
Заглавная страница Избранные статьи Случайная статья Познавательные статьи Новые добавления Обратная связь FAQ Написать работу КАТЕГОРИИ: ТОП 10 на сайте Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрацииТехника нижней прямой подачи мяча. Франко-прусская война (причины и последствия) Организация работы процедурного кабинета Смысловое и механическое запоминание, их место и роль в усвоении знаний Коммуникативные барьеры и пути их преодоления Обработка изделий медицинского назначения многократного применения Образцы текста публицистического стиля Четыре типа изменения баланса Задачи с ответами для Всероссийской олимпиады по праву 
Мы поможем в написании ваших работ! ЗНАЕТЕ ЛИ ВЫ?
Влияние общества на человека
Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрации Практические работы по географии для 6 класса Организация работы процедурного кабинета Изменения в неживой природе осенью Уборка процедурного кабинета Сольфеджио. Все правила по сольфеджио Балочные системы. Определение реакций опор и моментов защемления |
Навчально-методичний посібникСодержание книги
Поиск на нашем сайте
Навчально-методичний посібник для студентів ІІІ курсів
Навчальні завдання призначено для студентів заочної форми навчання напряму підготовки «Організація та ремонт автомобілів» освітньо-кваліфікаційного рівня «Молодший спеціаліст». Навчальні завдання містять оригінальні тексти, які відображають комплекс основних понять, необхідних студентам напряму підготовки «Організація та ремонт автомобілів» для оволодіння іншомовним професійним спілкуванням. Вони готують студентів до читання і розуміння оригінальної англомовної літератури за фахом і мають за мету розвиток у студента навичок самостійної роботи, що включає: а) вивчаюче читання та завдання, спрямовані на засвоєння лексичного мінімуму та розвиток мовленнєвих навичок, б) перевірку якості засвоєних знань за допомогою міні-тестів, які виконуються студентами під час самостійної домашньої підготовки і перевіряються викладачем на практичних заняттях. Матеріал навчальних завдань складається з десяти уроків, текстів для додаткового читання та розмовних тем для розвитку усного мовлення, передбачених програмою. Кожен урок містить словник-мінімум, текст, вправи для перевірки розуміння тексту, закріплення лексичного матеріалу та розвитку професійної мовленнєвої компетенції, міні-тест. Добір текстів, розробку системи лексичних вправ та форм контролю виконано з урахуванням Типової програми з англійської мови для професійного спілкування.
UNIT 1. Translate the following words and learn them.
Read and translate the text. AUTOMOTIVE INDUSTRY The automotive industry includes all those companies and activities involved in the manufacture of motor vehicles, including most components, such as engines and bodies, but excluding tires, batteries, and fuel. The industry's principal product is passenger automobiles; commercial vehicles though important to the industry, are secondary. The history of the automobile industry, while brief compared with that of many other industries, has exceptional interest because of its effects on 20th century history. Although the automobile originated in Europe, the United States completely dominated the world industry for the first half of the 20th century through the invention of mass-production techniques. In the second half of the century the situation altered sharply as western European countries and Japan became major producers and exporters. Although steam-powered road vehicles were produced earlier, the origins of the automotive industry are rooted in the development of the gasoline engine in the 1860s and 1870s, principally in France and Germany. By the beginning of the 20th century, Germany, and France manufacturers had been joined by British, Italian, and U.S. makers.
The outstanding contribution of the automotive industry to technological advance was the introduction of full-scale mass production, a process combining precision, standardization, interchangeability, synchronization, and continuity. Mass production was a U.S. innovation. Mass production implies mass consumption, which in turn requires an elaborate distributive organization to sell the cars and to develop confidence among customers that adequate service will be available. In the early days of the industry, cars were sold directly from the factory or through independent dealers, who might handle several different makes. When sales in large quantities became the objective, however, more elaborate and better organized techniques of distribution became essential. The automotive industry has become a vital element in the economy of the industrialized countries: motor vehicle production and sales are one of the major indexes of the state of the economy of those countries.
MINI TEST 1 (Unit 1) Match the synonyms. 1. Producer. 2. Progress. 3. Originate. 4. Precision. 5. Makes. A. Advance. B. To be rooted. C. Accuracy. D. Models. E. Manufacturer.
Match the antonyms. 1. Include. 2. Principal. 3. Major. 4. Sell. 5. Better. A. Worse. B. Buy. C. Minor. D. Secondary. E. Exclude. UNIT 2. THE MODERN AUTOMOBILE The modern automobile is a complex technical system employing subsystems with specific design functions. Some of those consist of thousands of component parts that have evolved from breakthroughs in existing technology or from new discoveries such as electronic computers, high strength plastics, and new alloys of steel and nonferrous metals, as well as from factors such as pollution, safety legislation, and foreign competition. Passenger cars have emerged as the primary means of family transportation, with the total number in use worldwide expected to reach half a billion in the 1990s. One-third of these are in the United States, where more than 1,5 trillion miles are travelled each year. Approximately 500 different models have been offered to U.S. car buyers, about half domestic and half foreign in origin. New designs have been brought into the market more quickly in recent years than in the past to permit manufacturer to capitalize on their proprietary technological advances. With more than 30 mill. new units built each year worldwide, manufacturers have been able to split up the total into many very small segments that nonetheless remained economical to market. New technical developments are recognized to be the key to successful competition. Research and development engineers and scientists have been employed by all automobile manufacturers and suppliers to improve the car body, engine, drivetrain, vehicle control systems, occupant safety, and environmental emissions, and further work by the industry is necessary to meet the needs of the 21st century. 3. Are the following statements true or false? Explain your answers. 1. The modern automobile is a single technical system with definite functions. 2. Some of those subsystems consist of many parts evolved from breakthrough in existing technology or from new discoveries. 3. The total number of passenger cars in use worldwide was expected to reach half a billion in the 2000. 4. Research and development engineers and scientists have been employed to create new models of passenger cars.
Answer the questions. 1. Modern automobile is defined as a complex technical system. What does it employ? 2. Passenger cars have emerged as the primary means of transportation. How are they distributed through out the world? 3. What models have been offered to the U.S. car buyers? 4. What is recognized to be key to successful competition? 5. Who has been employed by all automobile manufacturers to improve all systems of automobile?
MINI TEST 2 (Unit 2) Match the synonyms. 1. Modern. 2. Alloy. 3. Emerge. 4. Supplier. 5. Breakthrough. A. Achievements. B. Originate. C. Dealer. D. Mixture. E. Contemporary.
UNIT 3. VEHICLE DESIGN Vehicle design depends to a large extend on its intended use. Automobile for off-road use in countries that lack service facilities must be durable, simple systems with high resistance to severe overloads and extremes in operating conditions. Conversely, the customers for products that intended for the high-speed, limited-access road systems in Europe and North America expect more passenger comfort options, increased engine performance, and optimized high-speed handling and vehicle stability. Stability depends principally on the distribution of weight between front and rear wheels, the height of the centre of gravity and its position relative to the aerodynamic centre of the vehicle, suspension characteristics, and whether front or rear wheels are used for propulsion. Weight distribution depends principally on the location and size of the engine. The common practice of front mounted engines exploits the stability that is more readily achieved with this layout. The development of aluminium engines and new manufacturing processes, have however, made it possible to locate the engine at the rear without necessarily compromising stability. MINI TEST 3 (Unit 3) Match the synonyms. 1. Performance. 2. Position. 3. Propulsion. 4. Operate. 5. Customer. А. Notable action. B. Layout. C. Work. D. Propelling force. E. User. Match the antonyms. 1. Increase. 2. Front wheels. 3. Common. 4. High-speed. 5. Front-mounted engine. А. Decrease. B. Unusual. C. Rear wheels. D. Low-speed. E. Rear-mounted engine.
UNIT 4. Read and render the text. BUSES A bus is a self-propelled road vehicle, designed to carry more passengers than any automobile, generally on a fixed route. It was developed at the beginning of the 20th century to compete with streetcars by providing greater route flexibility. The bus was a natural outgrowth of the horse-driven coach. Today buses are defined as vehicles that accommodate more than 10 passengers. There are four main types of buses: city or transit, suburban, intercity or tour, and school. The city bus operates within the city limits and is characterized by low maximum speed, low-ride platform, provision for standing and wheelchair passenger, two entrances on the curb side, low-back seats, and no luggage space. The suburban bus is designed for short intercity runs and has high-back seats, luggage compartments and racks, and a single front entrance. The intercity type has a high-ride platform to provide maximum luggage space under the passengers, high-back seats, overhead luggage racks, individual reading lights, and a washroom. A typical intercity coach weighs about 26,000 pounds (12,000 kilograms), has a capacity of up to 47 passengers, a two-stroke-cycle diesel engine with up to 450 horsepower, an electronically controlled automatic transmission, and air brakes. School buses generally consist of a 50-passenger bus body, with special signal lamp and safety provisions, mounted on a long-wheelbase truck chassis. Articulated buses were first used in Europe in the 1950s. In this arrangement a trailer body is connected to the rear of conventional front-engine bus by means of a hitch, a flexible diaphragm, and a continuous floor panel with accurate mating surface during turn manoeuvres. This arrangement permits up to a 75 percent increase in seating capacity and 20 percent improvement in fuel efficiency per seat-mile. The turning radius is the same as that of conventional bus. Manufacture of this design was begun in the United States in the 1980s by several European firms. Double decking, increased seating comfort and larger glass areas have been trends in tour buses, principally in Europe and Asia. MINI TEST 4 (Unit 4) Match the synonyms. 1. Operate. 2. Rack. 3. City bus. 4. Increase. 5. Suburban bus. A. Transit bus. B. Improvement. C. Intercity bus. D. Travel. E. Luggage shelf. Match the antonyms. 1. Suburbs. 2. High-back seat. 3. Entrance. 4. Articulated bus. 5. Maximum. A. Exit. B. Minimum. C. Conventional bus. D. Low-back seat. E. Downtown.
UNIT 5. LORRIES A lorry, or truck, is a motor vehicle designed to carry freight or goods or to perform special services. The lorry was derived from horse-driven wagon technology and some of the pioneer manufacturers came from the wagon business. Because of their speed and flexibility, lorry carries a quater of the intercity freight. Lorries enjoy almost total monopoly in freight delivery. In 1896 Gottlieb Daimler of Germany built the first motor lorry. It was equipped with a four-horsepower engine and a belt drive with two speeds forward and one in reverse. In 1896 the Winton Company of the United States produced a gasoline-powered wagon with a single-cylinder six-horse-power engine. In World War I motor lorries were widely used, and in World War II they largely replaced horse-drawn equipment. A notable vehicle was the four wheel-drive, short-wheelbase jeep, capable of performing a variety of military tasks. Lorries can be classified as either straight or articulated. A straight lorry is one in which all axles are attached to a single frame. An articulated vehicle is one that consists of two or more separate frames connected by suitable couplings. Axle assemblies of heavy lorries may be made up of two or more axles, any of which may be powered. Normally, they are so spaced that the distance between axle centers is not more than one-half times the overall diameter of the wheel and tyre. If the axles are separated by a large distance, the assembly is called a spread tandem.
The ratio of lorries to the passenger cars in the world is increasing annually.
MINI TEST 5 (Unit 5) Match the synonyms. 1. Lorry. 2. Freight. 3. Monopoly. 4. Perform. 5. Seat belt. A. Truck. B. Do. C. Load. D. Control. E. Safety belt.
Match the antonyms. 1. Separate. 2. Thefirst. 3. Heavy. 4. Large. 5. Straight. A. Small. B. The last. C. Articulated. D. Single. E. Light.
UNIT 6. FUTURE SYSTEMS Expansion of the total potential automotive market in the future and concern for the environment may be expected to change cars of the future. Special-purpose vehicles designed for specific urban or rural functions, with appropriate power system for each type of use, may be needed. Possibilities include electric, solar, steam, gasturbine, hybrid combinations, and other power sources. Modern electric cars and trucks were manufactured in small numbers in Europe, Japan, and United States beginning in the 1980s. However, electric propulsion is only possible for relatively short-range vehicles, using power from batteries of fuel cells. In a typical system, a group of lead-acid batteries, connected in a series, power electric AC induction motors to propel the vehicle. A solid state rectifier, or power inventor, changes the direct current supplied by the battery pack to an alternating current output that is controlled by the driver using an accelerator pedal to vary the output voltage. Because of the torque characteristics of the electric motors, conventional gear-type transmissions are not needed in most designs. Compressed gas and blends derived from methanol and ethanol are being studied as fuels for the future because they may be produced from readily available biomass sources and have potential for high efficiency and lower emissions. Gas turbines have been tested extensively and have good torque characteristics, operate on a wide variety of fuels, have high power-to-weight ratios, meet emission standards, and offer quiet operation. Some studies have shown that the advantages of the system are best realized in heavy-duty vehicles. Nuclear energy offers the advantage of extremely low fuel weight. The obstacle for automotive use, however, is the great weight and volume of shielding required to protect the occupants from excessive nuclear radiating. The advent during the 1990s of regulating requiring "zero emissions" from some vehicles in certain areas rekindled world interest in new battery technology. Battery system that offers higher energy density became the subject of joint research by auto industry scientists. Non commercial solar powered electric demonstration vehicles were built by universities and manufactures.
MINI TEST 6 (Unit 6) Match the synonyms. 1. Rectifier. 2. Advent. 3. Advantage. 4. Battery packs. 5. Extremely. A. Arrival. B. Benefit. C. Invertor. D. Battery series. E. Very.
Match the antonyms. 1. Advantage. 2. Special-purpose. 3. Automatic transmission. 4. Urban. 5. Modern. 6. Direct current. A. Rural. B. Old-fashioned. C. General-purpose. D. Disadvantage. E. Alternating current. F. Gear-type transmission.
UNIT 7. MINI TEST 7 (Unit 7) Translate the words. 1. self-propelled vehicle. 2. internal combustion engine. 3. horsepower of the engine. 4. number of cylinders. 5. operating cycle. 6. cooling system. 7. upper limit of piston movement. 8. bottom dead center. 9. complete a stroke. 10. change the direction of a motion.
Fill in the gaps. 1. Automobiles are … vehicles for land transportation of people or goods. 2. A passenger car is propelled by an …. 3. Engines may differ in … of cylinders. 4. The lower limit of piston movement is called …. 5. The upper limit of piston movement is called …. A. internal combustion engine. B. self-propelled. C. bottom dead center. D. top dead center. E. the number.
Match the synonyms. 1. Goods. 2. Differ. 3. Operate. 4. Constitute. 5. Operation. A. Distinguish. B. Materials. C. Work. D. Complete. E. Activity.
Match the antonyms.
1. TDC. 2. Lower limit. 3. Self- propelled. 4. Different. 5. Work. A. Upper limit. B. Horse-driven. C. Idle. D. BDC. E. Similar.
UNIT 8. BODY Automotive body designs are frequently categorized according to the number of doors, the arrangement of seats, and the roof structure. Automobile roofs are conventionally supported by pillars on each side of the body. Convertible models with retractable fabric tops rely on the pillar at the side of the windshield for upper body strength as convertible mechanisms and glass areas are essentially non-structural. Glass areas have been increased for improved visibility and for aesthetic reasons. The high cost of new factory tools makes it impracticable for manufacturers to produce totally new designs every year. New designs usually have been programmed on three- to six-year cycles with generally minor refinements appearing during the cycle. In the past, as much as four years of planning and new tool purchasing was needed for a completely new design. Computer-aided design and computer aided manufacturing techniques may now be used to reduce this time requirement by 50 percent or more. Automotive bodies are generally formed out of sheet steel. Elements are added to the alloy to improve its ability to be formed deeper depressions without wrinkling or tearing in manufacturing presses. Steel is used because of its availability, low cost, and good workability. For certain applications, however, other materials, such as aluminium, fiberglass, and carbon-fiber reinforced plastic, are used because of their special properties. Polyamide, polyester, polystyrene, polypropylene and ethylene plastics have been formulated for greater toughness and resistance to brittle deformation. This material has been designed successfully for some body panels. Tooling for plastic component generally costs less and requires less time to develop than that for steel components and therefore may be changed by designers at lower costs. To protect body from corrosive elements and to maintain their strength and appearance, special priming and painting processes are used. MINI TEST 8 (Unit 8) 1. Translate the words given below. 1. arrangement of seats. 2. roof structure. 3. conventionally supported. 4. convertible model. 5. improved visibility. 6. high cost. 7. new factory tools. 8. make it impractical. 9. completely new design. 10. without wrinkling in manufacturing presses
Match the synonyms. 1. Conventionally. 2. Frequently. 3. Form. 4. Application. 5. Windshield. 6. Pillar. A. Make. B. Windscreen. C. Use. D. Supporter. E. Usually. F. Often.
Find the antonyms. 1. Retractable. 2. Increase. 3. High cost. 4. Conventional. 5. Minor. A. Major. B. Alternative. C. Stationary. D. Low cost. E. Decrease.
UNIT 9. CHASSIS The chassis of the modern automobile is the main structure of the vehicle. In most designs a pressed steel frame forms a skeleton on which the engine, wheels, axle assemblies, transmission, steering mechanism, brakes, and suspension members are mounted. The body is flexibly bolted to the chassis during the manufacturing process. The combination of body and frame absorbs the reactions from the movement of the engine and axle, receives the reaction forces of the wheels in acceleration and braking, absorbing aerodynamic wind forces and road shocks through the suspension, and absorbs the major energy of impact in the event of an accident. In modern small car designs there has been a trend toward combining the chassis frame and the body into a single structural element. In this arrangement the steel body shell is reinforced with braces that makes it rigid enough to resist the forces that are applied to it. Separate frames are used for other cars to achieve better noise isolation characteristics. The presence of heavier gauge steel components in modern separate frame designs also tends to limit intrusion in accidents.
MINI-TEST 9 (UNIT 9) Match the synonyms. 1. Component 2. Skeleton. 3. Movement. 4. Device 5. Pattern. A. Motion. B. Tool C. Model. D. Part. E. Basis.
Match the antonyms. 1. Acceleration. 2. Resist. 3. Separate. 4. Presence. 5. Modern. A. Absence. B. Braking. C. Give up. D. Single. E. Old fashioned.
Name the parts. A. Base framework of a motor-vehicle on which the body and working parts are mounted. B. Clutch, gears and drive, which transmit power from the engine to the rear axle of a motor-vehicle. C. Device for directing the course of a car. D. Device for reducing speed or stopping motion. E. Parts by which a motor-vehicle is supported on its axles. 7. Translate the 1st paragraph of the text.
UNIT 10. ENGINE A wide range of energy-conversion systems has been used experimentally and in automotive production. These include electric, steam, solar, turbine, rotary, and a variety of piston-type internal combustion engines. The most successful for automobiles has been the reciprocating piston internal-combustion engine, operating on four-stroke cycle, while diesel engines are widely used for lorries and buses. The gasoline engine was originally selected for automobiles because it could operate more flexible over a wide range of speeds, and power developed for a given weight engine was reasonable; it could be available, moderately priced fuel-gasoline model. Reliability, compact size, and range of operations later became important factors.
There has been an ongoing reassessment of these priorities with new emphasis on the pollution-producing characteristics of automotive power system. This has created new interest in alternate power sources and internal-combustion engine refinements that were not economically feasible in prior years. Although a few limited-production batteries powered electric vehicles have appeared from time to time, they have not proved to be competitive owing costs and operating characteristics. The gasoline engine, with new emission-control devices to improve emission performance, has not yet been challenged significantly. In the late 1940s a trend began to increase engine horse-power, particularly in American models. Design changes incorporated all known methods of raising engine capacity, including increasing the pressure in the cylinders to improve efficiency, increasing the size of the engine and increasing the speed at brought a return to smaller engines, four– and six-cylinder designs rated as low as 80 horsepower. European automobile engines were of a much wider variety, ranging from 1 to 12 cylinders, with corresponding differences in overall size, weight, piston displacement, and horsepower ratings from 19 to 120.
MINI TEST 10 (UNIT 10) Match the synonyms. 1. Require. 2. Equipment. 3. Convert. 4. Velocity. 5. Rotate. 6. Suitable. A. Tools. B. Change. C. Need. D. Speed. E. Right. F. Revolve.
Find the antonyms. 1. Independent. 2. Mobile. 3. Move. 4. To-and-fro motion. 5. Output. A. Rotary motion. B. Input. C. Stationary. D. Dependent. E. Idle.
ADDITIONAL TEXTS. ENGINE OPERATION An automobile, powered by a petrol engine, begins to operate when the driver turns a flywheel connected to the engine crankshaft. As the crankshaft revolves, a mixture of fuel and air is drawn from a carburettor into the engine cylinders. The ignition system provides the electric sparks that ignite this mixture. The resultant explosions of the mixture turn the crankshaft, and the engine starts moving. By regulating the flow of the fuel and air with a throttle, the driver controls the rotational speed of the crankshaft. Cooling, electrical ignition and lubrication systems are of great importance for the good performance of a car. The lights, radio and heater add to the flexibility, comfort, and convenience of the car. The indicating devices keep the driver informed as to engine temperature, oil pressure, amount of fuel, and battery charging rate. Brakes are of drum and disk types. The steering system consists of a manually operated steering wheel, which is connected by a steering column to the steering gear from which linkages run to the front wheels. It is difficult to turn the steering wheel, and special hydraulic power mechanisms are used to lessen this effort. Suitable springs are used against shocks. There are leaf springs, coil springs, torsion bars and air suspensions.
AIR-COOLED ENGINES All vehicle engines are air-cooled to some degree. Even in water-cooled engines heat is transmitted first from cylinder to water and afterwards, in the radiator, from water to air. This method of cooling is not difficult to accomplish, because the heat taken off the hot cylinder walls by large cooling surface of the radiator and so easy transmission of heat to air is made possible. Reciprocating engines used in aircraft are almost entirely air-cooled. Aircraft engines cooled by air are manufactured today in sizes ranging from 50 to 3500 hp and they have superseded water-cooled engines. The principal advantages of air-cooled aircraft engines are low weight, and greater reliability in operation. Modern motor-cycles are also designed almost exclusively with air-cooled engines. New designs of air-cooled vehicle engines are notable for their easy maintenance, reliability and economical operation.
COOLING SYSTEM Almost all automobiles employ liquid systems for their engines. All typical automotive cooling system comprises (1) a series of channels cast into engine block and cylinder head, surrounding the combustion with circulating water or other coolant to carry away excessive heat, (2) a radiator consisting of many small tubes equipped with honeycomb of fins to radiate heat rapidly, that receives and cools hot liquid from the engine, (3) a centrifugal-type water pump with which to circulate coolant, (4) a thermostat, which maintains constant temperature by automatically varying the amount of coolant passing into the radiator, (5) and a fan, which draws fresh air through the radiator. For operation at temperature below 32 F (0 C), it is necessary to prevent the coolant from freezing. This is usually done adding some compound to depress the freezing point of the coolant. Alcohol formerly was commonly used, but it has a relatively low boiling point and evaporates quite easily, making it less desirable than organic compounds with a high boiling point. Air-cooled cylinders operate at higher, more efficient temperatures, and air-cooling offers the important advantage of eliminating not only freezing and boiling of the coolant at temperature extremes but also corrosion damage to the cooling system. Control of engine temperature is more difficult, however, and high-temperature-resistant ceramic parts more difficult, however, and high-temperature is significantly increased.
ELECTRICAL SYSTEM Originally, the electrical system of the automobile was to the ignition equipment. With the advent of the electric starter, electric lights and horns began to replace the kerosene and acetylene lights and bulb horns. Electrification was rapid and complete, and by 1930, six-volt systems were standard everywhere. The electrical system comprises a storage battery, generator, starting motor, lighting system, ignition system, and various accessories and controls. The ignition system provides the spark to ignite the air-fuel mixture in the cylinders of the engine. The system consists of the spark plugs, coil, distributor, and battery. In order to jump the gap between the electrodes of the spark plugs, the 12-volt potential of the electrical system must be stepped up to about 20,000 volts. This is done by a circuit that starts with the battery, one side of which is grounded on the chassis and leads through the ignition switch to the primary winding of the ignition coil and back to the ground through an interrupter switch. Interrupting the primary circuit induces a high voltage across the secondary of the coil to each of the wires leading to the spark plugs. The source of energy for the various electrical devices of the automobile is a generator, or alternator, that is belt-driven from the engine crankshaft. A lead-acid battery serves as a reservoir to store excess output of the generator. Energy for the starting motor is thus made available along with power for operating other electric devices when the engine is not running or when the generator speed is not sufficiently high to carry the load.
STEERING Automobiles are steered by a system of gears and linkages that transmit the motion of the steering wheel to the pivoted front wheel hubs. The gear mechanism, located at the lower end of the shaft carrying the steering wheel, is usually a worm-and-nut or cam-and-lever combination that rotates a shaft with an attached crank arm through a small angle as a steering wheel is turned. Tie rods attached to the arm convey its motion to the wheels. In concerning, the inner wheel must turn through a slightly greater angle than the outer wheel, because the inner wheel negotiates a sharper turn. The geometry of the linkage is designate to provide for this. When the front wheels are independently suspended, the steering must be designed so that the wheels are not turned as tie-roads lengthen and shorten as result of spring action. The point of linkage attachment to the steering gear must be placed so that it can move vertically with respect to the wheel mountings without turning the wheels. The distribution of weight between the front and rear wheels of automobiles shifted toward the front as the engine and passenger compartment were moved forward to improve riding comfort and road-handling characteristics. As the weight carried on the front wheels increased to more than the half of the total vehicle weight, the effort necessary to turn the wheels in steering increased. Larger, heavier cars with wider tires and lower tire pressure also contribute to drag between tire and road that must overcome in steering, particularly in parking. It was originally considered satisfactory to limit the pull on the rim of the steering wheel to 30 pounds (14 kilograms), but this limit proved to be too high. Considerable reduction in the work of steering resulted from increased efficiency of the steering wheel was accomplished by increasing the overall steering gear ratio. Large steering gear ratios make high-speed maneuverability more difficult, however, because the steering wheel must be turned through greater angles. On the other hand, steering mechanisms of higher efficiency are also more reversible; that is, road shocks are transmitted more completely from the wheels and must be overcome to a greater extend by the driver. This causes a dangerous situation on rough roads or when a front tire blows out, because the wheel may be jerked from the driver's hands.
WHEELED VEHICLES After the early efforts to domesticate animals for their burden-carrying abilities, the most significant addition to human locomotion was the wheeled vehicle. It was one of the great inventions of all times because of the contribution that the wheel, and its utilization in a vehicle, makes up applying supplemental sources of power to an individual's mobility. Horses and camels can travel faster than the humans on their backs, but to transport more than one person with a single animal – something most horses had the strength to do – vehicle was needed. Probably the first conveyance of this sort was a plank or log dragged along the ground; the Plains Indians of North America used such a travois of two poles in their transhuman wandering until the 19th century. Its mechanical inefficiency must have prompted the search for improvements. The invention of the wheel made the contribution of a horse more productive. The power provided by any one horse has grown with changes in vehicles, in harnessing and in the surface on which it operates. Much of human history saw no technology superior to the sling or travois but when the wheel was devised changes was both substantial and probably fairly rapid. It seems that there were versions of the travois shaped like a platform, with a great reduction in the extent of actual contact with the ground; only the ends of the poles supporting the platform dragged along the surface, where friction would be great. Improvement came with placing a revolving wheel at the end of each of the drag poles. From this advance it was but a minor step to arrive at a two-wheel cart.
ANTITHEFT DEVICES Most vehicle theft is an increasing problem for owners, insurers, and manufacturers. The annual number of thefts increases almost every year, and the rate of thefts mat by expected to exceed 1 out of every 100 registered vehicles per year in the United States by the end of the 20th century. The problem is, however not new. The 1900 Leach automobile featured a removable steering wheel that the driver could carry away to prevent unauthorized vehicle use. More recently, sophisticated electronic alarms, some of which incorporate radio beacons, and more tamper-resistant wiring electronic locks have been produced.
SAFETY SYSTEMS From its beginnings, the automobile posed serious hazards to public safety. Vehicle speed and weight provided an impact capacity for occupants and pedestrians that produced great numbers of fatalities (13,000 in 1920) and serious injuries. During the 20th century, the rates of death and injury declined significantly in terms of vehicle miles. Because of the increased number of vehicles on the road, however, total fatalities have declined only slightly. Most fatal accidents occur on either city streets or secondary roads. Federal expressway systems are relatively safer. Driver training, vehicle maintenance, highway improvement, and law enforcement were identified as key areas with potential for improving safety, but the basic design of the vehicle itself and the addition of special safety features received increased attention. Safety features of automobiles come under two distinct headings: accident avoidance and occupant protection.
INTERNATIONAL TRANSPORT International transport refers to any of goods between countries. The journey may involve carriage only, but if the countries are separated by strength of water (sea or ocean), the crossing, or voyage if the distance is longer, will have to be organized specifically. In both cases, the operations will normally resort to surface transport. The transport of goods may be classified according to the countries where operation take place or to the means of transport – transport facilities – involved. The choice of the means of conveyance depends on the communication network of the countries as well as on the nature of the goods and the cost of the transport operation. Inland waterways (navigable rivers and canals) can also be of use for certain type of goods. Associating different means of transport gives rise to what is known as multimodal transport – or intermodal/combined transport – which has become more common with the development of containerization.
ROAD TRANSPORT Road transport is perhaps the most visible and common means of conveyance because of the presence on our roads of a great number of lorries whose variety stems from the necessity for carriers to meet the wide range of needs from shippers. A road hauler (GB) or trucker (US) may own a fleet of vehicles, but part of their equipment can be rented from specialized firms for special shipments. They usually set up their business by determining a specific route and serving a few well-defined areas. Lorry drivers then commonly ply between the same cities and the experience they gain by so doing reinforces the efficiency of the service. A semi-trailer – or articulated lorry – with an important payload, is mostly resorted to for a long haul in order to reduce transport costs. When an open-top trailer is used, a tarpaulin – or tilt – will protect the goods from the rain. A removal van carries all the furniture and belongings of a family moving house. A tanker lorry is especially designed for the transport of liquid cargoes, whether foodstuff, oil products or chemicals. Retailers and shopkeepers often have their orders brought to them by means of a delivery van. More and more goods are transported in containers by both road and rail. This bimodal transport makes it necessary to tranship the goods from train onto lorries in a piggy-back terminal. Road transport depends on the road network. Not all roads can be used by any sort of lorry and if motorways and main roads – or trunk roads – are generally available, as well as dual carriageways in great Britain, there may be a few limitations on secondary roads in order to prevent lorries from causing obstructions – or "hod-ups", "traffic-jams", "congestions". This may indeed be the case at certain junctions – or "crossroads" – which is one of the reasons why these are gradually being replaced by roundabouts. In the same way, level crossings which halt the traffic at regular intervals tend to disappear in modern road networks. Road works are another cause of delays and a diversion may have to be set up to avoid inconvenience. Finally, when planning a route, haulers must remember that not all the roads and bridges are free, and they may have to pay a toll for part of the route. Topics My life’s story Let me introduce myself. My name is Victor Ivanov. I am 18 now. I was born on the 21st of September in Rivne, so I have been living in Rivne since my childhood. I am not married and live with my family. We are a family of six people: my parents, my elder brother Pete, his wife, his son and I. My father works as a mechanical engineer at a private motor pool. My mother is an accountant in a private company. My elder brother is 23. He graduated from Lviv Polytechnic University and works as a manager. His wife is an economist. Their daughter Kate, my niece, is 3 years old and she goes to a nursery school. I think we are a friendly family and happy to live together. This year I have left secondary school and entered National University of Water Management and Natural Resources Use. Now I am a first year student of the Mechanical-Energetic Faculty and study at the correspondence department. My speciality is Automobile Transport. At the University we study many general educational and special subjects. Two times a year we have sessions during which we have practical classes, lectures and pass tests and exams. Besides my studies I work as a mechanic at a motor pool. My duties are to diagnose car breakdown and to remedy it. My working day lasts 8 hours a day with an hour for lunch. In the evening when I come home I have a short rest, watch TV or read something for my studies. At about 11 o’clock I go to bed.
And Natural Resources Use The National University of Water Management and Natural Resources Use came into existence in Kiev as a Hydromeliorative technical school over 80 years ago. In 1959 it moved to the city of Rivne and since that time it has passed a long way from the institute, academy to the national university. Our University trains engineers, economists, managers, ecologists, accountants, programmers and other specialists for different branches of national economy. There are more than 11 thousand day-time and correspondence students. They study at nine faculties among them is Mechanical-Energetic Faculty which trains students by Automobile Transport, Mechanical Engineering, Mineral Mining Engineering and Heat Power Engineering specialities. The academic programmes lead to the degrees of Bachelor and Master. The term of study for correspondence students lasts 5 or 6 years. At the correspondence department the academic year lasts from September to June and is divided into three terms: Autumn, Winter and Spring. At the end of each term students take tests, exams and give in course papers. At the end of training they defend their diploma projects. The University has a teaching staff of well-educated professors, associate professors, senior and junior lecturers. A modern University campus is situated not far from the city centre. It includes seven academic buildings, eight halls of residence, a library and computing centres, sports and recreation facilities. Our University is one of the prestige higher educational institutions in Ukraine and is highly rated by young people.
Rivne Rivne is administrative, economic, educational and cultural centre of the region. It is situated in the north-west of Ukraine. The population of Rivne is about 250 thousand residents. Rivne has a long history. It was first mentioned in manuscripts dating back to 1282, so Rivne is more than 800 years old. During the centuries it was often destroyed by invaders. The heroic past of our city is described in numerous books. Rivne has a lot of historical places and monuments associated with the period of the Liberation war of 1654-1658, the Civil and Great Patriotic wars. The streets of the city bear the names of war heroes and outstanding people who lived, studied or stayed here in different times. Today Rivne is a developing city. There are different enterprises in Rivne whose output is known in Ukraine and abroad. The city has general educational, vocational and technical schools, music and fine arts schools. National University of Water Management and Natural Resources Use, Humanitarian University and some private higher schools train skilled specialists for national economy, education and culture. The residents of Rivne have the Regional Music and Drama Theatre named after M.Ostrovsky, Puppet-show, movie-theatres, libraries, museums. Rivne is an attractive city. There are a lot of green trees, flower-beds, wide streets and squares, quiet corners and beautiful lanes here. Rivne is called a city if spring and flowers. The city is growing very fast and its residents want to make it a nice place to live in.
Great Britain Great Britain, formally known as the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, is situated on the British Isles. They consist of Great Britain, Ireland and some 5,500 smaller islands. The total area of the United Kingdom is 244,027 square kilometres. Great Britain is divided into 92 administrative counties. The surface of England and Ireland is rather flat. The highest mountain in the United Kingdom is Ben Nevis in Scotland (1343 m). There are many rivers in Great Britain but they are not very long. The rivers are deep and do not freeze in winter. The chief rivers are the Severn and the Thames. Great Britain is known for its typically maritime climate with frequent rains, strong winds and continuous fogs. The population of Great Britain is nearly 56 million people.. Great Britain is parliamentary monarchy. Queen Elizabeth II is the head of the state. In practice she reigns but does not rule. The country is governed in her name by the Government. Parliament is the supreme legislative body. It consists of two chambers: the House of Commons and the House of Lords. The Prime Minister is usually the head of the party which is in power. Great Britain is a highly developed industrial country. Shipbuilding is one of the principal industries in the country. The biggest centres of iron and steel industries are situated in Newcastle, Cardiff, Glasgow and Sheffield. Coal-mining, metallurgy, textile, shipbuilding are the older branches of industry. The new industries are the chemical, pharmaceutical, electro-technical, automobile, aviation and electronics. The new industries have developed hand in hand with science and technology and are equipped to meet present technical demands. Big cities and towns such as London, Glasgow, Manchester, Liverpool, Newcastle, Sheffield and Birmingham have enterprises of nearly all branches of industry. The main centres of cotton and woolen industry are Leeds, Bradford and Manchester. London, Liverpool and Glasgow are the biggest English ports. Agriculture is one of the largest and most important activities in Great Britain. The greater part of the land here is used for sheep-, cattle-, and dairy-farming. Vegetables are grown in all parts of the country. The chief grain crops are wheat and barley. The capital of the country is London, the third largest city in the world after New York and Tokyo. It was founded by Romans on the River Thames 2000 years ago. There are four main parts in London: the City, Westminster, the West End and the East End. All the principal streets of London lead to the heart of the City, the financial and business centre. In London there is so much to see that even Londoners can always find new sights. They like to say: "When a man is tired of London, he is tired of life".
Ukraine Ukraine is an independent, sovereign state. The declaration of Ukrainian independence was proclaimed on August 24, 1991 by the Ukrainian Parliament. Ukraine has its own territory, higher and local bodies of state power (the Supreme Council and local Councils), government, national emblem, state flag and anthem. By the form of government it combines the elements of presidential and parliamentary republic. The head of the state is the President. Ukraine is one of the largest European countries. Its total area is 603,700 square kilometers. Ukraine borders on the Russian Federation, Belarus, Moldova, Poland, Slovakia, Hungary and Romania. Our country is washed by the Black Sea and the Sea of Azov and it has very important ports. The population of Ukraine is about 46 million people. There are 24 administrative regions and the Crimean autonomous republic. The territory of our country has a variety of landscapes. We have high mountains, beautiful rivers and lakes. The largest lake of Ukraine is Swytyaz. The Dnipro is the main river in Ukraine which divides the country into Right-bank and Left-bank territories. Our country has many industrial raw materials; it has rich deposits of iron, metal, coal, oil, gas, different ores, marble and other natural resources. Over 40% of the labour force is employed in industry. Ukraine has well-developed metallurgical and heavy industries; extractive industries (the mining of coal, iron ore, and other minerals) have long been very important. The fertile black soil and the favourable climate have long facilitated the growth of agriculture in Ukraine. Ukraine pursues a policy of peace. Now Ukraine establishes new relations with countries throughout the world. It sets direct contacts with signing agreements and treaties. So, Ukraine has been and is being recognized by a vast number of countries. The capital of Ukraine is Kyiv. It is the seat of the Supreme Council and the Cabinet of Ministers. It is one of the most ancient cities. In 1982 it was 1500 years old. Kyiv is an industrial, scientific and cultural centre of Ukraine. It is one of the oldest cities and has many places of interest. Among them are the Golden Gate, St. Sophia's Cathedral, Kyiv-Pechersk Lavra, the monuments to many prominent Ukrainian people, fine museum and theatres. Kyiv is the centre of science and education. There are many scientific research institutes, colleges and universities there.
My Speciality "Automobile Transport Engineer" Modern Automobile engineering is a branch of vehicle engineering, incorporating elements of mechanical, electrical, electronic, software and safety engineering as applied to the design, manufacture and operation of motorcycles, automobiles, buses and trucks and their respective engineering subsystems. Automobile engineers are involved in almost every aspect of designing cars and trucks, from the initial concepts right through to manufacturing them. Broadly speaking, Automobile engineers are separated into three main streams: product engineering, development engineering and manufacturing engineering. · Product engineer (also called design engineer), that would design components/systems (i.e. brake engineer and battery engineer). This engineer designs and tests a part, seeing that it meets all its requirements, performs as required, material meets desired durability. · Development engineer, that engineers the attributes of the automobile. This engineer may provide to the design engineer what spring rate he/she requires to provide the "ride" characteristics required for the automobile to perform as desired, etc. · Manufacturing engineer, determines how to make it. Automobile engineering emplo ys different areas. Safety Engineering which is the assessment of various crash scenarios and their impact on the vehicle occupants. These are tested against governmental regulations including: seat belt and air bag functionality, front and side crash worthiness, resistance to rollover. Fuel Economy/Emissions is the measured fuel efficiency of the vehicle in miles per gallon or litres per 100 kilometres. Vehicle Dynamics which is the vehicle's response of the following attributes: ride, handling, steering, braking, and traction. Design of the chassis systems of suspension, steering, braking, structure (frame), wheels and tires, and traction control are highly leveraged by the Vehicle Dynamics engineer to deliver the Vehicle Dynamics qualities desired. Performance is a measurable and testable value of a vehicles ability to perform in various conditions. Durability / Corrosion engineering is the evaluation testing of a vehicle for its useful life. This includes mileage accumulation, severe driving conditions, and corrosive salt baths. Package / Ergonomics Engineering: Package Engineering is a discipline that designs/analyzes other areas of the vehicle like the engine compartment, and the component to component placement. Ergonomics is the discipline that assesses the occupant's access to the steering wheel, pedals, and other driver/passenger controls. Climate Control: Climate Control is the customer’s impression of the cabin environment and level of comfort related to the temperature and humidity. Drivability: Drivability is the vehicle’s response to general driving conditions. Manufacturing Engineers at Automobile companies are involved in a wide array of manufacturing activities. They plan and engineer the assembly of whole vehicles as well as the individual parts that go into the vehicles. Design and layout of equipment and people, machine rates and line rates, specification of automation equipment, and manufacturing safety procedures are all some of the jobs that Manufacturing Engineers do. Manufacturing engineers at assembly plants plan out the body shop, engine and transmission placement, and the trim and chassis area of the final assembly. Seats, radios, interior trim panels and wheels are examples of parts that need to be manufactured for a vehicle and whose creation would be overseen by an Automobile Manufacturing Engineer. An Automobile Manufacturing Engineer typically works with statistics and process controls, validating that the process that produces parts will always produce those parts with quality. They also search for ways to continuously improve the process between product upgrades generally the engineering related pure development procedures.
Навчально-методичний посібник для студентів ІІІ курсів
Навчальні завдання призначено для студентів заочної форми навчання напряму підготовки «Організація та ремонт автомобілів» освітньо-кваліфікаційного рівня «Молодший спеціаліст». Навчальні завдання містять оригінальні тексти, які відображають комплекс основних понять, необхідних студентам напряму підготовки «Організація та ремонт автомобілів» для оволодіння іншомовним професійним спілкуванням. Вони готують студентів до читання і розуміння оригінальної англомовної літератури за фахом і мають за мету розвиток у студента навичок самостійної роботи, що включає: а) вивчаюче читання та завдання, спрямовані на засвоєння лексичного мінімуму та розвиток мовленнєвих навичок, б) перевірку якості засвоєних знань за допомогою міні-тестів, які виконуються студентами під час самостійної домашньої підготовки і перевіряються викладачем на практичних за
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Последнее изменение этой страницы: 2020-12-09; просмотров: 61; Нарушение авторского права страницы; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! infopedia.su Все материалы представленные на сайте исключительно с целью ознакомления читателями и не преследуют коммерческих целей или нарушение авторских прав. Обратная связь - 3.141.201.46 (0.018 с.) |

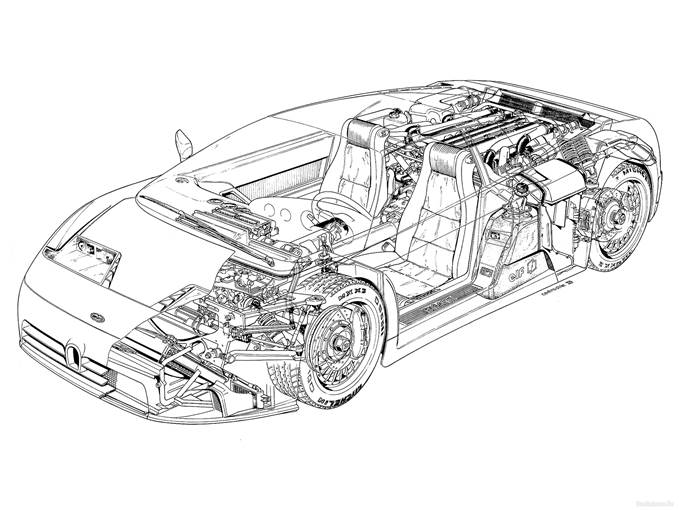 транспортних спеціальностей
транспортних спеціальностей  J
J


