Заглавная страница Избранные статьи Случайная статья Познавательные статьи Новые добавления Обратная связь FAQ Написать работу КАТЕГОРИИ: ТОП 10 на сайте Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрацииТехника нижней прямой подачи мяча. Франко-прусская война (причины и последствия) Организация работы процедурного кабинета Смысловое и механическое запоминание, их место и роль в усвоении знаний Коммуникативные барьеры и пути их преодоления Обработка изделий медицинского назначения многократного применения Образцы текста публицистического стиля Четыре типа изменения баланса Задачи с ответами для Всероссийской олимпиады по праву 
Мы поможем в написании ваших работ! ЗНАЕТЕ ЛИ ВЫ?
Влияние общества на человека
Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрации Практические работы по географии для 6 класса Организация работы процедурного кабинета Изменения в неживой природе осенью Уборка процедурного кабинета Сольфеджио. Все правила по сольфеджио Балочные системы. Определение реакций опор и моментов защемления |
The high temperature burning of gypsum method (multiphase gypsum) on the grateСодержание книги
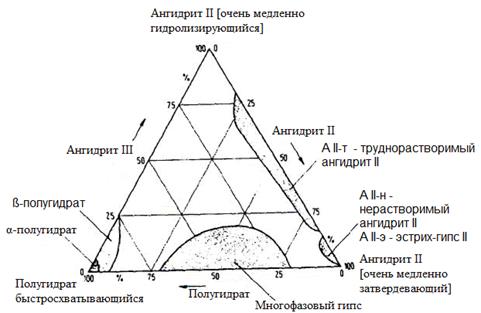
Поиск на нашем сайте When this method is used to grate gypsum grit 5-60 mm or UUSDG-gypsum in the form of briquettes (20 × 20 × 80 mm). Loaded grate passes through the fiery furnace, and hot gases are sucked through the advancing layer of gypsum mass. In the upper layer of gypsum temperature reaches to 700, and the lower layer 300 0C. cooled and the cooled air flows back into the combustion chamber in the rear of the grate hot cast. Performance is about 1200 tons / day. Figure 1.66 shows schematically a furnace grate. Burnt gypsum subsequently milled (approximately 2.3 <2 mm, about 3.1 mm is 0.2-1.0). This product is gypsum of high-temperature roasting with a predominant amount of burnt anhydrite II with a reaction step A II-t (hardly soluble anhydrite), A II-N (insoluble anhydrite) and A II-e (Oestrich-gypsum) and ß-anhydrite III, a small amount of impurities ß-hemihydrate (cp. Figure 1.67 and table 1.28). Gypsum constantly high temperature firing of a mixture composed of several phases, and therefore is also called a multiphase gypsum. In mixtures with gypsum from the rotary kilns it serves mainly to prepare for gypsum machine plaster.
Figure 1.67 - Diagram of three modifications (s) of the gypsum is calcined to a phase transformation (cf. Table 1.28). [188] Properties capable of hardening calcium sulphates Manufactured by the method described before this calcium sulphate binders may be characterized by their properties. They differ in particle size distribution, structure and composition of the particles and thus their practical and technical properties like shuts amount of material behavior and grasp strength. Sum of these differences they can be used in various gypsum building materials. Table 1.30 shows some examples Table - Properties and the possibility of using different gypsum building materials
Hydration CaSO4-binding The basis for the use of calcium sulphate is solidified their ability to regidratizatsii. Gypsum products when used mixed with water in most part, spreadable mush and transformed into calcium sulphate dihydrate. It crystallizes in fused together in a felt needles and solidifies thereby forming a strong, having a constant volume body ("structure"). This occurs through hydration of the solids dissolved (skvozrastvorny hydration mechanism). Occur crystallization processes and topochemical reaction. CaSO4-part binder solution in a supersaturated solution and forms a dihydrate which then crystallizes due to its weaker in comparison with the binder solubility. Speed setting is determined to a large extent, the difference in solubility between the binder and CaSO4-dihydrate. CaSO4 hydration kinetics significantly less dependent on temperature than the hydration kinetics tsementa.Gidratatsiya CaSO4-binders may as well as in cements traced using ESEM-art. 104. α-, ß- hemihydrates α-hemihydrate, due to the lower solubility as compared with the ß-hemihydrate (see. Figure 1.68) penetrates slowly into the solution and gidratiziruetsya or hardens relatively slowly. In most cases, you do not need any inhibitors to provide the required workability. ß-hemihydrate, due to its high solubility, and are often, because of manufacturing conditions with a high specific surface (small crystal size) reacts very fast with water. Therefore, in order to ensure good workability plaster solutions for many applications, setting time must be slow. When machine plastering, one of the main areas of application, as a moderator rather uses natural tartaric acids.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Последнее изменение этой страницы: 2017-02-05; просмотров: 405; Нарушение авторского права страницы; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! infopedia.su Все материалы представленные на сайте исключительно с целью ознакомления читателями и не преследуют коммерческих целей или нарушение авторских прав. Обратная связь - 216.73.216.214 (0.008 с.) |