
Заглавная страница Избранные статьи Случайная статья Познавательные статьи Новые добавления Обратная связь FAQ Написать работу КАТЕГОРИИ: ТОП 10 на сайте Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрацииТехника нижней прямой подачи мяча. Франко-прусская война (причины и последствия) Организация работы процедурного кабинета Смысловое и механическое запоминание, их место и роль в усвоении знаний Коммуникативные барьеры и пути их преодоления Обработка изделий медицинского назначения многократного применения Образцы текста публицистического стиля Четыре типа изменения баланса Задачи с ответами для Всероссийской олимпиады по праву 
Мы поможем в написании ваших работ! ЗНАЕТЕ ЛИ ВЫ?
Влияние общества на человека
Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрации Практические работы по географии для 6 класса Организация работы процедурного кабинета Изменения в неживой природе осенью Уборка процедурного кабинета Сольфеджио. Все правила по сольфеджио Балочные системы. Определение реакций опор и моментов защемления |
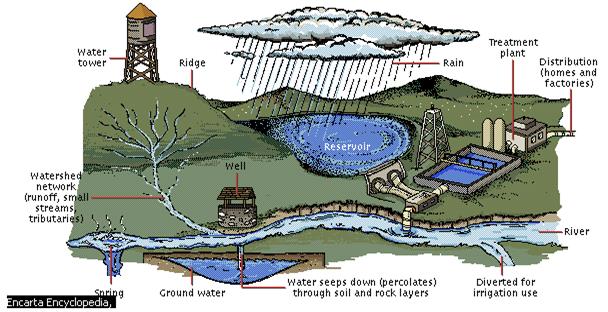
Where Does Our Tap Water Come From?Содержание книги
Поиск на нашем сайте
Drinking water starts as rainwater. It's collected underground or on the earth's surface, and then it's piped to our taps. Most big cities have complicated water supply systems that pipe water to many thousands of people. In rural areas, the water in each house may come directly from an underground well. Where does the tap water in your home/university come from? It may come from one of the sources below. 1. A public well pumps water from underground and distributes it to entire communities. 2. A private well is built on private property and shared by only a few people, such as the members of a family. A farmer may own many wells that provide both drinking water and irrigation water. 3. A public reservoir is a specially built basin in which water is stored. (A natural lake may be modified to serve as a reservoir.) A small reservoir may provide water for just one community. Large reservoirs may supply many communities with water. Underground pipes or aqueducts may transport water hundreds of miles from a reservoir to a community. 4. A river or lake can provide water to a public facility that distributes the water or the water from a river or lake can be piped directly to the tap without going through a public facility. You'll probably need to do some research to find out more about your home/university water source. Use the next questions to help focus your research. Some possible sources of information: · your university custodial staff; · your local water authority; · your community's public works department; · local health officials. Identify your watershed. Once you and your students have identified your watershed, select a surface-water site, such as a stream, river, or lake in your area. Make observations about the water site. · What plants or animals do you observe? · How is the land used? · What does the area look like? · What indicators of pollution have you observed? What do they signal about? Describe the water site. Share your findings in small groups, and then open the discussion to the entire class.
Task 14. You’ve been invited to interpret at the ecological conference. Ask your friend to assist you in training for your future job. Work as interpreters in pairs or small groups. Use topical vocabulary to help you. 1. Турбуючись лише про економічне зростання, люди часто зловживають природою і її ресурсами. 2. Надмірне використання агрохімікатів шкідливе не лише для людини, а й для екосистеми взагалі. 3. Щоб знизити коефіцієнт забруднення повітря, ми повинні збалансувати промисловість з суспільством, встановити очисне обладнання, захороняти відходи у призначених для цього місцях, захищати та відновлювати ліси, які є легенями нашої планети. 4. Вирубуючи ліс, вбиваючи тварин, спотворюючи ландшафти людина зловживає природою, що призводить до забруднення води, землі та повітря. 5. На планеті, де водний простір значно переважає земний, населення зіткнулося з проблемою забезпечення питною водою через постійне забруднення води витоками нафти і викидами токсичних речовин, що призводить до виснаження водних ресурсів та порушення водного циклу. 6. Хоча знати все про природу не означає турбуватись про неї, екологічна освіта нині дуже важлива. 7. Високо індустріалізовані країни не повинні ігнорувати проблеми захисту навколишнього середовища. 8. Будучи занепокоєними економічним зростання і необмеженою індустріалізацією, ми часто забуваємо бути екологічно-свідомими, що призводить до зловживання природою і порушення біологічної рівноваги. 9. Сьогодні нагальним питанням є збереження екосистеми, створення програм по запобіганню катастроф і зниження рівня забруднення. 10. Тільки лісосмуги можуть запобігти вивітрюванню та ерозії ґрунту. 11. Створення лісництв – це спроба зупинити безжальне вбивство тварин і знищення їх ареалів. 12. Коли цілина земля стає культивованою, вона потерпає від надмірного використання агрохімікатів і швидко перетворюється на спустошену землю. 13. Проблеми навколишнього середовища включають такі пункти: забруднення землі, води та повітря й порушення біологічної рівноваги. 14. Багато захисників навколишнього середовища дуже стурбовані необмеженою індустріалізацією, яка призвела до швидкого економічного зростання, розростання ділянок під забудови і надмірних викидів в гідросферу і атмосферу; в результаті чього земля, вода і повітря забруднюються. 15. Транспорт – один з головних шумових забруднювачів. 16. Полювання – це безжальне знищення рідкісних тварин. 17. Людство зловживає природою, не розуміючи, що її багатство не безмежне. 18. Основні завдання, зазначені у всесвітній програмі по захисту навколишнього середовища – зберігати екосистему, захищати і відновлювати популяції тварин і рослин, встановити відчисне обладнання на заводах та фабриках, скидати сміття у спеціально призначених територіях. 19. Необмежена індустріалізація призводить до спотворення та засмічення ландшафтів, а також до концентрації диму та токсичних газів в атмосфері. 20. Щоб зберегти та відновити популяції тварин та птахів ми повинні боротись з забрудненням землі, повітря, води, охороняти середовища існування тварин, звести до мінімуму шумове забруднення та виховати покоління екологічно-свідомих людей. Task 15. Study these “earthly” phrases. Match them with their explanation. Find their equivalents in Ukrainian and use them in the situations of your own. 1) out of this world a) as far or as long as possible 2) Mother Earth b) to succeed, to make a name for one’s self 3) on top of the earth c) earthlike in terms of colour or texture, an informal, solid, realist, and honest personality 4) as big as the equator d) sleeping very soundly or concentrating so deeply that one is unaware of immediate environment (sound, movement, etc.) 5) as big as the ocean e) wonderful, fantastic, unbelievable 6) down to earth f) extremely happy and content, very successful 7) move heaven and earth g) an exaggeration for extremely large in area or amount, huge 8) to the ends of the earth h) seeming to be unaffected by the immediate environment or activity 9) carry the weight of the world i) close to being fired or kicked or thrown out, close to being beat up, close to dying 10) not for anything in the world j) an exaggeration for extremely large in circumference 11) don’t have a care in the world k) without question the answer is “no” 12) move up in the world l) a literary expression for the name of the one who has on one’s shoulders planet 13) earthly m) a person doesn’t (or acts as if he/she doesn’t) have any responsibility, guilt or worry 14) dead to the world n) realistic, a solid and calm personality 15) in a world of one’s own o) to do everything possible to get something accomplished 16) set the world on fire p) to carry a large burden, guilt or responsibility for something 17) not long for this world q) improve one’s personal or professional standing or relationships either economically speaking in terms of position Task 16. Comment on a list of practical ideas given below. What of them are the easiest for you? What is your idea to help the environment? What can you do? · Buy fresh food that doesn't need a lot of packaging. · Try to buy “organic” fruit and vegetables from farmers who don't use chemicals. · Save as much water as possible. · Find out more about Green organizations in your area. · Write letters to the government in your country about Green problems which worry you. · Use products that won't stay forever in the earth or sea when you throw them away. · Use bottles more than once (or take them to a bottle bank). · Try to save paper. Also, buy and use recycled paper as often as possible. · Avoid “throw-away” products. · Make sure that your family and friends use unleaded petrol in their cars. · Don't buy products (fur or ivory, for example) made from rare or protected species. · Use public transport as often as possible. · If you're buying wood, don't choose hardwood from tropical rainforests. · Look for aerosols which haven't got any of the chemicals called CFCs (chlorofluorocarbons) in them. · Try to eat a healthier diet. Avoid too much fat or sugar. · Don't buy hamburgers or pizzas in plastic boxes which contain CFCs. · Use batteries as little as possible. It takes 50 times more energy to make them than they produce. · Don't leave on electric lights, TV, hi-fi, etc, if you're not using them. · Take aerobic exercise at least three times per week. · Find out more about conservation issues in your area. Are there any woods, fields, etc, in danger, for example? · Try to throw away at least 25% less rubbish. · Help old people in your area to insulate their homes. This saves energy and helps to keep them warm in winter. · Visit any local nature reserves or zoos and talk to the people who run them. Add your own conservation ideas to this list.
Task 17. Make a copy of the following statements and rank each on a scale of 1 to 10 from strongest disagreement "1" to strongest agreement "10". A. Natural resources should not be left untapped if using them could improve living conditions for a group of people. B. It is important for people to preserve wilderness areas even if a vast majority of people will never visit them. C. The world's natural resources exist for people to use. Preserving these resources as wilderness is a luxury we often cannot afford. D. Environmental degradation is the biggest problem facing humanity today. E. People will eventually develop new technologies to cope with environmental problems. F. People have a responsibility to protect all life forms on Earth. G. Protecting a country's natural resources and natural heritage is primarily the Government's responsibility. H. The Government is doing a good job of protecting your country's environment. I. Recycling is the most important thing people can do to help improve the environment. J. People should be able to use their own land (i.e., farming, housing, logging, wildlife habitat) in whatever way they see fit. K. All people have a legal right to clean air and water. L. When a dilemma arises between protecting wildlife and protecting jobs for people, we should consider the needs of people first. M. The fate of the human race is tied to the fate of other living things; if people are to survive, we must protect all species and their habitats. N. Human overpopulation is the single greatest factor contributing to Earth's environmental problems. O. The laws the Government has passed to control pollution are sufficient to ensure safe air and water for future generations.
Task 18. Read the text and discuss the most acute problems of environment in Ukraine.
Ukraine has the possibility to play an outstanding role among the countries of Central Europe. However, this potential is hampered by many economical, political and ecological problems.
The main pollution sources of air in Ukraine are thermal electric power stations and metallurgy that are emitting correspondingly 32% and 38% of the total pollution caused by stationary sources. Many enterprises of metallurgy, mining, etc. located in the Donetsk-Dnipro Region are one of the causes of the ecological crisis there. Moreover, most of them are located in the centres of the cities. The chemical industry also adds to pollution of the air. Oil refineries from time to time are polluting underground waters. Every year the economy of Ukraine is consuming 1.3-1.5 billion tons of natural materials. Most of them are returned back to the environment as waste of industries and consumers. Up to the present day problems concerning the treatment and storage of highly toxic waste have not yet been solved: 2.7 million tons of such waste are now dumped in Donetsk Region, 3.2 in Dnipropetrovsk Region, 1.3 in Kirovograd Region. About 52% of toxic chemicals are utilized in Ukraine. Still a pressing problem in Ukraine is the storage of radioactive waste (RAW) and the use of radioactive materials. First of all, this concerns the enormous amounts of RAW resulting from the Chernobyl radiation accident. Secondly, attention should be drawn to more than one thousand sources of radiation that are being applied for industrial, agricultural, medical and scientific purposes. In the third place, more than 70 million cub. m. of RAW are dumped or stored by the uranium industry, mining and processing industries. Some years ago some attempts were made by foreign companies to bring into Ukraine from abroad raw materials that were in reality mere waste. Usually this is waste that is difficult or expensive to treat and often it consists of toxic chemicals. There is an urgent need for arranging an ecological service that will operate at the country’s borders and regulations should be worked out and adopted at the international level in order to stop Ukraine becoming a dumping place for the rest of Europe.
Task 19. Summarize the given information and expand on the consequences of the Chernobyl nuclear accident.
|
|||||
|
Последнее изменение этой страницы: 2016-08-26; просмотров: 285; Нарушение авторского права страницы; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! infopedia.su Все материалы представленные на сайте исключительно с целью ознакомления читателями и не преследуют коммерческих целей или нарушение авторских прав. Обратная связь - 3.138.134.140 (0.009 с.) |

 by Sharon Cowley
by Sharon Cowley ature protection, conservation of a favourable for life environment, ecological safety all together are becoming top national priorities in Ukraine. In this area the Ministry for Environmental Protection of Ukraine was organized in 1991.
ature protection, conservation of a favourable for life environment, ecological safety all together are becoming top national priorities in Ukraine. In this area the Ministry for Environmental Protection of Ukraine was organized in 1991. Rivers and reservoirs of Ukraine are polluted mainly by organic compounds, nitrogenous compounds, heavy metals, phenols and petroleum products. The most heavily polluted rivers are in the catchment areas of the rivers Zakhidny Bug, Siversky Donets and in the area of the Sea of Azov. The capacity and effectiveness of water purification facilities are not growing adequately to the increase of quantities of waste-water. In some cases this leads to accidental discharge of polluted waste-water to the outside environment. The Dnipro River, the main water-body of Ukraine, can serve an excellent example: only 45% of the total amount of wastewater discharged to it is treated.
Rivers and reservoirs of Ukraine are polluted mainly by organic compounds, nitrogenous compounds, heavy metals, phenols and petroleum products. The most heavily polluted rivers are in the catchment areas of the rivers Zakhidny Bug, Siversky Donets and in the area of the Sea of Azov. The capacity and effectiveness of water purification facilities are not growing adequately to the increase of quantities of waste-water. In some cases this leads to accidental discharge of polluted waste-water to the outside environment. The Dnipro River, the main water-body of Ukraine, can serve an excellent example: only 45% of the total amount of wastewater discharged to it is treated.



