Заглавная страница Избранные статьи Случайная статья Познавательные статьи Новые добавления Обратная связь FAQ Написать работу КАТЕГОРИИ: ТОП 10 на сайте Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрацииТехника нижней прямой подачи мяча. Франко-прусская война (причины и последствия) Организация работы процедурного кабинета Смысловое и механическое запоминание, их место и роль в усвоении знаний Коммуникативные барьеры и пути их преодоления Обработка изделий медицинского назначения многократного применения Образцы текста публицистического стиля Четыре типа изменения баланса Задачи с ответами для Всероссийской олимпиады по праву 
Мы поможем в написании ваших работ! ЗНАЕТЕ ЛИ ВЫ?
Влияние общества на человека
Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрации Практические работы по географии для 6 класса Организация работы процедурного кабинета Изменения в неживой природе осенью Уборка процедурного кабинета Сольфеджио. Все правила по сольфеджио Балочные системы. Определение реакций опор и моментов защемления |
Box 1: Coordinating the Covid-19 Response with Economic and Social DevelopmentСодержание книги
Поиск на нашем сайте
3) International cooperation in combating the epidemic was promoted. China has acted in an open, transparent, and responsible manner, and has earnestly fulfilled its international obligations. The Chinese government reported the outbreak of the epidemic to the world at the first opportunity, released the genome sequence of the virus to the world as soon as it was determined, immediately shared China’s diagnostic and therapeutic protocols and containment measures, and firmly supported the World Health Organization (WHO) in playing its leading role. We set up an online Covid-19 knowledge center open to all, and published eight versions of diagnostic and therapeutic protocols and seven versions of containment protocols, unreservedly sharing our prevention, control, and treatment experiences with all.
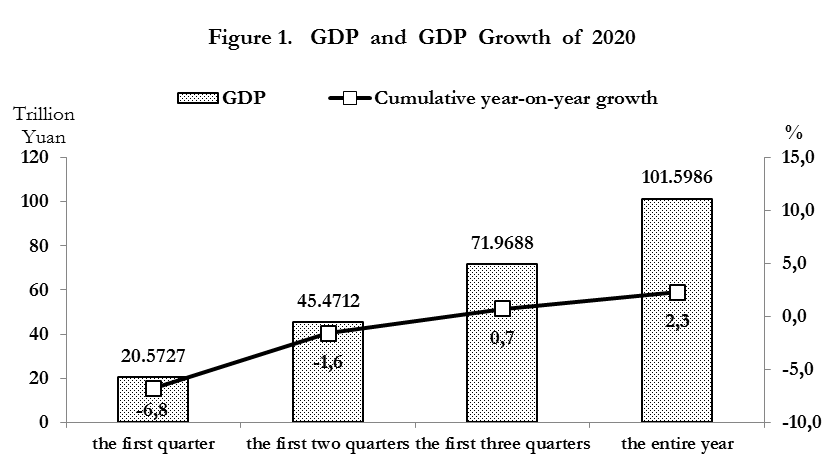
We launched the largest global humanitarian assistance campaign since the founding of the PRC, provided assistance both to the WHO and for the Covid-19 Global Humanitarian Response Plan launched by the United Nations, dispatched 36 teams of medical experts to 34 countries in need of them, and provided assistance in combating the epidemic to 150 countries and 13 international organizations. Giving full play to our strengths as the world’s largest supplier of epidemic prevention materials, over the course of the year we provided more than 200 countries with over 220 billion face masks, 2.3 billion protective gowns, and 1 billion testing kits. We actively pushed forward cooperation on drug and vaccine R&D as well as global joint prevention and control. We also helped developing countries to overcome the challenges brought by the epidemic. 2. We formulated and implemented macro policies to meet the urgent needs of market entities, and facilitated a stable and sustained economic recovery. Confronted with the impact of Covid-19, the severity of which has rarely been seen in history, we made ensuring stability on the six fronts the foundation of our efforts, and clearly defined the tasks required for maintaining security in the six areas, with a particular emphasis on securing employment, meeting basic living needs, and protecting market entities. We remained committed to maintaining security in order to deliver the stability needed to pursue progress. Taking into account China’s national conditions and realities, we took prompt and decisive action while maintaining our resolve, and refrained from resorting to a deluge of strong stimulus policies. Instead, we balanced large-scale economic policies and intensified our macro policies to counteract the negative impacts of Covid-19, thereby strengthening the internal forces driving economic growth and ensuring more balanced and more sustainable development. 1) Major indicators were better than expected. China’s gross domestic product (GDP) in 2020 reached 101.6 trillion yuan, an increase of 2.3%. A total of 11.86 million urban jobs were created and the year-end surveyed urban unemployment rate was 5.2%. The consumer price index (CPI) rose by 2.5%. A basic equilibrium was maintained with regard to the balance of payments, and foreign exchange reserves were kept at over US$ 3 trillion.
2) Epidemic relief policies for enterprises were effectively implemented. We implemented large-scale tax cuts and fee reductions on a time-limited basis in order to help enterprises. We reduced or eliminated VAT on small-scale taxpayers in the current stage, temporarily reduced or waived enterprises contributions to basic old-age insurance, unemployment insurance, and workers’ compensation schemes, halved enterprises contributions to basic medical insurance for urban workers, and implemented time-limited supportive policies on the housing provident fund, saving market entities more than 2.6 trillion yuan over the course of the year. We developed new methods for implementing macro policies. The central government established mechanisms for ensuring that the additional two trillion yuan of government bonds went directly to prefecture and county governments, and provincial-level governments channeled more financial resources to lower-level governments. These combined measures supported prefecture and county governments in implementing policies to benefit both enterprises and the people. We introduced supportive monetary measures with a value of over nine trillion yuan by means such as required reserve ratio reductions, medium-term lending facilities, open market operations, re-lending and rediscounts, and by developing new monetary policy instruments that directly serve the real economy. We also implemented the loan prime rate (LPR) mechanism to reduce the cost of financing. Large commercial banks increased inclusive loans to micro and small enterprises (MSEs) by more than 50%. Over the year, the financial sector saved enterprises 1.5 trillion yuan via measures to boost the real economy. Rental payments for certain MSEs and self-employed individuals in the service sector were reduced, waived, or postponed for a certain period of time.
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Последнее изменение этой страницы: 2021-04-12; просмотров: 42; Нарушение авторского права страницы; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! infopedia.su Все материалы представленные на сайте исключительно с целью ознакомления читателями и не преследуют коммерческих целей или нарушение авторских прав. Обратная связь - 3.14.245.172 (0.009 с.) |