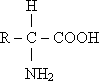Мы поможем в написании ваших работ!
ЗНАЕТЕ ЛИ ВЫ?
|
Chapter Eight : Reproduction
(1) There are two main theories about the origin of life.
(2) Reproduction in living organisms takes place in two main levels:
A- Molecular duplication in which the cellular molecules multiply.
B- The whole organism.
(3) There are two main methods of reproduction:
A- A sexual reproduction that includes:
1- Binary fission e.g Amoeba; paramecium simple algae and bacteria.
2- Budding e.g yeast, hydra, sponge
3- Regeneration e.g: Sponge, Hydra star fish - planaria.
4- Sporogony e.g: Mushroon - some algae, bread mould, and some ferns.
5- Parthenogensis e.g some worms, crustaceans and insects.
6- Tissue culture: e.g carrot, tobacco.
B- Sexual reproduction which may be:
1- By conjugation e.g spirogyra alga
2- By gametes e.g higher plants and animals.
(4) Alternation of generation is the phenomenon through which some living organisms reproduce sexually followed by one or two cycles asexually. e.g plasmodium (protozoan), schistosoma (worms) and fern plants (Adiantum), from the benefits of alternation of generation is the production of great number of life stages because most of them are lost or damaged during the life cycle, the two types of reproduction enable the living organism to adapt with changes in environmental conditions.
(5) The flower emerges from the axil of a leaf called bract (may be absent)
(6) A typical flower has four floral whorls
A- Calyx "Sepals"
B- Corolla "petals"
C- Androecium "Stamens" male organs
D- Gynoecium "Carpals" female organs
(7) Flowers of most monocot plants the calyx leaves are hardly differentiated from the corolla leaves so they are called perianth.
(8) Monoecious plants are those that carry male and female flowers.
(9) Diecious plants are those that male flowers exist on one plant and female ones exist on another plant. e.g palm tree
(10) Flowers are divided according to their symmetry into:
A- Actinomorphic e.g. onion.
B- Zygomorphic e.g. petunia
(11) The function of the flower is reproduction, the stages of reproduction in flowering plants are:
1- Formation of pollen grains
2- Formation of ovules
3- Pollination
4- Fertilization.
(12) Pollination could be:
A- Self pollination
B - Cross pollination which takes place when:
1- The flowers are unisexual
2- Early maleness or early femaleness
3- Height of another is lower than the stigma.
(13) The pollin grain germinates on the stigma forming a pollen tube which penetrates the stigma and passes through the style till it reaches the ovule micropyle, the tube nucleus degenerates and the generative nucleus divides forming two male nuclei, one of them fuses with the two polar nuclei (or embryo sac nucleus) forming the endosperm nucleus which divides to give the endosperm tissue, it supplies the embryo with food, the other male nucleus fuses with the egg cell forming the zygote.
This process is called double fertilization.
(14) We can divide seeds into:
A- endospermic seeds e.g wheat, dates
B- exoendospermic seeds e.g bean, pea
(15) After fertilization
a- The two integuments will form the testa
b- The ovary wall becomes the pericarp
c- The ovary will form the fruit
d- Other floral whorls wither and fall down except in cases that they share in fruit formation.
(16) If the two integuments are fused with the ovary wall "pericarp" This forms single seeded fruit or grain e.g. Maize - wheat.
(17) Parthenocarpy means that some ovaries can develop naturally into seedless fruits without pollination or fertilization. E.g. Banana, pine, Apple, it can be carried out artificially e.g. tomato and cucumber by some stimulants e.g. indole acetic acid or naphthol acetic acid.
(18) The male reproductive system in man has two functions:
A- Production of sperms. (300 - 500 millions for each ejaculation)
B- Production of male hormone which is responsible for the appearance of secondary sexual characters.
(19) The position of testes outside the body exists in some mammals like primates and ungulates, because spermatogenesis needs lower temp.
(20) The female reproductive system in human consists of:
a- Two ovaries.
b- Two oviducts
c- The uterus
d- the vagina.
(21) The female reproductive system has the following functions:
a- Production of ova ("about 400 ova" during the fecundity period)
b- production of female hormones estrogen and progesterone.
c- safe place for the development of the embryo.
(22) The breeding cycle of placental mammals is a period where the ovary becomes active and the uterus becomes ready for fertilization, this cycle is periodic and coincide with mating and reproduction:
a- Lion and tiger its annual (12 month)
b- Cats and dogs biannual (6 month)
c- Rabbits - rats every month.
d- Human being every 28 days.
(23) The menstrual cycle is differentiated into ovarian cycle and uterine cycle.
(24) Menstruation cycle is divided into 3 phases:
1- Phase of proliferation (10 days)
2) Phase of ovulation (14 days)
3- Phase of menstruation (3 - 5 days)
(25) Pregnancy occurs if the ovum is fertilized in the second phase (ovulation).
(26) During pregnancy the corpus luteum remains to secrete the progesterone and estrogen, these two hormones inhibit the ovulation, preserve the endometrium and stimulate the mammary glands to secrete milk after delivary.
(27) Contraceptive methods of birth control:
A- The oral contraceptives "pills" which are combination of synthetic estrogen and progesterone.
B- Intra uterine device "Coil" which is inserted into the lumen of the uterus and prevents the implantation of the ovum.
(28) The inner membrane "amnion" and the outer membrane "chorion" are formed around the embryo in addition to the extension of the endometrium.
(29) Both the chorionic villi and the endometrium intermingle to form the placenta.
(30) After short time both margins of the amnion join forming the umbilical cord which extends from the placenta to the intestine of the embryo.
(31) The mother's blood and foetus blood do not mix but their vessels are only adjacent to allow movement of substances by diffusion.
(32) There are two types of twins:
A- Fraternal "Two ova and two sperms" .
B- Identical "one ovum and one sperm"
- One mature ovum and one sperm, then dividing cells separate into two masses they are similar in all genetic characters, some time they are attached together form the head. Abdomen or chest this case is called siamese.
- Extra - uterine fertilization "test tube babies" is done in 1977 when scientists succeeded to get a mature ovum from a wife's ovary and fertilized it externally with the husband's semen in a certain nutritive medium.
- Embryo culture exp. have been conducted on rabbits and mice, the cells from their early embryonic stages were separated and cultured as separate masses of cells in a female's uterus to proudce complete individual.
- Renucleation is a type of embryo cutlute through which the nucleus is removed from an embryo body cell of an Amphibian. Then the nucleus of an unfertilized ovum is destroyed by radiations, then the nucleus from the somatic cells of the embryo is implaned in the ovum which develops normally and give individuals identical to individual from which the cultured nucleus was taken.
- Gamete banks are used to store gametes of selected animals to keep them available for external fertilization.
- The gametes are stored in, frozen conditions up to 20 years.
- Centrifugation or exposure to limited electric field can separate the sperms with X chromosomes from sperms with Y chromosomes.
Chapter One
Main concepts of chapter 9
Genetics
1- Methods of studying genetics:
A- Bredding and crossing in which organisms with well known characters are grown and crossed and then we follow the inheritance of their characters.
B- Family pedigree
This is a diagram in which males are represented by squares and females by circles, the shaded squares or circles indicate to the studied character.
C- Cytological and biochemical studies.
2- Mendel's first law:
When two homozygous individuals different in a pair of allelomorphic characters are corssed, only the dominant character appears in F1 generation while the two characters appear in F2 by 3: 1
3- Mendel's second law:
When two homozygous individuals different in two pairs of allelomorphic characters are crossed, each pair is assorted randomly and inherited independantly from the other pair, the ratio of the second generation is 9: 3: 3: 1
4- In case of lack of dominance there is no gene that completely dominates over the other, so together they produce an intermediate character. e.g. colour in Antirrhinum flowers.
5- Incase of incomplete dominance the recessive gene shows the character in certain conditions only e.g sickle-cell onemia in man.
6- Complementary genes "qualitative". This is a genetic case through which the character is controlled by 2 pairs of genes, the dominant character appears if at least one dominant gene is found in each pair. The ratio is 9: 7 in the second generation. e.g some strains of pea flowers.
7- Lethal genes are genes which cause the death of forth of the offspring when they are in a pure state
8- Multiple alleles is a case in which the genetic traits are controlled by more than one pair of allelomorphic genes but each individual carries only two genes e.g. inheritance of fur colour in rabbits and blood groups in man.
9- Blood groups in man represents three genetic cases.
A- Complete dominance because both gene A and B dominate over 0.
B- Lack of dominance because gene A and gene B give AB.
C- Multiple alleles because there are three genes A, B, O but the share of each individual is only one pair.
10- Blood groups in man are A, B, AB, O and they are determined according to the antigens and antibodies "chemical bases"
11- Rhesus factor is an antigen, it is found in about 85% of human beings which are RH+ the other 15% are RH- , there are three pairs of genes that control the production of rhesus antigens, they are very similar in their effect.
12- Linked genes are genes that carried on the same chromosome and transferred from parents to their off spring as one unit Mendel ratio can not be applied e.g. the inheritance of wing length and body colour in drosophila fly.
13- In some cases linkage between genes is broken due to the crossing over which occurs during meiosis.
14- The chromosomal maps was done by Morgan and they represent the chromosome and the arrangement of genes on these chromosomes and the distances between genes.
15- In each somatic cell there is the total number of chromosome, they are divided into one pair called sex chromosomes and the rest are called autosomes.
16- In man there are 46 chromosomes 44 autosomes + XX for females, 44 autosomes + xy for males.
17- The reproductive cells or gametes contain half the number of chromosomes.
18- There are some abnormal cases
A- Down's syndrome: male 45xy, female 45xx
B- Klinefeltersyndrome: 44xxy
C- Turner's syndrome: 44x
D- Multiple sex genes: 44xxx or 44 xxxx
19- Barr body is a sex chromosome x which is compact and can be stained it is used to determine the sex of some players or competitors at the Olympics.
20- Sex-lined inheritance means that the trait is determined by the genes located or carried on the sex chromosome x examples: White eye colour in drosophila, colour blindness in man, hemophili. The female passes these traits to her sons and the sick man passes them to his grand sons through his daughters.
21- Sex influenced inheritance means the genes are carried on the autosomes but the action of genes is influenced by sex hormones. Examples: Sheep horns [dorset-suffolk] and premature baldness in man.
22- The environment has an effect on the genes and their characters e.g. orbanch has no genes for chlorophyll formation so it can not make photosynthesis even if it is exposed to light.
23- The appearance of any character in a living organism depends on:
A- The presence of its genes
B- Suitable environmental conditions.
24- The effect of heat on genetic characters is seen in the following:
A- The white fur changed to black in low temp. in Himalayan rabbits.
B- The drosophila wings grew curved in high temp. (25o C)
Molecular biology
Main Concepts of chapter-10
Molecular Biology
1- Genetic information control the inheritance of the characters and the development of the fertilized egg into an individual.
2- Genes are the units of genetic information.
3- Chromosomes are composed of DNA and proteins.
4- Evidences that DNA is the genetic material:
A- Bacterial transformation.
B- Bacteriophages.
C- The quantity of DNA in cells.
C- The base content of DNA in cells.
5- DNA is a polymer which consists of four monomers called nucleotides.
6- Each nucleotide consists of :
A- Nitrogenous base [purines or prymidines]
B- Ribose or deoxyribose sugar.
C- Phosphate group.
7- Adenine pairs to thymine and guanine pairs to cytosin through hydrogen bonds.
8- The replication of DNA needs a number of enzymes and proteins:
A- DNA helicase which moves along the double helix, separating the two strands
B- DNA polymerase which works only on the 3 to 5 template and it adds new nucleotides.
C- DNA ligase which joins pieces of DNA together.
9- All Biological polymers are damaged by :
A- The body heat.
B- The aqueous state inside the cell.
C- Various chemicals and radiations.
10- DNA in prokaryote is circular , its two ends are joined, it is attached to the plasma membrane at a point or more where douplication starts, it is not complexed with proteins, 100% coding sequences, there are some additional small circular DNA called plasmids.
11- DNA of Eukaryotes is organized into several chromosomes, each one contains a single DNA molecule which is associated with various protein (chromatin) these proteins may be:
A: histone proteins
B: Non- histone proteins.
12- Genome is the total of all the genes (DNA) in any body cell.
13- Any gene is a sequence of nucleotides.
14- DNA can be divided into:
A- Coding DNA which is responsible for the production of RNA and protein synthesis.
B- Non-coding DNA.
15- Transcription is to change the sequence of nitrogenous bases in a DNA strand into a sequence of nitrogenous bases in m-RNA strand.
16- There are three types of RNA:
A- Messenger RNA
B- Ribosomal RNA
C- Transfer RNA
17- Most of genes are present in only one copy or few copies in the genome, but sometimes some sequences of nucleotides are repeated which we call repetitive DNA or satellite DNA.
18- In 1960 it was discovered that the genes that make bacterial resistant against drugs transfer from one bacterium to another by plasmids.
19- Proteins are divided into two main groups:
A- Structural proteins
Fibrous proteins - collagens - keratins
B- Regulatory proteins - Enzymes - Antibodies - Hormones
20- Proteins are formed of un branched linear chains join between amino acids.
21- There are 20 different amino acids, which have the same basic structure
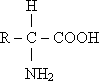
22- Amino acids are joined together by peptide bonds through dehydration reaction.
23- RNA is formed of a single strand, the sugar is ribose and pyrimidines bases are uracil and cytosine.
24- M.RNA has the following main parts:
A- Ribosome binding site (5 end)
B- Start codon [AUG]
C- Polyadenine tail (3 end)
D- Stop codon [UAA - UAG - UGA]
25- Ribosomes consists of 4 types of rRNA and about 70 kinds of polypeptides.
26- The production of ribosomes takes place in the nucleolus.
27- T.RNA carries amino acids from the cytoplasm to the ribosomes.
28- For each kind of amino acids there is a specific kind of t.RNA molecule that can recognize and transport it.
29- There are 2 sites on T.RNA:
A- The amino acid attachement site
B- The anti-codon.
30- The genetic code is the triplet sequence of nucleotides in DNA and it is transcribed into a complementary sequence in m-RNA which goes to the ribosome where it is translated into a sequence of amino acids in a poly-peptide (protein)
31- Protein synthesis passes through three main stages:
A- Initiation
B- Elongation
C- Termination
32- Nucleic acid hybridization :
- If DNA is heated to 100 o C the hydrogen bonds between base pairs are broken down and the two strands of DNA molecule are separated producing single stranded DNA.
- Hybridization technique is used in producing hybrid or mixed double helices, to tell if a particular gene is present in a genome, and also to determine the degree of relationship between two different species of living organisms.
33- Bacterial restriction enzymes are secreted by some strains of E-coli, they attack specific sequences of nucleotides in the viral DNA and break it down into useless fragments, the bacteria protect themselves from these enzymes with the help of modification enzymes which add or bind methyl groups to the recognition sites.
34- Several copies of a desired gene can be produced by splicing it to a molecule that carry it into bacterial cells, this carrier may be a phage or plasmid in case of prokaryotes and jumping genes in case of eukaryotes.
35- Recombinant DNA technology is the introducing of DNA from one organism into cells of another living organism.
36- Interferons are proteins that interfere with replication of viruses specially viruses with RNA genomes such as influenza and poliomyelities.
|