and insurance. The technology to build such a service was possible, but navigating the regulatory hell of creating an online bank from scratch looked like an intractable problem to optimists and an impossibility to more level heads. This was not dishing out directions to a pizzeria or putting up a house listing. It was dealing with people’s finances, and there would be real repercussions if the service did not work as billed. Undaunted, Musk kicked this new plan into action before Zip2 had even been sold. He chatted up some of the best engineers at the company to get a feel for who might be willing to join him in another venture. Musk also bounced his ideas off some contacts he’d made at the bank in Canada. In January 1999, with Zip2’s board seeking a buyer, Musk began to formalize his banking plan. The deal with Compaq was announced the next month. And in March, Musk incorporated X.com, a finance start-up with a pornographic-sounding name. It had taken Musk less than a decade to go from being a Canadian backpacker to becoming a multimillionaire at the age of twenty-seven. With his $22 million, he moved from sharing an apartment with three roommates to buying an 1,800-square-foot condo and renovating it. He also bought a $1 million McLaren F1 sports car and a small prop plane and learned to fly. Musk embraced the newfound celebrity that he’d earned as part of the dot-com millionaire set. He let CNN show up at his apartment at 7 A.M. to film the delivery of the car. A black eighteen-wheeler pulled up in front of Musk’s place and then lowered the sleek, sliver vehicle onto the street, while Musk stood slack-jawed with his arms folded. “There are sixty-two McLarens in the world, and I will own one of them,” he told CNN. “Wow, I can’t believe it’s actually here. That’s pretty wild, man.” CNN interspersed video of the car delivery with interviews with Musk. The whole time he looked like a caricature of an engineer who had made it big. Musk’s hair had started thinning, and he had a closely cropped cut that accentuated his boyish face. He wore an all-too-big brown sport coat and checked his cell phone from his lavish car, sitting next to his gorgeous girlfriend, Justine, and he seemed spellbound by his life. Musk rolled out one laughable rich-guy line after another, talking first about the Zip2 deal—“Receiving cash is cash. I mean, those are just a large number of Ben Franklins”—next about the awesomeness of his life—“There it is, gentlemen, the fastest car in the world”—and then about his prodigious ambition—“I could go and buy one of the islands in the Bahamas and turn it into my personal fiefdom, but I am much more interested in trying to build and create a new company.” The camera crew followed Musk to the X.com offices, where his cocksure delivery led to another round of cringe-worthy statements: “I do not fit the picture of a banker,” “Raising fifty million dollars is a matter of making a series of phone calls, and the money is there,” “I think X.com could absolutely be a multibillion-dollar bonanza.” Musk purchased the McLaren from a seller in Florida, snatching the car away from Ralph Lauren, who had also inquired about buying it. Even very wealthy people like Lauren would tend to reserve something like a McLaren for special events or the occasional Sunday drive. Not Musk. He drove it all around Silicon Valley and parked it on the street by the X.com offices. His friends were horrified to see such a work of art covered with bird droppings or in the parking lot of a Safeway. One day, Musk e-mailed fellow McLaren owner Larry Ellison, the billionaire cofounder of the software maker Oracle, out of the blue to see if he wanted to go race cars around a track for fun. Jim Clark, another billionaire who liked fast things, caught wind of the proposal and told a friend that he needed to rush over to the local Ferrari dealership to buy something that could compete. Musk had joined the big boys’ club. “Elon was super-excited about all of this,” said George Zachary, a venture capitalist and close friend of Musk’s. “He showed me the correspondence with Larry.” The next year, while driving down Sand Hill Road to meet with an investor, Musk turned to a friend in the car and said, “Watch this.” He floored the car, did a lane change, spun out, and hit an embankment, which started the car spinning in midair like a Frisbee. The windows and wheels were blown to smithereens, and the body of the car damaged. Musk again turned to his companion and said, “The funny part is it wasn’t insured.” The two of them then thumbed a ride to the venture capitalist’s office. To his credit, Musk did not fully buy in to this playboy persona. He actually plowed the majority of the money he made from Zip2 into X.com. There were practical reasons for this decision. Investors catch a break under the tax law if they roll a windfall into a new venture within a couple of months. But even by Silicon Valley’s high-risk standards, it was shocking to put so much of one’s newfound wealth into something as iffy as an online bank. All told, Musk invested about $12 million into X.com, leaving him, after taxes, with $4 million or so for personal use. “That’s part of what separates Elon from mere mortals,” said Ed Ho, the former Zip2 executive, who went on to cofound X.com. “He’s willing to take an insane amount of personal risk. When you do a deal like that, it either pays off or you end up in a bus shelter somewhere.” Musk’s decision to invest so much money in X.com looks even more unusual in hindsight. Much of the point of being a dot-com success in 1999 was to prove yourself once, stash away your millions, and then use your credentials to talk other people into betting their money on your next venture. Musk would certainly go on to rely on outside investors, but he put major skin in the game as well. So while Musk could be found on television talking like the rest of the self-absorbed dot-com schmucks, he behaved more like a throwback to Silicon Valley’s earlier days, when the founders of companies like Intel were willing to take huge gambles on themselves. Where Zip2 had been a neat, useful idea, X.com held the promise of fomenting a major revolution. Musk, for the first time, would be confronting a deep-pocketed, entrenched industry head-on with the hopes of upending all of the incumbents. Musk also began to hone his trademark style of entering an ultracomplex business and not letting the fact that he knew very little about the industry’s nuances bother him in the slightest. He had an inkling that the bankers were doing finance all wrong and that he could run the business better than everyone else. Musk’s ego and confidence had started heading toward the levels that would inspire some and leave others thinking of him as pompous and unscrupulous. The creation of X.com would ultimately reveal a great deal about Musk’s creativity, relentless drive, confrontational style, and foibles as a leader. Musk would also get another taste of being pushed aside at his own company and the pain that accompanies a grand vision left unfulfilled. Musk assembled what looked like an all-star crew to start X.com. Ho had worked at SGI and Zip2 as an engineer, and his peers marveled at his coding and team-management skills. They were joined by a pair of Canadians with finance experience—Harris Fricker and Christopher Payne. Musk had met Fricker during his time as an intern at the Bank of Nova Scotia, and the two really hit it off. A Rhodes scholar, Fricker brought the knowledge of the banking world’s mechanics that X.com would need. Payne was Fricker’s friend from the Canadian finance community. All four men were considered cofounders of the company, while Musk emerged as the largest shareholder thanks to his hefty up-front investment. X.com began, like so many Silicon Valley operations, at a house where the cofounders began brainstorming, and then moved to more formal offices at 394 University Avenue in Palo Alto. The cofounders were aligned philosophically around the idea that the banking industry had fallen behind the times. Visiting a branch bank to speak with a teller seemed pretty archaic now that the Internet had arrived. The rhetoric sounded good, and the four men were enthused. The only thing stopping them was reality. Musk had a modicum of banking experience and had resorted to buying a book on the industry to help understand its inner workings. The more the cofounders thought about their plan of attack, the more they realized the regulatory issues blocking the creation of an online bank were insurmountable. “As four and five months went by, the onion just kept unwrapping,” said Ho. /At one point, the founders thought the easiest way to solve their problems would just be to buy a bank and revamp it. While that didn’t happen, they did snag a high-profile controller from Bank of America, who in turn explained, in painful detail, the complexities of sourcing loans, transferring money, and protecting accounts./ From the outset, there were personality clashes as well. Musk had become a budding superstar in Silicon Valley and had the press fawning over him. This didn’t sit that well with Fricker, who’d moved from Canada and pegged X.com as his chance to make a mark on the world as a banking whiz. Fricker, according to numerous people, wanted to run X.com and do so in a more conventional manner. He found Musk’s visionary statements to the press about rethinking the entire banking industry silly since the company was struggling to build much of anything. “We were out promising the sun, moon, and the stars to the media,” Fricker said. “Elon would say that this is not a normal business environment, and you have to suspend normal business thinking. He said, ‘There is a happy-gas factory up on the hill, and it’s pumping stuff into the Valley.’” Fricker would not be the last person to accuse Musk of overhyping products and playing the public, although whether this is a flaw or one of Musk’s great talents as a businessman is up for debate. The squabble between Fricker and Musk came to a quick, nasty end. Just five months after X.com had started, Fricker initiated a coup. “He said either he takes over as CEO or he’s just going to take everyone from the company and create his own company,” Musk said. “I don’t do well with blackmail. I said, ‘You should go do that.’ So he did.” Musk tried to talk Ho and some of the other key engineers into staying, but they sided with Fricker and left. Musk ended up with a shell of a company and a handful of loyal employees. “After all that went down, I remember sitting with Elon in his office,” said Julie Ankenbrandt, an early X.com employee who stayed. “There were a million laws in place to block something like X.com from happening, but Elon didn’t care. He just looked at me and said, ‘I guess we should hire some more people.’” /Fricker disputed that he yearned to be CEO, saying instead that the other employees had encouraged him to take over because of Musk’s struggles getting the business off the ground. Fricker and Musk, once close friends, remain unimpressed with each other. “Elon has his own code of ethics and honor and plays the game extraordinarily hard,” Fricker said. “When it comes down to it, for him, business is war.” According to Musk, “Harris is very smart, but I don’t think he has a good heart. He had a really intense desire to be running the show, and he wanted to take the company in ridiculous directions.” Fricker went on to have a very successful career as CEO of GMP Capital, a Canadian financial services company. Payne founded a private equity firm in Toronto./ Musk had been trying to raise funding for X.com and had been forced to go to venture capitalists and confess that there wasn’t much in the way of a company left. Mike Moritz, a famed investor from Sequoia Capital, backed the company nonetheless, making a bet on Musk and little else. Musk hit the streets of Silicon Valley once again and managed to attract engineers with his rah-rah speeches about the future of Internet banking. Scott Anderson, a young computer scientist, started on August 1, 1999, just a few days after the exodus, and bought right into the vision. “You look back, and it was total insanity,” Anderson said. “We had what amounted to a Hollywood movie set of a website. It barely got past the VCs.” Week by week, more engineers arrived and the vision became more real. The company secured a banking license and a mutual fund license and formed a partnership with Barclays. By November, X.com’s small software team had created one of the world’s first online banks complete with FDIC insurance to back the bank accounts and three mutual funds for investors to choose. Musk gave the engineers $100,000 of his own money to conduct their testing. On the night before Thanksgiving in 1999, X.com went live to the public. “I was there until two A.M.,” Anderson said. “Then, I went home to cook Thanksgiving dinner. Elon called me a few hours later and asked me to come into the office to relieve some of the other engineers. Elon stayed there forty-eight straight hours, making sure things worked.” Under Musk’s direction, X.com tried out some radical banking concepts. Customers received a $20 cash card just for signing up to use the service and a $10 card for every person they referred. Musk did away with niggling fees and overdraft penalties. In a very modern twist, X.com also built a person-to-person payment system in which you could send someone money just by plugging their e-mail address into the site. The whole idea was to shift away from slow-moving banks with their mainframes taking days to process payments and to create a kind of agile bank account where you could move money around with a couple of clicks on a mouse or an e-mail. This was revolutionary stuff, and more than 200,000 people bought into it and signed up for X.com within the first couple of months of operation. Soon enough, X.com had a major competitor. A couple of brainy kids named Max Levchin and Peter Thiel had been working on a payment system of their own at their start-up called Confinity. The duo actually rented their office space—a glorified broom closet—from X.com and were trying to make it possible for owners of Palm Pilot handhelds to swap money via the infrared ports on the devices. Between X.com and Confinity, the small office on University Avenue had turned into the frenzied epicenter of the Internet finance revolution. “It was this mass of adolescent men that worked so hard,” Ankenbrandt said. “It stunk so badly in there. I can still smell it—leftover pizza, body odor, and sweat.” The pleasantries between X.com and Confinity came to an abrupt end. The Confinity founders moved to an office down the street and, like X.com, began focusing their attention on Web and e-mail-based payments with their service known as PayPal. The companies became locked in a heated battle to match each other’s features and attract more users, knowing that whoever got bigger faster would win. Tens of millions of dollars were spent on promotions, while millions more were lost battling hackers who had seized upon the services as new playgrounds for fraud. “It was like the Internet version of making it rain at a strip club,” said Jeremy Stoppelman, an X.com engineer who went on to become the CEO of Yelp. “You gave away money as fast as you could.” The race to win Internet payments gave Musk a chance to show off his quick thinking and work ethic. He kept devising plans to counter the advantage PayPal had established on auction sites like eBay. And he rallied the X.com employees to implement the tactics as fast as possible using brute-force appeals to their competitive natures. “There really wasn’t anything suave about him,” Ankenbrandt said. “We all worked twenty hours a day, and he worked twenty-three hours.” In March 2000, X.com and Confinity finally decided to stop trying to spend each other into oblivion and to join forces. Confinity had what looked like the hottest product in PayPal but was paying out $100,000 a day in awards to new customers and didn’t have the cash reserves to keep going. X.com, by contrast, still had plenty of cash reserves and the more sophisticated banking products. It took the lead in setting the merger terms, leaving Musk as the largest shareholder of the combined company, which would be called X.com. Shortly after the deal closed, X.com raised $100 million from backers including Deutsche Bank and Goldman Sachs and boasted that it had more than one million customers. /Musk had been pushed out as CEO of X.com by the company’s investors, who wanted a more seasoned executive to lead the company toward an IPO. In December 1999, X.com hired Bill Harris, the former CEO of the financial software maker Intuit, as its new chief. After the merger, many in the company turned on Harris, he resigned, and Musk returned as the CEO./ The two companies tried hard to mesh their cultures, with modest success. Groups of employees from X.com tied their computer monitors to their desk chairs with power cords and rolled them down the street to the Confinity offices to work alongside their new colleagues. But the teams could never quite see eye to eye. Musk kept championing the X.com brand, while most everyone else favored PayPal. More fights broke out over the design of the company’s technology infrastructure. The Confinity team led by Levchin favored moving toward open-source software like Linux, while Musk championed Microsoft’s data-center software as being more likely to keep productivity high. This squabble may sound silly to outsiders, but it was the equivalent of a religious war to the engineers, many of whom viewed Microsoft as a dated evil empire and Linux as the modern software of the people. Two months after the merger, Thiel resigned and Levchin threatened to walk out over the technology rift. Musk was left to run a fractured company. The technology issues X.com had been facing worsened as the computing systems failed to keep up with an exploding customer base. Once a week, the company’s website collapsed. Most of the engineers were ordered to start work designing a new system, which distracted key technical personnel and left X.com vulnerable to fraud. “We were losing money hand over fist,” said Stoppelman. As X.com became more popular and its transaction volume exploded, all of its problems worsened. There was more fraud. There were more fees from banks and credit card companies. There was more competition from start-ups. X.com lacked a cohesive business model to offset the losses and turn a profit from the money it managed. Roelof Botha, the start-up’s chief financial officer and now a prominent venture capitalist at Sequoia, did not think Musk provided the board with a true picture of X.com’s issues. A growing number of other people at the company questioned Musk’s decision-making in the face of all the crises. What followed was one of the nastiest coups in Silicon Valley’s long, illustrious history of nasty coups. A small group of X.com employees gathered one night at Fanny & Alexander, a now-defunct bar in Palo Alto, and brainstormed about how to push out Musk. They decided to sell the board on the idea of Thiel returning as CEO. Instead of confronting Musk directly with this plan, the conspirators decided to take action behind Musk’s back. Musk and Justine had been married in January 2000 but had been too busy for a honeymoon. Nine months later, in September, they planned to mix business and pleasure by going on a fund-raising trip and ending it with a honeymoon in Sydney to catch the Olympics. As they boarded their flight one night, X.com executives delivered letters of no confidence to X.com’s board. Some of the people loyal to Musk had sensed something was wrong, but it was too late. “I went to the office at ten thirty that night, and everyone was there,” Ankenbrandt said. “I could not believe it. I am frantically trying to call Elon, but he’s on a plane.” By the time he landed, Musk had been replaced by Thiel. When Musk finally heard what had happened, he hopped on the next plane back to Palo Alto. “It was shocking, but I will give Elon this—I thought he handled it pretty well,” Justine said. For a brief period, Musk tried to fight back. He urged the board to reconsider its decision. But when it became clear that the company had already moved on, Musk relented. “I talked to Moritz and a few others,” Musk said. “It wasn’t so much that I wanted to be CEO but more like, ‘Hey, I think there are some pretty important things that need to happen, and if I’m not CEO, I’m not sure they are going to happen.’ But then I talked to Max and Peter, and it seemed like they would make these things happen. So then, I mean, it’s not the end of the world.” Many of the X.com employees who had been with Musk since early on were less than impressed by what had happened. “I was floored by it and angry,” said Stoppelman. “Elon was sort of a rock star in my view. I was very vocal about how I thought it was bullshit. But I knew fundamentally that the company was doing well. It was a rocket ship, and I wasn’t going to leave.” Stoppelman, then twenty-three, went into a conference room and tore into Thiel and Levchin. “They let me vent it all out, and their reaction was part of the reason I stayed.” Others remained embittered. “It was backhanded and cowardly,” said Branden Spikes, a Zip2 and X.com engineer. “I would have been more behind it if Elon had been in the room.” By June 2001, Musk’s influence on the company was fading quickly. That month, Thiel rebranded X.com as PayPal. Musk rarely lets a slight go unpunished. Throughout this ordeal, however, he showed incredible restraint. He embraced the role of being an advisor to the company and kept investing in it, increasing his stake as PayPal’s largest shareholder. “You would expect someone in Elon’s position to be bitter and vindictive, but he wasn’t,” said Botha. “He supported Peter. He was a prince.” The next few months would end up being key for Musk’s future. The dot-com joyride was coming to a quick end, and people wanted to try to cash out in any way possible. When executives from eBay began approaching PayPal about an acquisition, the inclination for most people was to sell and sell fast. Musk and Moritz, though, urged the board to reject a number of offers and hold out for more money. PayPal had revenue of about $240 million per year, and looked like it might make it as an independent company and go public. Musk and Moritz’s resistance paid off and then some. In July 2002, eBay offered $1.5 billion for PayPal, and Musk and the rest of the board accepted the deal. Musk netted about $250 million from the sale to eBay, or $180 million after taxes—enough to make what would turn out to be his very wild dreams possible. The PayPal episode was a mixed bag for Musk. His reputation as a leader suffered in the aftermath of the deal, and the media turned on him in earnest for the first time. Eric Jackson, an early Confinity employee, wrote The PayPal Wars: Battles with eBay, the Media, the Mafia, and the Rest of Planet Earth in 2004 and recounted the company’s tumultuous journey. The book painted Musk as an egomaniacal, stubborn jerk, making wrong decisions at every turn, and portrayed Thiel and Levchin as heroic geniuses. Valleywag, the technology industry gossip site, piled on as well and turned bashing Musk into one of its pet projects. The criticisms grew to the point that people started wondering aloud whether or not Musk counted as a true cofounder of PayPal or had just ridden Thiel’s coattails to a magical payday. The tone of the book along with the blog posts goaded Musk in 2007 into writing a 2,200-word e-mail to Valleywag meant to set the record straight with his version of events. In the e-mail, Musk let his literary flair loose and gave the public a direct look at his combative side. He described Jackson as “a sycophantic jackass” and “one notch above an intern,” who had little insight into the high-level goings-on at the company. “Since Eric worships Peter, the outcome was obvious—Peter sounds like Mel Gibson in Braveheart and my role is somewhere between negligible and a bad seed,” Musk wrote. Musk then detailed seven reasons why he deserved cofounder status of PayPal, including his role as its largest shareholder, the hiring of a lot of the top talent, the creation of a number of the company’s most successful business ideas, and his time as CEO when the company went from sixty to several hundred employees. Almost everyone I interviewed from the PayPal days leaned toward agreeing with Musk’s overall assessment. They said that Jackson’s account bordered on fantasy when it came to celebrating the Confinity team over Musk and the X.com team. “There are a lot of PayPal people that suffer from warped memories,” said Botha. But these same people reached another consensus, saying that Musk had mishandled the branding, technology infrastructure, and fraud situations. “I think it would have killed the company if Elon had stayed on as CEO for six more months,” said Botha. “The mistakes Elon was making at the time were amplifying the risk of the business.” (For more on Musk’s take on the PayPal years, see Appendix 2.) The suggestions that Musk did not count as a “true” cofounder of PayPal seem asinine in retrospect. Thiel, Levchin, and other PayPal executives have said as much in the years since the eBay deal closed. The only useful thing such criticisms produced were the bombastic counteroffensives from Musk, which revealed touches of insecurity and the seriousness with which Musk insists that the historical record reflect his take on events. “He comes from the school of thought in the public relations world that you let no inaccuracy go uncorrected,” said Vince Sollitto, the former communications chief at PayPal. “It sets a precedent, and you should fight every out-of-place comma tooth and nail. He takes things very personally and usually seeks war.” The stronger critique of Musk during this period of his life was that he had succeeded to a large degree despite himself. Musk’s traits as a confrontational know-it-all and his abundant ego created deep, lasting fractures within his companies. While Musk consciously tried to temper his behavior, these efforts were not enough to win over investors and more experienced executives. At both Zip2 and PayPal, the companies’ boards came to the conclusion that Musk was not yet CEO material. It can also be argued that Musk had become a hyperbolic huckster, who overreached and oversold his companies’ technology. Musk’s biggest detractors have made all of these arguments either in public or private and a half dozen or so of them said far worse things to me about his character and actions, describing Musk as unethical in business and vicious with his personal attacks. Almost universally, these people were unwilling to go on the record with their comments, claiming to be afraid Musk would pursue litigation against them or ruin their ability to do business. These criticisms must be weighed against Musk’s track record. He demonstrated an innate ability to read people and technology trends at the inception of the consumer Web. While others tried to wrap their heads around the Internet’s implications, Musk had already set off on a purposeful plan of attack. He envisioned many of the early pieces of technology—directories, maps, sites that focused on vertical markets—that would become mainstays on the Web. Then, just as people became comfortable with buying things from Amazon.com and eBay, Musk made the great leap forward to full-fledged Internet banking. He would bring standard financial instruments online and then modernize the industry with a host of new concepts. He exhibited a deep insight into human nature that helped his companies pull off exceptional marketing, technology, and financial feats. Musk was already playing the entrepreneur game at the highest level and working the press and investors like few others could. Did he hype things up and rub people the wrong way? Absolutely—and with spectacular results. Based in large part on Musk’s guidance, PayPal survived the bursting of the dot-com bubble, became the first blockbuster IPO after the 9/11 attacks, and then sold to eBay for an astronomical sum while the rest of the technology industry was mired in a dramatic downturn. It was nearly impossible to survive let alone emerge as a winner in the midst of such a mess. PayPal also came to represent one of the greatest assemblages of business and engineering talent in Silicon Valley history. Both Musk and Thiel had a keen eye for young, brilliant engineers. The founders of start-ups as varied as YouTube, Palantir Technologies, and Yelp all worked at PayPal. Another set of people—including Reid Hoffman, Thiel, and Botha—emerged as some of the technology industry’s top investors. PayPal staff pioneered techniques in fighting online fraud that have formed the basis of software used by the CIA and FBI to track terrorists and of software used by the world’s largest banks to combat crime. This collection of super-bright employees has become known as the PayPal Mafia—more or less the current ruling class of Silicon Valley—and Musk is its most famous and successful member. Hindsight also continues to favor Musk’s unbridled vision over the more cautious pragmatism of executives at Zip2 and PayPal. Had it chased consumers as Musk urged, Zip2 may have ended up as a blockbuster mapping and review service. As for PayPal, an argument can still be made that the investors sold out too early and should have listened more to Musk’s demands to remain independent. By 2014, PayPal had amassed 153 million users and was valued at close to $32 billion as a stand-alone company. A flood of payment and banking start-ups have appeared as well—Square, Stripe, and Simple, to name three among the S’s—that have looked to fulfill much of the original X.com vision. If X.com’s board had been a bit more patient with Musk, there’s good reason to believe he would have succeeded with delivery of the “online bank to rule them all” that he had set out to create. History has demonstrated that while Musk’s goals can sound absurd in the moment, he certainly believes in them and, when given enough time, tends to achieve them. “He always works from a different understanding of reality than the rest of us,” Ankenbrandt said. “He is just different than the rest of us.” While navigating the business tumult of Zip2 and PayPal, Musk found a moment of peace in his personal life. He’d spent years courting Justine Wilson from afar, flying her out for visits on the weekends. For a long time, his oppressive hours and his roommates put a crimp on the relationship. But the Zip2 sale let Musk buy a place of his own and pay a bit more attention to Justine. Like any couple, they had their ups and downs, but that passion of young love remained. “We fought a lot, but when we weren’t fighting, there was a deep sense of compassion—a bond,” Justine said. The couple had been sparring for a few days about phone calls Justine kept getting from an ex-boyfriend—“Elon didn’t like that”—and had a major spat while walking near the X.com offices. “I remember thinking it was a lot of drama, and that if I was going to put up with it, we might as well be married. I told him he should just propose to me,” Justine said. It took Musk a few minutes to cool down and then he did just that, proposing on the spot. A few days later, a more chivalrous Musk returned to the sidewalk, got down on bended knee, and presented Justine with a ring. Justine knew all about Musk’s grim childhood and the intense range of emotions he could exhibit. Her romantic sensibilities overrode any trepidation she might have had about these parts of Musk’s history and character and centered instead on his strength. Musk often talked fondly about Alexander the Great, and Justine saw him as her own conquering hero. “He wasn’t afraid of responsibility,” she said. “He didn’t run from things. He wanted to get married and have kids early on.” Musk also exuded a confidence and passion that made Justine think life with him would always be okay. “Money is not his motivation, and, quite frankly, I think it just happens for him,” Justine said. “It’s just there. He knows he can generate it.” At their wedding reception, Justine encountered the other side of the conquering hero. Musk pulled Justine close while they danced, and informed her, “I am the alpha in this relationship.” [http://www.marieclaire.com/sex-love/relationship-issues/millionaire-starter-wife] Two months later, Justine signed a postnuptial financial agreement that would come back to haunt her and entered into an enduring power struggle. She described the situation years later in an article for Marie Claire, writing, “He was constantly remarking on the ways he found me lacking. ‘I am your wife,’ I told him repeatedly, ‘not your employee.’ ‘If you were my employee,’ he said just as often, ‘I would fire you.’” The newlyweds were not helped by the drama at X.com. They’d put off their honeymoon and then had it derailed by the coup. It took until late December 2000 for things to calm down enough for Musk to take his first vacation in years. He arranged a two-week trip, with the first part taking place in Brazil and the second in South Africa at a game reserve near the Mozambique border. While in Africa, Musk contracted the most virulent version of malaria—falciparum malaria—which accounts for the vast majority of malaria deaths. Musk returned to California in January, which is when the illness took hold. He started to get sick and was bedridden for a few days before Justine took him to a doctor who then ordered that Musk be rushed in an ambulance to Sequoia Hospital in Redwood City. /After feeling ill for a few days, Musk went to Stanford Hospital and informed them that he’d been in a malaria zone, although the doctors could not find the parasite during tests. The doctors performed a spinal tap and diagnosed him with viral meningitis. “I may very well have also had that, and they treated me for it, and it did get better,” Musk said. The doctors discharged Musk from the hospital and warned him that some symptoms would recur. “I started feeling bad a few days later, and it got progressively worse,” Musk said. “Eventually, I couldn’t walk. It was like, ‘Okay, this is even worse than the first time.’” Justine took Musk to a general practitioner in a cab, and he lay on the floor of the doctor’s office. “I was so dehydrated that she couldn’t take my vitals,” Musk said. The doctor called an ambulance, which transported Musk to Sequoia Hospital in Redwood City with IVs in both arms. Musk faced another misdiagnosis—this time of the type of malaria. The doctors declined to give Musk a more aggressive treatment that came with nasty side effects including heart palpitations and organ failure./ Doctors there misdiagnosed and mistreated his condition to the point that Musk was near death. “Then, there happened to be a guy visiting from another hospital who had seen a lot more malaria cases,” Musk said. He spied Musk’s blood work in the lab and ordered an immediate maximum dosage of doxycycline, an antibiotic. The doctor told Musk that if he had turned up a day later, the medicine likely would no longer have been effective. Musk spent ten agonizing days in the intensive care unit. The experience shocked Justine. “He’s built like a tank,” she said. “He has a level of stamina and an ability to deal with levels of stress that I’ve never seen in anyone else. To see him laid low like that in total misery was like a visit to an alternate universe.” It took Musk six months to recover. He lost forty-five pounds over the course of the illness and had a closet full of clothes that no longer fit. “I came very close to dying,” Musk said. “That’s my lesson for taking a vacation: vacations will kill you.”
MICE IN SPACE ELON MUSK TURNED THIRTY IN JUNE 2001, and the birthday hit him hard. “I’m no longer a child prodigy,” he told Justine, only half joking. That same month X.com officially changed its name to PayPal, providing a harsh reminder that the company had been ripped away from Musk and given to someone else to run. The start-up life, which Musk described as akin to “eating glass and staring into the abyss,” [The investor Bill Lee, one of Musk’s close friends, originated this phrase.] had gotten old and so had Silicon Valley. It felt like Musk was living inside a trade show where everyone worked in the technology industry and talked all the time about funding, IPOs, and chasing big paydays. People liked to brag about the crazy hours they worked, and Justine would just laugh, knowing Musk had lived a more extreme version of the Silicon Valley lifestyle than they could imagine. “I had friends who complained that their husbands came home at seven or eight,” she said. “Elon would come home at eleven and work some more. People didn’t always get the sacrifice he made in order to be where he was.” The idea of escaping this incredibly lucrative rat race started to grow more and more appealing. Musk’s entire life had been about chasing a bigger stage, and Palo Alto seemed more like a stepping-stone than a final destination. The couple decided to move south and begin their family and the next chapter of their lives in Los Angeles. “There’s an element to him that likes the style and the excitement and color of a place like L.A.,” said Justine. “Elon likes to be where the action is.” A small group of Musk’s friends who felt similarly had also decamped to Los Angeles for what would be a wild couple of years. It wasn’t just Los Angeles’s glitz and grandeur that attracted Musk. It was also the call of space. After being pushed out of PayPal, Musk had started to revisit his childhood fantasies around rocket ships and space travel and to think that he might have a greater calling than creating Internet services. The changes in his attitude and thinking soon became obvious to his friends, including a group of PayPal executives who had gathered in Las Vegas one weekend to celebrate the company’s success. “We’re all hanging out in this cabana at the Hard Rock Cafe, and Elon is there reading some obscure Soviet rocket manual that was all moldy and looked like it had been bought on eBay,” said Kevin Hartz, an early PayPal investor. “He was studying it and talking openly about space travel and changing the world.” Musk had picked Los Angeles with intent. It gave him access to space or at least the space industry. Southern California’s mild, consistent weather had made it a favored city of the aeronautics industry since the 1920s, when the Lockheed Aircraft Company set up shop in Hollywood. Howard Hughes, the U.S. Air Force, NASA, Boeing, and myriad other people and organizations have performed much of their manufacturing and cutting-edge experimentation in and around Los Angeles. Today the city remains a major hub for the military’s aeronautics work and commercial activity. While Musk didn’t know exactly what he wanted to do in space, he realized that just by being in Los Angeles he would be surrounded by the world’s top aeronautics thinkers. They could help him refine any ideas, and there would be plenty of recruits to join his next venture. Musk’s first interactions with the aeronautics community were with an eclectic collection of space enthusiasts, members of a nonprofit group called the Mars Society. Dedicated to exploring and settling the Red Planet, the Mars Society planned to hold a fund-raiser in mid-2001. The $500-per-plate event was to take place at the house of one of the well-off Mars Society members, and invitations to the usual characters had been mailed out. What stunned Robert Zubrin, the head of the group, was the reply from someone named Elon Musk, whom no one could remember inviting. “He gave us a check for five thousand dollars,” Zubrin said. “That made everyone take notice.” Zubrin began researching Musk, determined he was rich, and invited him for coffee ahead of the dinner. “I wanted to make sure he knew the projects we had under way,” Zubrin said. He proceeded to regale Musk with tales of the research center the society had built in the Arctic to mimic the tough conditions of Mars and the experiments they had been running for something called the Translife Mission, in which there would be a spinning capsule orbiting Earth that was piloted by a crew of mice. “It would spin to give them one-third gravity—the same you would have on Mars—and they would live there and reproduce,” Zubrin told Musk. When it was time for dinner, Zubrin placed Musk at the VIP table next to himself, the director and space buff James Cameron, and Carol Stoker, a planetary scientist for NASA with a deep interest in Mars. “Elon is so youthful-looking and at that time he looked like a little boy,” Stoker said. “Cameron was chatting him up right away to invest in his next movie, and Zubrin was trying to get him to make a big donation to the Mars Society.” In return for being hounded for cash, Musk probed about for ideas and contacts. Stoker’s husband was an aerospace engineer at NASA working on a concept for an airplane that would glide over Mars looking for water. Musk loved that. “He was much more intense than some of the other millionaires,” Zubrin said. “He didn’t know a lot about space, but he had a scientific mind. He wanted to know exactly what was being planned in regards to Mars and what the significance would be.” Musk took to the Mars Society right away and joined its board of directors. He donated another $100,000 to fund a research station in the desert as well. Musk’s friends were not entirely sure what to make of his mental state. He’d lost a tremendous amount of weight fighting off malaria and looked almost skeletal. With little prompting, Musk would start expounding on his desire to do something meaningful with his life—something lasting. His next move had to be either in solar or in space. “He said, ‘The logical thing to happen next is solar, but I can’t figure out how to make any money out of it,’” said George Zachary, the investor and close friend of Musk’s, recalling a lunch date at the time. “Then he started talking about space, and I thought he meant office space like a real estate play.” Musk had actually started thinking bigger than the Mars Society. Rather than send a few mice into Earth’s orbit, Musk wanted to send them to Mars. Some very rough calculations done at the time suggested that the journey would cost $15 million. “He asked if I thought that was crazy,” Zachary said. “I asked, ‘Do the mice come back? Because, if they don’t, yeah, most people will think that’s crazy.’” As it turned out, the mice were not only meant to go to Mars and come back but were also meant to procreate along the way, during a journey that would take months. Jeff Skoll, another one of Musk’s friends who made a fortune at eBay, pointed out that the fornicating mice would need a hell of a lot of cheese and bought Musk a giant wheel of Le Brouère, a type of Gruyère. Musk did not mind becoming the butt of cheese jokes. The more he thought about space, the more important its exploration seemed to him. He felt as if the public had lost some of its ambition and hope for the future. The average person might see space exploration as a waste of time and effort and rib him for talking about the subject, but Musk thought about interplanetary travel in a very earnest way. He wanted to inspire the masses and reinvigorate their passion for science, conquest, and the promise of technology. His fears that mankind had lost much of its will to push the boundaries were reinforced one day when Musk went to the NASA website. He’d expected to find a detailed plan for exploring Mars and instead found bupkis. “At first I thought, jeez, maybe I’m just looking in the wrong place,” Musk once told Wired. “Why was there no plan, no schedule? There was nothing. It seemed crazy.” Musk believed that the very idea of America was intertwined with humanity’s desire to explore. He found it sad that the American agency tasked with doing audacious things in space and exploring new frontiers as its mission seemed to have no serious interest in investigating Mars at all. The spirit of Manifest Destiny had been deflated or maybe even come to a depressing end, and hardly anyone seemed to care. Like so many quests to revitalize America’s soul and bring hope to all of mankind, Musk’s journey began in a hotel conference room. By this time, Musk had built up a decent network of contacts in the space industry, and he brought the best of them together at a series of salons—sometimes at the Renaissance hotel at the Los Angeles airport and sometimes at the Sheraton hotel in Palo Alto. Musk had no formal business plan for these people to debate. He mostly wanted them to help him develop the mice-to-Mars idea or at least to come up with something comparable. Musk hoped to hit on a grand gesture for mankind—some type of event that would capture the world’s attention, get people thinking about Mars again, and have them reflect on man’s potential. The scientists and luminaries at the meetings were to figure out a spectacle that would be technically feasible at a price tag of approximately $20 million. Musk resigned from his position as a director of the Mars Society and announced his own organization—the Life to Mars Foundation. The collection of talent attending these sessions in 2001 was impressive. Scientists showed up from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, or JPL. James Cameron appeared, lending some celebrity to the affair. Also attending was Michael Griffin, whose academic credentials were spectacular and included degrees in aerospace engineering, electrical engineering, civil engineering, and applied physics. Griffin had worked for the CIA’s venture capital arm called In-Q-Tel, at NASA, and at JPL and was just in the process of leaving Orbital Sciences Corporation, a maker of satellites and spacecraft, where he had been chief technical officer and the general manager of the space systems group. It could be argued that no one on the planet knew more about the realities of getting things into space than Griffin, and he was working for Musk as space thinker in chief. (Four years later, in 2005, Griffin took over as head of NASA.) The experts were thrilled to have another rich guy appear who was willing to fund something interesting in space. They happily debated the merits and feasibility of sending up rodents and watching them hump. But, as the discussion wore on, a consensus started to build around pursuing a different project—something called “Mars Oasis.” Under this plan, Musk would buy a rocket and use it to shoot what amounted to a robotic greenhouse to Mars. A group of researchers had already been working on a space-ready growth chamber for plants. The idea was to modify their structure, so that it could open up briefly and suck in some of the Martian regolith, or soil, and then use it to grow a plant, which would in turn produce the first oxygen on Mars. Much to Musk’s liking, this new plan seemed both ostentatious and feasible. Musk wanted the structure to have a window and a way to send a video feedback to Earth, so that people could watch the plant grow. The group also talked about sending out kits to students around the country who would grow their own plants simultaneously and take notice, for example, that the Martian plant could grow twice as high as its Earth-bound counterpart in the same amount of time. “This concept had been floating around in various forms for a while,” said Dave Bearden, a space industry veteran who attended the meetings. “It would be, yes, there is life on Mars, and we put it there. The hope was that it might turn on a light for thousands of kids that this place is not that hostile. Then they might start thinking, Maybe we should go there.” Musk’s enthusiasm for the idea started to inspire the group, many of whom had grown cynical about anything novel happening in space again. “He’s a very smart, very driven guy with a huge ego,” Bearden said. “At one point someone mentioned that he might become Time magazine’s Man of the Year, and you could see him light up. He has this belief that he is the guy who can change the world.” The main thing troubling the space experts was Musk’s budget. Following the salons, it seemed like Musk wanted to spend somewhere between $20 million and $30 million on the stunt, and everyone knew that the cost of a rocket launch alone would eat up that money and then some. “In my mind, you needed two hundred million dollars to do it right,” Bearden said. “But people were reluctant to bring too much reality into the situation too early and just get the whole idea killed.” Then there were the immense engineering challenges that would need solving. “To have a big window on this thing was a real thermal problem,” Bearden said. “You could not keep the container warm enough to keep anything alive.” Scooping Martian soil into the structure seemed not only hard to do physically but also like a flat-out bad idea since the regolith would be toxic. For a while, the scientists debated growing the plant in a nutrient-rich gel instead, but that felt like cheating and like it might undermine the whole point of the endeavor. Even the optimistic moments were awash in unknowns. One scientist found some very resilient mustard seeds and thought they could possibly survive a treated version of the Martian soil. “There was a pretty big downside if the plant didn’t survive,” Bearden said. “You have this dead garden on Mars that ends up giving off the opposite of the intended effect.” /When Zubrin and some of the other Mars buffs heard of Musk’s plant project, they were upset. “It didn’t make any sense,” Zubrin said. “It was a purely symbolic thing to do, and the second they opened that door, millions of microbes would escape and plague all of NASA’s contamination protocols.”/ Musk never flinched. He turned some of the volunteer thinkers into consultants, and put them to work on the plant machine’s design. He also plotted a trip to Russia to find out exactly how much a launch would cost. Musk intended to buy a refurbished intercontinental ballistic missile, or ICBM, from the Russians and use that as his launch vehicle. For help with this, Musk reached out to Jim Cantrell, an unusual fellow who had done a mix of classified and unclassified work for the United States and other governments. Among other claims to fame, Cantrell had been accused of espionage and placed under house arrest in 1996 by the Russians after a satellite deal went awry. “After a couple of weeks, Al Gore made some calls, and it got worked out,” Cantrell said. “I didn’t want anything to do with the Russians again—ever.” Musk had other ideas. Cantrell was driving his convertible on a hot July evening in Utah when a call came in. “This guy in a funny accent said, ‘I really need to talk to you. I am a billionaire. I am going to start a space program.’” Cantrell could not hear Musk well—he thought his name was Ian Musk—and said he would call back once he got home. The two men didn’t exactly trust each other at the outset. Musk refused to give Cantrell his cell phone number and made the call from his fax machine. Cantrell found Musk both intriguing and all too eager. “He asked if there was an airport near me and if I could meet the next day,” Cantrell said. “My red flags started going off.” Fearing one of his enemies was trying to orchestrate an elaborate setup, Cantrell told Musk to meet him at the Salt Lake City airport, where he would rent a conference room near the Delta lounge. “I wanted him to meet me behind security so he couldn’t pack a gun,” Cantrell said. When the meeting finally took place, Musk and Cantrell hit it off. Musk rolled out his “humans need to become a multiplanetary species” speech, and Cantrell said that if Musk was really serious, he’d be willing to go to Russia—again—and help buy a rocket. In late October 2001, Musk, Cantrell, and Adeo Ressi, Musk’s friend from college, boarded a commercial flight to Moscow. Ressi had been playing the role of Musk’s guardian and trying to ascertain whether his best friend had started to lose his mind. Compilation videos of rockets exploding were made, and interventions were held with Musk’s friends trying to talk him out of wasting his money. While these measures failed, Adeo went along to Russia to try to contain Musk as best as he could. “Adeo would call me to the side and say, ‘What Elon is doing is insane. A philanthropic gesture? That’s crazy,’” Cantrell said. “He was seriously worried but was down with the trip.” And why not? The men were heading to Russia at the height of its freewheeling post-Soviet days when rich guys could apparently buy space missiles on the open market. Team Musk would grow to include Mike Griffin, and meet with the Russians three times over a period of four months. /Most of the stories written about Musk that touch on this period say he went to Moscow three times. According to Cantrell’s detailed records, this is not the case. Musk met with the Russians twice in Moscow, and once in Pasadena, California. He also met with Arianespace in Paris, and in London with Surrey Satellite Technology Ltd., which Musk considered buying./ The group set up a few meetings with companies like NPO Lavochkin, which had made probes intended for Mars and Venus for the Russian Federal Space Agency, and Kosmotras, a commercial rocket launcher. The appointments all seemed to go the same way, following Russian decorum. The Russians, who often skip breakfast, would ask to meet around 11 A.M. at their offices for an early lunch. Then there would be small talk for an hour or more as the meeting attendees picked over a spread of sandwiches, sausages, and, of course, vodka. At some point during this process, Griffin usually started to lose his patience. “He suffers fools very poorly,” Cantrell said. “He’s looking around and wondering when we’re going to get down to fucking business.” The answer was not soon. After lunch came a lengthy smoking and coffee-drinking period. Once all of the tables were cleared, the Russian in charge would turn to Musk and ask, “What is it you’re interested in buying?” The big windup may not have bothered Musk as much if the Russians had taken him more seriously. “They looked at us like we were not credible people,” Cantrell said. “One of their chief designers spit on me and Elon because he thought we were full of shit.” The most intense meeting occurred in an ornate, neglected, prerevolutionary building near downtown Moscow. The vodka shots started—“To space!” “To America!”—while Musk sat on $20 million, which he hoped would be enough to buy three ICBMs that could be retooled to go to space. Buzzed from the vodka, Musk asked point-blank how much a missile would cost. The reply: $8 million each. Musk countered, offering $8 million for two. “They sat there and looked at him,” Cantrell said. “And said something like, ‘Young boy. No.’ They also intimated that he didn’t have the money.” At this point, Musk had decided the Russians were either not serious about doing business or determined to part a dot-com millionaire from as much of his money as possible. He stormed out of the meeting. The Team Musk mood could not have been worse. It was near the end of February 2002, and they went outside to hail a cab and drove straight to the airport surrounded by the snow and dreck of the Moscow winter. Inside the cab, no one talked. Musk had come to Russia filled with optimism about putting on a great show for mankind and was now leaving exasperated and disappointed by human nature. The Russians were the only ones with rockets that could possibly fit within Musk’s budget. “It was a long drive,” Cantrell said. “We sat there in silence looking at the Russian peasants shopping in the snow.” The somber mood lingered all the way to the plane, until the drink cart arrived. “You always feel particularly good when the wheels lift off in Moscow,” Cantrell said. “It’s like, ‘My God. I made it.’ So, Griffin and I got drinks and clinked our glasses.” Musk sat in the row in front of them, typing on his computer. “We’re thinking, Fucking nerd. What can he be doing now?” At which point Musk wheeled around and flashed a spreadsheet he’d created. “Hey, guys,” he said, “I think we can build this rocket ourselves.” Griffin and Cantrell had downed a couple of drinks by this time and were too deflated to entertain a fantasy. They knew all too well the stories of gung-ho millionaires who thought they could conquer space only to lose their fortunes. Just the year before, Andrew Beal, a real estate and finance whiz in Texas, folded his aerospace company after having poured millions into a massive test site. “We’re thinking, Yeah, you and whose fucking army,” Cantrell said. “But, Elon says, ‘No, I’m serious. I have this spreadsheet.’” Musk passed his laptop over to Griffin and Cantrell, and they were dumbfounded. The document detailed the costs of the materials needed to build, assemble, and launch a rocket. According to Musk’s calculations, he could undercut existing launch companies by building a modest-sized rocket that would cater to a part of the market that specialized in carrying smaller satellites and research payloads to space. The spreadsheet also laid out the hypothetical performance characteristics of the rocket in fairly impressive detail. “I said, ‘Elon, where did you get this?’” Cantrell said. Musk had spent months studying the aerospace industry and the physics behind it. From Cantrell and others, he’d borrowed Rocket Propulsion Elements, Fundamentals of Astrodynamics, and Aerothermodynamics of Gas Turbine and Rocket Propulsion, along with several more seminal texts. Musk had reverted to his childhood state as a devourer of information and had emerged from this meditative process with the realization that rockets could and should be made much cheaper than what the Russians were offering. Forget the mice. Forget the plant with its own video feed growing—or possibly dying—on Mars. Musk would inspire people to think about exploring space again by making it cheaper to explore space. As word traveled around the space community about Musk’s plans, there was a collective ho-hum. People like Zubrin had seen this show many times before. “There was a string of zillionaires that got sold a good story by an engineer,” Zubrin said. “Combine my brains and your money, and we can build a rocket ship that will be profitable and open up the space frontier. The techies usually ended up spending the rich guy’s money for two years, and then the rich guy gets bored and shuts the thing down. With Elon, everyone gave a sigh and said, ‘Oh well. He could have spent ten million dollars to send up the mice, but instead he’ll spend hundreds of millions and probably fail like all the others that proceeded him.’” While well aware of the risks tied to starting a rocket company, Musk had at least one reason to think he might succeed where others had failed. That reason’s name was Tom Mueller. Mueller grew up the son of a logger in the tidy Idaho town of St. Maries, where he developed a reputation as an oddball. While the rest of the kids were outside exploring the woods in winter, Mueller stayed warm in the library reading books or watching Star Trek at his house. He also tinkered. Walking to grade school one day, Mueller discovered a smashed clock in an alley and turned it into a pet project. Each day, he fixed some part of the clock—a gear, a spring—until he got it working. A similar thing happened with the family’s lawn mower, which Mueller disassembled one afternoon on the front lawn for fun. “My dad came home and was so mad because he thought he’d have to buy a new mower,” Mueller said. “But I put it back together, and it ran.” Mueller then got stuck on rockets. He started buying mail order kits and following the instructions to build small rockets. Rather quickly, Mueller graduated to constructing his own devices. At the age of twelve, he crafted a mock-up space shuttle that could be attached to a rocket, sent up into the air, and then glide back to the ground. For a science project a couple of years later, Mueller borrowed his dad’s oxyacetylene welding equipment to make a rocket engine prototype. Mueller cooled the device by placing it upside down in a coffee can full of water—“I could run it like that all day long”—and invented equally creative ways to measure its performance. The machine was good enough for Mueller to win a couple of regional science fair competitions and end up at an international event. “That’s where I promptly got my ass kicked,” Mueller said. Tall, lanky, and with a rectangular face, Mueller is an easygoing sort who muddled through college for a bit, teaching his friends how to make smoke bombs, and then eventually settled down and did well as a mechanical engineering student. Fresh out of college, he worked for Hughes Aircraft on satellites—“It wasn’t rockets, but it was close”—and then went to TRW Space & Electronics. It was the latter half of the 1980s, and Ronald Reagan’s Star Wars program had the space gearheads dreaming about kinetic weapons and all sorts of mayhem. At TRW, Mueller experimented with crazy types of propellants and oversaw the development of the company’s TR-106 engine, a giant machine fueled by liquid oxygen and hydrogen. As a hobby, Mueller hung out with a couple hundred amateur rocketry buffs in the Reaction Research Society, a group formed in 1943 to encourage the building and firing of rockets. On the weekends, Mueller traveled out to the Mojave Desert with the other RRS members to push the limits of amateur machines. Mueller was one of the club’s standouts, able to build things that actually worked, and could experiment with some of the more radical concepts that were quashed by his conservative bosses at TRW. His crowning achievement was an eighty-pound engine that could produce thirteen thousand pounds of thrust and earned accolades as the world’s largest liquid-fuel rocket engine built by an amateur. “I still keep the rockets hanging in my garage,” Mueller said. In January 2002, Mueller was hanging out in the workshop of John Garvey, who had left a job at the aerospace company McDonnell Douglas to start building his own rockets. Garvey’s facility was in Huntington Beach, where he rented an industrial space about the size of a six-car garage. The two men were fiddling around with the eighty-pound engine when Garvey mentioned that a guy named Elon Musk might be stopping by. The amateur rocketry scene is tight, and it was Cantrell who recommended that Musk check out Garvey’s workshop and see Mueller’s designs. On a Sunday, Musk arrived with a pregnant Justine, wearing a stylish black leather trench coat and looking like a high-paid assassin. Mueller had the eighty-pound engine on his shoulder and was trying to bolt it to a support structure when Musk began peppering him with questions. “He asked me how much thrust it had,” Mueller said. “He wanted to know if I had ever worked on anything bigger. I told him that yeah, I’d worked on a 650,000-pound thrust engine at TRW and knew every part of it.” Mueller set the engine down and tried to keep up with Musk’s interrogation. “How much would that big engine cost?” Musk asked. Mueller told him TRW built it for about $12 million. Musk shot back, “Yeah, but how much could you really do it for?” Mueller ended up chatting with Musk for hours. The next weekend, Mueller invited Musk to his house to continue their discussion. Musk knew he had found someone who really knew the ins and outs of making rockets. After that, Musk introduced Mueller to the rest of his roundtable of space experts and their stealthy meetings. The caliber of the people impressed Mueller, who had turned down past job offers from Beal and other budding space magnates because of their borderline insane ideas. Musk, by contrast, seemed to know what he was doing, weeding out the naysayers meeting by meeting and forming a crew of bright, committed engineers. Mueller had helped Musk fill out that spreadsheet around the performance and cost metrics of a new, low-cost rocket, and, along with the rest of Team Musk, had subsequently refined the idea. The rocket would not carry truck-sized satellites like some of the monster rockets flown by Boeing, Lockheed, the Russians, and others countries. Instead, Musk’s rocket would be aimed at the lower end of the satellite market, and it could end up as ideal for an emerging class of smaller payloads that capitalized on the massive advances that had taken place in recent years in computing and electronics technology. The rocket would cater directly to a theory in the space industry that a whole new market might open for both commercial and research payloads if a company could drastically lower the price per launch and perform launches on a regular schedule. Musk relished the idea of being at the forefront of this trend and developing the workhorse of a new era in space. Of course, all of this was theoretical—and then, suddenly, it wasn’t. PayPal had gone public in February with its shares shooting up 55 percent, and Musk knew that eBay wanted to buy the company as well. While noodling on the rocket idea, Musk’s net worth had increased from tens of millions to hundreds of millions. In April 2002, Musk fully abandoned the publicity-stunt idea and committed to building a commercial space venture. He pulled aside Cantrell, Griffin, Mueller, and Chris Thompson, an aerospace engineer at Boeing, and told the group, “I want to do this company. If you guys are in, let’s do it.” (Griffin wanted to join but ended up declining when Musk rebuffed his request to live on the East Coast, and Cantrell only stuck around for a few months after this meeting, seeing the venture as too risky.) Founded in June 2002, Space Exploration Technologies came to life in humble settings. Musk acquired an old warehouse at 1310 East Grand Avenue in El Segundo, a suburb of Los Angeles humming with the activity of the aerospace industry. The previous tenant of the 75,000-square-foot building had done lots of shipping and had used the south side of the facility as a logistics depot, outfitting it with several receiving bays for delivery trucks. This allowed Musk to drive his silver McLaren right into the building. Beyond that the surroundings were sparse—just a dusty floor and a forty-foot-high ceiling with its wooden beams and insulation exposed and which curved at the top to give the place a hangarlike feel. The north side of the building was an office space with cubicles and room for about fifty people. During the first week of SpaceX’s operations, delivery trucks showed up packed full of Dell laptops and printers and folding tables that would serve as the first desks. Musk walked over to one of the loading docks, rolled up the door, and off-loaded the equipment himself. Musk had soon transformed the SpaceX office with what has become his signature factory aesthetic: a glossy epoxy coating applied over concrete on the floors, and a fresh coat of white paint slathered onto the walls. The white color scheme was intended to make the factory look clean and feel cheerful. Desks were interspersed around the factory so that Ivy League computer scientists and engineers designing the machines could sit with the welders and machinists building the hardware. This approach stood as SpaceX’s first major break with traditional aerospace companies that prefer to cordon different engineering groups off from each other and typically separate engineers and machinists by thousands of miles by placing their factories in locations where real estate and labor run cheap. As the first dozen or so employees came to the offices, they were told that SpaceX’s mission would be to emerge as the “Southwest Airlines of Space.” SpaceX would build its own engines and then contract with suppliers for the other components of the rocket. The company would gain an edge over the competition by building a better, cheaper engine and by fine-tuning the assembly process to make rockets faster and cheaper than anyone else. This vision included the construction of a type of mobile launch vehicle that could travel to various sites, take the rocket from a horizontal to vertical position, and send it off to space—no muss, no fuss. SpaceX was meant to get so good at this process that it could do multiple launches a month, make money off each one, and never need to become a huge contractor dependent on government funds. SpaceX was to be America’s attempt at a clean slate in the rocket business, a modernized reset. Musk felt that the space industry had not really evolved in about fifty years. The aerospace companies had little competition and tended to make supremely expensive products that achieved maximum performance. They were building a Ferrari for every launch, when it was possible that a Honda Accord might do the trick. Musk, by contrast, would apply some of the start-up techniques he’d learned in Silicon Valley to run SpaceX lean and fast and capitalize on the huge advances in computing power and materials that had taken place over the past couple of decades. As a private company, SpaceX would also avoid the waste and cost overruns associated with government contractors. Musk declared that SpaceX’s first rocket would be called the Falcon 1, a nod to Star Wars’ Millennium Falcon and his role as the architect of an exciting future. At a time when the cost of sending a 550-pound payload started at $30 million, he promised that the Falcon 1 would be able to carry a 1,400-pound payload for $6.9 million. Bowing to his nature, Musk set an insanely ambitious timeline for all of this. One of the earliest SpaceX presentations suggested that the company would complete its first engine in May 2003, a second engine in June, the body of the rocket in July, and have everything assembled in August. A launchpad would then be prepared by September, and the first launch would take place in November 2003, or about fifteen months after the company started. A trip to Mars was naturally slated for somewhere near the end of the decade. This was Musk the logical, naïve optimist tabulating how long it should take people physically to perform all of this work. It’s the baseline he expects of himself and one that his employees, with their human foibles, are in a never-ending struggle to match. As space enthusiasts started to learn about the new company, they didn’t really obsess over whether Musk’s delivery schedule sounded realistic or not. They were just thrilled that someone had decided to take the cheap and fast approach. Some members of the military had already been promoting the idea of giving the armed forces more aggressive space capabilities, or what they called “responsive space.” If a conflict broke out, the military wanted the ability to respond with purpose-built satellites for that mission. This would mean moving away from a model where it takes ten years to build and deploy a satellite for a specific job. Instead, the military desired cheaper, smaller satellites that could be reconfigured through software and sent up on short notice, almost like disposable satellites. “If we could pull that off, it would be really game-changing,” said Pete Worden, a retired air force general, who met with Musk while serving as a consultant to the Defense Department. “It could make our response in space similar to what we do on land, sea and in the air.” Worden’s job required him to look at radical technologies. While many of the people he encountered came off as eccentric dreamers, Musk seemed grounded, knowledgeable, and capable. “I talked to people building ray guns and things in their garages. It was clear that Elon was different. He was a visionary who really understood the rocket technology, and I was impressed with him.” Like the military, scientists wanted cheap, quick access to space and the ability to send up experiments and get data back on a regular basis. Some companies in the medical and consumer-goods industries were also interested in rides to space to study how a lack of gravity affected the properties of their products. As good as a cheap launch vehicle sounded, the odds of a private citizen building one that worked were beyond remote. A quick search on YouTube for “rocket explosions” turns up thousands of compilation videos documenting U.S. and Soviet launch disasters that have occurred over the decades. From 1957 to 1966, the United States alone tried to blast more than 400 rockets into orbit and about 100 of them crashed and burned. [http://archive.wired.com/science/space/magazine/15-06/ff_ space_musk?currentPage=all] The rockets used to transport things to space are mostly modified missiles developed through all of this trial and error and funded by billions upon billions of government dollars. SpaceX had the advantage of being able to learn from this past work and having a few people on staff that had overseen rocket projects at companies like Boeing and TRW. That said, the start-up did not have a budget that could support a string of explosions. At best, SpaceX would have three or four shots at making the Falcon 1 work. “People thought we were just crazy,” Mueller said. “At TRW, I had an army of people and government funding. Now we were going to make a low-cost rocket from scratch with a small team. People just didn’t think it could be done.” In July 2002, Musk was gripped by the excitement of this daring enterprise, and eBay made its aggressive move to buy PayPal for $1.5 billion. This deal gave Musk some liquidity and supplied him with more than $100 million to throw at SpaceX. With such a massive up-front investment, no one would be able to wrestle control of SpaceX away from Musk as they had done at Zip2 and PayPal. For the employees who had agreed to accompany Musk on this seemingly impossible journey, the windfall provided at least a couple of years of job security. The acquisition also upped Musk’s profile and celebrity, which he could leverage to score meetings with top government officials and to sway suppliers. And then all of a sudden none of this seemed to matter. Justine had given birth to a son—Nevada Alexander Musk. He was ten weeks old when, just as the eBay deal was announced, he died. The Musks had tucked Nevada in for a nap and placed the boy on his back as parents are taught to do. When they returned to check on him, he was no longer breathing and had suffered from what the doctors would term a sudden infant death syndrome–related incident. “By the time the paramedics resuscitated him, he had been deprived of oxygen for so long that he was brain-dead,” Justine wrote in her article for Marie Claire. “He spent three days on life support in a hospital in Orange County before we made the decision to take him off it. I held him in my arms when he died. Elon made it clear that he did not want to talk about Nevada’s death. I didn’t understand this, just as he didn’t understand why I grieved openly, which he regarded as ‘emotionally manipulative.’ I buried my feelings instead, coping with Nevada’s death by making my first visit to an IVF clinic less than two months later. Elon and I planned to get pregnant again as swiftly as possible. Within the next five years, I gave birth to twins, then triplets.” Later, Justine chalked up Musk’s reaction to a defense mechanism that he’d learned from years of suffering as a kid. “He doesn’t do well in dark places,” she told Esquire magazine. “He’s forward-moving, and I think it’s a survival thing with him.” Musk did open up to a couple of close friends and expressed the depth of his misery. But for the most part, Justine read her husband right. He didn’t see the value in grieving publicly. “It made me extremely sad to talk about it,” Musk said. “I’m not sure why I’d want to talk about extremely sad events. It does no good for the future. If you’ve got other kids and obligations, then wallowing in sadness does no good for anyone around you. I’m not sure what should be done in such situations.” Following Nevada’s death, Musk threw himself at SpaceX and rapidly expanded the company’s goals. His conversations with aerospace contractors around possible work for SpaceX left Musk disenchanted. It sounded like they all charged a lot of money and worked slowly. The plan to integrate components made by these types of companies gave way to the decision to make as much as practical right at SpaceX. “While drawing upon the ideas of many prior launch vehicle programs from Apollo to the X-34/Fastrac, SpaceX is privately developing the entire Falcon rocket from the ground up, including both engines, the turbo-pump, the cryogenic tank structure and the guidance system,” the company announced on its website. “A ground up internal development increases difficulty and the required investment, but no other path will achieve the needed improvement in the cost of access to space.” The SpaceX executives Musk hired were an all-star crew. Mueller set to work right away building the two engines—Merlin and Kestrel, named after two types of falcons. Chris Thompson, a onetime marine who had managed the production of the Delta and Titan rockets at Boeing, joined as the vice president of operations. Tim Buzza also came from Boeing, where he’d earned a reputation as one of the world’s leading rocket testers. Steve Johnson, who had worked at JPL and at two commercial space companies, was tapped as the senior mechanical engineer. The aerospace engineer Hans Koenigsmann came on to develop the avionics, guidance, and control systems. Musk also recruited Gwynne Shotwell, an aerospace veteran who started as SpaceX’s first salesperson and rose in the years that followed to be president and Musk’s right-hand woman. These early days also marked the arrival of Mary Beth Brown, a now-legendary character in the lore of both SpaceX and Tesla. Brown—or MB, as everyone called her—became Musk’s loyal assistant, establishing a real-life version of the relationship between Iron Man’s Tony Stark and Pepper Potts. If Musk worked a twenty-hour day, so too did Brown. Over the years, she brought Musk meals, set up his business appointments, arranged time with his children, picked out his clothes, dealt with press requests, and when necessary yanked Musk out of meetings to keep him on schedule. She would emerge as the only bridge between Musk and all of his interests and was an invaluable asset to the companies’ employees. Brown played a key role in developing SpaceX’s early culture. She paid attention to small details like the office’s red spaceship trash cans and helped balance the vibe around the office. When it came to matters related directly to Musk, Brown put on her firm countenance and no-nonsense attitude. The rest of the time she usually had a warm, broad smile and a disarming charm. “It was always, ‘Oh, dear. How are you, dear?’” recalled a SpaceX technician. Brown collected the weird e-mails that arrived for Musk and sent them out as “Kook of the Week” missives to make people laugh. One of the better entries included a pencil sketch of a lunar spacecraft that had a red spot on the page. The person who sent in the letter had circled the spot on his own drawing and then written “What is that? Blood?” next to it. In other letters there were plans for a perpetual motion machine and a proposal for a giant inflatable rabbit that could be used to plug oil spills. For a short time, Brown’s duties extended to managing SpaceX’s books and handling the flow of business in Musk’s absence. “She pretty much called the shots,” the technician said. “She would say, ‘This is what Elon would want.’” Her greatest gift, though, may have been reading Musk’s moods. At both SpaceX and Tesla, Brown placed her desk a few feet in front of Musk’s, so that people had to pass her before having a meeting with him. If someone needed to request permission to buy a big-ticket item, they would stop for a moment in front of Brown and wait for a nod to go see Musk or the shake-off to go away because Musk was having a bad day. This system of nods and shakes became particularly important during periods of romantic strife for Musk, when his nerves were on edge more than usual. The rank-and-file engineers at SpaceX tended to be young, male overachievers. Musk would personally reach out to the aerospace departments of top colleges and inquire about the students who had finished with the best marks on their exams. It was not unusual for him to call the students in their dorm rooms and recruit them over the phone. “I thought it was a prank call,” said Michael Colonno, who heard from Musk while attending Stanford. “I did not believe for a minute that he had a rocket company.” Once the students looked Musk up on the Internet, selling them on SpaceX was easy. For the first time in years if not decades, young aeronautics whizzes who pined to explore space had a really exciting company to latch on to and a path toward designing a rocket or even becoming an astronaut that did not require them to join a bureaucratic government contractor. As word of SpaceX’s ambitions spread, top engineers from Boeing, Lockheed Martin, and Orbital Sciences with a high tolerance for risk fled to the upstart, too. Throughout the first year at SpaceX, one or two new employees joined almost every week. Kevin Brogan was employee No. 23 and came from TRW, where he’d been used to various internal policies blocking him from doing work. “I called it the country club,” he said. “Nobody did anything.” Brogan started at SpaceX the day after his interview and was told to go hunting in the office for a computer to use. “It was go to Fry’s and get whatever you need and go to Staples and get a chair,” Brogan said. He immediately felt in over his head and would work for twelve hours, drive home, sleep for ten hours, and then head right back to the factory. “I was exhausted and out of shape mentally,” he said. “But soon I loved it and got totally hooked.” One of the first projects SpaceX decided to tackle was the construction of a gas generator, a machine not unlike a small rocket engine that produces hot gas. Mueller, Buzza, and a couple of young engineers assembled the generator in Los Angeles and then packed it into the back of a pickup truck and drove it out to Mojave, California, to test it. A desert town about one hundred miles from Los Angeles, Mojave had become a hub for aerospace companies like Scaled Composites and XCOR. A lot of the aerospace projects were based out of the Mojave airport, where companies had their workshops and sent up all manner of cutting-edge airplanes and rockets. The SpaceX team fit right into this environment and borrowed a test stand from XCOR that was just about the perfect size to hold the gas generator. The first ignition run took place at 11 A.M. and lasted ninety seconds. The gas generator worked, but it had let out a billowing black smoke cloud that on this windless day parked right over the airport tower. The airport manager came down to the test area and lit into Mueller and Buzza. The airport official and some of the guys from XCOR who had been helping out urged the SpaceX engineers to take it easy and wait until the next day to run another test. Instead, Buzza a strong leader ready to put SpaceX’s relentless ethos into play, coordinated a couple of trucks to pick up more fuel, talked the airport manager down, and got the test stand ready for another fire. In the days that followed, SpaceX’s engineers perfected a routine that let them do multiple tests a day—an unheard-of practice at the airport—and had the gas generator tuned to their liking after two weeks of work. They made a few more trips to Mojave and some other spots, including a test stand at Edwards Air Force Base and another in Mississippi. While on this countrywide rocketry tour, the SpaceX engineers came across a three-hundred-acre test site in McGregor, Texas, a small city near the center of the state. They really liked this spot, and talked Musk into buying it. The navy had tested rockets on the land years before and so too had Andrew Beal before his aerospace company collapsed. “After Beal saw it was going to cost him $300 million to develop a rocket capable of sending sizeable satellites into orbit, he called it quits, leaving behind a lot of useful infrastructure for SpaceX, including a three-story concrete tripod with legs as big around as redwood tree trunks,” wrote journalist Michael Belfiore in Rocketeers, a book that captured the rise of a handful of private space companies. Jeremy Hollman was one of the young engineers who soon found himself living in Texas and customizing the test site to SpaceX’s needs. Hollman exemplified the kind of recruit Musk wanted: he’d earned an aerospace engineering degree from Iowa State University and a master’s in astronautical engineering from the University of Southern California. He’d spent a couple of years working as a test engineer at Boeing dealing with jets, rockets, and spacecraft. /Buzza knew Hollman’s work at Boeing and coaxed him to SpaceX about six months after the company started./ The stint at Boeing had left Hollman unimpressed with big aerospace. His first day on the job came right as Boeing completed its merger with McDonnell Douglas. The resultant mammoth government contractor held a picnic to boost morale but ended up failing at even this simple exercise. “The head of one of the departments gave a speech about it being one company with one vision and then added that the company was very cost constrained,” Hollman said. “He asked that everyone limit themselves to one piece of chicken.” Things didn’t improve much from there. Every project at Boeing felt large, cumbersome, and costly. So, when Musk came along selling radical change, Hollman bit. “I thought it was an opportunity I could not pass up,” he said. At twenty-three, Hollman was young, single, and willing to give up any semblance of having a life in favor of working at SpaceX nonstop, and he became Mueller’s second in command. Mueller had developed a pair of three-dimensional computer models of the two engines he wanted to build. Merlin would be the engine for the first stage of the Falcon 1, which lifted it off the ground, and Kestrel would be the smaller engine used to power the upper, second stage of the rocket and guide it in space. Together, Hollman and Mueller figured out which parts of the engines SpaceX would build at the factory and which parts it would try to buy. For the purchased parts, Hollman had to head out to various machine shops and get quotes and delivery dates for the hardware. Quite often, the machinists told Hollman that SpaceX’s timelines were nuts. Others were more accommodating and would try to bend an existing product to SpaceX’s needs instead of building something from scratch. Hollman also found that creativity got him a long way. He discovered, for example, that changing the seals on some readily available car wash valves made them good enough to be used with rocket fuel. After SpaceX completed its first engine at the factory in California, Hollman loaded it and mounds of other equipment into a U-Haul trailer. He hitched the U-Haul to the back of a white Hummer H2 and drove four thousand pounds of gear /Including a 1,300-pound hunk of copper./ across Interstate 10 from Los Angeles to Texas and the test site. The arrival of the engine in Texas kicked off one of the great bonding exercises in SpaceX’s history. Amid rattlesnakes, fire ants, isolation, and searing heat, the group led by Buzza and Mueller began the process of exploring every intricacy of the engines. It was a high-pressure slog full of explosions—or what the engineers politely called “rapid unscheduled disassemblies”—that would determine whether a small band of engineers really could match the effort and skill of nation-states. The SpaceX employees christened the site in fitting fashion, downing a $1,200 bottle of Rémy Martin cognac out of paper cups and passing a sobriety test on the drive back to the company apartments in the Hummer. From that point on, the trek from California to the test site became known as the Texas Cattle Haul. The SpaceX engineers would work for ten days straight, come back to California for a weekend, and then head back. To ease the burden of travel, Musk sometimes let them use his private jet. “It carried six people,” Mueller said. “Well, seven if someone sat in the toilet, which happened all the time.” While the navy and Beal had left some testing apparatus, SpaceX had to build a large amount of custom gear. One of the largest of these structures was a horizontal test stand about 30 feet long, 15 feet wide, and 15 feet tall. Then there was the complementary vertical test stand that stood two stories high. When an engine needed to be fired, it would be fastened to one of the test stands, outfitted with sensors to collect data, and monitored via several cameras. The engineers took shelter in a bunker protected on one side by a dirt embankment. If something went wrong, they would look at feeds from the webcams or slowly lift one of the bunker’s hatches to listen for any clues. The locals in town rarely complained about the noise, although the animals on nearby farms seemed less impressed. “Cows have this natural defense mechanism where they gather and start running in a circle,” Hollman said. “Every time we fired an engine, the cows scattered and then got in that circle with the younger ones placed in the middle. We set up a cow cam to watch them.” Both Kestrel and Merlin came with challenges, and they were treated as alternating engineering exercises. “We would run Merlin until we ran out of hardware or did something bad,” Mueller said. “Then we’d run Kestrel and there was never a shortage of things to do.” For months, the SpaceX engineers arrived at the site at 8 A.M. and spent twelve hours there working on the engines before retiring to the Outback Steakhouse for dinner. Mueller had a particular knack for looking over test data and spotting some place where the engine ran hot or cold or had another flaw. He would call California and prescribe hardware changes, and engineers would refashion parts and send them off to Texas. Often the workers in Texas modified parts themselves using a mill and lathe that Mueller had brought out. “Kestrel started out as a real dog, and one of my proudest moments was taking it from terrible to great performance with stuff we bought online and did in the machine shop,” Mueller said. Some members of the Texas crew honed their skills to the point that they could build a test-worthy engine in three days. These same people were required to be adept at software. They’d pull an all-nighter building a turbo pump for the engine and then dig in the next night to retool a suite of applications used to control the engines. Hollman did this type of work all the time and was an all-star, but he was not alone among this group of young, nimble engineers who crossed disciplines out of necessity and the spirit of adventure. “There was an almost addictive quality to the experience,” Hollman said. “You’re twenty-four or twenty-five, and they’re trusting you with so much. It was very empowering.” To get to space, the Merlin engine would need to burn for 180 seconds. That seemed like an eternity for the engineers at the outset of their stint in Texas, when the engine would burn for only a half second before it conked out. Sometimes Merlin vibrated too much during the tests. Sometimes it responded badly to a new material. Sometimes it cracked and needed major part upgrades, like moving from an aluminum manifold to a manifold made out of the more exotic Inconel, an alloy suited to extreme temperatures. On one occasion, a fuel valve refused to open properly and caused the whole engine to blow up. Another test gone wrong ended up with the whole test stand burning down. It usually came to Buzza and Mueller to make the unpleasant call back to Musk and recap the day’s foibles. “Elon had pretty good patience,” Mueller said. “I remember one time we had two test stands running and blew up two things in one day. I told Elon we could put another engine on there, but I was really, really frustrated and just tired and mad and was kinda short with Elon. I said, ‘We can put another fucking thing on there, but I’ve blown up enough shit today.’ He said, ‘Okay, all right, that’s fine. Just calm down. We’ll do it again tomorrow.’” Coworkers in El Segundo later reported that Musk had been near tears during this call after hearing the frustration and agony in Mueller’s voice. What Musk would not tolerate were excuses or the lack of a clear plan of attack. Hollman was one of many engineers who arrived at this realization after facing one of Musk’s trademark grillings. “The worst call was the first one,” Hollman said. “Something had gone wrong, and Elon asked me how long it would take to be operational again, and I didn’t have an immediate answer. He said, ‘You need to. This is important to the company. Everything is riding on this. Why don’t you have an answer?’ He kept hitting me with pointed, direct questions. I thought it was more important to let him know quickly what happened, but I learned it was more important to have all the information.” From time to time, Musk participated in the testing process firsthand. One of the more memorable examples of this came as SpaceX tried to perfect a cooling chamber for its engines. The company had bought several of these chambers at $75,000 a pop and needed to put them under pressure with water to gauge their ability to handle stress. During the initial test, one of the pricey chambers cracked. Then the second one broke in the same place. Musk ordered a third test, as the engineers looked on in horror. They thought the test might be putting the chamber under undue stress and that Musk was burning through essential equipment. When the third chamber cracked, Musk flew the hardware back to California, took it to the factory floor, and, with the help of some engineers, started to fill the chambers with an epoxy to see if it would seal them. “He’s not afraid to get his hands dirty,” Mueller said. “He’s out there with his nice Italian shoes and clothes and has epoxy all over him. They were there all night and tested it again and it broke anyway.” Musk, clothes ruined, had decided the hardware was flawed, tested his hypothesis, and moved on quickly, asking the engineers to come up with a new solution. These incidents were all part of a trying but productive process. SpaceX had developed the feeling of a small, tight-knit family up against the world. In late 2002, the company had an empty warehouse. One year later, the facility looked like a real rocket factory. Working Merlin engines were arriving back from Texas, and being fed into an assembly line where machinists could connect them to the main body, or first stage, of the rocket. More stations were set up to link the first stage with the upper stage of the rocket. Cranes were placed on the floor to handle the heavy lifting of components, and blue metal transport tracks were positioned to guide the rocket’s body through the factory from station to station. SpaceX had also started to build the fairing, or case, that protects payloads atop the rocket during launch and then opens up like a clam in space to let out the cargo. SpaceX had picked up a customer as well. According to Musk, its first rocket would launch in “early 2004” from Vandenberg Air Force Base, carrying a satellite called TacSat-1 for the Department of Defense. With this goal looming, twelve-hour days, six days a week were considered the norm, although many people worked longer than that for extended periods of time. Respites, as far as they existed, came around 8 P.M. on some weeknights when Musk would allow everyone to use their work computers to play first-person-shooter video games like Quake III Arena and Counter-Strike against each other. At the appointed hour, the sound of guns loading would cascade throughout the office as close to twenty people armed themselves for battle. Musk—playing under the handle Random9—often won the games, talking trash and blasting away his employees without mercy. “The CEO is there shooting at us with rockets and plasma guns,” said Colonno. “Worse, he’s almost alarmingly good at these games and has insanely fast reactions. He knew all the tricks and how to sneak up on people.” The pending launch ignited Musk’s salesman instincts. He wanted to show the public what his tireless workers had accomplished and drum up some excitement around SpaceX. Musk decided to unveil a prototype of Falcon 1 to the public in December 2003. The company would haul the seven-story-high Falcon 1 across the country on a specially built rig and leave it—and the SpaceX mobile launch system—outside of the Federal Aviation Administration’s headquarters in Washington, D.C. An accompanying press conference would make it clear to Washington that a modern, smarter, cheaper rocket maker had arrived. This marketing song and dance didn’t sound sensible to SpaceX’s engineers. They were working more than one hundred hours per week to make the actual rocket that SpaceX would need to be in business. Musk wanted them to do that and build a slick-looking mock-up. Engineers were called back from Texas and assigned another ulcer-inducing deadline to craft this prop. “In my mind, it was a boondoggle,” Hollman said. “It wasn’t advancing anything. In Elon’s mind, it would get us a lot of backing from important people in the government.” While making the prototype for the event, Hollman experienced the full spectrum of highs and lows that came with working for Musk. The engineer had lost his regular glasses weeks earlier when they slipped off his face and fell down a flame duct at the Texas test site. Hollman had since made do by wearing an old pair of prescription safety glasses, /Before returning to El Segundo, Hollman used a drill press to remove the glasses’ safety shield. “I didn’t want to look like a nerd on the flight home,” he said./ but they too were ruined when he scratched the lenses while trying to duck under an engine at the SpaceX factory. Without a spare moment to visit an optometrist, Hollman started to feel his sanity fray. The long hours, the scratch, the publicity stunt—they were all too much. He vented about this in the factory one night, unaware that Musk stood nearby and could hear everything. Two hours later, Mary Beth Brown appeared with an appointment card to see a Lasik eye surgery specialist. When Hollman visited the doctor, he discovered that Musk had already agreed to pay for the surgery. “Elon can be very demanding, but he’ll make sure the obstacles in your way are removed,” Hollman said. Upon reflection, he also warmed to the long-term thinking behind Musk’s Washington plan. “I think he wanted to add an element of realism to SpaceX, and if you park a rocket in someone’s front yard, it’s hard to deny it,” Hollman said. The event in Washington ended up being well received, and just a few weeks after it took place, SpaceX made another astonishing announcement. Despite not having even flown a rocket yet, SpaceX revealed plans for a second rocket. Along with the Falcon 1, it would build the Falcon 5. Per the name, this rocket would have five engines and could carry more weight—9,200 pounds—to low orbit around Earth. Crucially, the Falcon 5 could also theoretically reach the International Space Station for resupply missions—a capability that would open up SpaceX for some large NASA contracts. And, in a nod to Musk’s obsession with safety, the rocket was said to be able to complete its missions even if three of the five engines failed, which was a level of added reliability that had not been seen in the market in decades. The only way to keep up with all of this work was to do what SpaceX had promised from the beginning: operate in the spirit of a Silicon Valley start-up. Musk was always looking for brainy engineers who had not just done well at school but had done something exceptional with their talents. When he found someone good, Musk was relentless in courting him or her to come to SpaceX. Bryan Gardner, for example, first met Musk at a space rave in the hangars at the Mojave airport and a short while later started talking about a job. Gardner was having some of his academic work sponsored by Northrop Grumman. “Elon said, ‘We’ll buy them out,’” Gardner said. “So, I e-mailed him my resume at two thirty A.M., and he replied back in thirty minutes addressing everything I put in there point by point. He said, ‘When you interview make sure you can talk concretely about what you do rather than use buzzwords.’ It floored me that he would take the time to do this.” After being hired, Gardner was tasked with improving the system for testing the valves on the Merlin engine. There were dozens of valves, and it took three to five hours to manually test each one. Six months later, Gardner had built an automated system for testing the valves in minutes. The testing machine tracked the valves individually, so that an engineer in Texas could request what the metrics had been on a specific part. “I had been handed this redheaded stepchild that no one else wanted to deal with and established my engineering credibility,” Gardner said. As the new hires arrived, SpaceX moved beyond its original building to fill up several buildings in the El Segundo complex. The engineers were running demanding software and rendering large graphics files and needed high-speed connections between all of these offices. But SpaceX had neighbors who were blocking an initiative to connect all of its buildings via fiber optic lines. Instead of taking the time to haggle with the other companies for right of way, the IT chief Branden Spikes, who had worked with Musk at Zip2 and PayPal, came up with a quicker, more devious solution. A friend of his worked for the phone company and drew a diagram that demonstrated a way to squeeze a networking cable safely between the electricity, cable, and phone wires on a telephone pole. At 2 A.M., an off-the-books crew showed up with a cherry picker and ran fiber to the telephone poles and then ran cables straight to the SpaceX buildings. “We did that over a weekend instead of taking months to get permits,” Spikes said. “There was always this feeling that we were facing a sort of insurmountable challenge and that we had to band together to fight the good fight.” SpaceX’s landlord, Alex Lidow, chuckled when thinking back to all of the antics of Musk’s team. “I know they did a lot of hanky stuff at night,” he said. “They were smart, needed to get things done, and didn’t always have time to wait for things like city permits.” Musk never relented in asking his employees to do more and be better, whether it was at the office or during extracurricular activities. Part of Spikes’s duties included building custom gaming PCs for Musk’s home that pushed their computational power to the limits and needed to be cooled with water running through a series of tubes inside the machines. When one of these gaming rigs kept breaking, Spikes figured out that Musk’s mansion had dirty power lines and had a second, dedicated power circuit built for the gaming room to correct the problem. Doing this favor bought Spikes no special treatment. “SpaceX’s mail server crashed one time, and Elon word for word said, ‘Don’t ever fucking let that happen again,’” Spikes said. “He had a way of looking at you—a glare—and would keep looking at you until you understood him.” Musk had tried to find contractors that could keep up with SpaceX’s creativity and pace. Instead of always hitting up aerospace guys, for example, he located suppliers with similar experience from different fields. Early on, SpaceX needed someone to build the fuel tanks, essentially the main body of the rocket, and Musk ended up in the Midwest talking to companies that had made large, metal agricultural tanks used in the dairy and food processing businesses. These suppliers also struggled to keep up with SpaceX’s schedule, and Musk found himself flying across the country to pay visits—sometimes surprise ones—on the contractors to check on their progress. One such inspection took place at a company in Wisconsin called Spincraft. Musk and a couple of SpaceX employees flew his jet across the country and arrived late at night expecting to see a shift of workers doing extra duty to get the fuel tanks completed. When Musk discovered that Spincraft was well behind schedule, he turned to a Spincraft employee and informed him, “You’re fucking us up the ass, and it doesn’t feel good.” David Schmitz was a general manager at Spincraft and said Musk earned a reputation as a fearsome negotiator who did indeed follow up on things personally. “If Elon was not happy, you knew it,” Schmitz said. “Things could get nasty.” In the months that followed that meeting, SpaceX increased its internal welding capabilities so that it could make the fuel tanks in El Segundo and ditch Spincraft. Another salesman flew down to SpaceX to sell the company on some technology infrastructure equipment. He was doing the standard relationship-building exercise practiced by salespeople for centuries. Show up. Speak for a while. Feel each other out. Then, start doing business down the road. Musk was having none of it. “The guy comes in, and Elon asks him why they’re meeting,” Spikes said. “He said, ‘To develop a relationship.’ Elon replied, ‘Okay. Nice to meet you,’ which basically meant, ‘Get the fuck out of my office.’ This guy had spent four hours traveling for what ended up as a two-minute meeting. Elon just has no tolerance for that kind of stuff.” Musk could be equally brisk with employees who were not hitting his standards. “He would often say, ‘The longer you wait to fire someone the longer it has been since you should have fired them,’” Spikes said. Most of the SpaceX employees were thrilled to be part of the company’s adventure and tried not to let Musk’s grueling demands and harsh behavior get to them. But there were some moments where Musk went too far. The engineering corps flew into a collective rage every time they caught Musk in the press claiming to have designed the Falcon rocket more or less by himself. Musk also hired a documentary crew to follow him around for a while. This audacious gesture really grated on the people toiling away in the SpaceX factory. They felt like Musk’s ego had gotten the best of him and that he was presenting SpaceX as the conqueror of the aerospace industry when the company had yet to launch successfully. Employees who made detailed cases around what they saw as flaws in the Falcon 5 design or presented practical suggestions to get the Falcon 1 out the door more quickly were often ignored or worse. “The treatment of staff was not good for long stretches of this era,” said one engineer. “Many good engineers, who everyone beside ‘management’ felt were assets to the company, were forced out or simply fired outright after being blamed for things they hadn’t done. The kiss of death was proving Elon wrong about something.” Early 2004, when SpaceX had hoped to launch its rocket, came and went. The Merlin engine that Mueller and his team had built appeared to be among the most efficient rocket engines ever made. It was just taking longer than Musk had expected to pass tests needed to clear the engine for a launch. Finally, in the fall of 2004, the engines were burning consistently and meeting all their requirements. This meant that Mueller and his team could breathe easy and that everyone else at SpaceX should prepare to suffer. Mueller had spent SpaceX’s entire existence as the “critical path”—the person holding up the company from achieving its next steps—working under Musk’s scrutiny. “With the engine ready, it was time for mass panic,” Mueller said. “No one else knew what it was like to be on critical path.” Lots of people soon found out, as major problems abounded. The avionics, which included the electronics for the navigation, communication, and overall management of the rocket, turned into a nightmare. Seemingly trivial things like getting a flash storage drive to talk to the rocket’s main computer failed for undetectable reasons. The software needed to manage the rocket also became a major burden. “It’s like anything else where you find out that the last ten percent is where all the integration happens and things don’t play together,” Mueller said. “This process went on for six months.” Finally, in May 2005, SpaceX transported the rocket 180 miles north to Vandenberg Air Force Base for a test fire and completed a five-second burn on the launchpad. Launching from Vandenberg would have been very convenient for SpaceX. The site is close to Los Angeles and has several launchpads to pick from. SpaceX, though, became an unwelcome guest. The air force gave the newcomer a cool welcome, and the people assigned to manage the launch sites did not go out of their way help SpaceX. Lockheed and Boeing, which fly $1 billion spy satellites for the military from Vandenberg, didn’t care for SpaceX’s presence, either—in part because SpaceX represented a threat to their business and in part because this startup was mucking around near their precious cargo. As SpaceX started to move from the testing phase to the launch, it was told to get in line. They would have to wait months to launch. “Even though they said we could fly, it was clear that we would not,” said Gwynne Shotwell. Searching for a new site, Shotwell and Hans Koenigsmann put a Mercator projection of the world up on the wall and looked for a name they recognized along the equator, where the planet spins faster and gives rockets an added boost. The first name that jumped out was Kwajalein Island—or Kwaj—the largest island in an atoll between Guam and Hawaii in the Pacific Ocean and part of the Republic of the Marshall Islands. This spot registered with Shotwell because the U.S. Army had used it for decades as a missile test site. Shotwell looked up the name of a colonel at the test site and sent him an e-mail, and three weeks later got a call back with the army saying they would love to have SpaceX fly from the islands. In June 2005, SpaceX’s engineers began to fill containers with their equipment to ship them to Kwaj. About one hundred islands make up the Kwajalein Atoll. Many of them stretch for just a few hundred yards and are much longer than they are wide. “From the air, the place looks like these beautiful beads on a string,” said Pete Worden, who visited the site in his capacity as a Defense Department consultant. Most of the people in the area live on an island called Ebeye, while the U.S. military has taken over Kwajalein, the southernmost island, and turned it into part tropical paradise and part Dr. Evil’s secret lair. The United States spent years lobbing its ICBMs from California at Kwaj and used the island to run experiments on its space weapons during the “Star Wars” period. Laser beams would be aimed at Kwaj from space in a bid to see if they were accurate and responsive enough to take out an ICBM hurtling toward the islands. The military presence resulted in a weird array of buildings including hulking, windowless trapezoidal concrete structures clearly conceived by someone who deals with death for a living. To get to Kwaj, the SpaceX employees either flew on Musk’s jet or took commercial flights through Hawaii. The main accommodations were two-bedroom affairs on Kwajalein Island that looked more like dormitories than hotel rooms, with their military-issued dressers and desks. Any materials that the engineers needed had to be flown in on Musk’s plane or were more often brought by boat from Hawaii or the mainland United States. Each day, the SpaceX crew gathered their gear and took a forty-five-minute boat ride to Omelek, a seven-acre, palm-tree-and vegetation-covered island that would be transformed into their launchpad. Over the course of several months, a small team of people cleared the brush, poured concrete to support the launchpad, and converted a double-wide trailer into offices. The work was grueling and took place in soul-sapping humidity under a sun powerful enough to burn the skin through a T-shirt. Eventually, some of the workers preferred to spend the night on Omelek rather than make the journey through rough waters back to the main island. “Some of the offices were turned into bedrooms with mattresses and cots,” Hollman said. “Then we shipped over a very nice refrigerator and a good grill and plumbed in a shower. We tried to make it less like camping and more like living.” The sun rose at 7 A.M. each day, and that’s when the SpaceX team got to work. A series of meetings would take place with people listing what needed to get done, and debating solutions to lingering problems. As the large structures arrived, the workers placed the body of the rocket horizontally in a makeshift hangar and spent hours melding together all of its parts. “There was always something to do,” Hollman said. “If the engine wasn’t a problem, then there was an avionics problem or a software problem.” By 7 P.M., the engineers wound down their work. “One or two people would decide it was their night to cook, and they would make steak and potatoes and pasta,” Hollman said. “We had a bunch of movies and a DVD player, and some of us did a lot of fishing off the docks.” For many of the engineers, this was both a torturous and magical experience. “At Boeing you could be comfortable, but that wasn’t going to happen at SpaceX,” said Walter Sims, a SpaceX tech expert who found time to get certified to dive while on Kwaj. “Every person on that island was a fucking star, and they were always holding seminars on radios or the engine. It was such an invigorating place.” The engineers were constantly baffled by what Musk would fund and what he wouldn’t. Back at headquarters, someone would ask to buy a $200,000 machine or a pricey part that they deemed essential to Falcon 1’s success, and Musk would deny the request. And yet he was totally comfortable paying a similar amount to put a shiny surface on the factory floor to make it look nice. On Omelek, the workers wanted to pave a two-hundred-yard pathway between the hangar and the launchpad to make it easier to transport the rocket. Musk refused. This left the engineers moving the rocket and its wheeled support structure in the fashion of the ancient Egyptians. They laid down a series of wooden planks and rolled the rocket across them, grabbing the last piece of wood from the back and running it forward in a continuous cycle. The whole situation was ludicrous. A start-up rocket company had ended up in the middle of nowhere trying to pull off one of the most difficult feats known to man, and, truth be told, only a handful of the SpaceX team had any idea how to make a launch happen. Time and again, the rocket would get marched out to the launchpad and hoisted vertical for a couple of days, while technical and safety checks would reveal a litany of new problems. The engineers worked on the rocket for as long as they could before laying it horizontal and marching it back to the hangar to avoid damage from the salty air. Teams that had worked separately for months back at the SpaceX factory—propulsion, avionics, software—were thrust together on the island and forced to become an interdisciplinary whole. The sum total was an extreme learning and bonding exercise that played like a comedy of errors. “It was like Gilligan’s Island except with rockets,” Hollman said. In November 2005, about six months after they had first gotten to the island, the SpaceX team felt ready to give launching a shot. Musk flew in with his brother, Kimbal, and joined the majority of the SpaceX team in the barracks on Kwaj. On November 26, a handful of people woke up at 3 A.M. and filled the rocket with liquid oxygen. They then scampered off to an island about three miles away for protection, while the rest of the SpaceX team monitored the launch systems from a control room twenty-six miles away on Kwaj. The military gave SpaceX a six-hour launch window. Everyone was hoping to see the first stage take off and reach about 6,850 miles per hour before giving way to the second stage, which would ignite up in the air and reach 17,000 miles per hour. But, while going through the pre-launch checks, the engineers detected a major problem: a valve on a liquid oxygen tank would not close, and the LOX was boiling off into the air at 500 gallons per hour. SpaceX scrambled to fix the issue but lost too much of its fuel to launch before the window closed. With that mission aborted, SpaceX ordered major LOX reinforcements from Hawaii and prepared for another attempt in mid-December. High winds, faulty valves, and other errors thwarted that launch attempt. Before another attempt could be made, SpaceX discovered on a Saturday night that the rocket’s power distribution systems had started malfunctioning and would need new capacitors. On Sunday morning, the rocket was lowered and split into its two stages so that a technician could slide in and remove the electrical boards. Someone found an electronics supplier that was open on Sunday in Minnesota, and off a SpaceX employee flew to get some fresh capacitors. By Monday he was in California and testing the parts at SpaceX’s headquarters to make sure they passed various heat and vibration checks, then on a plane again back to the islands. In under eighty hours, the electronics had been returned in working order and installed in the rocket. The dash to the United States and back showed that SpaceX’s thirty-person team had real pluck in the face of adversity and inspired everyone on the island. A traditional three-hundred-person-strong aerospace launch crew would never have tried to fix a rocket like that on the fly. But the energy, smarts, and resourcefulness of the SpaceX team still could not overcome their inexperience or the difficult conditions. More problems arose and blocked any thoughts of a launch. Finally, on March 24, 2006, it was all systems go. The Falcon 1 stood on its square launchpad and ignited. It soared into the sky, turning the island below it into a green spec amid a vast, blue expanse. In the control room, Musk paced as he watched the action, wearing shorts, flip-flops, and a T-shirt. Then, about twenty-five seconds in, it became clear that all was not well. A fire broke out above the Merlin engine and suddenly this machine that had been flying straight and true started to spin and then tumble uncontrollably back to Earth. The Falcon 1 ended up falling directly down onto the launch site. Most of the debris went into a reef 250 feet from the launchpad, and the satellite cargo smashed through SpaceX’s machine shop roof and landed more or less intact on the floor. Some of the engineers put on their snorkeling and scuba gear and recovered the pieces, fitting all of the rocket’s remnants into two refrigerator-sized crates. “It is perhaps worth noting that those launch companies that succeeded also took their lumps along the way,” Musk wrote in a postmortem. “A friend of mine wrote to remind me that only 5 of the first 9 Pegasus launches succeeded; 3 of 5 for Ariane; 9 of 20 for Atlas; 9 of 21 for Soyuz; and 9 of 18 for Proton. Having experienced firsthand how hard it is to reach orbit, I have a lot of respect for those that persevered to produce the vehicles that are mainstays of space launch today.” Musk closed the letter writing, “SpaceX is in this for the long haul and, come hell or high water, we are going to make this work.” Musk and other SpaceX executives blamed the crash on an unnamed technician. They said this technician had done some work on the rocket one day before the launch and failed to properly tighten a fitting on a fuel pipe, which caused the fitting to crack. The fitting in question was something basic—an aluminum b-nut that’s often used to connect a pair of tubes. The technician was Hollman. In the aftermath of the rocket crash, Hollman flew to Los Angeles to confront Musk directly. He’d spent years working day and night on the Falcon 1 and felt enraged that Musk had called out him and his team in public. Hollman knew that he’d fastened the b-nut correctly and that observers from NASA had been looking over his shoulder to check the work. When Hollman charged into SpaceX’s headquarters with a head full of fury, Mary Beth Brown tried to calm him and stop him from seeing Musk. Hollman kept going anyway, and the two of them proceeded to have a shouting match at Musk’s cubicle. After all the debris was analyzed, it turned out that the b-nut had almost certainly cracked due to corrosion from the months in Kwaj’s salty atmosphere. “The rocket was literally crusted with salt on one side, and you had to scrape it off,” Mueller said. “But we had done a static fire three days earlier, and everything was fine.” SpaceX had tried to save about fifty pounds of weight by using aluminum components instead of stainless steel. Thompson, the former marine, had seen the aluminum parts work just fine in helicopters that sat on aircraft carriers, and Mueller had seen aircraft resting outside of Cape Canaveral for forty years with aluminum b-nuts in fine condition. Years later, a number of SpaceX’s executives still agonize over the way Hollman and his team were treated. “They were our best guys, and they kind of got blamed to get an answer out to the world,” Mueller said. “That was really bad. We found out later that it was dumb luck.” /Hollman left the company after this incident in November 2007 and then returned for a spell to train new personnel. A number of people I interviewed for the book said that Hollman was so key to SpaceX’s early days that they feared the company might flame out without him./ After the crash, there was a lot of drinking at a bar on the main island. Musk wanted to launch again within six months, but putting together a new machine would again require an immense amount of work. SpaceX had some pieces for the vehicle ready in El Segundo but certainly not a ready-to-fire rocket. As they downed drinks, the engineers vowed to take a more disciplined approach with their next craft and to work better as a collective. Worden hoped the SpaceX engineers would raise their game as well. He’d been observing them for the Defense Department and loved the energy of the young engineers but not their methodology. “It was being done like a bunch of kids in Silicon Valley would do software,” Worden said. “They would stay up all night and try this and try that. I’d seen hundreds of these types of operations, and it struck me that it wouldn’t work.” Leading up to the first launch, Worden tried to caution Musk, sending a letter to him and the director of DARPA, the research arm of the Defense Department, that made his views clear. “Elon didn’t react well. He said, ‘What do you know? You’re just an astronomer,’” Worden said. But, after the rocket blew up, Musk recommended that Worden perform an investigation for the government. “I give Elon huge credit for that,” Worden said. Almost exactly a year later, SpaceX was ready to try another launch. On March 15, 2007, a successful test fire took place. Then, on March 21, the Falcon 1 finally behaved. From its launchpad surrounded by palm trees, the Falcon 1 surged up and toward space. It flew for a couple of minutes with engineers now and again reporting that the systems were “nominal,” or in good shape. At three minutes into the flight, the first stage of the rocket separated and fell back to Earth, and the Kestrel engine kicked in as planned to carry the second stage into orbit. Ecstatic cheers went out in the control room. Next, at the four-minute mark, the fairing atop the rocket separated as planned. “It was doing exactly what it was supposed to do,” said Mueller. “I was sitting next to Elon and looked at him and said, ‘We’ve made it.’ We’re hugging and believe it’s going to make it to orbit. Then, it starts to wiggle.” For more than five glorious minutes, the SpaceX engineers got to feel like they had done everything right. A camera on board the Falcon 1 pointed down and showed Earth getting smaller and smaller as the rocket made its way methodically into space. But then that wiggle that Mueller noticed turned into flailing, and the machine swooned, started to break apart, and then blew up. This time the SpaceX engineers were quick to figure out what went wrong. As the propellant was consumed, what was left started to move around the tank and slosh against the sides, much like wine spinning around a glass. The sloshing propellant triggered the wobbling, and at one point it sloshed enough to leave an opening to the engine exposed. When the engine sucked in a big breath of air, it flamed out. The failure was another crushing blow to SpaceX’s engineers. Some of them had spent close to two years shuffling back and forth between California, Hawaii, and Kwaj. By the time SpaceX could attempt another launch, it would be about four years after Musk’s original target, and the company had been chewing through his Internet fortune at a worrying rate. Musk had vowed publicly that he would see this thing through to the end, but people inside and outside the company were doing back-of-the-envelope math and could tell that SpaceX likely could only afford one more attempt—maybe two. To the extent that the financial situation unnerved Musk, he rarely if ever let it show to employees. “Elon did a great job of not burdening people with those worries,” said Spikes. “He always communicated the importance of being lean and of success, but it was never ‘if we fail, we’re done for.’ He was very optimistic.” The failures seemed to do little to curtail Musk’s vision for the future or raise doubts about his capabilities. In the midst of the chaos, he took a tour of the islands with Worden. Musk began thinking aloud about how the islands could be unified into one landmass. He suggested that walls could be built through the small channels between the islands, and the water could be pumped out in the spirit of the manmade systems in the Netherlands. Worden, also known for his out-there ideas, was attracted to Musk’s bravado. “That he is thinking of this stuff is kind of cool,” Worden said. “From that point on, he and I discussed settling Mars. It really impressed me that this is a guy that thinks big.”
PHOTOGRAPHIC INSERT
The Haldeman children had lots of downtime in the African bush while on wild adventures with their parents. ©Maye Musk
As a toddler, Musk would often drift off into his own world and ignore those around him. Doctors theorized that he might be hard of hearing and had his adenoid glands removed. ©Maye Musk
Musk was a loner throughout grade school and suffered for years at the hands of bullies. ©Maye Musk
Musk’s original video-game code for Blastar, the game he wrote as a twelve-year-old and published in a local magazine. ©Maye Musk
(From left to right:) Elon, Kimbal, and Tosca at their house in South Africa. All three children now live in the United States. ©Maye Musk
Musk ran away on his own to Canada and ended up at Queen’s University in Ontario, living in a dormitory for foreign students. ©Maye Musk
J. B. Straubel puts together one of Tesla Motors’ early battery packs at his house. Photograph courtesy of Tesla Motors
A handful of engineers built the first Tesla Roadster in a Silicon Valley warehouse that they had turned into a garage workshop and research lab. Photograph courtesy of Tesla Motors
Musk and Martin Eberhard prepare to take the early Roadster for a test-drive. The relationship between the two men would fall apart in the years to come. Photograph courtesy of Tesla Motors
SpaceX built its rocket factory from the ground up in a Los Angeles warehouse to give birth to the Falcon 1 rocket. Photograph courtesy of SpaceX
Tom Mueller (far right, gray shirt) led the design, testing, and construction of SpaceX’s engines. Photograph courtesy of SpaceX
SpaceX had to conduct its first flights from Kwajalein Atoll (or Kwaj) in the Marshall Islands. The island experience was a difficult but ultimately fruitful adventure for the engineers. Photograph courtesy of SpaceX
SpaceX built a mobile mission-control trailer, and Musk and Mueller used it to monitor the later launches from Kwaj. Photograph courtesy of SpaceX
Musk hired Franz von Holzhausen in 2008 to design the Tesla Model S. The two men speak almost every day, as can be seen in this meeting in Musk’s SpaceX cubicle. ©Steve Jurvetson
SpaceX’s ambitions grew over the years to include the construction of the Dragon capsule, which could take people to the International Space Station and beyond. ©Steve Jurvetson
Musk has long had a thing for robots and is always evaluating new machines for both the SpaceX and Tesla factories. ©Steve Jurvetson
When SpaceX moved to a new factory in Hawthorne, California, it was able to scale out its assembly line and work on multiple rockets and capsules at the same time. ©Steve Jurvetson
SpaceX tests new engines and crafts at a site in McGregor, Texas. Here the company is testing a reusable rocket, code-named “Grasshopper,” that can land itself. Photograph courtesy of SpaceX
Musk has a tradition of visiting Dairy Queen ahead of test flights in Texas, in this case with SpaceX investor and board member Steve Jurvetson (left) and fellow investor Randy Glein (right). ©Steve Jurvetson
With a Dragon capsule hanging overhead, SpaceX employees peer into the company’s mission control center at the Hawthorne factory. Photograph courtesy of SpaceX
Gwynne Shotwell is Musk’s right-hand woman at SpaceX and oversees the day-to-day operations of the company, including monitoring a launch from mission control. Photograph courtesy of SpaceX
Tesla took over the New United Motor Manufacturing Inc. (or NUMMI) car factory in Fremont, California, which is where workers produce the Model S sedan. Photograph courtesy of Tesla Motors
Tesla began shipping the Model S sedan in 2012. The car ended up winning most of the automotive industry’s major awards. Photograph courtesy of Tesla Motors
The Tesla Model S sedan with its electric motor (near the rear) and battery pack (bottom) exposed. Photograph courtesy of Tesla Motors
Tesla’s next car will be the Model X SUV with its signature “falcon-wing doors.” Photograph courtesy of Tesla Motors
In 2013, Musk visited Cuba with Sean Penn (driving) and the investor Shervin Pishevar (back seat next to Musk). They met with students and members of the Castro family, and tried to free an American prisoner. ©Shervin Pishevar
Musk unveiled the Hyperloop in 2013. He proposed it as a new mode of transportation, and multiple groups have now set to work on building it. Photograph courtesy of SpaceX
In 2014, Musk unveiled a radical new take on the space capsule—the Dragon V2. It comes with a drop-down touch-screen display and slick interior. Photograph courtesy of SpaceX
The Dragon V2 will be able to return to Earth and land with pinpoint accuracy. Photograph courtesy of SpaceX
Musk is a nonstop traveler. Here’s a look at one year in his life via records obtained through a Freedom of Information Act request.
Musk married, divorced, remarried, and then divorced the actress Talulah Riley. Photograph courtesy of Talulah Riley
Musk and Riley relax at home in Los Angeles. Musk shares the home with his five young boys. Photograph courtesy of Talulah Riley
ALL ELECTRIC J. B. STRAUBEL HAS A TWO-INCH-LONG SCAR that cuts across the middle of his left cheek. He earned it in high school, during a chemistry class experiment. Straubel whipped up the wrong concoction of chemicals, and the beaker he was holding exploded, throwing off shards of glass, one of which sliced through his face. The wound lingers as a tinkerer’s badge of honor. It arrived near the end of a childhood full of experimentation with chemicals and machines. Born in Wisconsin, Straubel constructed a large chemistry lab in the basement of his family’s home that included fume hoods and chemicals ordered, borrowed, or pilfered. At thirteen, Straubel found an old golf cart at the dump. He brought it back home and restored it to working condition, which required him to rebuild the electric motor. It seemed that Straubel was always taking something apart, sprucing it up, and putting it back together. All of this fit into the Straubel family’s do-it-yourself traditions. In the late 1890s Straubel’s great-grandfather started the Straubel Machine Company, which built one of the first internal combustion engines in the United States and used it to power boats. Straubel’s inquisitive spirit carried him west to Stanford University, where he enrolled in 1994 intending to become a physicist. After flying through the hardest courses he could take, Straubel concluded that majoring in physics would not be for him. The advanced courses were too theoretical, and Straubel liked to get his hands dirty. He developed his own major called energy systems and engineering. “I wanted to take software and electricity and use it to control energy,” Straubel said. “It was computing combined with power electronics. I collected all the things I love doing in one place.” There was no clean-technology movement at this time, but there were companies dabbling with new uses for solar power and electric vehicles. Straubel ended up hunting down these startups, hanging out in their garages and pestering the engineers. He began tinkering once again on his own as well in the garage of a house he shared with a half dozen friends. Straubel bought a “piece of shit Porsche” for $1,600 and turned it into an electric car. This meant that Straubel had to create a controller to manage the electric motor, build a charger from scratch, and write the software that made the entire machine work. The car set the world record for electric vehicle (EV) acceleration, traveling a quarter mile in 17.28 seconds. “The thing I took away was that the electronics were great, and you could get acceleration on a shoestring budget, but the batteries sucked,” Straubel said. “It had a thirty-mile range, so I learned firsthand about some of the limitations of electric vehicles.” Straubel gave his car a hybrid boost, building a gasoline-powered contraption that could be towed behind the Porsche and used to recharge the batteries. It was good enough for Straubel to drive the four hundred miles down to Los Angeles and back. By 2002, Straubel was living in Los Angeles. He’d gotten a master’s degree from Stanford and bounced around a couple of companies looking for something that called out to him. He decided on Rosen Motors, which had built one of the world’s first hybrid vehicles—a car that ran off a flywheel and a gas turbine and had electric motors to drive the wheel. After it folded, Straubel followed Harold Rosen, an engineer famed for inventing the geostationary satellite, to create an electric plane. “I’m a pilot and love to fly, so this was perfect for me,” Straubel said. “The idea was that it would stay aloft for two weeks at a time and hover over a specific spot. This was way before drones and all that.” To help make ends meet, Straubel also worked nights and on the weekend doing electronics consulting for a start-up. It was in the midst of toiling away on all these projects that Straubel’s old buddies from the Stanford solar car team came to pay him a visit. A group of rogue engineers at Stanford had been working on solar cars for years, building them in a World War II–era Quonset hut full of toxic chemicals and black widows. Unlike today, when the university would jump at the chance to support such a project, Stanford tried to shut down this group of fringe freaks and geeks. The students proved very capable of doing the work on their own and competed in cross-country solar-powered car races. Straubel helped build the vehicles during his time at university and even after, forming relationships with the incoming crop of engineers. The team had just raced 2,300 miles from Chicago to Los Angeles, and Straubel offered the strapped, exhausted kids a place to stay. About a half dozen students showed up at Straubel’s place, took their first showers in many days, and then spread across his floor. As they chatted late into the night, Straubel and the solar team kept fixating on one topic. They realized that lithium ion batteries—such as the ones in their car being fed by the sun—had gotten much better than most people realized. Many consumer electronics devices like laptops were running on so-called 18650 lithium ion batteries, which looked a lot like AA batteries and could be strung together. “We wondered what would happen if you put ten thousand of the battery cells together,” Straubel said. “We did the math and figured you could go almost one thousand miles. It was totally nerdy shit, and eventually everyone fell asleep, but the idea really stuck with me.” Soon enough, Straubel was stalking the solar car crew, trying to talk them into building an electric car based on the lithium ion batteries. He would fly up to Palo Alto, spend the night sleeping in his plane, and then ride a bicycle to the Stanford campus to make his sales pitch while helping with their current projects. The design Straubel had come up with was a super-aerodynamic vehicle with 80 percent of its mass made up of the batteries. It looked quite a bit like a torpedo on wheels. No one knew the exact details of Straubel’s long-term vision for this thing, including Straubel. The plan seemed to be less about forming a car company than about building a proof-of-concept vehicle just to get people thinking about the power of the lithium ion batteries. With any luck, they would find a race to compete in. The Stanford students agreed to join Straubel, if he could raise some money. He began going to trade shows handing out brochures about his idea and e-mailing just about anyone he could think of. “I was shameless,” he said. The only problem was that no one had any interest in what Straubel was selling. Investors dealt him one rejection after another for months on end. Then, in the fall of 2003, Straubel met Elon Musk. Harold Rosen had set up a lunch with Musk at a seafood restaurant near the SpaceX headquarters in Los Angeles and brought Straubel along to help talk up the electric plane idea. When Musk didn’t bite on that, Straubel announced his electric car side project. The crazy idea struck an immediate chord with Musk, who had been thinking about electric vehicles for years. While Musk had mostly focused on using ultracapacitors for the vehicles, he was thrilled and surprised to hear how far the lithium ion battery technology had progressed. “Everyone else had told me I was nuts, but Elon loved the idea,” Straubel said. “He said, ‘Sure, I will give you some money.’” Musk promised Straubel $10,000 of the $100,000 he was seeking. On the spot, Musk and Straubel formed a kinship that would survive more than a decade of extreme highs and lows as they set out to do nothing less than change the world. After the meeting with Musk, Straubel reached out to his friends at AC Propulsion. The Los Angeles–based company started in 1992 and was the bleeding edge of electric vehicles, building everything from zippy midsize passenger jobs right on up to sports cars. Straubel really wanted to show Musk the tzero (from “t-zero”)—the highest-end vehicle in AC Propulsion’s stable. It was a type of kit car that had a fiberglass body sitting on top of a steel frame and went from zero to 60 miles per hour in 4.9 seconds when first unveiled in 1997. Straubel had spent years hanging out with the AC Propulsion crew and asked Tom Gage, the company’s president, to bring a tzero over for Musk to drive. Musk fell for the car. He saw its potential as a screaming-fast machine that could shift the perception of electric cars from boring and plodding to something aspirational. For months Musk offered to fund an effort to transform the kit car into a commercial vehicle but got rebuffed time and again. “It was a proof of concept and needed to be made real,” Straubel said. “I love the hell out of the AC Propulsion guys, but they were sort of hopeless at business and refused to do it. They kept trying to sell Elon on this car called the eBox that looked like shit, didn’t have good performance, and was just uninspiring.” While the meetings with AC Propulsion didn’t result in a deal, they had solidified Musk’s interest in backing something well beyond Straubel’s science project. In a late February 2004 e-mail to Gage, Musk wrote, “What I’m going to do is figure out the best choice of a high performance base car and electric powertrain and go in that direction.” Unbeknownst to Straubel, at about the same time, a couple of business partners in Northern California had also fallen in love with the idea of making a lithium ion battery powered car. Martin Eberhard and Marc Tarpenning had founded NuvoMedia in 1997 to create one of the earliest electronic book readers, called the Rocket eBook. The work at NuvoMedia had given the men insight into cutting-edge consumer electronics and the hugely improved lithium ion batteries used to power laptops and other portable devices. While the Rocket eBook was too far ahead of its time and not a major commercial success, it was innovative enough to attract the attention of Gemstar International Group, which owned TV Guide and some electronic programming guide technology. Gemstar paid $187 million to acquire NuvoMedia in March 2000. Spoils in hand, the cofounders stayed in touch after the deal. They both lived in Woodside, one of the wealthiest towns in Silicon Valley, and chatted from time to time about what they should tackle next. “We thought up some goofball things,” said Tarpenning. “There was one plan for these fancy irrigation systems for farms and the home based on smart water-sensing networks. But nothing really resonated, and we wanted something more important.” Eberhard was a supremely talented engineer with a do-gooder’s social conscience. The United States’ repeated conflicts in the Middle East bothered him, and like many other science-minded folks around 2000 he had started to accept global warming as a reality. Eberhard began looking for alternatives to gas-guzzling cars. He investigated the potential of hydrogen fuel cells but found them lacking. He also didn’t see much point in leasing something like the EV1 electric car from General Motors. What did catch Eberhard’s interest, however, were the all-electric cars from AC Propulsion that he spied on the Internet. Eberhard went down to Los Angeles around 2001 to visit the AC Propulsion shop. “The place looked like a ghost town and like they were going out of business,” Eberhard said. “I bailed them out with five hundred thousand dollars so that they could build one of their cars for me with lithium ion instead of lead acid batteries.” Eberhard too tried to goad AC Propulsion into being a commercial enterprise rather than a hobby shop. When they rejected his overtures, Eberhard decided to form his own company and see what the lithium ion batteries could really do. Eberhard’s journey began with him building a technical model of the electric car on a spreadsheet. This let him tweak various components and see how they might affect the vehicle’s shape and performance. He could adjust the weight, number of batteries, resistance of the tires and body, and then get back answers on how many batteries it would take to power the various designs. The models made it clear that SUVs, which were very popular at the time, and things like delivery trucks were unlikely candidates. The technology seemed instead to favor a lighter-weight, high-end sports car, which would be fast, fun to drive, and have far better range than most people would expect. These technical specifications complemented the findings of Tarpenning, who had been doing research into a financial model for the car. The Toyota Prius had started to take off in California, and it was being purchased by wealthy eco-crusaders. “We also learned that the average income for EV1 owners was around two hundred thousand dollars per year,” Tarpenning said. People who used to go after the Lexus, BMW, and Cadillac brands saw electric and hybrid cars as a different kind of status symbol. The men figured they could build something for the $3 billion per year luxury auto market in the United States that would let rich people have fun and feel good about themselves too. “People pay for cool and sexy and an amazing zero-to-sixty time,” Tarpenning said. On July 1, 2003, Eberhard and Tarpenning incorporated their new company. While at Disneyland a few months earlier on a date with his wife, Eberhard had come up with the name Tesla Motors, both to pay homage to the inventor and electric motor pioneer Nikola Tesla and because it sounded cool. The cofounders rented an office that had three desks and two small rooms in a decrepit 1960s building located at 845 Oak Grove Avenue in Menlo Park. The third desk was occupied a few months later by Ian Wright, an engineer who grew up on a farm in New Zealand. He was a neighbor of the Tesla cofounders in Woodside, and had been working with them to hone his pitch for a networking startup. When the start-up failed to raise any money from venture capitalists, Wright joined Tesla. As the three men began to tell some of their confidants of their plans, they were confronted with universal derision. “We met a friend at this Woodside pub to tell her what we had finally decided to do and that it was going to be an electric car,” Tarpenning said. “She said, ‘You have to be kidding me.’” Anyone who tries to build a car company in the United States is quickly reminded that the last successful start-up in the industry was Chrysler, founded in 1925. Designing and building a car from the ground up comes with plenty of challenges, but it’s really getting the money and know-how to build lots of cars that has thwarted past efforts to get a new company going. The Tesla founders were aware of these realities. They figured that Nikola Tesla had built an electric motor a century earlier and that creating a drivetrain to take the power from the motor and send it to the wheels was doable. The really frightening part of their enterprise would be building the factory to make the car and its associated parts. But the more the Tesla guys researched the industry, the more they realized that the big automakers don’t even really build their cars anymore. The days of Henry Ford having raw materials delivered to one end of his Michigan factory and then sending cars out the other end had long passed. “BMW didn’t make its windshields or upholstery or rearview mirrors,” Tarpenning said. “The only thing the big car companies had kept was internal combustion research, sales and marketing, and the final assembly. We thought naïvely that we could access all the same suppliers for our parts.” The plan the Tesla cofounders came up with was to license some technology from AC Propulsion around the tzero vehicle and to use the Lotus Elise chassis for the body of their car. Lotus, the English carmaker, had released the two-door Elise in 1996, and it certainly had the sleek, ground-hugging appeal to make a statement to high-end car buyers. After talking to a number of people in the car dealership business, the Tesla team decided to avoid selling their cars through partners and sell direct. With these basics of a plan in place, the three men went hunting for some venture capital funding in January 2004. To make things feel more real for the investors, the Tesla founders borrowed a tzero from AC Propulsion and drove it to the venture capital corridor of Sand Hill Road. The car accelerated faster than a Ferrari, and this translated into visceral excitement for the investors. The downside, though, was that venture capitalists are not a terribly imaginative bunch, and they struggled to see past the crappy plastic finish of this glorified kit car. The only venture capitalists that bit were Compass Technology Partners and SDL Ventures, and they didn’t sound altogether thrilled. The lead partner at Compass had made out well on NuvoMedia and felt some loyalty to Eberhard and Tarpenning. “He said, ‘This is stupid, but I have invested in every automotive start-up for the last forty years, so why not,’” Tarpenning recalled. Tesla still needed a lead investor who would pony up the bulk of the $7 million needed to make what’s known as a mule or a prototype vehicle. That would be their first milestone and give them something physical to show off, which could aid a second round of funding. Eberhard and Tarpenning had Elon Musk’s name in the back of their heads as a possible lead investor from the outset. They had both seen him speak a couple of years earlier at a Mars Society conference held at Stanford where Musk had laid out his vision of sending mice into space, and they got the impression that he thought a bit differently and would be open to the idea of an electric car. The idea to pitch Musk on Tesla Motors solidified when Tom Gage from AC Propulsion called Eberhard and told him that Musk was looking to fund something in the electric car arena. Eberhard and Wright flew down to Los Angeles and met with Musk on a Friday. That weekend, Musk peppered Tarpenning, who had been away on a trip, with questions about the financial model. “I just remember responding, responding, and responding,” Tarpenning said. “The following Monday, Martin and I flew down to meet him again, and he said, ‘Okay, I’m in.’” The Tesla founders felt like they had lucked into the perfect investor. Musk had the engineering smarts to know what they were building. He also shared their larger goal of trying to end the United States’ addiction to oil. “You need angel investors to have some belief, and it wasn’t a purely financial transaction for him,” Tarpenning said. “He wanted to change the energy equation of the country.” With an investment of $6.5 million, Musk had become the largest shareholder of Tesla and the chairman of the company. Musk would later wield his position of strength well while battling Eberhard for control of Tesla. “It was a mistake,” Eberhard said. “I wanted more investors. But, if I had to do it again, I would take his money. A bird in the hand, you know. We needed it.” Not long after this meeting took place, Musk called Straubel and urged him to meet with the Tesla team. Straubel heard that their offices in Menlo Park were about a half a mile from his house, and he was intrigued but very skeptical of their story. No one on the planet was more dialed into the electric vehicle scene than Straubel, and he found it hard to believe that a couple of guys had gotten this far along without word of their project reaching him. Nonetheless, Straubel stopped by the office for a meeting, and was hired right away in May 2004 at a salary of $95,000 per year. “I told them that I had been building the battery pack they need down the street with funding from Elon,” Straubel said. “We agreed to join forces and formed this ragtag group.” Had anyone from Detroit stopped by Tesla Motors at this point, they would have ended up in hysterics. The sum total of the company’s automotive expertise was that a couple of the guys at Tesla really liked cars and another one had created a series of science fair projects based on technology that the automotive industry considered ridiculous. What’s more, the founding team had no intention of turning to Detroit for advice on how to build a car company. No, Tesla would do what every other Silicon Valley start-up had done before it, which was hire a bunch of young, hungry engineers and figure things out as they went along. Never mind that the Bay Area had no real history of this model ever having worked for something like a car and that building a complex, physical object had little in common with writing a software application. What Tesla did have, ahead of anyone else, was the realization that 18650 lithium ion batteries had gotten really good and were going to keep getting better. Hopefully that coupled with some effort and smarts would be enough. Straubel had a direct pipeline into the smart, energetic engineers at Stanford and told them about Tesla. Gene Berdichevsky, one of the members of the solar-powered-car team, lit up the second he heard from Straubel. An undergraduate, Berdichevsky volunteered to quit school, work for free, and sweep the floors at Tesla if that’s what it took to get a job. The founders were impressed with his spirit and hired Berdichevsky after one meeting. This left Berdichevsky in the uncomfortable position of calling his Russian immigrant parents, a pair of nuclear submarine engineers, to tell them that he was giving up on Stanford to join an electric car start-up. As employee No. 7, he spent part of the workday in the Menlo Park office and the rest in Straubel’s living room designing three-dimensional models of the car’s powertrain on a computer and building battery pack prototypes in the garage. “Only now do I realize how insane it was,” Berdichevsky said. Tesla soon needed to expand to accommodate its budding engineer army and to create a workshop that would help bring the Roadster, as they were now calling the car, to life. They found a two-story industrial building in San Carlos at 1050 Commercial Street. The 10,000-square-foot facility wasn’t much, but it had room to build a research and development shop capable of knocking out some prototype cars. There were a couple of large assembly bays on the ride side of the building and two large rollup doors big enough for cars to drive in and out. Wright divided the open floor space into segments—motors, batteries, power electronics, and final assembly. The left half of the building was an office space that had been modified in weird ways by the previous tenant, a plumbing supply company. The main conference room had a wet bar and a sink where the faucet was a swan’s mouth, and the hot and cold knobs were wings. Berdichevsky painted the office white on a Sunday night, and the next week the employees made a field trip to IKEA to buy desks and hopped online to order their computers from Dell. As for tools, Tesla had a single Craftsman toolbox loaded with hammers, nails, and other carpentry basics. Musk would visit now and again from Los Angeles and was unfazed by the conditions, having seen SpaceX grow up in similar surroundings. The original plan for producing a prototype vehicle sounded simple. Tesla would take the AC Propulsion tzero powertrain and fit it into the Lotus Elise body. The company had acquired a schematic for an electric motor design and figured it could buy a transmission from a company in the United States or Europe and outsource any other parts from Asia. Tesla’s engineers mostly needed to focus on developing the battery pack systems, wiring the car, and cutting and welding metal as needed to bring everything together. Engineers love to muck around with hardware, and the Tesla team thought of the Roadster as something akin to a car conversion project that could be done with two or three mechanical engineers, and a few assembly people. The main team of prototype builders consisted of Straubel, Berdichevsky, and David Lyons, a very clever mechanical engineer and employee No. 12. Lyons had about a decade of experience working for Silicon Valley companies and had met Straubel a few years before when the two men struck up a conversation at a 7-Eleven about an electric bike Straubel was riding. Lyons had helped Straubel pay bills by hiring him as a consultant for a company building a device to measure people’s core body temperature. Straubel thought he could return the favor by bringing Lyons on early to such an exciting project. Tesla would benefit in a big way as well. As Berdichevsky put it, “Dave Lyons knew how to get shit done.” The engineers bought a blue lift for the car and set it up inside the building. They also purchased some machine tools, hand tools, and floodlights to work at night and started to turn the facility into a hotbed of R&D activity. Electrical engineers studied the Lotus’s base-level software to figure out how it tied together the pedals, mechanical apparatus, and the dashboard gauges. The really advanced work took place with the battery pack design. No one had ever tried to combine hundreds of lithium ion batteries in parallel, so Tesla ended up at the cutting edge of the technology. The engineers started trying to understand how heat would dissipate and current flow would behave across seventy batteries by supergluing them together into groups called bricks. Then ten bricks would be placed together, and the engineers would test various types of air and liquid cooling mechanisms. When the Tesla team had developed a workable battery pack, they stretched the yellow Lotus Elise chassis five inches and lowered the pack with a crane into the back of the car, where its engine would normally be. These efforts began in earnest on October 18, 2004, and, rather remarkably, four months later, on January 27, 2005, an entirely new kind of car had been built by eighteen people. It could even be driven around. Tesla had a board meeting that day, and Musk zipped about in the car. He came away happy enough to keep investing. Musk put in $9 million more as Tesla raised a $13 million funding round. The company now planned to deliver the Roadster to consumers in early 2006. Once they’d finished building a second car a few months later, the engineers at Tesla decided they needed to face up to a massive potential flaw in their electric vehicle. On July 4, 2005, they were at Eberhard’s house in Woodside celebrating Independence Day and figured it was as good a moment as any to see what happened when the Roadster’s batteries caught on fire. Someone taped twenty of the batteries together, put a heating strip wire into the bundle, and set it off. “It went up like a cluster of bottle rockets,” Lyons said. Instead of twenty batteries, the Roadster would have close to 7,000, and the thought of what an explosion at that scale would be like horrified the engineers. One of the perks of an electric car was meant to be that it moved people away from a flammable liquid like gasoline and the endless explosions that take place in an engine. Rich people were unlikely to pay a high price for something even more dangerous, and the early nightmare scenario for the employees at Tesla was that a rich, famous person would get caught in a fire caused by the car. “It was one of those ‘oh shit’ moments,” Lyons said. “That is when we really sobered up.” Tesla formed a six-person task force to deal with the battery issue. They were pulled off all other work and given money to begin running experiments. The first explosions started taking place at the Tesla headquarters, where the engineers filmed them in slow motion. Once saner minds prevailed, Tesla moved its explosion research to a blast area behind an electrical substation maintained by the fire department. Blast by blast, the engineers learned a great deal about the inner workings of the batteries. They developed methods for arranging them in ways that would prevent fires spreading from one battery to the next and other techniques for stopping explosions altogether. Thousands of batteries exploded along the way, and the effort was worth it. It was still early days, for sure, but Tesla was on the verge of inventing battery technology that would set it apart from rivals for years to come and would become one of the company’s great advantages. The early success at building two prototype cars, coupled with Tesla’s engineering breakthroughs around the batteries and other technological pieces, boosted the company’s confidence. It was time to put Tesla’s stamp on the vehicle. “The original plan had been to do the bare minimum we could get away with as far as making the car stylistically different from a Lotus but electric,” said Tarpenning. “Along the way, Elon and the rest of the board said, ‘You only get to do this once. It has to delight the customer, and the Lotus just isn’t good enough to do that.’” The Elise’s chassis, or base frame, worked fine for Tesla’s engineering purposes. But the body of the car had serious issues in both form and function. The door on the Elise was all of a foot tall, and you were meant to either jump into the car or fall into it, depending on your flexibility and/or dignity. The body also needed to be longer to accommodate Tesla’s battery pack and a trunk. And Tesla preferred to make the Roadster out of carbon fiber instead of fiberglass. On these design points, Musk had a lot of opinion and influence. He wanted a car that Justine could feel comfortable getting into and that had some measure of practicality. Musk made these opinions clear when he visited Tesla for board meetings and design reviews. Tesla hired a handful of designers to mock up new looks for the Roadster. After settling on a favorite, the company paid to build a quarter-scale model of the vehicle in January 2005 and then a full-scale model in April. This process provided the Tesla executives with yet another revelation of everything that went into making a car. “They wrap this shiny Mylar material around the model and vacuum it, so that you can really see the contours and shine and shadows,” Tarpenning said. The silver model was then turned into a digital rendering that the engineers could manipulate on their computers. A British company took the digital file and used it to create a plastic version of the car called an “aero buck” for aerodynamics testing. “They put it on a boat and shipped it to us, and then we took it to Burning Man,” Tarpenning said, referring to the annual drug-infused art festival held in the Nevada desert. About a year later, after many tweaks and much work, Tesla had a pencils-down moment. It was May 2006, and the company had grown to a hundred employees. This team built a black version of the Roadster known as EP1, or engineering prototype one. “It was saying, ‘We now think we know what we will build,’” Tarpenning said. “You can feel it. It’s a real car, and it’s very exciting.” The arrival of the EP1 provided a great excuse to show existing investors what their money had bought and to ask for more funds from a wider audience. The venture capitalists were impressed enough to overlook the fact that engineers sometimes had to manually fan the car to cool it down in between test drives and were now starting to grasp Tesla’s long-term potential. Musk once again put money into Tesla—$12 million—and a handful of other investors, including the venture capital firm Draper Fisher Jurvetson, VantagePoint Capital Partners, J.P. Morgan, Compass Technology Partners, Nick Pritzker, Larry Page, and Sergey Brin, joined the $40 million round. /In a press release announcing the funding round, Musk was not listed as a founder of the company. In the “About Tesla Motors” section, the company stated, “Tesla Motors was founded in June 2003 by Martin Eberhard and Marc Tarpenning to create efficient electric cars for people who love to drive.” Musk and Eberhard would later spar over Musk’s founder status./ In July 2006, Tesla decided to tell the world what it had been up to. The company’s engineers had built a red prototype—EP2—to complement the black one, and they both went on display at an event in Santa Clara. The press flocked to the announcement and were quite taken with what they saw. The Roadsters were gorgeous, two-seater convertibles that could go from zero to 60 in about four seconds. “Until today,” Musk said at the event, “all electric cars have sucked.” [http://news.cnet.com/Electric-sports-car-packs-a-punch%2C-but-will-it-sell/2100-11389_3-6096377.xhtml] Celebrities like then-governor Arnold Schwarzenegger and former Disney CEO Michael Eisner showed up at the event, and many of them took test rides in the Roadsters. The vehicles were so fragile that only Straubel and a couple of other trusted hands knew how to run them, and they were swapped out every five minutes to avoid overheating. Tesla revealed that each car would cost about $90,000 and had a range of 250 miles per charge. Thirty people, the company said, had committed to buying a Roadster, including the Google cofounders Brin and Page and a handful of other technology billionaires. Musk promised that a cheaper car—a four-seat, four-door model under $50,000, would arrive in about three years. Around the time of this event, Tesla made its debut in the New York Times via a mini-profile on the company. Eberhard vowed—optimistically—to begin shipments of the Roadster in the middle of 2007, instead of early 2006 as once planned, and laid out Tesla’s strategy of starting with a high-priced, low-volume product and moving down to more affordable products over time, as underlying technology and manufacturing capabilities advanced. Musk and Eberhard were big believers in this strategy, having seen it play out with a number of electronic devices. “Cellphones, refrigerators, color TV’s, they didn’t start off by making a low-end product for masses,” Eberhard told the paper. [http://www.nytimes.com/2006/07/19/business/19electric.xhtml] “They were relatively expensive, for people who could afford it.” While the story was a coup for Tesla, Musk didn’t appreciate being left out of the article entirely. “We tried to emphasize him, and told the reporter about him over and over again, but they weren’t interested in the board of the company,” Tarpenning said. “Elon was furious. He was livid.” You could understand why Musk might want some of the shine of Tesla to rub off on him. The car had turned into a cause célèbre of the automotive world. Electric vehicles tended to invoke religious overreactions from both the pro and con camps, and the appearance of a good-looking, fast electric car stoked everyone’s passions. Tesla had also turned Silicon Valley into a real threat, at least conceptually, to Detroit for the first time. The month after the Santa Monica event was the Pebble Beach Concours d’Elegance, a famous showcase for exotic cars. Tesla had become such a topic of conversation that the organizers of the event begged to have a Roadster and waived the usual display fees. Tesla set up a booth, and people showed up by the dozens writing $100,000 checks on the spot to pre-order their cars. “This was long before Kickstarter, and we just had not thought of trying to do that,” Tarpenning said. “But then we started getting millions of dollars at these types of events.” Venture capitalists, celebrities, and friends of Tesla employees began trying to buy their way onto the waiting list. Some of Silicon Valley’s wealthy elite went so far as to show up at the Tesla office and knock on the door, looking to buy a car. The entrepreneurs Konstantin Othmer and Bruce Leak, who had known Musk from his internship days at Rocket Science Games, did just that one weekday and ended up getting a personal tour of the car from Musk and Eberhard that stretched over a couple of hours. “At the end we said, ‘We’ll take one,’” Othmer said. “They weren’t actually allowed to sell cars yet, though, so we joined their club. It cost one hundred thousand dollars, but one of the benefits of membership was that you’d get a free car.” As Tesla switched from marketing back into R&D mode, it had some trends working in its favor. Advances in computing had made it so that small car companies could sometimes punch at the same weight as the giants of the industry. Years ago, automakers would have needed to make a fleet of cars for crash testing. Tesla could not afford to do that, and it didn’t have to. The third Roadster engineering prototype went to the same collision testing facility used by large automakers, giving Tesla access to top-of-the-line high-speed cameras and other imaging technology. Thousands of other tests, though, were done by a third party that specialized in computer simulations and saved Tesla from building a fleet of crash vehicles. Tesla also had equal access to the big guys’ durability tracks made out of cobblestones and concrete embedded with metal objects. It could replicate 100,000 miles and ten years of wear at these facilities. Quite often, the Tesla engineers brought their Silicon Valley attitude to the automakers’ traditional stomping grounds. There’s a break and traction testing track in northern Sweden near the Arctic Circle where cars get tuned on large plains of ice. It would be standard to run the car for three days or so, get the data, and return to company headquarters for many weeks of meetings about how to adjust the car. The whole process of tuning a car can take the entire winter. Tesla, by contrast, sent its engineers along with the Roadsters being tested and had them analyze the data on the spot. When something needed to be tweaked, the engineers would rewrite some code and send the car back on the ice. “BMW would need to have a confab between three or four companies that would all blame each other for the problem,” Tarpenning said. “We just fixed it ourselves.” Another testing procedure required that the Roadsters go into a special cooling chamber to check how they would respond to frigid temperatures. Not wanting to pay the exorbitant costs to use one of these chambers, the Tesla engineers opted to rent an ice cream delivery truck with a large refrigerated trailer. Someone would drive a Roadster into the truck, and the engineers would don parkas and work on the car. Every time Tesla interacted with Detroit it received a reminder of how the once-great city had been separated from its own can-do culture. Tesla tried to lease a small office in Detroit. The costs were incredibly low compared with space in Silicon Valley, but the city’s bureaucracy made getting just a basic office an ordeal. The building’s owner wanted to see seven years of audited financials from Tesla, which was still a private company. Then the building owner wanted two years’ worth of advanced rent. Tesla had about $50 million in the bank and could have bought the building outright. “In Silicon Valley, you say you’re backed by a venture capitalist, and that’s the end of the negotiation,” Tarpenning said. “But everything was like that in Detroit. We’d get FedEx boxes, and they couldn’t even decide who should sign for the package.” Throughout these early years, the engineers credited Eberhard with making quick, crisp decisions. Rarely did Tesla get hung up overanalyzing a situation. The company would pick a plan of attack, and when it failed at something, it failed fast and then tried a new approach. It was many of the changes that Musk wanted that started to delay the Roadster. Musk kept pushing for the car to be more comfortable, asking for alterations to the seats and the doors. He made the carbon-fiber body a priority, and he pushed for electronic sensors on the doors so that the Roadster could be unlocked with the touch of a finger instead of a tug on a handle. Eberhard groused that these features were slowing the company down, and many of the engineers agreed. “It felt at times like Elon was this unreasonably demanding overarching force,” said Berdichevsky. “The company as a whole was sympathetic to Martin because he was there all the time, and we all felt the car should ship sooner.” By the middle of 2007, Tesla had grown to 260 employees and seemed to be pulling off the impossible. It had produced the fastest, most beautiful electric car the world had ever seen almost from thin air. All it had to do next was build a lot of the cars—a process that would end up almost bankrupting the company. The greatest mistake Tesla’s executives made in the early days were assumptions around the transmission system for the Roadster. The goal had always been to get from zero to 60 mph as quickly as possible in the hopes that the raw speed of the Roadster would attract a lot of attention and make it fun to drive. To do this, Tesla’s engineers had decided on a two-speed transmission, which is the underlying mechanism in the car for transferring power from the motor to the wheels. The first gear would take the car from zero to 60 mph in less than four seconds, and then the second gear would take the car up to 130 mph. Tesla had hired Xtrac, a British company specializing in transmission designs, to build this part and had every reason to believe that this would be one of the smoother bits of the Roadster’s journey. “People had been making transmissions since Robert Fulton built the steam engine,” said Bill Currie, [A southern gentleman, Currie could never get used to Musk’s swearing—“he curses like a sailor and does it in mixed company”—or the way he would churn through prized talent. “He’d search through the woods, turn over every rock and dig through brambles to find the one person with the specific expertise and skill he wanted,” Currie said. “Then, that guy would be gone three months to a year later if he didn’t agree with Elon.” Currie, though, remembers Musk as inspirational. Even as Tesla’s funds dwindled, Musk urged the employees to do their jobs well and vowed to give them what they needed to be successful. Currie, like many people, also found Musk’s work ethic astonishing. “I would be in Europe or China and send him an email at two thirty in the morning his time,” Currie said. “Five minutes later, I’d get an answer back. It’s just unbelievable to have support on that level.”] a veteran Silicon Valley engineer and employee No. 86 at Tesla. “We thought you would just order one. But the first one we had lasted forty seconds.” The initial transmission could not handle the big jump from the first to the second gear, and the fear was that the second gear would engage at high speed and not be synchronized with the motor properly, which would result in catastrophic damage to the car. Lyons and the other engineers quickly set out to try to fix the issue. They found a couple of other contractors to design replacements and again hoped that these longtime transmission experts would deliver something usable with relative ease. It soon became apparent, however, that the contractors were not always putting their A team to work on this project for a tiny start-up in Silicon Valley and that the new transmissions were no better than the first. During tests, Tesla found that the transmissions would sometimes break after 150 miles and that the mean time between failures was about 2,000 miles. When a team from Detroit ran a root cause analysis of the transmission to find failures, they discovered fourteen separate issues that could cause the system to break. Tesla had wanted to deliver the Roadster in November 2007, but the transmission issues lingered, and by the time January 1, 2008, rolled around, the company had to once again start from scratch, on a third transmission push. Tesla also faced issues abroad. The company had decided to send a team of its youngest, most energetic engineers to Thailand to set up a battery factory. Tesla partnered with an enthusiastic although not totally capable manufacturing partner. The Tesla engineers had been told that they could fly over and manage the construction of a state-of-the-art battery factory. Instead of a factory, they found a concrete slab with posts holding up a roof. The building was about a three-hour drive south from Bangkok, and had been left mostly open like many of the other factories because of the incredible heat. The other manufacturing operations dealt with making stoves, tires, and commodities that could withstand the elements. Tesla had sensitive batteries and electronics, and like parts of the Falcon 1, they’d be chewed up by the salty, humid conditions. Eventually, Tesla’s partner paid about $75,000 to put in drywall, coat the floor, and create storage rooms with temperature controls. Tesla’s engineers ended up working maddening hours trying to train the Thai workers on how to handle the electronics properly. The development of the battery technology, which had once moved along at a rapid pace, slowed to a crawl. The battery factory was one part of a supply chain that stretched across the globe, adding cost and delays to the Roadster production. Body panels for the car were to be made in France, while the motors were to come from Taiwan. Tesla planned on buying battery cells in China and shipping them to Thailand to turn the piece parts into battery packs. The battery packs, which had to be stored for a minimal amount of time to avoid degradation, would then be taken to port and shipped to England, where they needed to clear customs. Tesla then planned for Lotus to build the body of the car, attach the battery packs, and ship the Roadsters by boat around Cape Horn to Los Angeles. In that scenario, Tesla would have paid for the bulk of the car and had no chance to recognize revenue on the parts until six to nine months had passed. “The idea was to get to Asia, get things done fast and cheap, and make money on the car,” said Forrest North, one of the engineers sent to Thailand. “What we found out was that for really complicated things, you can do the work cheaper here and have less delays and less problems.” When some new hires came on, they were horrified to discover just how haphazard Tesla’s plan appeared. Ryan Popple, who had spent four years in the army and then gotten an MBA from Harvard, arrived at Tesla as a director of finance meant to prep the company to go public. After examining the company’s books early in his tenure, Popple asked the manufacturing and operations head exactly how he would get the car made. “He said, ‘Well, we will decide we’re going into production and then a miracle is going to happen,’” Popple said. As word of the manufacturing issues reached Musk, he became very concerned about the way Eberhard had run the company and called in a fixer to address the situation. One of Tesla’s investors was Valor Equity, a Chicago-based investment firm that specialized in fine-tuning manufacturing operations. The company had been drawn to Tesla’s battery and powertrain technology and calculated that even if Tesla failed to sell many cars, the big automakers would end up wanting to buy its intellectual property. To protect its investment, Valor sent in Tim Watkins, its managing director of operations, and he soon reached some horrific conclusions. Watkins is a Brit with degrees in industrial robotics and electrical engineering. He’s built up a reputation as an ingenious solver of problems. While doing work in Switzerland, for example, Watkins found a way to get around the country’s rigid labor laws that limit the hours employees can work, by automating a metal stamping factory so that it could run twenty-four hours per day instead of sixteen hours like the factories or rivals. Watkins is also known for keeping his ponytail in place with a black scrunchie, wearing a black leather jacket, and toting a black fanny pack everywhere he goes. The fanny pack has his passport, checkbook, earplugs, sunscreen, food, and an assortment of other necessities. “It’s full of the everyday things I need to survive,” said Watkins. “If I walk ten feet away from this thing, I sense it.” While a bit eccentric, Watkins was thorough and spent weeks talking to employees and analyzing every part of Tesla’s supply chain to figure out how much it cost to make the Roadster. Tesla had done a decent job of keeping its employee costs down. It hired the kid fresh out of Stanford for $45,000 rather than the proven guy who probably didn’t want to work that hard anyway for $120,000. But when it came to equipment and materials, Tesla was a spending horror show. No one liked using the company’s software that tracked the bill of materials. So some people used it, and some people didn’t. Those that did use it often made huge errors. They would take the cost of a part from the prototype cars and then estimate how much of a discount they expected when buying that part in bulk, rather than actually negotiating to find a viable price. At one point, the software declared that each Roadster should cost about $68,000, which would leave Tesla making about $30,000 per vehicle. Everyone knew the figure was wrong, but it got reported to the board anyway. Around the middle of 2007, Watkins came to Musk with his findings. Musk was prepared for a high figure but felt confident that the price of the car would come down significantly over time as Tesla ironed out its manufacturing process and increased its sales. “That’s when Tim told me it was really bad news,” Musk said. It looked like each Roadster could cost up to $200,000 to make, and Tesla planned to sell the car for only around $85,000. “Even in full production, they would have been like $170,000 or something insane,” Musk said. “Of course, it didn’t much matter because about a third of the cars didn’t flat-out fucking work.” Eberhard made attempts to pull his team out of this mess. He’d gone to see a speech in which the famous venture capitalist John Doerr, who became a major investor in green technology companies, declared that he would devote his time and money to trying to save the Earth from global warming because he owed such an effort to his children. Eberhard promptly returned to the Tesla building and ginned up a similar speech. In front of about a hundred people, Eberhard had a picture of his young daughter projected onto the wall of the main workshop. He asked the Tesla engineers why he had put that picture up. One of them guessed that it was because people like his daughter would drive the car. To which Eberhard replied, “No. We are building this because by the time she is old enough to drive she will know a car as something completely different to how we know it today, just like you don’t think of a phone as a thing on the wall with a cord on it. It’s this future that depends on you.” Eberhard then thanked some of the key engineers and called out their efforts in public. Many of the engineers had been pulling all-nighters on a regular basis and Eberhard’s show boosted morale. “We were all working ourselves to the point of exhaustion,” said David Vespremi, a former Tesla spokesman. “Then came this profound moment where we were reminded that building the car was not about getting to an IPO or selling it to a bunch of rich dudes but because it might change what a car is.” These victories, though, were not enough to overcome the feeling shared by many of the Tesla engineers that Eberhard had reached the end of his abilities as a CEO. The company veterans had always admired Eberhard’s engineering smarts and continued to do so. Eberhard, in fact, had turned Tesla into a cult of engineering. Regrettably, other parts of the company had been neglected, and people doubted Eberhard’s ability to take the company from the R&D stage to production. The ridiculous cost of the car, the transmission, the ineffective suppliers were crippling Tesla. And, as the company started to miss its delivery dates, many of the once-fanatical consumers who had made their large up-front payments turned on Tesla and Eberhard. “We saw the writing on the wall,” Lyons said. “Everyone knew that the person who starts a company is not necessarily the right person to lead it in the long term, but whenever that is the case, it’s not easy.” Eberhard and Musk had battled for years over some of the design points on the car. But for the most part, they had gotten along well enough. Neither man suffered fools. And they certainly shared many of the same visions for the battery technology and what it could mean to the world. What their relationship could not survive were the cost figures for the Roadster unearthed by Watkins. It looked to Musk as if Eberhard had grossly mismanaged the company by allowing the parts costs to soar so high. Then, as Musk saw it, Eberhard failed to disclose the severity of the situation to the board. While on his way to give a talk to the Motor Press Guild in Los Angeles, Eberhard received a call from Musk and in a brief, uncomfortable chat learned that he would be replaced as CEO. In August 2007, Tesla’s board demoted Eberhard and named him president of technology, which only exacerbated the company’s issues. “Martin was so bitter and disruptive,” Straubel said. “I remember him running around the office and sowing discontent, as we’re trying to finish the car and are running out of money and everything is at knife’s edge.” As Eberhard saw it, other people at Tesla had foisted a wonky finance software application on him that made it tricky to accurately track costs. He contended that the delays and cost increases were partly due to the requests of other members of the management team and that he’d been up front with the board about the issues. Beyond that, he thought Watkins had made the situation out to be worse than it really was. Start-ups in Silicon Valley view mayhem as standard operating procedure. “Valor was used to dealing with older companies,” Eberhard said. “They found chaos and weren’t used to it. This was the chaos of a start-up.” Eberhard had also already been asking Tesla’s board to replace him as CEO and find someone with more manufacturing experience. A few months passed, and Eberhard remained pissed-off. Many of the Tesla employees felt like they were caught in the middle of a divorce and had to pick their parent—Eberhard or Musk. By the time December arrived, the situation was untenable, and Eberhard left the company altogether. Tesla said in a statement that Eberhard had been offered a position on its advisory board, although he denied that. “I am no longer with Tesla Motors—neither on its board of directors nor an employee of any sort,” Eberhard said in a statement at the time. “I’m not happy with the way I was treated.” Musk sent a note to a Silicon Valley newspaper saying, “I’m sorry that it came to this and wish it were not so. It was not a question of personality differences, as the decision to have Martin transition to an advisory role was unanimous among the board. Tesla has operational problems that need to be solved and if the board thought there was any way that Martin could be part of the solution, then he would still be an employee of the company.” [http://www.mercurynews.com/greenenergy/ci_7641424] These statements were the start of a war that would drag on between the two men in public for years and that in many ways continues to the present day. As 2007 played out, the problems mounted for Tesla. The carbon-fiber body that looked so good turned out to be a huge pain to paint, and Tesla had to cycle through a couple of companies to find one that could do the work well. Sometimes there were faults in the battery pack. The motor short-circuited now and again. The body panels had visible gaps. The company also had to face up to the reality that a two-speed transmission was not going to happen. In order for the Roadster to achieve its flashy zero-to-60 times with a single-speed transmission, Tesla’s engineers had to redesign the car’s motor and inverter and shave off some weight. “We essentially had to do a complete reboot,” Musk said. “That was terrible.” After Eberhard was removed as CEO, Tesla’s board tapped Michael Marks as its interim chief. Marks had run Flextronics, an enormous electronics supplier, and had deep experience with complex manufacturing operations and logistics issues. Marks began interrogating various groups at the company to try to figure out their problems and to prioritize the issues plaguing the Roadster. He also put in some basic rules like making sure that people all showed up at work at the same time to establish a baseline of productivity—a tricky ask in Silicon Valley’s work anywhere, anytime culture. All of these moves were part of the Marks List, a 10-point, 100-day plan that included eliminating all faults in the battery packs, getting gaps between body parts to less than 40 mm, and booking a specified number of reservations. “Martin had been falling apart and lacked a lot of the discipline key for a manager,” Straubel said. “Michael came in and evaluated the mess and was a bullshit filter. He didn’t really have a dog in the fight and could say, ‘I don’t care what you think or what you think. This is what we should do.’” For a while, Marks’s strategy worked, and the engineers at Tesla could once again focus on building the Roadster rather than on internal politics. But then Marks’s vision for the company began to diverge from Musk’s. By this time, Tesla had moved into a larger facility at 1050 Bing Street in San Carlos. The bigger building allowed Tesla to bring the battery work back in-house from Asia and for it to do some of the Roadster manufacturing, alleviating the supply chain issues. Tesla was maturing as a car company, although its wild-child start-up streak remained well intact. While strolling around the factory one day, Marks saw a Smart car from Daimler on a lift. Musk and Straubel had a small side project going on around the Smart car to see what it might be like as an electric vehicle. “Michael didn’t know about it, and he’s like, ‘Who is the CEO here?’” said Lyons. (The work on the Smart car eventually led to Daimler buying a 10 percent stake in Tesla.) Marks’s inclination was to try to package Tesla as an asset that could be sold to a larger car company. It was a perfectly reasonable plan. While running Flextronics, Marks had overseen a vast, global supply chain and knew the difficulties of manufacturing intimately. Tesla must have looked borderline hopeless to him at this point. The company could not make its one product well, was poised to hemorrhage money, and had missed a string of delivery deadlines and yet its engineers were still off doing side experiments. Making Tesla look as pretty as possible for a suitor was the rational thing to do. In just about every other case, Marks would be thanked for his decisive plan of action and saving the company’s investors from a big loss. But Musk had little interest in polishing up Tesla’s assets for the highest bidder. He’d started the company to put a dent in the automotive industry and force people to rethink electric cars. Instead of doing the fashionable Silicon Valley thing of “pivoting” toward a new idea or plan, Musk would dig in deeper. “The product was late and over budget and everything was wrong, but Elon didn’t want anything to do with those plans to either sell the whole company or lose control through a partnership,” Straubel said. “So, Elon decided to double down.” On December 3, 2007, Ze’ev Drori replaced Marks as CEO. Drori had experience in Silicon Valley starting a company that made computer memory and selling it to the chipmaker Advanced Micro Devices. Drori was not Musk’s first pick—a top choice had turned down the job because he didn’t want to move from the East Coast—and did not inspire much enthusiasm from the Tesla employees. Drori had about fifteen years on the youngest Tesla worker and no connection to this group bonded by suffering and toil. He came to be seen more as an executor of Musk’s wishes than as a commanding, independent CEO. Musk began making more public gestures to mitigate the bad press around Tesla. He issued statements and did interviews, promising that the Roadster would ship to customers in early 2008. He began talking up a car code-named WhiteStar—the Roadster had been code-named DarkStar—that would be a sedan possibly priced around $50,000, and a new factory to build the machine. “Given the recent management changes, some reassurances are in order regarding Tesla Motors’ future plans,” Musk wrote in a blog post. “The near term message is simple and unequivocal—we are going to deliver a great sports car next year that customers will love driving. . . . My car, production VIN 1, is already off the production line in the UK and final preparations are being made for importation.” Tesla held a series of town hall meetings with customers where it tried to fess up to its problems in the open, and it started building some showrooms for its car. Vince Sollitto, the former PayPal executive, visited the Menlo Park showroom and found Musk complaining about the public relations issues but clearly inspired by the product Tesla was building. “His demeanor changed the moment we got to this display of the motor,” Sollitto said. Dressed in a leather jacket and slacks, Musk started talking about the motor’s properties and then put on a performance worthy of a carnival strongman by lifting the hundred-or-so-pound hunk of metal. “He picks this thing up and wedges it between his two palms,” Sollitto said. “He’s holding it, and he’s shaking and beads of sweat are forming on his forehead. It wasn’t so much a display of strength as a physical demonstration of the beauty of the product.” While the customers complained a lot about the delays, they seemed to sense this passion from Musk and share his enthusiasm for the product. Only a handful of customers asked for their prepayments back. Tesla employees soon got to witness the same Musk that SpaceX employees had seen for years. When an issue like the Roadster’s faulty carbon-fiber body panels cropped up, Musk dealt with it directly. He flew to England in his jet to pick up some new manufacturing tools for the body panels and personally delivered them to a factory in France to ensure that the Roadster stayed on its production schedule. The days of people being ambiguous about the Roadster’s manufacturing costs were gone as well. “Elon got fired up and said we were going to do this intense cost-down program,” said Popple. “He gave a speech, saying we would work on Saturdays and Sundays and sleep under desks until it got done. Someone pushed back from the table and argued that everyone had been working so hard just to get the car done, and they were ready for a break and to see their families. Elon said, ‘I would tell those people they will get to see their families a lot when we go bankrupt.’ I was like, ‘Wow,’ but I got it. I had come out of a military culture, and you just have to make your objective happen.” Employees were required to meet at 7 A.M. every Thursday morning for bill-of-materials updates. They had to know the price of every part and have a cogent plan for getting parts cheaper. If the motor cost $6,500 a pop at the end of December, Musk wanted it to cost $3,800 by April. The costs were plotted and analyzed each month. “If you started falling behind, there was hell to pay,” Popple said. “Everyone could see it, and people lost their jobs when they didn’t deliver. Elon has a mind that’s a bit like a calculator. If you put a number on the projector that does not make sense, he will spot it. He doesn’t miss details.” Popple found Musk’s style aggressive, but he liked that Musk would listen to a well-argued, analytical point and often change his mind if given a good enough reason. “Some people thought Elon was too tough or hot-tempered or tyrannical,” Popple said. “But these were hard times, and those of us close to the operational realities of the company knew it. I appreciated that he didn’t sugarcoat things.” On the marketing front, Musk would run daily Google searches for news stories about Tesla. If he saw a bad story, he ordered someone to “fix it” even though the Tesla public relations people could do little to sway the reporters. One employee missed an event to witness the birth of his child. Musk fired off an e-mail saying, “That is no excuse. I am extremely disappointed. You need to figure out where your priorities are. We’re changing the world and changing history, and you either commit or you don’t.” /This was how the employee remembered the text. I did not see the actual e-mail. Musk later told the same employee, “I want you to think ahead and think so hard every day that your head hurts. I want your head to hurt every night when you go to bed.”/ Marketing people who made grammatical mistakes in e-mails were let go, as were other people who hadn’t done anything “awesome” in recent memory. “He can be incredibly intimidating at times but doesn’t have a real sense for just how imposing he can be,” said one former Tesla executive. “We’d have these meetings and take bets on who was going to get bloodied and bruised. If you told him that you made a particular choice because ‘it was the standard way things had always been done,’ he’d kick you out of a meeting fast. He’d say, ‘I never want to hear that phrase again. What we have to do is fucking hard and half-assing things won’t be tolerated.’ He just destroys you and, if you survive, he determines if he can trust you. He has to understand that you’re as crazy as he is.” This ethos filtered through the entire company, and everyone quickly understood that Musk meant business. Straubel, while sometimes on the bad end of the critiques, welcomed Musk’s hard-charging presence. The five years to get to this point had been an enjoyable slog for him. Straubel had transformed from a quiet, capable engineer who shuffled around Tesla’s factory floor with his head down into the most crucial member of the technical team. He knew more about the batteries and the electric drivetrain than just about anyone else at the company. He also began developing a role as a go-between for employees and Musk. Straubel’s engineering smarts and work ethic had earned Musk’s respect, and Straubel found that he could deliver difficult messages to Musk on behalf of other employees. As he would do for years to come, Straubel also proved willing to check his ego at the door. All that mattered was getting the Roadster and the follow-on sedan to market to popularize electric cars, and Musk looked like the best person to make that happen. Other employees had enjoyed the thrill of the engineering challenge over the past five years but were burnt-out beyond repair. Wright didn’t believe that an electric car for the masses would ever take off. He left and started his own company dedicated to making electric versions of delivery trucks. Berdichevsky had been a crucial, do-anything young engineer for much of Tesla’s existence. Now that the company employed about three hundred people, he felt less effective and didn’t relish the idea of suffering for another five years to bring the sedan to market. He would leave Tesla, get a couple of degrees from Stanford, and cofound a start-up looking to make a revolutionary new battery that could soon go into electric cars. With Eberhard gone, Tarpenning found Tesla less fun. He didn’t see eye to eye with Drori and also shied away from the idea of frying his soul to get the sedan out. Lyons stuck around longer, which is a minor miracle. At various points, he had led the development of most of the core technology behind the Roadster, including the battery packs, the motor, the power electronics, and, yes, the transmission. This meant that for about five years Lyons had been among Tesla’s most capable employees and the guy constantly in the doghouse for being behind on something and thus holding the rest of the company up. He suffered through some of Musk’s more colorful tirades—directed either at him or suppliers that had let Tesla down—that included talk of people’s balls being chopped off and other violent or sexual acts. Lyons also saw an exhausted, stressed-out Musk spit coffee across a conference room table because it was cold and then, without a pause, demand that the employees work harder, do more, and mess up less. Like so many people privy to these performances, Lyons came away with no illusions about Musk’s personality but with the utmost respect for his vision and drive to execute. “Working at Tesla back then was like being Kurtz in Apocalypse Now,” Lyons said. “Don’t worry about the methods or if they’re unsound. Just get the job done. It comes from Elon. He listens, asks good questions, is fast on his feet, and gets to the bottom of things.” Tesla could survive the loss of some of these early hires. Its strong brand had allowed the company to keep recruiting top talent, including people from large automotive companies who knew how to get over the last set of challenges blocking the Roadster from reaching customers. But Tesla’s major issue no longer revolved around effort, engineering, or clever marketing. Heading into 2008, the company was running out of money. The Roadster had cost about $140 million to develop, way over the $25 million originally estimated in the 2004 business plan. Under normal circumstances, Tesla had probably done enough to raise more funds. These, however, were not normal times. The big automakers in the United States were charging toward bankruptcy in the middle of the worst financial crisis since the Great Depression. In the midst of all this, Musk needed to convince Tesla’s investors to fork over tens of millions of additional dollars, and those investors had to go to their constituents to lay out why this made any sense. As Musk put it, “Try to imagine explaining that you’re investing in an electric car company, and everything you read about the car company sounds like it is shit and doomed and it’s a recession and no one is buying cars.” All Musk had to do to dig Tesla out of this conundrum was lose his entire fortune and verge on a nervous breakdown.
AS HE PREPARED TO BEGIN FILMING IRON MAN IN EARLY 2007, the director Jon Favreau rented out a complex in Los Angeles that once belonged to Hughes Aircraft, the aerospace and defense contractor started about eighty years earlier by Howard Hughes. The facility had a series of interlocking hangars and served as a production office for the movie. It also supplied Robert Downey Jr., who was to play Iron Man and his human creator Tony Stark, with a splash of inspiration. Downey felt nostalgic looking at one of the larger hangars, which had fallen into a state of disrepair. Not too long ago, that building had played host to the big ideas of a big man who shook up industries and did things his own way. Downey heard some rumblings about a Hughes-like figure named Elon Musk who had constructed his own, modern-day industrial complex about ten miles away. Instead of visualizing how life might have been for Hughes, Downey could perhaps get a taste of the real thing. He set off in March 2007 for SpaceX’s headquarters in El Segundo and wound up receiving a personal tour from Musk. “My mind is not easily blown, but this place and this guy were amazing,” Downey said. To Downey, the SpaceX facility looked like a giant, exotic hardware store. Enthusiastic employees were zipping about, fiddling with an assortment of machines. Young white-collar engineers interacted with blue-collar assembly line workers, and they all seemed to share a genuine excitement for what they were doing. “It felt like a radical start-up company,” Downey said. After the initial tour, Downey came away pleased that the sets being hammered out at the Hughes factory did have parallels to the SpaceX factory. “Things didn’t feel out of place,” he said. Beyond the surroundings, Downey really wanted a peek inside Musk’s psyche. The men walked, sat in Musk’s office, and had lunch. Downey appreciated that Musk was not a foul-smelling, fidgety, coder whack job. What Downey picked up on instead were Musk’s “accessible eccentricities” and the feeling that he was an unpretentious sort who could work alongside the people in the factory. Both Musk and Stark were the type of men, according to Downey, who “had seized an idea to live by and something to dedicate themselves to” and were not going to waste a moment. When he returned to the Iron Man production office, Downey asked that Favreau be sure to place a Tesla Roadster in Tony Stark’s workshop. On a superficial level, this would symbolize that Stark was so cool and connected that he could get a Roadster before it even went on sale. On a deeper level, the car was to be placed as the nearest object to Stark’s desk so that it formed something of a bond between the actor, the character, and Musk. “After meeting Elon and making him real to me, I felt like having his presence in the workshop,” Downey said. “They became contemporaries. Elon was someone Tony probably hung out with and partied with or more likely they went on some weird jungle trek together to drink concoctions with the shamans.” After Iron Man came out, Favreau began talking up Musk’s role as the inspiration for Downey’s interpretation of Tony Stark. It was a stretch on many levels. Musk is not exactly the type of guy who downs scotch in the back of a Humvee while part of a military convoy in Afghanistan. But the press lapped up the comparison, and Musk started to become more of a public figure. People who sort of knew him as “that PayPal guy” began to think of him as the rich, eccentric businessman behind SpaceX and Tesla. Musk enjoyed his rising profile. It fed his ego and provided some fun. He and Justine bought a house in Bel Air. Their neighbor to one side was Quincy Jones, the music producer, and their other neighbor was Joe Francis, the infamous creator of the Girls Gone Wild videos. Musk and some former PayPal executives, having settled their differences, produced Thank You for Smoking and used Musk’s jet in the movie. While not a hard-drinking carouser, Musk took part in the Hollywood nightlife and its social scene. “There were just a lot of parties to go to,” said Bill Lee, Musk’s close friend. “Elon was neighbors with two quasi-celebrities. Our friends were making movies and through this confluence of our networks, there was something to go out and do every night.” In one interview, Musk calculated that his life had become 10 percent playboy and 90 percent engineer. [http://www.telegraph.co.uk/culture/3666994/One-more-giant-leap.xhtml] “We had a domestic staff of five; during the day our home transformed into a workplace,” Justine wrote in magazine article. “We went to black-tie fundraisers and got the best tables at elite Hollywood nightclubs, with Paris Hilton and Leonardo DiCaprio partying next to us. When Google cofounder Larry Page got married on Richard Branson’s private Caribbean island, we were there, hanging out in a villa with John Cusack and watching Bono pose with swarms of adoring women outside the reception tent.” Justine appeared to relish their status even more than Musk. A writer of fantasy fiction novels, she kept a blog detailing the couple’s family life and their adventures on the town. In one entry, Justine had Musk saying that he’d prefer to sleep with Veronica than Betty from the Archie comics and that he’d like to visit a Chuck E. Cheese sometime. In another entry, she wrote about meeting Leonardo DiCaprio at a club and having him beg for a free Tesla Roadster, only to be turned down. Justine handed out nicknames to oft-occurring characters in the blog, so Bill Lee became “Bill the Hotel Guy” because he owns a hotel in the Dominican Republic, and Joe Francis appeared as “Notorious Neighbor.” It’s hard to imagine Musk, who keeps to himself, hanging out with someone as ostentatious as Francis, but the men got along well. When Francis took over an amusement park for his birthday, Musk attended and then ended up partying at Francis’s house. Justine wrote, “E was there for a bit but admitted he also found it ‘kind of lame’—he’s been to a couple of parties at NN’s house now and ends up feeling self-conscious, ‘because it just seems like there are always these skeevy guys wandering around the house trolling for girls. I don’t want to be seen as one of those guys.’” When Francis got ready to buy a Roadster, he stopped by the Musks’ house and handed over a yellow envelope with $100,000 in cash. For a while, the blog provided a rare, welcome glimpse into the life of an unconventional CEO. Musk seemed charming. The public learned that he bought Justine a nineteenth-century edition of Pride and Prejudice, that Musk’s best friends gave him the nickname “Elonius,” and that Musk likes to place one-dollar wagers on all manner of things—Can you catch herpes from the Great Barrier Reef? Is it possible to balance two forks with a toothpick?—that he knows he will win. Justine told one story about Musk traveling to Necker Island, in the British Virgin Islands, to hang out with Tony Blair and Richard Branson. A photo of the three men appeared later in the press that depicted Musk with a vacant stare. “This was E’s I’m-thinking-about-a-rocket-problem stance, which makes me pretty sure that he had just gotten some kind of bothersome work-related e-mail, and was clearly oblivious to the fact that a picture was being taken at all,” she wrote. “This is also the reason I get suck [sic] a kick out of it—the spouse the camera caught is the exact spouse I encountered, say, last night en route to the bathroom, standing in the hallway frowning with his arms folded.” Justine letting the world into the couple’s bathroom should have served as a warning of things to come. Her blog would soon turn into one of Musk’s worst nightmares. The press had not run into a guy like Musk for a very long time. His shine as an Internet millionaire kept getting, well, shinier thanks to PayPal’s ongoing success. He also had an element of mystery. There was the weird name. And there was the willingness to spend vast sums of money on spaceships and electric cars, which came across as a combination of daring, flamboyant, and downright flabbergasting. “Elon Musk has been called ‘part playboy, part space cowboy,’ an image hardly dispelled by a car collection that has boasted a Porsche 911 Turbo, 1967 Series 1 Jaguar, a Hamann BMW M5 plus the aforementioned McLaren F1—which he has driven at up to 215mph on a private airstrip,” a British reporter gushed in 2007. “Then there was the L39 Soviet military jet, which he sold after becoming a father.” The press had picked up on the fact that Musk tended to talk a huge game and then struggle to deliver on his promises in time, but they didn’t much care. The game he talked was so much bigger than anyone else’s that reporters were comfortable giving Musk leeway. Tesla became the darling of Silicon Valley’s bloggers, who tracked its every move and were breathless in their coverage. Similarly, reporters covering SpaceX were overjoyed that a young, feisty company had arrived to needle Boeing, Lockheed, and, to a large extent, NASA. All Musk had to do was eventually bring some of these wondrous things he’d been funding to market. While Musk put on a good show for the public and press, he’d started to get very worried about his businesses. SpaceX’s second launch attempt had failed, and the reports coming in from Tesla kept getting worse. Musk had started these two adventures with a fortune nearing $200 million and had chewed through more than half the money with little to show for it. As each Tesla delay turned into a PR fiasco, the Musk glow dimmed. People in Silicon Valley began to gossip about Musk’s money problems. Reporters who months earlier had been heaping adulation on Musk turned on him. The New York Times picked up on Tesla’s transmission problems. Automotive websites griped that the Roadster might never ship. By the end of 2007, things got downright nasty. Valleywag, Silicon Valley’s gossip blog, began to take a particular interest in Musk. Owen Thomas, the site’s lead writer, dug into the histories of Zip2 and PayPal and played up the times Musk was ousted as CEO to undermine some of his entrepreneurial street cred. Thomas then championed the premise that Musk was a master manipulator who played fast and loose with other people’s money. “It’s wonderful that Musk has realized even a small part of his childhood fantasies,” Thomas wrote. “But he risks destroying his dreams by refusing to reconcile them with reality.” Valleywag anointed the Tesla Roadster as its No. 1 fail of 2007 among technology companies. As his businesses and public persona suffered, Musk’s home life degraded as well. His triplets—Kai, Damian, and Saxon—had arrived near the end of 2006 and joined their brothers Griffin and Xavier. According to Musk, Justine suffered from postpartum depression following the birth of the triplets. “In the spring of 2007, our marriage was having real issues,” Musk said. “It was on the rocks.” Justine’s blog posts back up his sentiments. She described a much less romantic Musk and felt people treated her as “an arm ornament who couldn’t possibly have anything interesting to say” rather than as an author and her husband’s equal. During one trip to St. Barts, the Musks ended up sharing dinner with some wealthy, influential couples. When Justine let out her political views, one of the men at the table made a crack about her being so opinionated. “E chuckled back, patted my hand the way you pat a child’s,” Justine wrote on her blog. From that point on, Justine ordered Musk to introduce her as a published novelist and not just his wife and mother of his children. The results? “E’s way of doing this throughout the rest of the trip: ‘Justine wants me to tell you that she’s written novels,’ which made people look at me like oh, that’s just so cute and didn’t really help my case.” As 2007 rolled into 2008, Musk’s life became more tumultuous. Tesla basically had to start over on much of the Roadster, and SpaceX still had dozens of people living in Kwajalein awaiting the next launch of the Falcon 1. Both endeavors were vacuuming up Musk’s money. He started selling off prized possessions like the McLaren to generate extra cash. Musk tended to shield employees from the gravity of his fiscal situation by always encouraging them to do their best work. At the same time, he personally oversaw all significant purchases at both companies. Musk also trained employees to make the right trade-offs between spending money and productivity. This struck many of the SpaceX employees as a novel idea, since they were used to traditional aerospace companies that had huge, multiyear government contracts and no day-to-day survival pressure. “Elon would always be at work on Sunday, and we had some chats where he laid out his philosophy,” said Kevin Brogan, the early SpaceX employee. “He would say that everything we did was a function of our burn rate and that we were burning through a hundred thousand dollars per day. It was this very entrepreneurial, Silicon Valley way of thinking that none of the aerospace engineers in Los Angeles were dialed into. Sometimes he wouldn’t let you buy a part for two thousand dollars because he expected you to find it cheaper or invent something cheaper. Other times, he wouldn’t flinch at renting a plane for ninety thousand dollars to get something to Kwaj because it saved an entire workday, so it was worth it. He would place this urgency that he expected the revenue in ten years to be ten million dollars a day and that every day we were slower to achieve our goals was a day of missing out on that money.” Musk had become all consumed with Tesla and SpaceX out of necessity, and there can be no doubt that this exacerbated the tensions in his marriage. The Musks had a team of nannies to help with their five children, but Elon could not spend much time at home. He worked seven days a week and quite often split his time between Los Angeles and San Francisco. Justine needed a change. During moments of self-reflection, she felt sickened, perceiving herself a trophy wife. Justine longed to be Elon’s partner again and to feel some of that spark from their early days before life had turned so dazzling and demanding. It’s not clear how much Musk let on to Justine about his dwindling bank account. She has long maintained that Musk kept her in the dark about the family’s financial arrangements. But some of Musk’s closest friends did get a glimpse into the worsening financial situation. In the first half of 2008, Antonio Gracias, the founder and CEO of Valor Equity, met Musk for dinner. Gracias had been an investor in Tesla and had become one of Musk’s closest friends and allies, and he could see Musk agonizing over his future. “Things were starting to be difficult with Justine, but they were still together,” Gracias said. “During that dinner, Elon said, ‘I will spend my last dollar on these companies. If we have to move into Justine’s parents’ basement, we’ll do it.’” The option of moving in with Justine’s parents expired on June 16, 2008, when Musk filed for divorce. The couple did not disclose the situation right away, although Justine left hints on her blog. In late June, she posted a quotation from Moby without any additional context: “There’s no such thing as a well-adjusted public figure. If they were well adjusted they wouldn’t try to be a public figure.” The next entry had Justine house hunting for undisclosed reasons with Sharon Stone, and a couple of entries later she talked about “a major drama” that she’d been dealing with. In September, Justine wrote her first blog post explicitly about the divorce, saying, “We had a good run. We married young, took it as far as we could and now it is over.” Valleywag naturally followed with a story about the divorce and noted that Musk had been seen out with a twenty-something actress. The media coverage and divorce freed Justine to write about her private life in a much more liberated way. In the posts that followed, she gave her account of how the marriage ended, her views on Musk’s girlfriend and future second wife, and the inner workings of the divorce proceedings. For the first time, the public had access to a deeply unpleasant portrayal of Musk and received some firsthand accounts—albeit from an ex-wife—of his hardline behavior. The writing may have been biased, but it provided a window into how Musk operated. Here’s one post about the lead-up to the divorce and its rapid execution: Divorce, for me, was like the bomb you set off when all other options have been exhausted. I had not yet given up on the diplomacy option, which was why I hadn’t already filed. We were still in the early stages of marital counseling (three sessions total). Elon, however, took matters into his own hands—he tends to like to do that—when he gave me an ultimatum: “Either we fix [the marriage] today, or I will divorce you tomorrow.” That night, and again the next morning, he asked me what I wanted to do. I stated emphatically that I was not ready to unleash the dogs of divorce; I suggested that “we” hold off for at least another week. Elon nodded, touched the top of my head, and left. Later that same morning I tried to make a purchase and discovered that he had cut off my credit card, which is when I also knew that he had gone ahead and filed (as it was, E did not tell me directly; he had another person do it). For Musk, each online missive from Justine created another public relations crisis that added to the endless stream of issues faced by his companies. The image he’d sculpted over the years appeared ready to crumble alongside his businesses. It was a disaster scenario. Soon enough, the Musks had achieved celebrity divorce status. Mainstream outlets joined Valleywag in poring over court filings tied to the breakup, particularly as Justine fought for more money. During the PayPal days, Justine had signed a postnuptial agreement and now argued that she didn’t really have the time or inclination to dig into the ramifications of the paperwork. Justine took to her blog in an entry titled “golddigger,” and said she was fighting for a divorce settlement that would include their house, alimony and child support, $6 million in cash, 10 percent of Musk’s Tesla stock, 5 percent of Musk’s SpaceX stock, and a Tesla Roadster. Justine also appeared on CNBC’s show Divorce Wars and wrote an article for Marie Claire titled “‘I Was a Starter Wife’: Inside America’s Messiest Divorce.” The public tended to side with Justine during all of this and couldn’t quite figure out why a billionaire was fighting his wife’s seemingly fair requests. A major problem for Musk, of course, was that his assets were anything but liquid with most of his net worth being tied up in Tesla and SpaceX stock. The couple eventually settled with Justine getting the house, $2 million in cash (minus her legal fees), $80,000 a month in alimony and child support for seventeen years, and a Tesla Roadster. /Musk fought to set the record straight, as he saw it, on the Huffington Post and wrote a 1,500-word essay. Musk maintained that two months of negotiations with independent parties had gone into the postnuptial agreement, which kept the couple’s assets separate so that Musk could get the spoils from his companies and Justine could get the spoils from her books. “In mid 1999, Justine told me that if I proposed to her, she would say yes,” Musk wrote. “Since this was not long after the sale of my first company, Zip2, to Compaq, and the subsequent cofounding of PayPal, friends and family advised me to separate whether the marriage was for love or money.” After the settlement, Musk asked Arianna Huffington to remove his essay about the divorce from her website. “I don’t want to dwell on past negativity,” Musk said. “You can always find things on the Internet. So it’s not like it’s gone. It’s just not easily found.”/ Years after the settlement, Justine still struggled to speak about her relationship with Musk. During our interview, she broke down in tears several times and needed moments to compose her thoughts. Musk, she said, had hidden many things from her during their marriage and ultimately treated her much like a business adversary to be conquered during the divorce. “We were at war for a while, and when you go to war with Elon, it’s pretty brutal,” she said. Well after their marriage ended, Justine continued to blog about Musk. She wrote about Riley and provided commentary on his parenting. One post gave Musk a hard time for banning stuffed animals from the house when their twins turned seven. Asked about this, Justine said, “Elon is hard-core. He grew up in a tough culture and tough circumstances. He had to become very tough to not only thrive but to conquer the world. He doesn’t want to raise soft overprivileged kids with no direction.” Comments like these seemed to indicate that Justine still admired or at least understood Musk’s strong will. /The pair have continued to have their difficulties. For a long time, Musk ran all of the child-sharing scheduling through his assistant Mary Beth Brown rather than dealing directly with Justine. “I was really pissed-off about that,” Justine said. And the time Justine cried the most during our conversation came as she weighed the pros and cons of the children growing up on a grand stage where they’re whisked away to the Super Bowl or Spain in a private jet on a moment’s notice or asked to play at the Tesla factory. “I know the kids really look up to him,” she said. “He takes them everywhere and provides a lot of experiences for them. My role as the mother is to create this reality where I provide a sense of normalcy. They are not growing up in a normal family with a normal dad. Their life with me is a lot more low-key. We value different things. I am a lot more about empathy.”/ In the weeks after he first filed for divorce in mid-June of 2008, Musk tumbled into a deep funk. Bill Lee started to worry about his friend’s mental state and, as one of Musk’s more free-spirited friends, wanted to do something to cheer him up. Now and again, Musk and Lee, an investor, would take trips overseas and mix business and pleasure. The time was right for just such a journey, and they set off for London at the start of July. The decompression program began poorly. Musk and Lee visited the headquarters of Aston Martin to see the company’s CEO and get a tour of his factory. The executive treated Musk like an amateur car builder, talking down to him and suggesting that he knew more about electric vehicles than anyone else on the planet. “He was a complete douche,” as Lee put it, and the men did their best to make a hasty exit back to central London. Along the way, Musk had a nagging stomach pain turn severe. At the time, Lee was married to Sarah Gore, the daughter of former vice president Al Gore, who had been a medical student, and so he called her for advice. They decided that Musk might be suffering from appendicitis, and Lee took him to a medical clinic in the middle of a shopping mall. When the tests came back negative, Lee set to work trying to goad Musk into a night on the town. “Elon didn’t want to go out, and I didn’t really, either,” Lee said. “But I was like, ‘No, come on. We’re all the way here.’” Lee coaxed Musk into going to a club called Whisky Mist, in Mayfair. People had packed the small, high-end dance spot and Musk wanted to leave after ten minutes. The well-connected Lee texted a promoter friend of his, who pulled some strings to get Musk escorted into the VIP area. The promoter then reached out to some of his prettiest friends, including a twenty-two-year-old up-and-coming actress named Talulah Riley, and they soon arrived at the club as well. Riley and her two gorgeous friends had come from a charity gala and were in full-length, flowing gowns. “Talulah was in this huge Cinderella thing,” Lee said. Musk and Riley were introduced by people at the club, and he perked at the sight of her dazzling figure. Musk and Riley sat at a table with their friends but immediately zeroed in on each other. Riley had just hit it big with her portrayal of Mary Bennet in Pride and Prejudice and thought of herself as quite the hotshot. The older Musk, meanwhile, took on the role of the soft-spoken, sweet engineer. He whipped out his phone and displayed photos of the Falcon 1 and Roadster, although Riley thought he had just done some work on these projects and didn’t realize he ran the companies building the machines. “I remember thinking that this guy probably didn’t get to talk to young actresses a lot and that he seemed quite nervous,” Riley said. “I decided to be really nice to him and give him a nice evening. Little did I know that he’d spoken to a lot of pretty girls in his life.” /Musk recalled their meeting as follows: “She did look great, but what was going through my mind was ‘Oh, I guess they are a couple of models.’ You know, you can’t actually talk to most models. You just can’t have a conversation. But, you know, Talulah was really interested in talking about rockets and electric cars. That was the interesting thing.”/ The more Musk and Riley talked, the more Lee egged them on. It was the first time in weeks that his friend appeared happy. “His stomach didn’t hurt; he’s not bummed, this is great,” Lee said. Despite being dressed for a fairy tale, Riley didn’t fall in love with Musk at first sight. But she did become more impressed and intrigued as the night went on, particularly after the club promoter introduced Musk to a stunning model, and he politely said “Hello” and then sat right back down with Riley. “I figured he couldn’t be all bad after that,” said Riley, who then allowed Musk to place his hand on her knee. Musk asked Riley out to dinner the next night, and she accepted. With her curvy figure, sultry eyes, and playful good-girl demeanor, Riley was a budding film star but didn’t really act the part. She grew up in the idyllic English countryside, went to a top school, and, until a week before she met Musk, had been living at home with her parents. After the night at Whisky Mist, Riley called her family to tell them about the interesting guy she had met who builds rockets and cars. Her father used to head up the National Crime Squad and went straight to his computer to conduct a background check that illuminated Musk’s resume as a married international playboy with five kids. Riley’s father chided his daughter for being a fool, but she held out hope that Musk had an explanation and went to dinner with him anyway. Musk brought Lee to the dinner, and Riley brought her friend Tamsin Egerton, also a beautiful actress. Things were cooler throughout the meal as the group dined in a depressingly empty restaurant. Riley waited to see what Musk would bring up on his own. Eventually, he did announce his five sons and his pending divorce. The confession proved enough to keep Riley interested and curious about where things would lead. Following the meal, Musk and Riley broke off on their own. They went for a walk through Soho and then stopped at Cafe Boheme, where Riley, a lifelong teetotaler, sipped an apple juice. Musk kept Riley’s attention, and the romance began in earnest. The couple had lunch the next day and then went to the White Cube, a modern art gallery, and then back to Musk’s hotel room. Musk told Riley, a virgin, that he wanted to show her his rockets. “I was skeptical, but he did actually show me rocket videos,” she said. Once Musk went back to the United States, /He asked Riley to go with him, but she turned Musk down./ they kept in touch via e-mail for a couple of weeks, and then Riley booked a flight to Los Angeles. “I wasn’t even thinking girlfriend or anything like that,” Riley said. “I was just having fun.” Musk had other ideas. Riley had been in California for just five days when he made his move as they lay in bed talking in a tiny room at the Peninsula hotel in Beverley Hills. “He said, ‘I don’t want you to leave. I want you to marry me.’ I think I laughed. Then, he said, ‘No. I’m serious. I’m sorry I don’t have a ring.’ I said, ‘We can shake on it if you like.’ And we did. I don’t remember what I was thinking at the time, and all I can say is that I was twenty-two.” Riley had been a model daughter up to that point, never giving her parents much of anything to worry about. She did well at school, had scored some tremendous acting gigs, and had a soft, sweet personality that her friends described as Snow White brought to life. But there she was on the hotel’s balcony, informing her parents that she had agreed to marry a man fourteen years her senior, who had just filed for divorce from his first wife, had five kids and two companies, and she didn’t even see how she could possibly love him after knowing him for a matter of weeks. “I think my mother had a nervous breakdown,” Riley said. “But I had always been highly romantic, and it actually didn’t strike me as that strange.” Riley flew back to England to gather her things, and her parents flew back with her to the United States to meet Musk, who belatedly asked Riley’s father for his blessing. Musk did not have his own house, which left the couple moving into a home that belonged to Musk’s friend the billionaire Jeff Skoll. “I had been living there a week when this random guy walked in,” Riley said. “I said, ‘Who are you?’ He said, ‘I am the homeowner. Who are you?’ I told him, and then he just walked out.” Musk later proposed to Riley again on the balcony of Skoll’s house, unveiling a massive ring. (He has since bought her three engagement rings, including the giant first one, an everyday ring, and one designed by Musk that has a diamond surrounded by ten sapphires.) “I remember him saying, ‘Being with me was choosing the hard path.’ I didn’t quite understand at the time, but I do now. It’s quite hard, quite the crazy ride.” Riley experienced a baptism by fire. The whirlwind romance had given her the impression that she was engaged to a world conquering, jet-setting billionaire. That was true in theory but a murkier proposition in practice. As late July rolled around, Musk could see that he had just enough cash on hand to scrape through to the end of the year. Both SpaceX and Tesla would need cash infusions at some point just to pay the employees, and it was unclear where that money would come from with the world’s financial markets in disarray and investments being put on hold. If things had been going more smoothly at the companies, Musk could have felt more confident about raising money, but they were not. “He would come home every day, and there would be some calamity,” Riley said. “He was under immense pressure from all quarters. It was horrendous.” SpaceX’s third flight from Kwajalein jumped out as Musk’s most pressing concern. His team of engineers had remained camped out on the island, preparing the Falcon 1 for another run. A typical company would focus just on the task at hand. Not SpaceX. It had shipped the Falcon 1 to Kwaj in April with one set of engineers and then put another group of engineers on a new project to develop the Falcon 9, a nine-engine rocket that would take the place of the Falcon 5 and serve as a possible replacement to the retiring space shuttle. SpaceX had yet to prove it could get to space successfully, but Musk kept positioning it to bid on big-ticket NASA contracts. /By this time, Musk had built up a reputation as the hardest-charging man in the space business. Before settling on the Falcon 9, Musk planned to build something called the BFR, a.k.a. the Big Falcon Rocket or Big Fucking Rocket. Musk wanted it to have the biggest rocket engine in history. Musk’s bigger, faster mentality amused, horrified and impressed some of the suppliers that SpaceX occasionally turned to for help, like Barber-Nichols Inc., a Colorado-based maker of rocket engine turbo pumps and other aerospace machinery. A few executives at Barber-Nichols—Robert Linden, Gary Frey, and Mike Forsha—were kind enough to recount their first meeting with Musk in the middle of 2002 and their subsequent dealings with him. Here’s a snippet: “Elon showed up with Tom Mueller and started telling us it was his destiny to launch things into space at lower costs and to help us become space faring people. We thought the world of Tom but weren’t quite sure whether to take Elon too seriously. They began asking us for the impossible. They wanted a turbo pump to be built in less than a year for under one million dollars. Boeing might do a project like that over five years for one hundred million. Tom told us to give it our best shot, and we built it in thirteen months. Build quick and learn quickly was Elon’s philosophy. He was relentless in wanting the costs to come down. Regardless of what we showed him on paper with regard to the cost of materials, he wanted the cost lower because that was part of his business model. It could be very frustrating to work with Elon. He has a singular view and doesn’t deviate from that. We don’t know too many people that have worked for him that are happy. That said, he has driven the cost of space down and been true to his original business plan. Boeing, Lockheed, and the rest of them have become overly cautious and spend a lot of money. SpaceX has balls.”/ On July 30, 2008, the Falcon 9 had a successful test fire in Texas with all nine of its engines lighting up and producing 850,000 pounds of thrust. Three days later, in Kwaj, SpaceX’s engineers fueled up the Falcon 1 and crossed their fingers. The rocket had an air force satellite as its payload, along with a couple of experiments from NASA. All told, the cargo weighed 375 pounds. SpaceX had been making significant changes to its rocket since the last, failed launch. A traditional aerospace company would not have wanted the added risk, but Musk insisted that SpaceX push its technology forward while at the same time trying to make it work right. Among the biggest changes for the Falcon 1 was a new version of the Merlin 1 engine that relied on a tweaked cooling system. The first launch attempt on August 2, 2008, aborted at T minus zero seconds. SpaceX regrouped and tried to launch again the same day. This time everything seemed to be going well. The Falcon 1 soared into the sky and flew spectacularly without any indication of a problem. SpaceX employees watching a webcast of the proceedings back in California let out hoots and whistles. Then, right at the moment when the first stage and second stage were to separate, there was a malfunction. An analysis after the fact would show that the new engines had delivered an unexpected thrust during the separation process that caused the first stage to bump up into the second stage, damaging the top part of the rocket and its engine. /To provide a glimpse of how well Musk knows the rockets, here he is explaining what happened from memory six years after the fact: “It was because we had upgraded the Merlin engine to a regeneratively cooled engine and the thrust transient of that engine was a few seconds longer. It was only like one percent thrust for about another 1.5 seconds. And the chamber pressure was only ten PSI, which is one percent of the total. But that’s below sea level pressure. On the test stand, we didn’t notice anything. We thought it was fine. We thought it was just the same as before, but actually it just had this slight difference. The ambient sea level pressure was higher at roughly fifteen PSI, which disguised some effects during the test. The extra thrust caused the first stage to continue moving after stage separation and recontact the other stage. And the upper stage then started the engine inside the interstage, which caused the plasma blowback which destroyed that upper stage.”/ The failed launch left many SpaceX employees shattered. “It was so profound seeing the energy shift over the room in the course of thirty seconds,” said Dolly Singh, a recruiter at SpaceX. “It was like the worst fucking day ever. You don’t usually see grown-ups weeping, but there they were. We were tired and broken emotionally.” Musk addressed the workers right away and encouraged them to get back to work. “He said, ‘Look. We are going to do this. It’s going to be okay. Don’t freak out,’” Singh recalled. “It was like magic. Everyone chilled out immediately and started to focus on figuring out what just happened and how to fix it. It went from despair to hope and focus.” Musk put up a positive front to the public as well. In a statement, he said that SpaceX had another rocket waiting to attempt a fourth launch and a fifth launch planned shortly after that. “I have also given the go-ahead to begin fabrication of flight six,” he said. “Falcon 9 development will also continue unabated.” In reality, the third launch was a disaster with cascading consequences. Since the second stage of the rocket did not fire properly, SpaceX never got a chance to see if it had really fixed the fuel-sloshing issues that had plagued the second flight. Many of the SpaceX engineers were confident that they had solved this problem and were anxious to get to the fourth launch, believing that they had an easy answer for the recent thrust problem. For Musk, the situation seemed graver. “I was super depressed,” Musk said. “If we hadn’t solved the slush coupling problem on flight two, or there was just some random other thing that occurred—say a mistake in the launch process or the manufacturing process unrelated to anything previous—then game over.” SpaceX simply did not have enough money to try a fifth flight. He’d put $100 million into the company and had nothing to spare because of the issues at Tesla. “Flight four was it,” Musk said. If, however, SpaceX could nail the fourth flight, it would instill confidence on the part of the U.S. government and possible commercial customers, paving the way for the Falcon 9 and even more ambitious projects. Leading up to the third launch, Musk had been his usual ultra-involved self. Anyone at SpaceX who held the launch back went onto Musk’s critical-path shit list. Musk would hound the person responsible about the delays but, typically, he would also do everything in his power to help solve problems. “I was personally holding up the launch once and had to give Elon twice-daily updates about what was going on,” said Kevin Brogan. “But Elon would say, ‘There are five hundred people at this company. What do you need?’” One of the calls must have taken place while Musk courted Riley because Brogan remembered Musk phoning from the bathroom of a London club to find out how welding had gone on a large part of the rocket. Musk fielded another call in the middle of the night while sleeping next to Riley and had to whisper as he berated the engineers. “He’s giving us the pillow talk voice, so we all have to huddle around the speakerphone, while he tells us, ‘You guys need to get your shit together,’” Brogan said. With the fourth launch, the demands and anticipation had ratcheted to the point that people started making silly mistakes. Typically, the body of the Falcon 1 rocket traveled to Kwaj via barge. This time Musk and the engineers were too excited and desperate to wait for the ocean journey. Musk rented a military cargo plane to fly the rocket body from Los Angeles to Hawaii and then on to Kwaj. This would have been a fine idea except the SpaceX engineers forgot to factor in what the pressurized plane would do to the body of the rocket, which is less than an eighth of an inch thick. As the plane started its descent into Hawaii, everyone inside of it could hear strange noises coming from the cargo hold. “I looked back and could see the stage crumpling,” said Bulent Altan, the former head of avionics at SpaceX. “I told the pilot to go up, and he did.” The rocket had behaved much like an empty water bottle will on a plane, with the air pressure pushing against the sides of the bottle and making it buckle. Altan calculated that the SpaceX team on the plane had about thirty minutes to do something about the problem before they would need to land. They pulled out their pocketknives and cut away the shrink wrap that held the rocket’s body tight. Then they found a maintenance kit on the plane and used wrenches to open up some nuts on the rocket that would allow its internal pressure to match that of the plane’s. When the plane landed, the engineers divvied up the duties of calling SpaceX’s top executives to tell them about the catastrophe. It was 3 A.M. Los Angeles time, and one of the executives volunteered to deliver the horrific news to Musk. The thinking at the time was that it would take three months to repair the damage. The body of the rocket had caved in in several places, baffles placed inside the fuel tank to stop the sloshing problem had broken, and an assortment of other issues had appeared. Musk ordered the team to continue on to Kwaj and sent in a reinforcement team with repair parts. Two weeks later, the rocket had been fixed inside of the makeshift hangar. “It was like being stuck in a foxhole together,” Altan said. “You weren’t going to quit and leave the person next to you behind. When it was all done, everyone felt amazing.” The fourth and possibly final launch for SpaceX took place on September 28, 2008. The SpaceX employees had worked nonstop shifts under agonizing pressure for six weeks to reach this day. Their pride as engineers and their hopes and dreams were on the line. “The people watching back at the factory were trying their best not to throw up,” said James McLaury, a machinist at SpaceX. Despite their past flubs, the engineers on Kwaj were confident that this launch would work. Some of these people had spent years on the island going through one of the more surreal engineering exercises in human history. They had been separated from their families, assaulted by the heat, and exiled on their tiny launchpad outpost—sometimes without much food—for days on end as they waited for the launch windows to open and dealt with the aborts that followed. So much of that pain and suffering and fear would be forgotten if this launch went successfully. In the late afternoon on the twenty-eighth, the SpaceX team raised the Falcon 1 into its launch position. Once again, it stood tall, looking like a bizarre artifact of an island tribe as palm trees swayed beside it and a smattering of clouds crossed through the spectacular blue sky. By this time, SpaceX had upped its webcast game, turning each launch into a major production both for its employees and the public. Two SpaceX marketing executives spent twenty minutes before the launch going through all the technical ins and outs of the launch. The Falcon 1 was not carrying real cargo this time; neither the company nor the military wanted to see something else blow up or get lost at sea, so the rocket held a 360-pound dummy payload. The fact that SpaceX had been reduced to launch theater did not faze the employees or dampen their enthusiasm. As the rocket rumbled and then climbed higher, the employees back at SpaceX headquarters let out raucous cheers. Each milestone that followed—clearing the island, engine checks coming back good—was again met with whistles and shouts. As the first stage fell away, the second stage fired up about ninety seconds into the flight and the employees turned downright rapturous, filling the webcast with their ecstatic hollering. “Perfect,” said one of the talking heads. The Kestrel engine glowed red and started its six-minute burn. “When the second stage cleared, I could finally start breathing again and my knees stopped buckling,” said McLaury. The fairing opened up around the three-minute mark and fell back toward Earth. And, finally, around nine minutes into its journey, the Falcon 1 shut down just as planned and reached orbit, making it the first privately built machine to accomplish such a feat. It took six years—about four and half more than Musk had once planned—and five hundred people to make this miracle of modern science and business happen. Earlier in the day, Musk had tried to distract himself from the mounting pressure by going to Disneyland with his brother Kimbal and their children. Musk then had to race back to make the 4 P.M. launch and walked into SpaceX’s trailer control room about two minutes before blastoff. “When the launch was successful, everyone burst into tears,” Kimbal said. “It was one of the most emotional experiences I’ve had.” Musk left the control room and walked out to the factory floor, where he received a rock star’s welcome. “Well, that was freaking awesome,” he said. “There are a lot of people who thought we couldn’t do it—a lot actually—but as the saying goes, ‘the fourth time is the charm,’ right? There are only a handful of countries on Earth that have done this. It’s normally a country thing, not a company thing. . . . My mind is kind of frazzled, so it’s hard for me to say anything, but, man, this is definitely one of the greatest days in my life, and I think probably for most people here. We showed people we can do it. This is just the first step of many. . . . I am going to have a really great party tonight. I don’t know about you guys.” Mary Beth Brown then tapped Musk on the shoulder and pulled him away to a meeting. The afterglow of this mammoth victory faded soon after the party ended, and the severity of SpaceX’s financial hell became top of mind again for Musk. SpaceX had the Falcon 9 efforts to support and had also immediately green-lighted the construction of another machine—the Dragon capsule—that would be used to take supplies, and one day humans, to the International Space Station. Historically, either project would cost more than $1 billion to complete, but SpaceX would have to find a way to build both machines simultaneously for a fraction of the cost. The company had dramatically increased the rate at which it hired employees and moved into a much larger headquarters in Hawthorne, California. SpaceX had a commercial flight booked to carry a satellite into orbit for the Malaysian government, but that launch and the payment for it would not arrive until the middle of 2009. In the meantime, SpaceX simply struggled to make its payroll. The press did not know the extent of Musk’s financial woes, but they knew enough to turn detailing Tesla’s precarious financial situation into a favored pastime. A website called the Truth About Cars began a “Tesla Death Watch” in May 2008 and followed up with dozens of entries throughout the year. The blog took special pleasure in rejecting the idea that Musk was a true founder of the company, presenting him as the moneyman and chairman who had more or less stolen Tesla from the genius engineer Eberhard. When Eberhard started a blog detailing the pros and cons of being a Tesla customer, the auto site was all too happy to echo his gripes. Top Gear, a popular British television show, ripped the Roadster apart, making it look as if the car had run out of juice during a road test. “People joke about the Tesla Death Watch and all that, but it was harsh,” said Kimbal Musk. “One day there were fifty articles about how Tesla will die.” Then, in October 2008 (just a couple weeks after SpaceX’s successful launch), Valleywag appeared on the scene again. First it ridiculed Musk for officially taking over as CEO of Tesla and replacing Drori, on the grounds that Musk had just lucked into his past successes. It followed that by printing a tell-all e-mail from a Tesla employee. The report said that Tesla had just gone through a round of layoffs, shut down its Detroit office, and had only $9 million left in the bank. “We have over 1,200 reservations, which manes [sic] we’ve taken multiples of tens of millions of cash from our customers and have spent them all,” the Tesla employee wrote. “Meanwhile, we only delivered less than 50 cars. I actually talked a close friend of mine into putting down $60,000 for a Tesla Roadster. I cannot conscientiously be a bystander anymore and allow my company to deceive the public and defraud our dear customers. Our customers and the general public are the reason Tesla is so loved. The fact that they are being lied to is just wrong.” /Musk would later discover the identity of this employee in an ingenious way. He copied the text of the letter into a Word document, checked the size of the file, sent it to a printer, and looked over the logs of printer activity to find one of the same size. He could then trace that back to the person who had printed the original file. The employee wrote a letter of apology and resigned./ Yes, Tesla deserved much of the negative attention. Musk, though, felt like the 2008 climate with the hatred of bankers and the rich had turned him into a particularly juicy target. “I was just getting pistol-whipped,” Musk said. “There was a lot of schadenfreude at the time, and it was bad on so many levels. Justine was torturing me in the press. There were always all these negative articles about Tesla, and the stories about SpaceX’s third failure. It hurt really bad. You have these huge doubts that your life is not working, your car is not working, you’re going through a divorce and all of those things. I felt like a pile of shit. I didn’t think we would overcome it. I thought things were probably fucking doomed.” When Musk ran through the calculations concerning SpaceX and Tesla, it occurred to him that only one company would likely even have a chance at survival. “I could either pick SpaceX or Tesla or split the money I had left between them,” Musk said. “That was a tough decision. If I split the money, maybe both of them would die. If I gave the money to just one company, the probability of it surviving was greater, but then it would mean certain death for the other company. I debated that over and over.” While Musk meditated on this, the economy worsened quickly and so too did Musk’s financial condition. As 2008 came to an end, Musk had run out of money. Riley began to see Musk’s life as a Shakespearean tragedy. Sometimes Musk would open up to her about the issues, and other times he retreated into himself. Riley spied on Musk while he read e-mail and watched him grimace as the bad news poured in. “You’d witness him having these conversations in his head,” she said. “It’s really hard to watch someone you love struggle like that.” Because of the long hours that he worked and his eating habits, Musk’s weight fluctuated wildly. Bags formed under his eyes, and his countenance started to resemble that of a shattered runner at the back end of an ultra-marathon. “He looked like death itself,” Riley said. “I remember thinking this guy would have a heart attack and die. He seemed like a man on the brink.” In the middle of the night, Musk would have nightmares and yell out. “He was in physical pain,” Riley said. “He would climb on me and start screaming while still asleep.” The couple had to start borrowing hundreds of thousands of dollars from Musk’s friend Skoll, and Riley’s parents offered to remortgage their house. Musk no longer flew his jet back and forth between Los Angles and Silicon Valley. He took Southwest. Burning through about $4 million a month, Tesla needed to close another major round of funding to get through 2008 and stay alive. Musk had to lean on friends just to try to make payroll from week to week, as he negotiated with investors. He sent impassioned pleas to anyone he could think of who might be able to spare some money. Bill Lee invested $2 million in Tesla, and Sergey Brin invested $500,000. “A bunch of Tesla employees wrote checks to keep the company going,” said Diarmuid O’Connell, the vice president of business development at Tesla. “They turned into investments, but, at the time, it was twenty-five or fifty thousand dollars that you didn’t expect to see again. It just seemed like holy shit, this thing is going to crater.” Kimbal had lost most of his money during the recession when his investments bottomed out but sold what he had left and put it into Tesla as well. “I was close to bankruptcy,” Kimbal said. Tesla had set the prepayments that customers made for the Roadsters aside, but Musk now needed to use that money to keep the company going and soon those funds were gone, too. These fiscal maneuvers worried Kimbal. “I’m sure Elon would have found a way to make things right, but he definitely took risks that seemed like they could have landed him in jail for using someone else’s money,” he said. In December 2008, Musk mounted simultaneous campaigns to try to save his companies. He heard a rumor that NASA was on the verge of awarding a contract to resupply the space station. SpaceX’s fourth launch had put it in a position to receive some of this money, which was said to be in excess of $1 billion. Musk reached out through some back channels in Washington and found out that SpaceX might even be a front-runner for the deal. Musk began doing everything in his power to assure people that the company could meet the challenge of getting a capsule to the ISS. As for Tesla, Musk had to go to his existing investors and ask them to pony up for another round of funding that needed to close by Christmas Eve to avoid bankruptcy. To give the investors some measure of confidence, Musk made a last-ditch effort to raise all the personal funds he could and put them into the company. He took out a loan from SpaceX, which NASA approved, and earmarked the money for Tesla. Musk went to the secondary markets to try to sell some of his shares in SolarCity. He also seized about $15 million that came through when Dell acquired a data center software start-up called Everdream, founded by Musk’s cousins, in which he had invested. “It was like the fucking Matrix,” Musk said, describing his financial maneuvers. “The Everdream deal really saved my butt.” Musk had cobbled together $20 million, and asked Tesla’s existing investors—since no new investors materialized—to match that figure. The investors agreed, and on December 3, 2008, they were in the process of finalizing the paperwork for the funding round when Musk noticed a problem. VantagePoint Capital Partners had signed all of the paperwork except for one crucial page. Musk phoned up Alan Salzman, VantagePoint’s cofounder and managing partner, to ask about the situation. Salzman informed Musk that the firm had a problem with the investment round because it undervalued Tesla. “I said, ‘I’ve got an excellent solution then. Take my entire portion of the deal. I had a real hard time coming up with the money. Based on the cash we have in the bank right now, we will bounce payroll next week. So unless you’ve got another idea, can you either just participate as much as you’d like, or allow the round to go through because otherwise we will be bankrupt.’” Salzman balked and told Musk to come in the following week at 7 A.M. to present to VantagePoint’s top brass. Not having a week of time to work with, Musk asked to come in the next day, and Salzman refused that offer, forcing Musk to continue taking on loans. “The only reason he wanted the meeting at his office was for me to come on bended knee begging for money so he could say, ‘No,’” Musk theorized. “What a fuckhead.” VantagePoint declined to speak about this period, but Musk believed that Salzman’s tactics were part of a mission to bankrupt Tesla. Musk feared that VantagePoint would oust him as CEO, recapitalize Tesla, and emerge as the major owner of the carmaker. It could then sell Tesla to a Detroit automaker or focus on selling electric drivetrains and battery packs instead of making cars. Such reasoning would have been quite practical from a business standpoint but did not match up with Musk’s goals for Tesla. “VantagePoint was forcing that wisdom down the throat of an entrepreneur who wanted to do something bigger and bolder,” said Steve Jurvetson, a partner at Draper Fisher Jurvetson and Tesla investor. “Maybe they’re used to a CEO buckling, but Elon doesn’t do that.” Instead, Musk took another huge risk. Tesla recharacterized the funding as a debt round rather than an equity round, knowing that VantagePoint could not interfere with a debt deal. The tricky part of this strategy was that investors like Jurvetson who wanted to help Tesla were put in a bind because venture capital firms are not structured to do debt deals, and convincing their backers to alter their normal rules of engagement for a company that could very well go bankrupt in a matter of days would be a very tough ask. Knowing this, Musk bluffed. He told the investors that he would take another loan from SpaceX and fund the entire round—all $40 million—himself. The tactic worked. “When you have scarcity, it naturally reinforces greed and leads to more interest,” Jurvetson said. “It was also easier for us to go back to our firms and say, ‘Here is the deal. Go or no go?’” The deal ended up closing on Christmas Eve, hours before Tesla would have gone bankrupt. Musk had just a few hundred thousand dollars left and could not have made payroll the next day. Musk ultimately put in $12 million, and the investment firms put up the rest. As for Salzman, Musk said, “He should be ashamed of himself.” At SpaceX, Musk and the company’s top executives had spent most of December in a state of fear. According to reports in the press, SpaceX, the onetime front-runner for the large NASA contract, had suddenly lost favor with the space agency. Michael Griffin, who had once almost been a cofounder of SpaceX, was the head of NASA and had turned on Musk. Griffin did not care for Musk’s aggressive business tactics, seeing him as borderline unethical. Others have suggested that Griffin ended up being jealous of Musk and SpaceX. /Griffin had pined to build a massive new spacecraft that would solidify his mark on the industry. But, with the election of Barack Obama in 2008, the Bush appointee knew that his time as NASA chief was coming to an end and that SpaceX appeared poised to build the most interesting machines moving forward./ On December 23, 2008, however, SpaceX received a shock. People inside NASA had backed SpaceX to become a supplier for the ISS. The company received $1.6 billion as payment for twelve flights to the space station. Staying with Kimbal in Boulder, Colorado, for the holidays, Musk broke down in tears as the SpaceX and Tesla transactions processed. “I hadn’t had an opportunity to buy a Christmas present for Talulah or anything,” he said. “I went running down the fucking street in Boulder, and the only place that was open sold these shitty trinkets, and they were about to close. The best thing I could find were these plastic monkeys with coconuts—those ‘see no evil, hear no evil’ monkeys.” For Gracias, the Tesla and SpaceX investor and Musk’s friend, the 2008 period told him everything he would ever need to know about Musk’s character. He saw a man who arrived in the United States with nothing, who had lost a child, who was being pilloried in the press by reporters and his ex-wife and who verged on having his life’s work destroyed. “He has the ability to work harder and endure more stress than anyone I’ve ever met,” Gracias said. “What he went through in 2008 would have broken anyone else. He didn’t just survive. He kept working and stayed focused.” That ability to stay focused in the midst of a crisis stands as one of Musk’s main advantages over other executives and competitors. “Most people who are under that sort of pressure fray,” Gracias said. “Their decisions go bad. Elon gets hyperrational. He’s still able to make very clear, long-term decisions. The harder it gets, the better he gets. Anyone who saw what he went through firsthand came away with more respect for the guy. I’ve just never seen anything like his ability to take pain.”
|
|||||||||
|
Последнее изменение этой страницы: 2024-06-27; просмотров: 4; Нарушение авторского права страницы; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! infopedia.su Все материалы представленные на сайте исключительно с целью ознакомления читателями и не преследуют коммерческих целей или нарушение авторских прав. Обратная связь - 3.12.151.11 (0.074 с.) |