Заглавная страница Избранные статьи Случайная статья Познавательные статьи Новые добавления Обратная связь КАТЕГОРИИ: ТОП 10 на сайте Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрацииТехника нижней прямой подачи мяча. Франко-прусская война (причины и последствия) Организация работы процедурного кабинета Смысловое и механическое запоминание, их место и роль в усвоении знаний Коммуникативные барьеры и пути их преодоления Обработка изделий медицинского назначения многократного применения Образцы текста публицистического стиля Четыре типа изменения баланса Задачи с ответами для Всероссийской олимпиады по праву 
Мы поможем в написании ваших работ! ЗНАЕТЕ ЛИ ВЫ?
Влияние общества на человека
Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрации Практические работы по географии для 6 класса Организация работы процедурного кабинета Изменения в неживой природе осенью Уборка процедурного кабинета Сольфеджио. Все правила по сольфеджио Балочные системы. Определение реакций опор и моментов защемления |
Сайт Wipo.int (зарубежные патенты) ⇐ ПредыдущаяСтр 3 из 3
Заходим на сайт www.fips.ru и спускаемся в самый низ, ищем кнопку «Ссылки»;
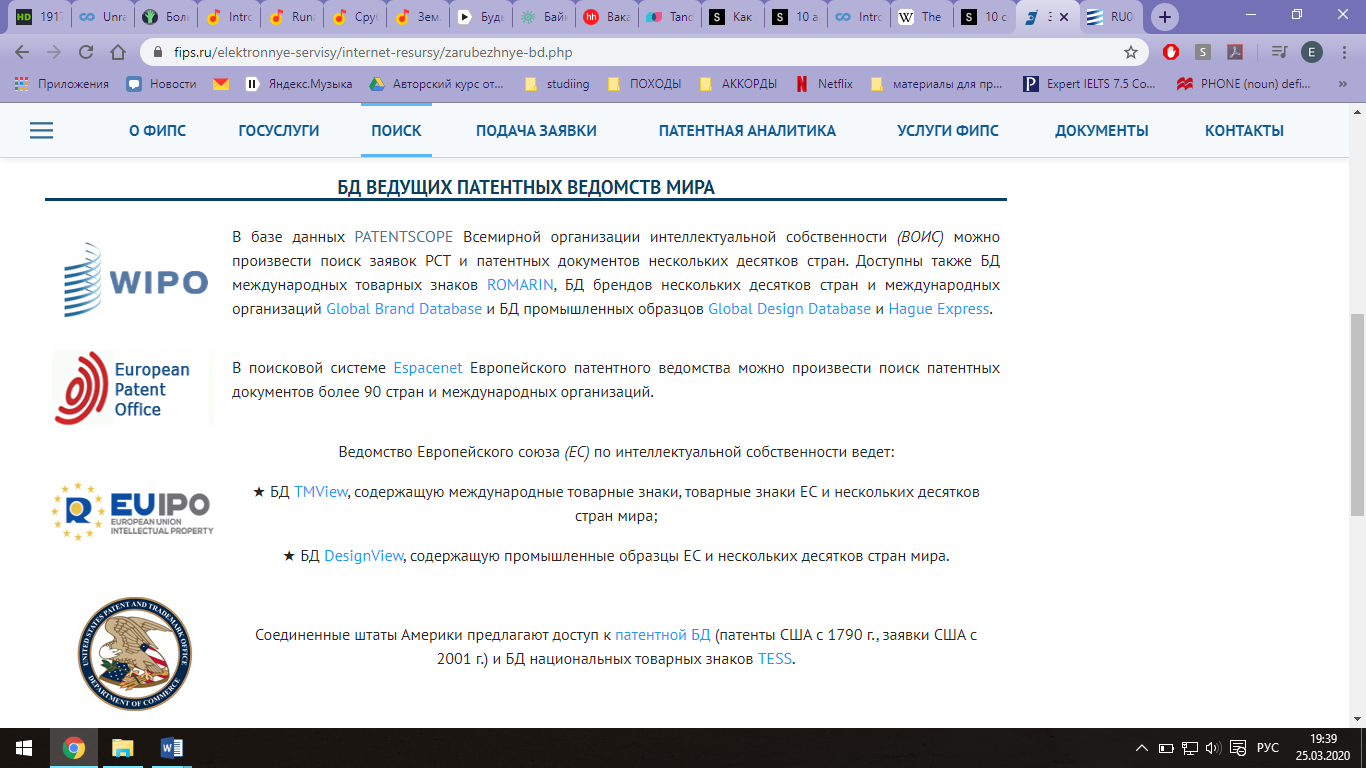
Спускаемся ниже, где изображены логотипы сайтов для поиска зарубежных патентов, ищем в разделе «БД ведущих патентных ведомств мира» ссылку «PATENTSCOP» (Всемирная организация интеллектуальной собственности (ВОИС)) нажимаем;
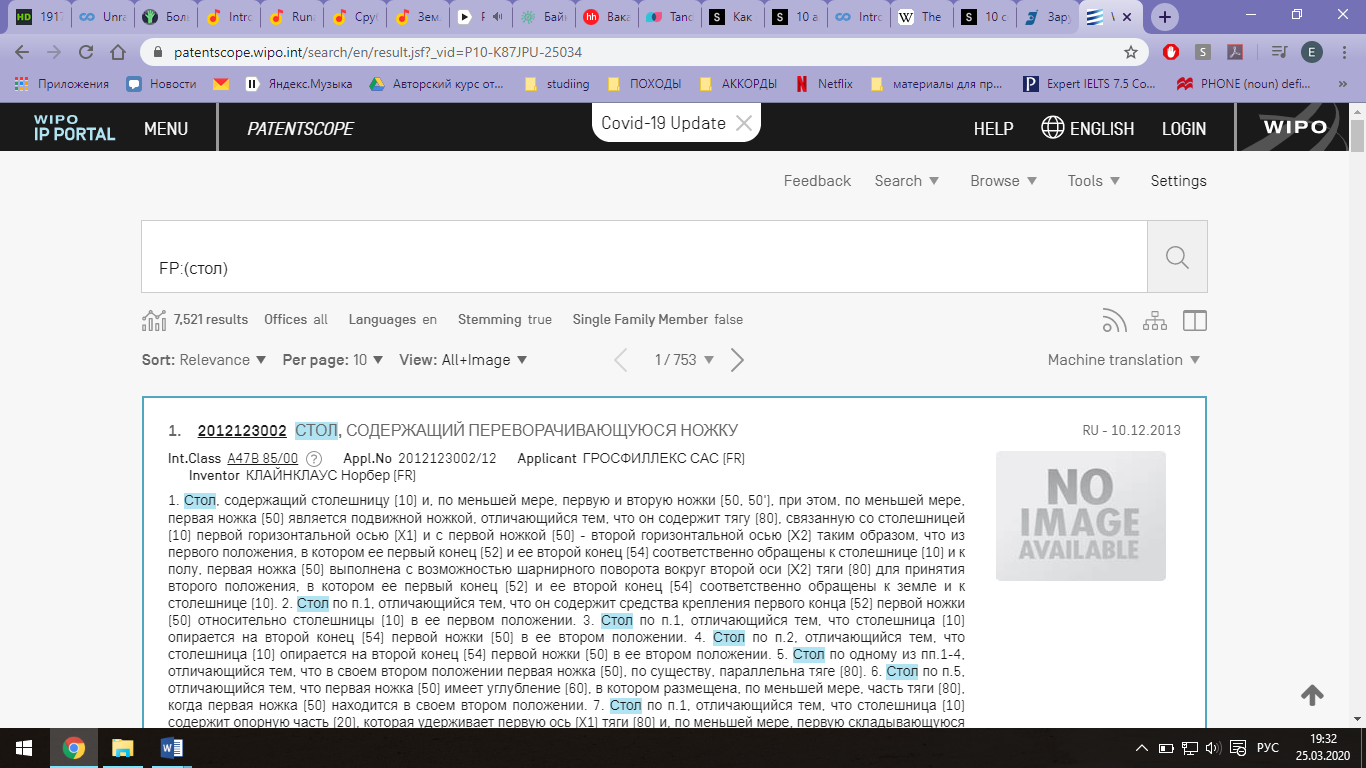
Листаем ниже, в строке «Искать термины» набираем ключевое слово поиска (например, «стол»), нажимаем на поиск; Когда сайт выдает варианты найденных изобретений, в шапке необходимо найти кнопку "Просмотреть" и нажать на выплывающее меню (на стрелочку) и выбрать из списка "All+image", чтобы увидеть не только текст изобретений, но и чертежи;
Выбираем подходящий патент, нажимаем на номер публикации (например, 0000109040), открывается страница патента, смотрим разделы в шапке страницы «Формула изобретения», «Чертежи», «Описание», «Нац. библиограф. данные», можем сохранить в формате PDF. Пример найденного патента:
Перваявкладка «Nationalbiblio. Data»:
OfficeRussian Federation Application Number2010154412/13 Application Date18.02.2011 Publication Number0000109040 Publication Date10.10.2011 Grant Number Grant Date10.10.2011 Publication KindU1 IPC E04G 1/32
E04G 25/00
B27B 21/00 InventorsГерасимовАлександрПетрович (RU)
3. Сайт www3.wipo.int Заходим на сайт www.fips.ru и спускаемся в самый низ, ищем кнопку «Ссылки»; На открывшейся странице ищем кнопку «Зарубежные БД» (БД – базы данных), нажимаем; Спускаемся ниже, где изображены Логотипы сайтов для поиска зарубежных патентов, ищем в разделе «БД ведущих патентных ведомств мира» ссылку «HagueExpress», нажимаем;
Открывается новая страница с сайтом www3.wipo.int;
Выбираем патент, близкий к теме исследования;
4. Сайт www.worldwide.espacenet.com Заходим на сайт www.fips.ru и спускаемся в самый низ, ищем кнопку «Ссылки»; На открывшейся странице ищем кнопку «Зарубежные БД» (БД – базы данных), нажимаем;
Спускаемся ниже и нажимаем на ссылку «ClassicEspacenet»;
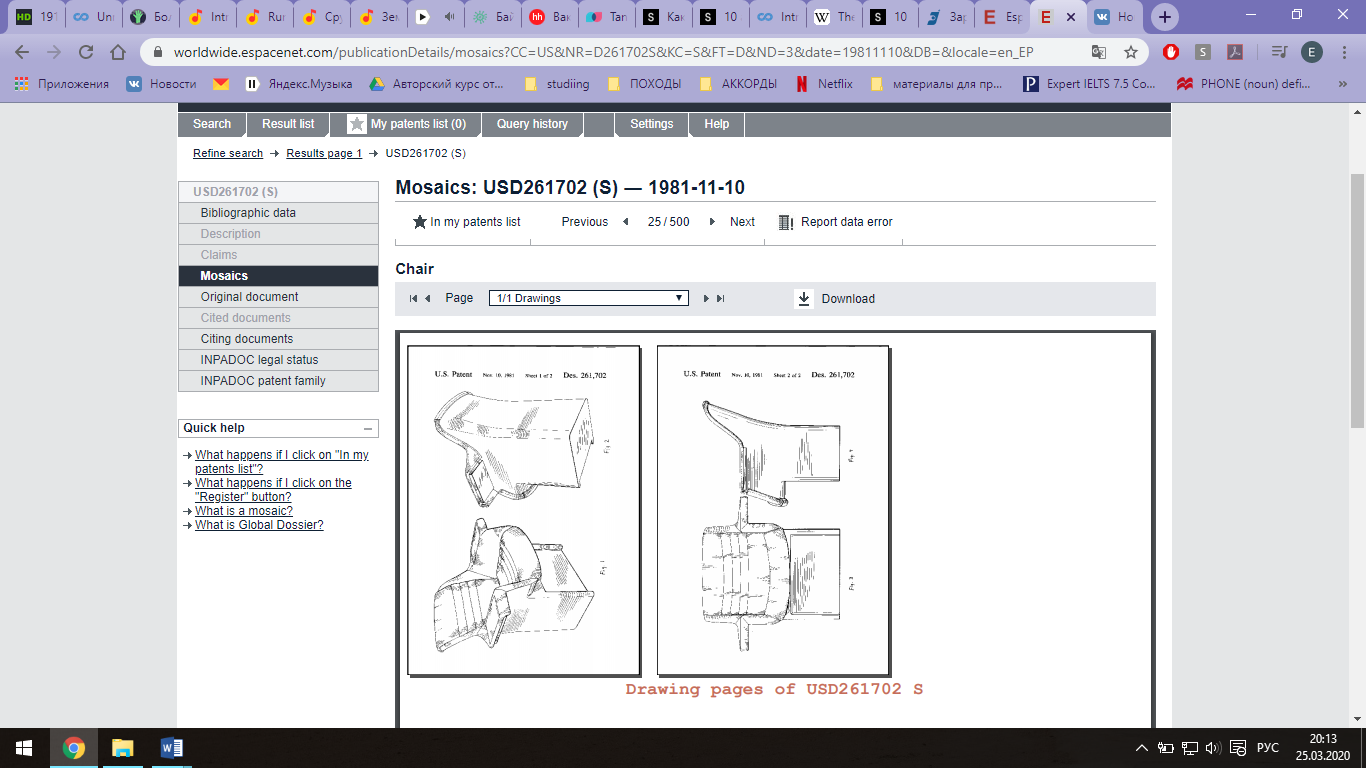
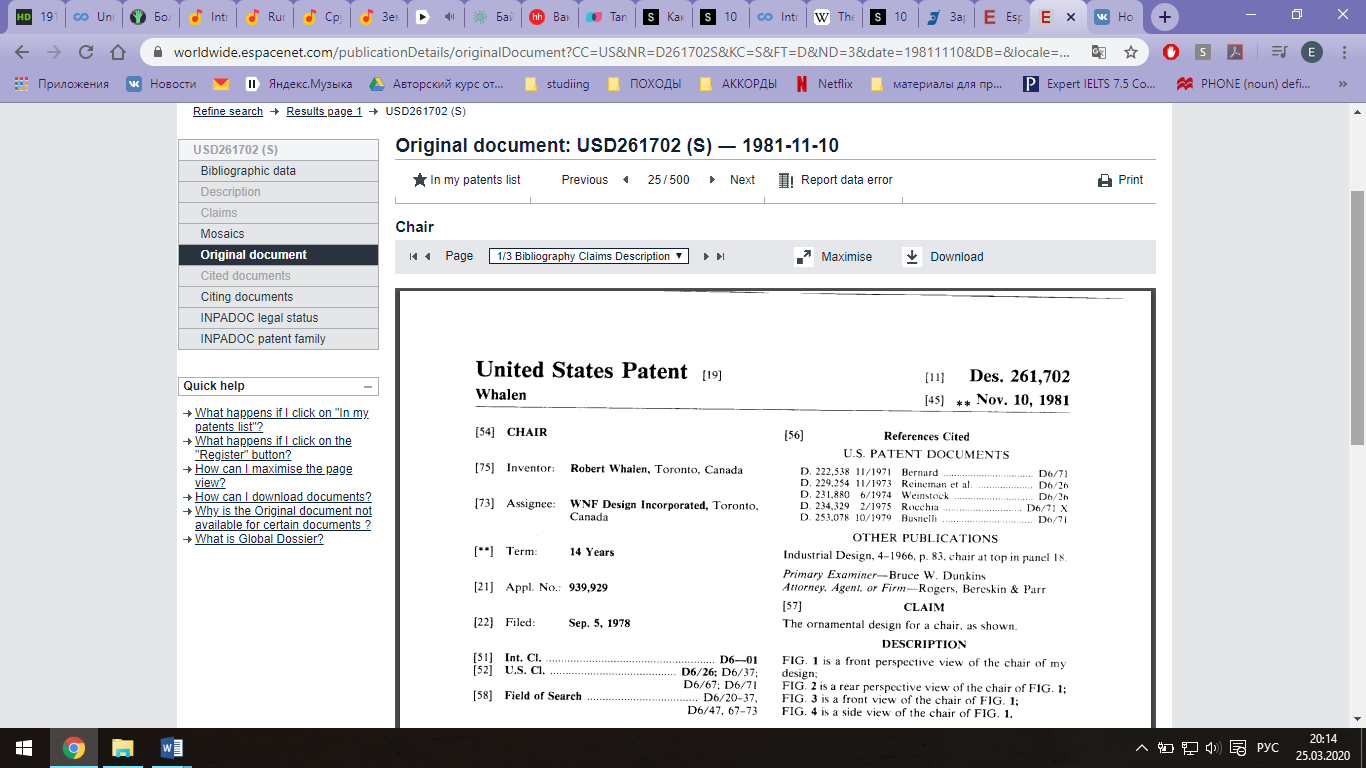
В строке поиска «Smartsearch» по английски вводим ключевое слово (например, «Design»), нажимаем «Search»; Из списка выбираем то, что ближе всего к теме; Открылась страница с изобретением, слева есть меню, где есть кнопки «Description» (чтобы увидеть весь текст изобретения), иногда текст изобретения не на английском, но можно перевести на русский или другой язык, сохраняем; Далее кнопка «Mosaics» (чтобы увидеть чертежи, если они есть), сохраняем;
Сайт patft.uspto.gov Заходим на сайт www.fips.ru и спускаемся в самый низ, ищем кнопку «Ссылки»; На открывшейся странице ищем ссылку «Зарубежные БД» (БД – базы данных), нажимаем;
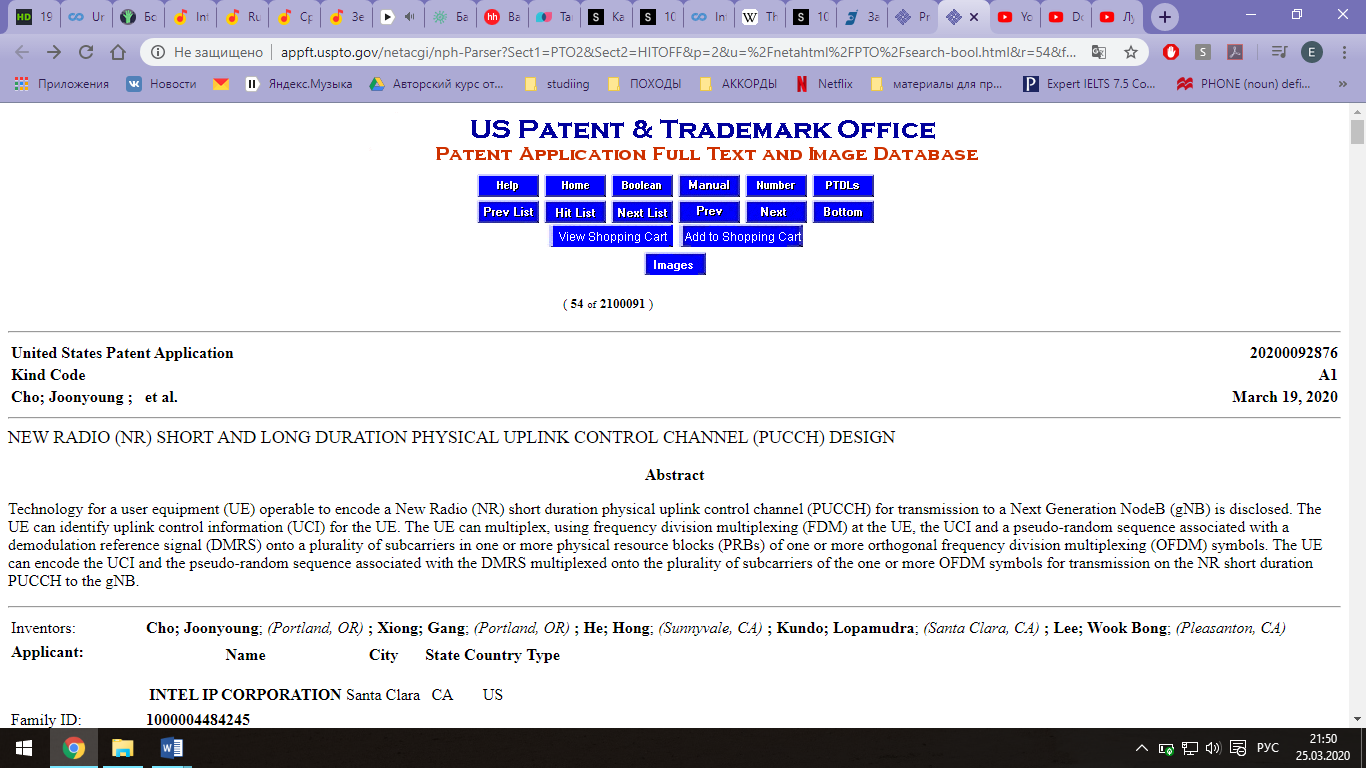
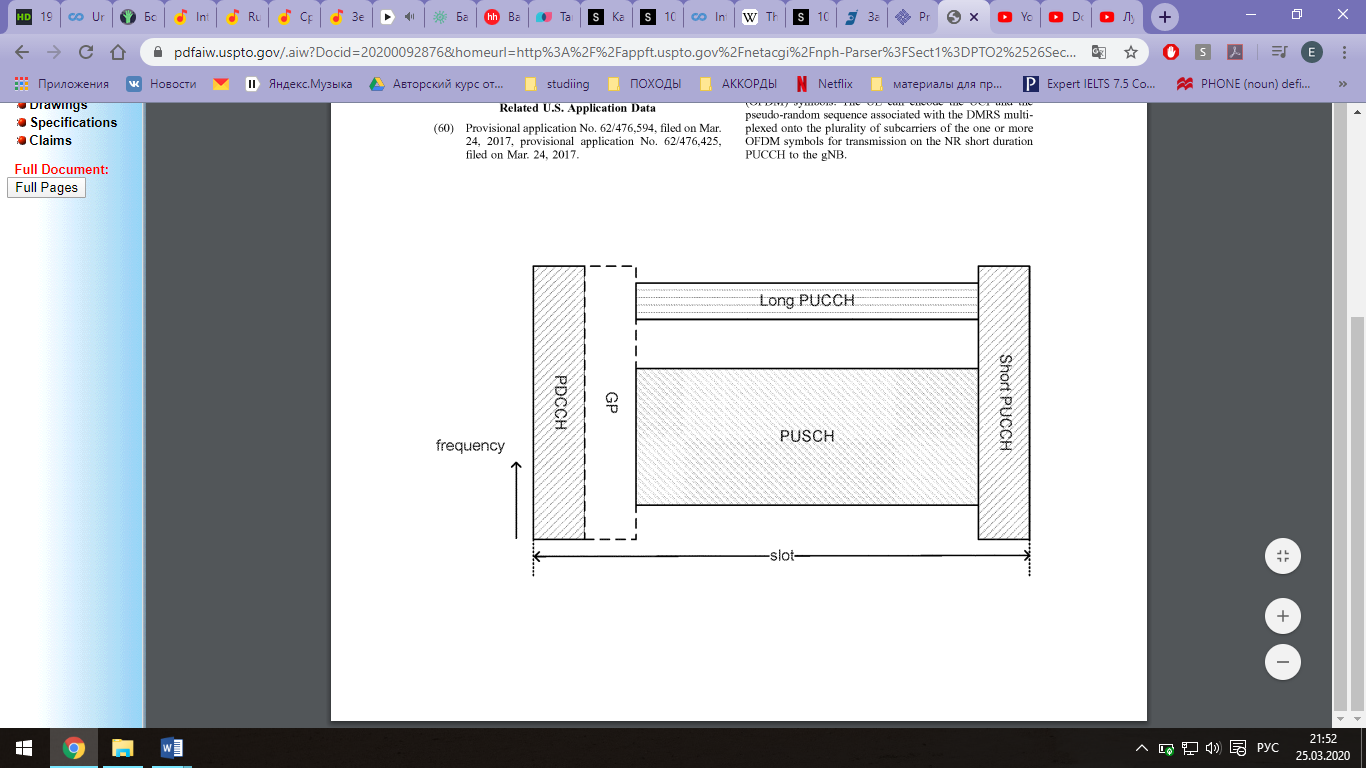
Открывается новая страница с сайтом www.patft.uspto.gov; Справа ищем ссылку «Quicksearch», нажимаем; В открывшейся странице, в строке поиска «Term 1» пишем ключевое слово на английском языке (например, «table»), нажимаем справа «Search»; Выбираем нужный патент. Чтобы посмотреть картинки – «Images», чертежи – «Drawings», весь документ – «Fulldocument».
Можем гулять по вкладкамслева и смотреть отдельные части патента в формате PDF
Полный текст из описания патента- фрагмент:
1-20. (canceled) 21. An apparatus of a user equipment (UE) operable to encode a physical uplink control channel (PUCCH) for transmission to a New Radio (NR) base station, the apparatus comprising: one or more processors configured to: identify, at the UE, uplink control information; identify, at the UE, a demodulation reference signal (DMRS); multiplex, using frequency division multiplexing (FDM) at the UE, the uplink control information and the DMRS onto a plurality of subcarriers in one or more physical resource blocks (PRBs) of one or more orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) symbols; and encode, at the UE, the uplink control information that is multiplexed with the DMRS for transmission on the PUCCH to the NR base station; and a memory interface configured to retrieve from a memory the uplink control information and the DMRS.
22. The apparatus of claim 21, further comprising a transceiver configured to transmit the uplink control information that is multiplexed with the DMRS to the NR base station over the PUCCH. 23. The apparatus of claim 21, wherein the DMRS is transmitted on four subcarriers per PRB. 24. The apparatus of claim 21, wherein the uplink control information transmitted over the PUCCH applies an orthogonal cover code over PUCCH symbols and the subcarriers within each OFDM symbol carry different modulation symbols. 25. The apparatus of claim 24, wherein a length of the orthogonal cover code is based on a PUCCH length. 26. The apparatus of claim 21, wherein one DMRS symbol is configured at a middle when a PUCCH length is four symbols. 27. The apparatus of claim 21, wherein the uplink control information transmitted over the PUCCH changes frequency during transmission and one DMRS symbol is configured in one transmission of the PUCCH with five symbols, and two DMRS symbols are configured in another transmission of the PUCCH with seven symbols, when a PUCCH length is 12 OFDM symbols. 28. At least one machine readable non-transitory storage medium having instructions embodied thereon for encoding a New Radio (NR) short duration physical uplink control channel (PUCCH) for transmission from a user equipment (UE) to a Next Generation NodeB (gNB), the instructions when executed by one or more processors at the UE perform the following: identifying, at the UE, uplink control information (UCI) for the UE; multiplexing, using frequency division multiplexing (FDM) at the UE, the UCI and a pseudo-random sequence associated with a demodulation reference signal (DMRS) onto a plurality of subcarriers in one or more physical resource blocks (PRBs) of one or more orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) symbols; and encoding, at the UE, the UCI and the pseudo-random sequence associated with the DMRS for transmission on the NR short duration PUCCH to the gNB. 29. The at least one non-transitory machine readable storage medium of claim 28, wherein the one or more PRBs used to form the NR short duration PUCCH include: two or more contiguous PRBs; or two or more non-contiguous PRBs. 30. The at least one non-transitory machine readable storage medium of claim 28, wherein a given PRB used to form the NR short duration PUCCH includes 12 subcarriers, wherein 4 subcarriers of the 12 subcarriers correspond to the pseudo-random sequence associated with the DMRS carried in the NR short duration PUCCH, and 8 subcarriers of the 12 subcarriers correspond to the UCI carried in the NR short duration PUCCH. 31. The at least one non-transitory machine readable storage medium of claim 30, wherein the 4 subcarriers of the 12 subcarriers that correspond to the pseudo-random sequence associated with the DMRS carried in the NR short duration PUCCH include subcarriers 1, 4, 7 and 11 of the NR short duration PUCCH. 32. The at least one non-transitory machine readable storage medium of claim 28, wherein the NR short duration PUCCH that carries the UCI and the pseudo-random sequence associated with the DMRS comprises one or two OFDM symbols. 33. The at least one non-transitory machine readable storage medium of claim 28, wherein the UCI carried in the NR short duration PUCCH includes one or more of: channel state information (CSI), hybrid automatic repeat request acknowledgements (HARQ-ACKs), scheduling request (SR), or beam information. 34. The at least one non-transitory machine readable storage medium of claim 28, wherein the UCI and the pseudo-random sequence associated with the DMRS carried in the NR short duration PUCCH employ length-12 constant amplitude zero autocorrelation (CAZAC) sequences, respectively, when the UCI and the pseudo-random sequence associated with the DMRS are multiplexed using alternating subcarriers in two PRBs. 35. The at least one non-transitory machine readable storage medium of claim 28, wherein the pseudo-random sequence associated with the DMRS carried in the NR short duration PUCCH employs a length-4 discrete Fourier transform (DFT) sequence for each PRB. 36. At least one non-transitory machine readable storage medium having instructions embodied thereon for encoding a New Radio (NR) long duration physical uplink control channel (PUCCH) for transmission from a user equipment (UE) to a Next Generation NodeB (gNB), the instructions when executed by one or more processors at the UE perform the following: identifying, at the UE, uplink control information (UCI) for the UE; multiplexing, using time division multiplexing (TDM) at the UE, UCI symbols associated with the UCI and pseudo-random sequence symbols associated with a demodulation reference signal (DMRS), wherein a number of pseudo-random sequence symbols that are multiplexed with the UCI symbols depends on a length of the NR long duration PUCCH; and encoding, at the UE, the UCI symbols and the pseudo-random sequence symbols associated with the DMRS for transmission to the gNB on the NR long duration PUCCH. 37. The at least non-transitory one machine readable storage medium of claim 36, wherein: the NR long duration PUCCH carries 2 pseudo-random sequence symbols associated with the DMRS when the length of the NR long duration PUCCH is 4 Discrete Fourier Transform-spread-OFDM (DFT-s-OFDM) symbols; or the NR long duration PUCCH carries 3 pseudo-random sequence symbols associated with the DMRS when the length of the NR long duration PUCCH is 7 DFT-s-OFDM symbols. 38. The at least non-transitory one machine readable storage medium of claim 36, wherein the NR long duration PUCCH carrying the UCI symbols and the pseudo-random sequence symbols associated with the DMRS is multiplexed to a PUCCH carrying a scheduling request (SR) sequence of a same length within a same physical resource block (PRB) using different cyclic shifts of a same constant amplitude zero autocorrelation (CAZAC) sequence.
39. The at least one non-transitory machine readable storage medium of claim 36, wherein the NR long duration PUCCH applies a unique orthogonal cover code (OCC) and a unique cyclic shift to the UCI symbols and the pseudo-random sequence symbols associated with the DMRS, respectively, as compared to other UEs when UE multiplexing is employed to multiplex NR long duration PUCCH transmissions for multiple UEs. 40. The at least one non-transitory machine readable storage medium of claim 36, wherein the NR long duration PUCCH that carries the UCI symbols and the pseudo-random sequence symbols associated with the DMRS ranges from 4 Discrete Fourier Transform-spread-OFDM (DFT-s-OFDM) symbols in length to 14 DFT-s-OFDM symbols in length. 41. The at least one non-transitory machine readable storage medium of claim 36, wherein the UCI symbols carried in the NR long duration PUCCH includes one or more of: channel state information (CSI), hybrid automatic repeat request acknowledgements (HARQ-ACKs), scheduling request (SR), or beam information. Description
[0001] Wireless systems typically include multiple User Equipment (UE) devices communicatively coupled to one or more Base Stations (BS). The one or more BSs may be Long Term Evolved (LTE) evolved NodeBs (eNB) or New Radio (NR) next generation NodeBs (gNB) that can be communicatively coupled to one or more UEs by a Third-Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) network. [0002] Next generation wireless communication systems are expected to be a unified network/system that is targeted to meet vastly different and sometimes conflicting performance dimensions and services. New Radio Access Technology (RAT) is expected to support a broad range of use cases including Enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB), Massive Machine Type Communication (mMTC), Mission Critical Machine Type Communication (uMTC), and similar service types operating in frequency ranges up to 100 GHz.
Отчет о патентных исследованиях
Руководитель работы:
ЗАДАНИЕ НА ПРОВЕДЕНИЕ ПАТЕНТНЫХ ИССЛЕДОВАНИЙ
Кафедра:
Наименование темы работы:
Задачи патентных исследований:
Сроки проведения поиска: Начало поиска: Окончание поиска и представление работы:
Студент Личная подпись Расшифровка подписи
Руководитель работы Личная подпись Расшифровка подписи
Таблица 1 – Регламент поиска
Студент Патентовед СПРАВКА О ПОИСКЕ Таблица 2 – Патентная документация
Таблица 3- Научно-техническая документация
Таблица 4 - Показатели технического уровня объекта техники
*Включают показатели объектов интеллектуальной собственности (устройство, технология, вещество): -технико-экономические, -эффективности использования по назначению, -технические, -эргономические, -безопасности, - уровня качества по ГОСТ стандартам, - объектов дизайна (в т.ч. логотипов, этикеток и т.д.).
Таблица 5
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Последнее изменение этой страницы: 2021-03-09; просмотров: 125; Нарушение авторского права страницы; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! infopedia.su Все материалы представленные на сайте исключительно с целью ознакомления читателями и не преследуют коммерческих целей или нарушение авторских прав. Обратная связь - 3.141.30.162 (0.044 с.) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
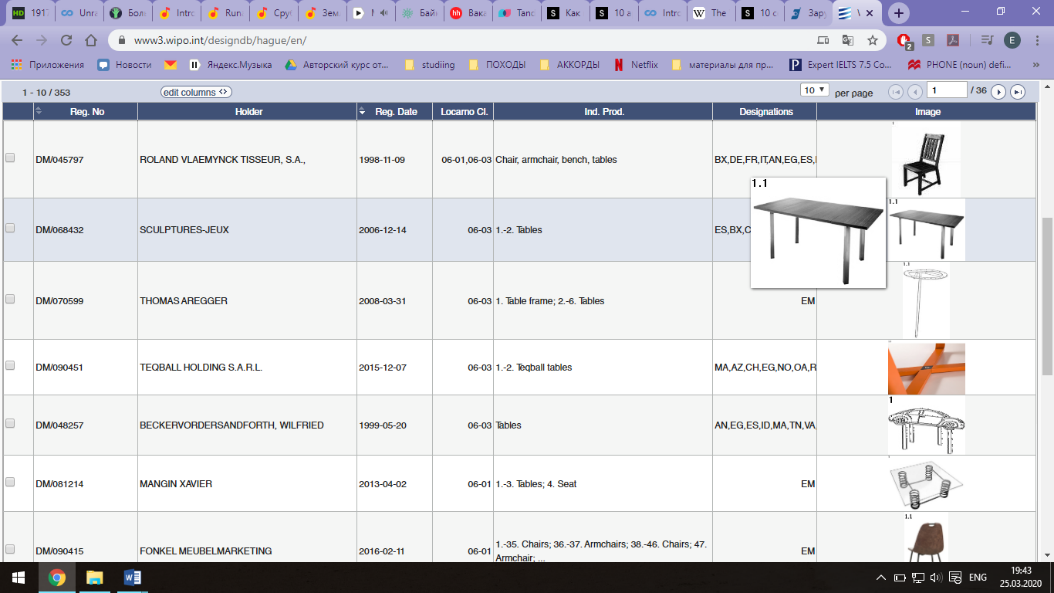 Спускаемся ниже и в строке поиска «Description» вводим ключевое слово поиска на английском (например, «table»), нажимаем «Search» и сайт выдает список патентов попадающие под критерии поиска по ключевому слову;
Спускаемся ниже и в строке поиска «Description» вводим ключевое слово поиска на английском (например, «table»), нажимаем «Search» и сайт выдает список патентов попадающие под критерии поиска по ключевому слову;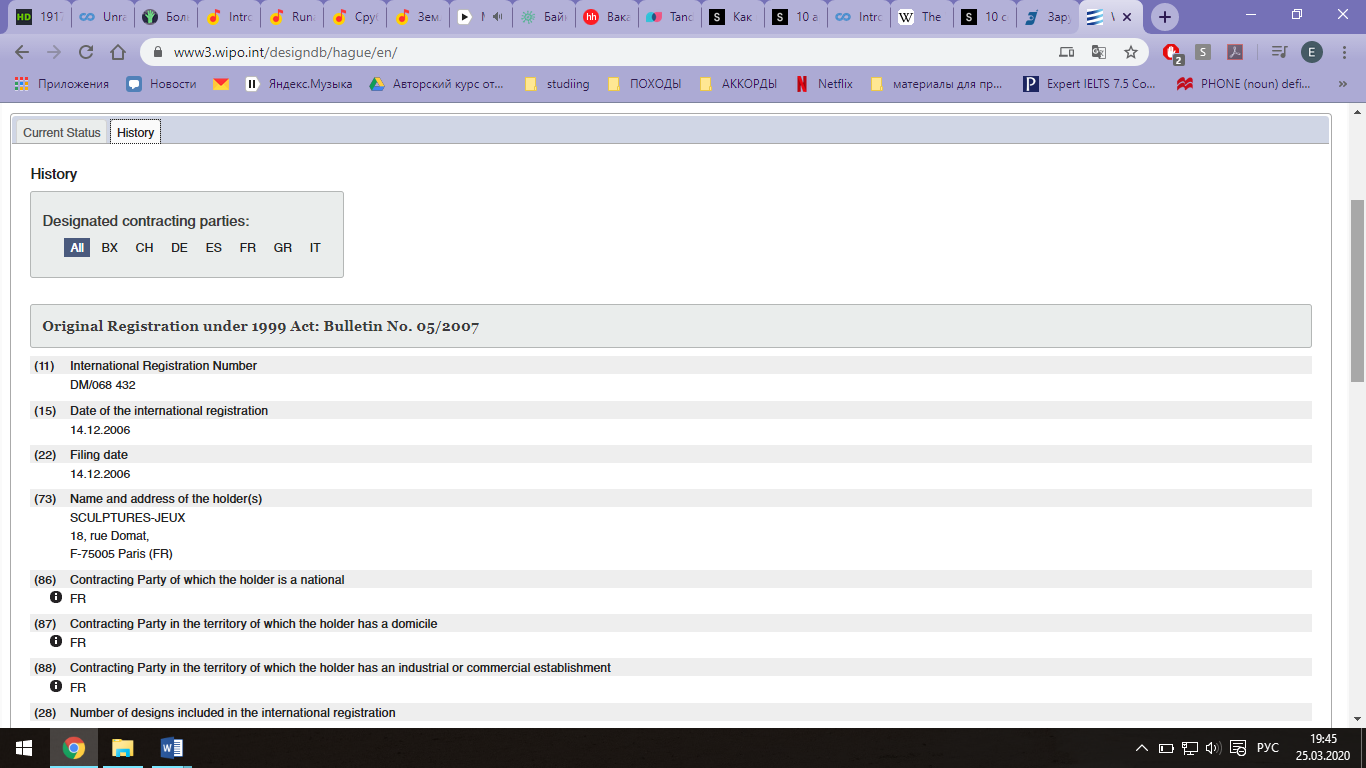 Ниже приведен пример найденного патента на промышленный образец:
Ниже приведен пример найденного патента на промышленный образец: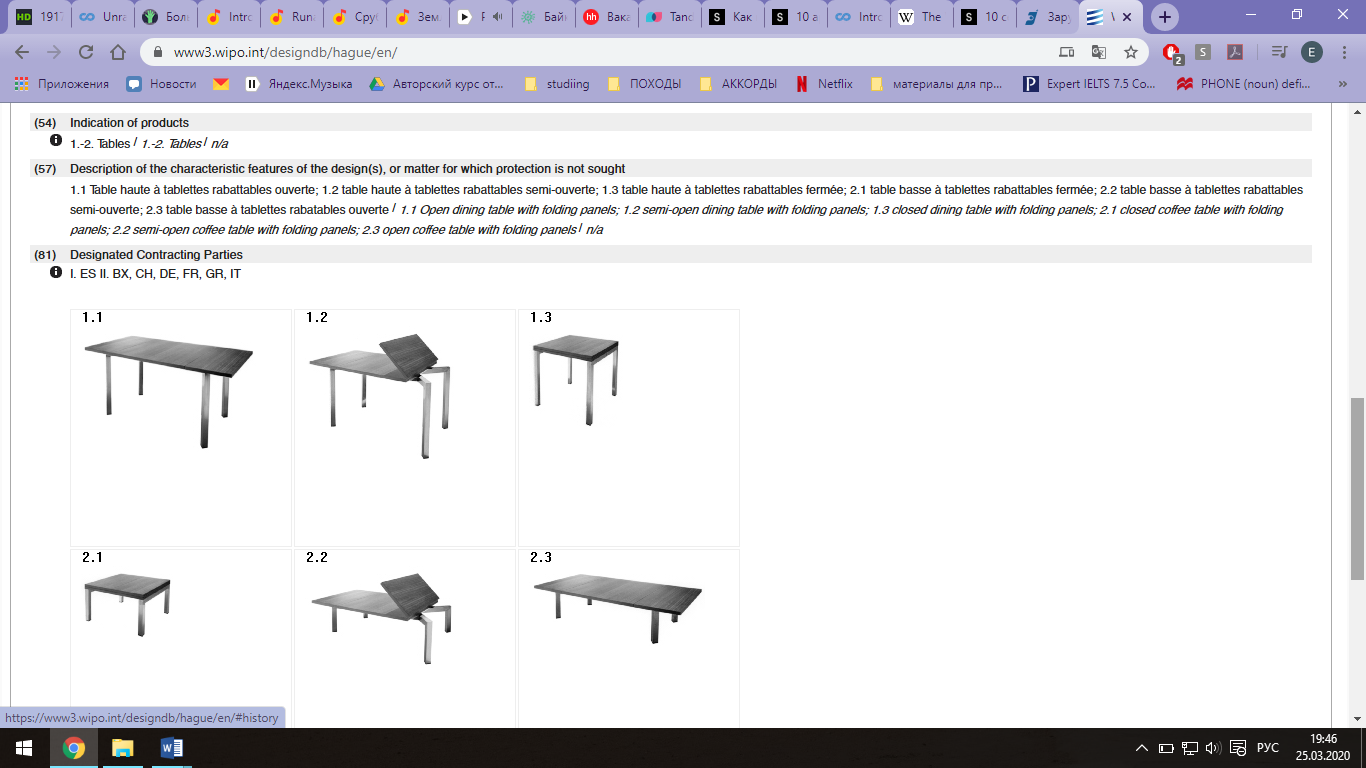
 Пример найденного изобретения:
Пример найденного изобретения: