
Заглавная страница Избранные статьи Случайная статья Познавательные статьи Новые добавления Обратная связь FAQ Написать работу КАТЕГОРИИ: ТОП 10 на сайте Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрацииТехника нижней прямой подачи мяча. Франко-прусская война (причины и последствия) Организация работы процедурного кабинета Смысловое и механическое запоминание, их место и роль в усвоении знаний Коммуникативные барьеры и пути их преодоления Обработка изделий медицинского назначения многократного применения Образцы текста публицистического стиля Четыре типа изменения баланса Задачи с ответами для Всероссийской олимпиады по праву 
Мы поможем в написании ваших работ! ЗНАЕТЕ ЛИ ВЫ?
Влияние общества на человека
Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрации Практические работы по географии для 6 класса Организация работы процедурного кабинета Изменения в неживой природе осенью Уборка процедурного кабинета Сольфеджио. Все правила по сольфеджио Балочные системы. Определение реакций опор и моментов защемления |
Description of installation and measuring methodСодержание книги
Поиск на нашем сайте
The cross-shaped pendulum is Oberbeck's pendulum. It consist of two sheaves with radii are r1 and r2, and four crosswise shafts. Four loads with equal masses m are able to move along shafts. A thread is wound on one of the sheaves. A load P = mg is fasten to the other end of the thread. When the load P falls, the thread unwinds. A mechanical brake is possible to operate the motion of the load from the start to the end of its motion. The displacement of the load can be measured by means of on indicator panel. It is not difficult to show that the acceleration of the load is
where h is the distance of the falling load; t is the time of the falling load. The load is allowed to fall under the action of its own weight. It equals mg. The line acceleration of the point at the sheaf surface is equal to the load acceleration. Then angular acceleration can be represented as
where r is radius of the sheaf. According to the second Newton's law
where N is pull of the thread. Then, pull of the thread is given by
Moment of force at the cross-shaped pendulum may be expressed as
In our experiment conditions usually a << g. Then
The fundamental equation of motion for a rotating body is as follows
where I is the moment of inertia of the pendulum; ε is the angular acceleration of the pendulum. From the formulas (15.2) and (15.3) it follows that
Taking (15.1) into consideration of formula (15.4) one may receive
If I = const, then
If M = const, then
Moment of inertia of the cross-shaped pendulum consists of the moment of inertia of the cross-shaped Il (as is shown on the device) and moment of inertia of four loads at the shafts
where m is the mean mass; R is the distance between the axis of revolution and the centre of gravity loads m. Task 5.1
THE AIM is to determine the angular accelerations and moments of forces of the pendulum when values of falling loads are different and when moment of inertia is constant. 1. Put down the data of measurements in table 15.1.
Table 15.1
2. Calculate Δε/ε. Put down the results of calculations in table 15.2.
Table 15.2
Σti = ΣΔti2=
3. Put M versus ε on the graph. 4. Determine the moment of the friction forces and moment of inertia on the graph. 5. Make analysis of the experiment results. Task 5.2
THE AIM is to determine the angular acceleration and moments of forces of the pendulum with different values of the sheaves radius and when moment of inertia is constant.
1. Put down the data of measurements in table 15.3.
Table 15.3
2. For the first five measurements use average time t, when you calculate ε. 3. Calculate 4. Calculate the half-width of the confidence interval for t using the first five measurements. 5. Put down the data of measurements in the table 15.4.
Table 15.4
6. Put M versus ε on the graph. 7. Determine moment of inertia on the graph. 8. Make analysis of the experiment results.
Task 5.3
THE AIM is to determine moment of inertia of four loads at the shafts with dynamics and theoretical methods. 1. Put the data of measurements in the table 15.5.
Table 15.5
2. Determine the moment of inertia of four loads at the shafts with the dynamics method.
where I0 is the moment of inertia of cross-shaped pendulum (I0 = 4,15×10-2 кg×m2); k is a coefficient, it takes into consideration the mean forces of friction and errors of the time measurements (k = 1.1). 3. Calculate the moment of inertia of four loads at the shafts by the formula
where 4. Calculate ΔI/I as an error of indirect measurement. Calculate the half- width of the confidence interval for r and h as a direct measurement errors, m and g are the table values. Calculate the half-width of the confidence interval of t as five direct measurements error. 5. Put the results of calculation in table 15.6.
Table 15.6
6. Analyse the experimental results and draw the conclusion. m0 = 0,5 kg; m(I) = 0,592 kg; m(II) = 0,59 kg; m(III) = 0,575 kg; m(IV) = 0,592 kg; I0 = 4,5˙10-2 kg˙m2
Task 5.4 THE AIM is to determine the angular accelerations and moments of inertia of the pendulum when the load masses at the shafts are changed and the moment of force is constant.
1. Put down the data of measurements in table 15.7.
Table 15.7
2. Calculate angular acceleration defined by
3. Calculate moments of inertia given by
where I0 is the moment of inertia of the pendulum without loads (I0 = 4,6×10-2 кg/m2); m is the mean mass of four loads at the shafts; R is the distance between the axis of revolution and the centre if gravity loads. 4. Calculate 5. Results of calculation carry in the table 15.8.
Table 15.8
∑ ti = ∑Δ ti2=
6. Make analysis of the experiment results.
Task 5.5 THE AIM is to determine the angular accelerations and moments of inertia of the pendulum with changed distance of the loads at the shafts and a moment of force is constant.
1. Measure t and h for five different distances of the loads at the shafts. 2. Put down the data of measurements in table 15.9.
Table 15.9
3. Calculate angular acceleration defined by
4. Calculate moment of inertia given by
where I0 is the moment of inertia of the pendulum without loads ( 5. Calculate ΔI and 6. Put down the results of calculations in table 15.10.
Table 15.10
∑ ti = ∑Δ ti2=
7. Put I versus R2 on the graph. 8. Put I versus ε on the graph. 9. Make analysis of the experimental results.
Task 5.6
THE AIM is to determine moment of inertia of the pendulum with dynamics and theoretical methods. NSTRUMENTATION AND APPLIANCES: cross-shaped pendulum, seconds counter, set of loads 1. Put down the data of measurement in table 15.11.
Table 15.11
2. Determine the moment of inertia of the pendulum by with the dynamics method
where k is the correct coefficient, it takes into consideration the mean forces of friction and errors of the time measurement (k=.3); m is the mass of the falling load; r is radius of the sheaf; t is the time of the load fall. 3. Determine the moment of inertia of the pendulum with the theoretical method
where 4. Calculate 5. Put down the results of calculation in table 15.12.
Table 15.12
∑ ti = ∑Δ ti2=
6. Compare I and I′. Make analysis of the experiment results.
Control questions 1. Obtain a relationship between linear and angular velocity. 2. Obtain a kinetic energy of rotation. 3. Obtain a formula for moment of inertia if the entire disk. 4. How is a moment of force determined? 5. Obtain the fundamental equation of rotation. 6. Make a comparison between the formulas of motion of a particle and derive the laws for the rotation of a solid body. 7. Obtain the law of conservation of momentum for the rotation motion. 8. What is a gyroscope?
Author: S.V. Loskutov, professor, doctor of physical and mathematical sciences. Reviewer: S.P. Lushchin, the reader, candidate of physical and mathematical sciences.
Approved by the chair of physics. Protocol № 3 from 01.12.2008.
16 ЛАБОРАТОРНА РОБОТА № 6. Перевірка ТЕОРЕМИ ШТЕЙНЕРА
ПРИЛАДИ: пристрій на тринитковому підвісі, два циліндри, штангенциркуль. МЕТА РОБОТИ: визначити момент iнерцiї циліндру, що обертається відносно вісі, яка не проходить через центр мас, дослідним шляхом та за теоремою Штейнера. ЗАВДАННЯ ДО РОБОТИ: 1. Розрахувати момент iнерцiї ненавантаженого диску Iд. 2. Обчислити момент iнерцiї системи I1, яка складається з диску i двох циліндрів. 3. Визначити момент iнерцiї циліндра 4. Впевнитись, що теореми Штейнера справедлива.
16.1 Опис пристрою та методу вимірювання
Момент iнерцiї матеріального тіла – це скалярна фізична величина, яка є мірою iнертностi тіла в обертальному русi. Момент iнерцiї залежить від маси, форми та розмiрiв тіла, розподілення маси відносно осi обертання, вибору осi обертання. У цій роботі використовується пристрій на тринитковому підвісі, який дозволяє визначити моменти iнерцiї простих тіл. Пристрій складається з диску (2), котрий приводиться у коливальний рух за допомогою приводу (6). Внаслідок повороту рукоятки приводу (5) відбувається закручування пружини (8), котра, розкручуючись, передає імпульс обертального руху верхньому диску (7). Металеві нитки (4) дещо нахиляться, від чого центр мас системи зміщується вздовж осi обертання. Момент сил пружності намагається повернути диск в положення рівноваги. Нижній диск здійснює обертальні коливання, період котрих залежить від моменту iнерцiї системи. Оскільки центр мас диску зміщується, то змінюється його потенціальна енергія. Використовуючи закон збереження механічної енергії, одержимо формулу, що дозволяє визначити момент iнерцiї нижнього диску:
де mД – маса нижнього диску; g - прискорення вільного падіння; R - відстань від центру диску до точок, в яких кріпляться нитки до нього; r - радіус нижнього диску; L – довжина ниток пiдвiсу; Т – період коливань.
де Формула (16.1) дає можливість визначити момент iнерцiї диску з розміщеними на ньому тілами. Згідно теореми Штейнера
де I0 – момент iнерцiї циліндру відносно осi 1 (рисунок 16.2а); I - момент iнерцiї циліндру відносно осi 2 (рисунок 16.2б); m - маса циліндра; a - відстань між осями (рисунок 16.2б).
Рисунок 16.1
Момент iнерцiї циліндра відносно осi 2 можна визначити i дослідним методом:
де I1 – момент iнерцiї системи, що складається з диску та двох цилiндрiв, розміщених на однакових відстанях a від осi обертання (рисунок 16.2б); IД – момент iнерцiї ненавантаженого диска (рисунок 16.2в). Момент iнерцiї циліндра I0 визначається за формулою:
де rц – радіус циліндра. Підставивши I0 в (16.3) i маючи, на увазі, що
Рисунок 16.2
Порядок виконання роботи
1. Відхилити ненавантажений диск на 5 маленьких поділок лімбу (1). 2. Визначити час tД 10 коливань. 3. Повторити вимірювання ще два рази. 4. Розташувати в отворах диску два циліндра на однакових відстанях a від осi обертання. 5. Визначити час t 10 коливань диску з двома циліндрами за п.1 ÷ 3. 6. Замiряти один раз відстань a та діаметр циліндру d. 7. Визначити період коливань ненавантаженого диску TД та період коливань диску з двома циліндрами Т за (16.2), використовуючи середні значення tД та t. 8. Обчислити момент iнерцiї ненавантаженого диску IД за (16.1), використовуючи значення: mД = 2 кг, R = 0,13 м, r =5,5×10-2, L = 2,2 м. 9. Обчислити момент iнерцiї диску з двома циліндрами I1 за (16.1), використовуючи замість mД значення mД + 2 10. Визначити момент iнерцiї циліндру 11. Обчислити момент iнерцiї циліндру I відносно осi 2 згідно теореми Штейнера за(16.6). Дані вимірювань та обчислень занести у таблицю 16.1.
Таблиця 16.1
12. Порівняйте одержані результати
Контрольні запитання 1. Дайте визначення для параметрів обертального руху: моменту сили, iнерцiї, імпульсу, кутової швидкості, кутового прискорення. 2. Запишiть формули для обчислення роботи та кінетичної енергії обертального руху. 3.Вивести основне рівняння динаміки обертального руху. 4.Записати закон збереження моменту імпульсу. 5.Вивести спiввiдношення для кінетичної енергії обертального руху. 6.Записати теорему Штейнера.
Рекомендована література
1. Савельев И.В. Курс общей физики.Т.1.- М.: Наука, 1982.- С. 45-48, 134-136, 140-144, 151-152. 2. Кортнев А.В. Практикум по физике. - Киев: Высшая школа, 1963.- С.79. 3. Оселедчик Ю.С. та ін. Інтерактивний модульний курс загальної фізики / Запоріжжя, 2004.- 442 с. 4. Г.Ф. Бушок, Є.Ф. Венгер Курс фізики. Кн.1 / К.: Вища школа.-2003.-311 с.
Iнструкцiю склав доцент кафедри фізики Єршов А.В.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Последнее изменение этой страницы: 2016-04-08; просмотров: 343; Нарушение авторского права страницы; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! infopedia.su Все материалы представленные на сайте исключительно с целью ознакомления читателями и не преследуют коммерческих целей или нарушение авторских прав. Обратная связь - 216.73.216.119 (0.009 с.) |

 ,
, , (15.1)
, (15.1)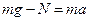 ,
, .
. .
. . (15.2)
. (15.2) , (15.3)
, (15.3)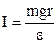 . (15.4)
. (15.4) . (15.5)
. (15.5)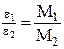 .
. .
. (15.6)
(15.6)
 for one measurement. Calculate the half-width of the confidence interval for r to use the main errors of measurement, m0 and g are table values.
for one measurement. Calculate the half-width of the confidence interval for r to use the main errors of measurement, m0 and g are table values. ,
s
,
s
 ,
g
,
g
 ,
g˙m2
,
g˙m2
 ,
, ,
, .
. ,
, and Δε for five measurements. Calculate the half-width of the confidence interval for r and h using the main errors of measurements. Calculate the half-width of the trust interval for t using five measurements.
and Δε for five measurements. Calculate the half-width of the confidence interval for r and h using the main errors of measurements. Calculate the half-width of the trust interval for t using five measurements.
 =
= ,
kg
,
kg
 .
. ) kg m2; m is the mean mass of four loads at the shafts; R is the distance between the axis of revolution and centre of gravity loads.
) kg m2; m is the mean mass of four loads at the shafts; R is the distance between the axis of revolution and centre of gravity loads. for one measurement. Calculate the half-width of the confidence interval for R to use main errors of measurements, and m is the table values; ΔI0 =
for one measurement. Calculate the half-width of the confidence interval for R to use main errors of measurements, and m is the table values; ΔI0 =
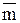 ,
kg
,
kg

 ,
, is the mean mass of four loads at the shafts; R is the distance between the axis of revolution and the centre of gravity loads; m is the mass of one shaft; m is the mass of the hoop; R1 is the radius of the hoop.
is the mean mass of four loads at the shafts; R is the distance between the axis of revolution and the centre of gravity loads; m is the mass of one shaft; m is the mass of the hoop; R1 is the radius of the hoop. . Calculate the half – width of the confidence interval for r and h using the main errors of measurements and m and g are the table values. Calculate the half-width of the trust interval for t using five measurements.
. Calculate the half – width of the confidence interval for r and h using the main errors of measurements and m and g are the table values. Calculate the half-width of the trust interval for t using five measurements. i
i  дослідним шляхом i за допомогою теореми Штейнера.
дослідним шляхом i за допомогою теореми Штейнера.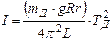 , (16.1)
, (16.1) , (16.2)
, (16.2) – час кількох коливань; k – число коливань.
– час кількох коливань; k – число коливань. , (16.3)
, (16.3)
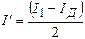 , (16.4)
, (16.4) , (16.5)
, (16.5)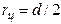 , одержимо
, одержимо . (16.6)
. (16.6)


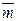 . Маса m в грамах означена на циліндрах.
. Маса m в грамах означена на циліндрах. відносно осi 2 дослідним методом за (16.4).
відносно осi 2 дослідним методом за (16.4). кг×м2
кг×м2
 i зробить висновок про справедливість теореми Штейнера.
i зробить висновок про справедливість теореми Штейнера.


