Заглавная страница Избранные статьи Случайная статья Познавательные статьи Новые добавления Обратная связь КАТЕГОРИИ: ТОП 10 на сайте Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрацииТехника нижней прямой подачи мяча. Франко-прусская война (причины и последствия) Организация работы процедурного кабинета Смысловое и механическое запоминание, их место и роль в усвоении знаний Коммуникативные барьеры и пути их преодоления Обработка изделий медицинского назначения многократного применения Образцы текста публицистического стиля Четыре типа изменения баланса Задачи с ответами для Всероссийской олимпиады по праву 
Мы поможем в написании ваших работ! ЗНАЕТЕ ЛИ ВЫ?
Влияние общества на человека
Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрации Практические работы по географии для 6 класса Организация работы процедурного кабинета Изменения в неживой природе осенью Уборка процедурного кабинета Сольфеджио. Все правила по сольфеджио Балочные системы. Определение реакций опор и моментов защемления |
Clear organizational mission ⇐ ПредыдущаяСтр 5 из 5
§ a clear organizational mission outlines a commitment to a type of business and a place in the market § it should be reviewed when: § a firm seeks new customer groups or abandons existing ones § adds or deletes product lines § acquires other firms or sells part of its own business § utilizes different marketing functions § shifts its technological focus Long-term competitive advantage ü long-term competitive advantages are attributes whose distinctiveness and appeal to consumers can be maintained over an extended period of time ü to sustain advantages, consumers must perceive a consistent positive difference in key attributes over firm’s competitors ü differences must be linked to a capability gap that competitors will have difficulty in closing ü a firm should stress customer service and a total quality program Precisely defined target market v by precisely defining target market(s), a firm identifies those to be addressed in its marketing plans v when a firm uses concentrated or differentiated marketing, each segment must be understood v the target market approach may need fine-tuning due to changing demographics and lifestyles—or declining sales v data-base marketing aids in achieving goals. Compatible short and long term plans · a firm’s marketing subplans need to be compatible with one another · long-term plans are the most general and set a broad framework for moderate-term plans · short-term plans are the most specific, but need to be derived from both moderate- term and long-term plans marketing plans must be flexible and adapt to changing customer priorities · frequent reviews are critical Coordination of marketing mix Ø The components of the marketing mix (product, distribution, promotion, and price) need to be coordinated and consistent with the firm’s organizational mission Stability over time o a marketing plan must have a certain degree of stability over time to be implemented and evaluated properly o the plan should be consistent with the firm’s mission and guide the firm’s long-term efforts o the plan should be fine-tuned regularly and be consistent with the firm’s total quality approach Benchmarking Customer satisfaction ü customer satisfaction is the degree to which there is a match between a customer’s expectations of a good or service and its actual performance. It “is undoubtedly one of the top strategic issues in the new decade.” ü the largest ongoing research project is the American Customer Satisfaction Index (ACSI), a joint effort by the University of Michigan, the American Society for Quality Control, and CFI Group ü to compute ACSI, 50,000 consumers are surveyed annually regarding 200 companies and government agencies in 34 different industries. ü ACSI links customer expectations, perceived quality, and perceived value to customer satisfaction Key concepts in sales analysis ü control units are the sales categories for which data are gathered. ü the 80-20 principle identifies large proportions of sales (profits) that come from a small proportion of customers, products, or territories. ü the iceberg principle states that superficial data are insufficient to make sound evaluations and errors will occur unless firms isolate and categorize data. ü sales exception reporting highlights situations where goals are not met or opportunities are not present Marketing audit a marketing audit is a systematic critical impartial review and appraisal of the basic goals and policies of the marketing function, and of the organization, methods, procedures, and personnel employed to implement the policies and achieve the goals Marketing audit process 1.The audit is conducted by company specialists, company division or department managers, or outside specialists.
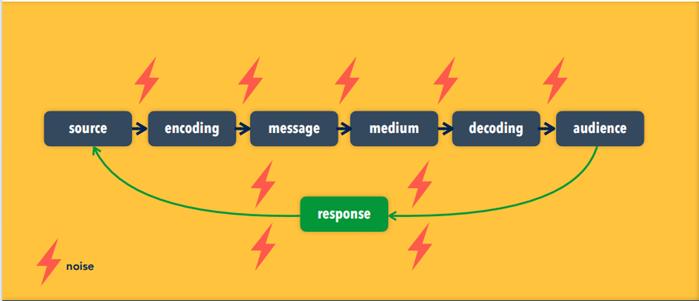
2. It may be done at the end of a calendar year, the of the annual reporting year, or when doing a physical inventory. 3. A horizontal audit studies the overall performance of a firm, emphasizing the interrelationship of variables. A vertical audit is an in-depth analysis of one aspect of a firm’s marketing strategy. 4. Audit forms list the topics to be examined and the exact information required to evaluate each topic. 5. Implementation decisions include: the timing and duration, employee awareness, when and how audit is performed, and how the audit report will be prepared. 6. Findings and recommendations are given to management. #7. integrated marketing communications promotion mix: ü Advertising ü Personal selling ü Sales Promotion ü Public Relations ü Direct Marketing Advertising advertising is paid, nonpersonal communication regarding goods, services, organizations, people, places, and ideas that is transmitted through various media by business firms, government and other nonprofit organizations, and individuals who are identified in the advertising message as the sponsor. The message is generally controlled by the sponsor. PR public relations includes any communication to foster a favorable image for goods, services, organizations, people, places, and ideas among their publics. It may be nonpersonal, personal, paid or non-paid, and sponsor controlled or not controlled. publicity is the form of public relations that entails nonpersonal communication passed on via various media but not paid for by an identified sponsor. personal selling personal selling involves oral communication with one or more prospective buyers by paid representatives for the purpose of making sales in sophisticated B2B sales SPIN approach to selling proved to be quite an effective technique sales promotion Sales promotion involves paid marketing communication activities (other than advertising, publicity, or personal selling) intended to stimulate purchases and dealer effectiveness. Included are trade shows, premiums, incentives, giveaways, demonstrations, and other efforts direct marketing Direct marketing is a form of advertising where organizations communicate directly to customers through a variety of media including cell phone text messaging, email, websites, online adverts, database marketing, fliers, catalog distribution, promotional letters and targeted television, newspaper and magazine advertisements as well as outdoor advertising. Among practitioners, it is also known as direct response. The prevalence of direct marketing and the unwelcome nature of some communications has led to regulations and laws such as the CAN-SPAM Act, requiring that consumers in the United States be allowed to opt out. Communication channel
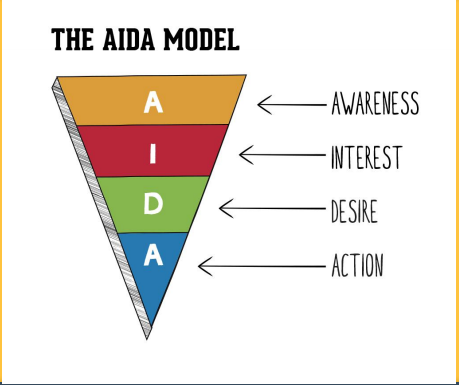
AIDA model
media planning and budgeting All-You-Can-Afford Method firm first allots funds for other elements of marketing, remaining marketing funds then go to the promotion budget Incremental Method a percentage is added to or subtracted from this year’s budget to determine next year’s Competitive Parity Method promotion budget is raised or lowered according to competitors’ actions. Percentage-of-Sales Method promotion budget is tied to sales revenue. Objective-and-Task Method firm sets promotion goals, determines the activities needed to satisfy them, and then establishes the proper budget.
|
|||||
|
Последнее изменение этой страницы: 2021-01-08; просмотров: 95; Нарушение авторского права страницы; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! infopedia.su Все материалы представленные на сайте исключительно с целью ознакомления читателями и не преследуют коммерческих целей или нарушение авторских прав. Обратная связь - 3.21.158.148 (0.008 с.) |