
Заглавная страница Избранные статьи Случайная статья Познавательные статьи Новые добавления Обратная связь КАТЕГОРИИ: ТОП 10 на сайте Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрацииТехника нижней прямой подачи мяча. Франко-прусская война (причины и последствия) Организация работы процедурного кабинета Смысловое и механическое запоминание, их место и роль в усвоении знаний Коммуникативные барьеры и пути их преодоления Обработка изделий медицинского назначения многократного применения Образцы текста публицистического стиля Четыре типа изменения баланса Задачи с ответами для Всероссийской олимпиады по праву 
Мы поможем в написании ваших работ! ЗНАЕТЕ ЛИ ВЫ?
Влияние общества на человека
Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрации Практические работы по географии для 6 класса Организация работы процедурного кабинета Изменения в неживой природе осенью Уборка процедурного кабинета Сольфеджио. Все правила по сольфеджио Балочные системы. Определение реакций опор и моментов защемления |
For the next class prepare a report about the system of testing for Higher Education Institutions admittance in your country. Tell about your personal experience of passing such tests.
Gather information about similar way of university life in Russia or other countries and use it to answer the questions in the plan. Use your answers to write your article. (150 words) (See Appendix 2, section III) Text B. The higher education system of the United States an informal configuration of varied institutions. March 12, 2020
https://www.studyexperience.fr/en/study-abroad/study-in-th e-usa/the-american-higher-education-system/ https://www.justlanded.com/english/United-States/USA-Guide/Education/Higher-Education
1. Do you think the system of higher education in America is similar to that in your country? 2. What most prestigious universities of the USA do you know? 3. What is the difference between a college and a university in America?
Look at the given words and tick those which might be connected with the information presented in the text you are going to read:
The higher education system of the United States an informal configuration of varied institutions. March 12, 2020
The higher education system of the United States is not so much a formal system as it is an informal configuration of varied institutions. The development of the American system has been unique when compared with other national postsecondary educational systems around the world. Unlike most other countries, where higher education systems have largely developed outward from a central, government-supported university, the United States has never had such an institution. Instead, the evolution of the U.S. system has been shaped by many different influences, including state and local needs, demographics, religion, and changing social contexts.
The higher education system of the United States an informal configuration of varied institutions.
In the United States, there are approximately 5,300 colleges and universities. These colleges and universities range from beauty schools and two-year ‘junior’ colleges to technical institutes and private Ivy League research universities like Harvard University. They may be small or large, rural or urban, highly selective or open to all. Combined, all of the colleges and universities are often referred to as “the American higher-education system.” Structurally, this system is very diverse. This diversity focuses on the ways in which institutions are organized and controlled. In terms of type of institutional control there are public or private. Public institutions While there is no national system of higher education, all states have developed some type of public postsecondary educational system. Publicly controlled institutions are funded primarily by the government (usually by state governments) and are typically part of a larger state system. Out of the 5,300 institutions in the USA 1,626 are public. Public institutions fall into one of three major categories: universities, state colleges, and community colleges. Public universities and state colleges tend to have a strong research emphasis, they offer a blend of natural and social sciences, technical, and humanistic studies and typically have large student enrollments.
The best known public universities and state colleges in the U.S. are University of California, University of Michigan, University of Virginia, Georgia Institute of Technology, University of North Carolina, University of Florida. Community colleges or ‘junior’ colleges are colleges to which students may be admitted at the end of their high school career, providing only the first two years of university work. Two-year community colleges are mostly locally controlled and publicly funded. These colleges offer studies leading to technical and semi-professional occupations, and studies which prepare students for entrance to a four-year degree institution.
The name community college originates from the fact the colleges primarily attract students from the local community and they are often supported by local taxes. The four-year liberal arts college may be one of the constituent parts of a university complex or an independent establishment. It provides pre-professional training of four years or less for students who proceed to advanced professional schools, such as law or medicine, and offers a liberal education for students who don’t enter professional or graduate school. Private institutions Private institutions are primarily funded by nongovernment sources of income, which are fees and endowments, and tend to be independent with their own private governing boards. There are many more private institutions in the United States than there are public colleges and universities. Out of the 5,300 institutions in the USA, 1,687 are private nonprofit schools, and 985 are private for-profit schools and there are great differences in quality and reputation among them.
The most famous universities include the Ivy League universities (called as such because they’re old enough for ivy to have grown on the walls): Brown, Columbia, Cornell, Dartmouth, Harvard, Pennsylvania, Princeton and Yale. The Ivy League, together with the ‘heavenly seven’ or ‘seven sisters’ (Barnard, Bryn Mawr, Mount Holyoke, Radcliffe, Smith, Vassar and Wellesley) of once all-female colleges, are some of the most prestigious American universities. Other world-renowned American higher education institutions include the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) in Cambridge (Massachusetts), the California Institute of Technology (Caltech) and Stanford University in California, all of which have earned distinguished international reputations for their research and academic excellence. Attending one of these colleges usually pays off in the job market, particularly at the executive level. The best-known of all is Harvard, Massachusetts, which was founded in 1636. There is much in common between Harvard and Yale, Connecticut, and together they occupy a position in American university life rather like Oxbridge in England. All universities are usually composed of an undergraduate college of arts and sciences, as well as graduate and professional schools and facilities, offering Bachelor’s, Master’s or Doctor’s degree. The methods of instruction in higher education institutions in the USA are lectures, discussions and labwork. The academic year is usually of nine months duration, or two semesters of four and a half months each.
Students are classified as freshmen, sophomores, juniors and seniors. A peculiar feature of American college and university life is numerous student’s unions, fraternities and sororities. The Greek alphabet is generally used in their names. These organizations, Greek letter societies, are descendants of the eighteenth century literary and social clubs which flourished in the early American colleges.
Formal – adj. public or official Varied – adj. containing or changing between several different things or types Influence – v. to affect or change how someone or something develops, behaves, or thinks Local – adj. existing in or belonging to the area where you live, or to the area that you are talking about Range – v. to have an upper and a lower limit in amount, number, etc College – n. any place for specialized education after the age of 18 where people study or train to get knowledge and/or skills University – n. a place where people people study for an undergraduate (= first) graduate or postgraduate (= higher level) degree
Public – adj. relating to or involving people in general, rather than being limited to a particular group of people Private – adj. owned or controlled by an individual person or a commercial company, rather than by the state or an official organization. Postsecondary – adj. any level of education after high school Humanistic – adj. relating to humanism Enrollment – n. the act of putting yourself or someone else onto the official list of members of a course, college or university, or group Semi-professional – adj. referring to an activity that is taken part in but is not done all the time Support – v. to agree with and give encouragement to someone or something because you want him, her, or it to succeed Primarily – adv. mainly Tax – n.(an amount of) money paid to the government that is based on your income or the cost of goods or services you have bought Liberal - adj. respecting and allowing many different types of beliefs or behavior Graduate – adj. relating to or working toward a university degree beyond the one you receive after four years of study Board n.the group of people whoare responsible for controlling and organizing a company or organization Profit - n.money that is earned in trade or business after paying the costs of producing and selling goods and services Research – n. a detailed study of a subject, especially in order to discover (new) information or reach a (new) understanding Academic - adj. relating to schools, colleges, and universities, or connected with studying and thinking, not with practical skills Pay off phrasal verb If something you have done pays off, it is successful Facility- n. a place, especially including buildings, where a particular activity happens Degree n. a course of study at a college or university, or the qualification given to a student after he or she has completed his or her studies Duration – n. the length of time that something lasts Freshmen – n. a student in the first year of high school, college, or university Sophomore – n. a student studying in the second year of a course at a US college or high school Junior – n. a student in the third year of a course that lasts for four years at a school or college Senior – n. a student in their final year of high school, college or university Feature – n. a typical quality or an important part of something Numerous - adj. meaning many Descendant - n. a person related to someone from an earlier generation
1. How many colleges and universities are there In the United States? 2. How can you characterize the system of Higher Education in the USA? 3. What is the difference between public and private higher education institutions in America? 4. What are the categories of public higher education institutions in America? 5. What are the best known public higher education institutions in America? 6. Why are there more private higher education institutions in the USA? 7. What are the most prestigious private higher education institutions in the USA? 8. What are the methods of instruction in higher education institutions in the USA? 9. How long does the academic year usually last? 10. How are the American Students classified?
Community colleges or ‘junior’ colleges are colleges to/on which students may be admitted at the end of their high school career, providing only the first two years of/for university work. Two-year community colleges are mostly locally controlled and publicly funded. These colleges offer studies leading to/for technical and semi-professional occupations, and studies which prepare students for/to entrance to a four-year degree institution.
The name community college originates from/of the fact the colleges primarily attract students from/of the local community and they are often supported by/from local taxes. The four-year liberal arts college may be one of/at the constituent parts of a university complex or an independent establishment. It provides pre-professional training of four years or less for/to students who proceed to advanced professional schools, such as law or medicine, and offers a liberal education for students who don’t enter professional or graduate school.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Последнее изменение этой страницы: 2020-12-17; просмотров: 182; Нарушение авторского права страницы; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! infopedia.su Все материалы представленные на сайте исключительно с целью ознакомления читателями и не преследуют коммерческих целей или нарушение авторских прав. Обратная связь - 18.191.5.239 (0.034 с.) |
 XI. Writing (a descriptive article of an event):
XI. Writing (a descriptive article of an event): Before reading:
Before reading: I. Brainstorm. Answer the following questions:
I. Brainstorm. Answer the following questions: II. Associative practices.
II. Associative practices. Read the text
Read the text Preface
Preface






 Study the vocabulary:
Study the vocabulary: III. Comprehension questions:
III. Comprehension questions: IV. Fill in all the advantages of the US Higher Education into the scheme:
IV. Fill in all the advantages of the US Higher Education into the scheme: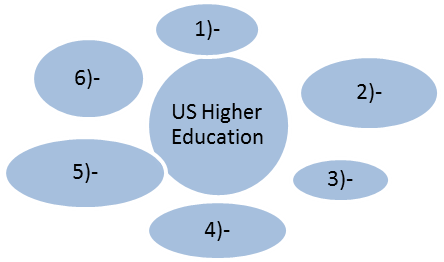
 V. Match the words 1-19 with the words a-s to make phrases from the text:
V. Match the words 1-19 with the words a-s to make phrases from the text: VI. Find 8 words from the text in the puzzle presented below (the marked is not among the 8):
VI. Find 8 words from the text in the puzzle presented below (the marked is not among the 8): VII. Choose the necessary preposition:
VII. Choose the necessary preposition: VIII. Mindmapping. Link your associations with the words from the exercise №2 with the factual information from the text and draw a scheme on the System of Higher Education in the USA.
VIII. Mindmapping. Link your associations with the words from the exercise №2 with the factual information from the text and draw a scheme on the System of Higher Education in the USA. IX. Fill in the table and share your ideas about the information from the article with the class.
IX. Fill in the table and share your ideas about the information from the article with the class.


