
Заглавная страница Избранные статьи Случайная статья Познавательные статьи Новые добавления Обратная связь FAQ Написать работу КАТЕГОРИИ: ТОП 10 на сайте Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрацииТехника нижней прямой подачи мяча. Франко-прусская война (причины и последствия) Организация работы процедурного кабинета Смысловое и механическое запоминание, их место и роль в усвоении знаний Коммуникативные барьеры и пути их преодоления Обработка изделий медицинского назначения многократного применения Образцы текста публицистического стиля Четыре типа изменения баланса Задачи с ответами для Всероссийской олимпиады по праву 
Мы поможем в написании ваших работ! ЗНАЕТЕ ЛИ ВЫ?
Влияние общества на человека
Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрации Практические работы по географии для 6 класса Организация работы процедурного кабинета Изменения в неживой природе осенью Уборка процедурного кабинета Сольфеджио. Все правила по сольфеджио Балочные системы. Определение реакций опор и моментов защемления |
The earliest systems of Weights and MeasuresСодержание книги
Поиск на нашем сайте
Англійська мова Методичні вказівки до практичних занять для студентів IІІ курсу спеціальностей „Якість стандартизація та сертифікація” „Метрологія та вимірювальна техніка”
КИЇВ КНУТД 2010
Англійська мова: Методичні вказівки до практичних занять для студентів IІІ курсу спеціальність „Якість, стандартизація та сертифікація, „Метрологія та вимірювальна техніка” / Упор.: О.В. Павлусенко, М.С. Копил – К.: КНУТД, 2010 – 36 с. – Англійською мовою Упорядники: О.В. Павлусенко М.С. Копил
Рецензент: Н.Д. Бабурова
Відповідальний за випуск завідуюча кафедрою іноземних мов ф-ту ТЛП к.ф.н., доцент, Т.В. Барамикова.
Затверджено на засіданні кафедри іноземних мов ф-ту ТЛП Протокол № 5 від 02. 12. 2009 р. UNIT 1 HISTORY OF METROLOGY TEXT A I Read and remember the words and their translation: 1. dactyl – палець 2. palаmi (palm) – рука (одиниця довжини) 3. stone shot – кам’яне ядро 4. pedestrian – пішохід, учасник змагань з спортивної ходьби 5. discovery– відкриття 6. widespread– широко вживаний 7. obol – срібна, пізніше мідна монета в Давній Греції II Read and translate the following text: HISTORY OF METROLOGY The first steps of humanity have already presented the need of finding units of measurement. Human body itself constituted the basis for the creation of the first metrical system. Some of the first units created were the dactyl, palami and step. In cases of long-distance measurement, the units were constituted by the distance of stone shot, the distance that covers in one day one pedestrian, the period of the sun, the moon etc. Depending on the circumstances similar units are still used. Despite the common root of most metrical systems, they differed from place to place. Thus we had the parallel growth of many systems that rendered the transactions among populations difficult. In ancient Greece the basic unit of measurement was foot. The size was not constant but depended on the point where the measurement was made. Subdivision of foot was the dactyl. Basic unit of measurement of weight was the obol. The following units derived from the obol are: drachma, mina and talent. Similar units of measurement were also used by other ancient cultures. In Egypt the most famous unit of length was the royal pechys. Its basic subdivision was the dactyl. Meters of liquids were the ro, hekat, har and cubic pechys. In Babylonia the most famous unit of length was the Babylonian dactyl. Meter of liquids was the ka. The most ancient of all known weights was mina. The Romans adopted the Greek units of measurement changing only the name of some of them. In earlier periods of middle Ages the use of Roman system of measurement was extended through all Europe and converted from place to place depending on local needs. This resulted in creating lots of different metric systems. During the years due to the growth of societies measurements became more complex, while mathematics allowed the creation of specialized metrical units suitable for commercial and scientific use. Finally the increase of commercial transactions among populations made obvious the need for existence of less metrical systems, which resulted in the predominance of two systems of units nowadays – English and International. Such countries as Britain and its colonies use the English system of measurements. The International system is widespread worldwide. III Answer the questions: 1. What were the first units? 3. What were the basic units of measurement in ancient Greece? 4. What is the most ancient of all known weights? 5. What systems of measurement do you know? IV Complete the sentences with the words from the text: 1. Some of … units created were the dactyl… etc. 2. In ancient Greece … unit of measurement … 3. Basic unit of measurement of weight… 4. … itself constituted the basis for the creation of the first… systems. 5. The first …of humanity have already presented the need of finding units of… 6. Nevertheless the development of… was not the expected… 7. The Romans adopted … units of measurement… them. 8. The most ancient of all known weights… 9. In Babylonia … unit of length was the …
V Find the English equivalents to the words: Рука, вимірювання, одиниці, давній, кам’яне ядро, Середні Віки, приймати, очікувати, Англійська система вимірювання. VI Match the English words with their Ukrainian equivalents: 1. ancient a. прийняти, затвердити 2. human body b. Англійська Система 3. units c. одиниці 4. suitable d. підходящий 5. dactyle. тіло людини 6. nevertheless f. не дивлячись на 7. adopt g. вимірювання 8. measurement h. палець 9. discoveries i. давній 10. English System j. відкриття VII True or false statements: 1. Human body itself constituted the basis for the creation of the first metrical systems. 2. The most ancient of all known measurements of weight was the dactyl. 3. The Romans adopted the Greek units of measurement changing only the name of all of them. 4. The development of metrical systems was the expected one. 5. The meter and weight were among the first discoveries made by human.
VIII Translate into English: 1. Тіло людини – основа для створення першої системи вимірювання. 2. В Давній Греції ступня була основною одиницею вимірювання. 3. Основною одиницею вимірювання ваги в Давній Греції був оболь. 4. Римляни прийняли Грецьку систему вимірювання, змінивши лише декілька назв одиниць. 5. Найдавнішою одиницею вимірювання ваги була міна. IX Make up sentences with the terms: Meter, increase of commercial transaction, long-distance measurement, basic unit of measurement, human body, ancient, Babylonian dactyl, Roman system, ka, the English System, Greek units. X Speak on the topic using the following words and word - combinations: The first steps of humanity, the creation of the first metrical systems, ro, the first units, dactyl, palm, mina, the Babylonian dactyl, Roman system, hekat, the increase of commercial transactions, step, the English System, long-distance measurement, obol. TEXT B I Read and remember: 1. morphology – морфологія 2. to refer to – відноситися 3. yard – ярд (міра довжини, яка дорівнює 91,4 см.) 4. cubit – лікоть, (старовинна лінійна міра довжини, яка дорівнює 45 см, довжині ліктьової частини руки людини) 5. to correspond – відповідати 6. dimension – розмір 7. consequently – в результаті 8. fraud – обман, шахрайство 9. endeavor – спроба, намагання 10. to resolve – вирішувати II Read text and define the main idea of it: TEXT C I Mind the following words and word - combinations: 1. to measure – вимірювати 2. to abbreviate – скорочувати 3. inverse – інверсія, зворотній порядок 4. resistance – опір 5. voltage – напруга II Listen to the text” WHAT IS OHM? “and decide if the statements are true (T) or false (F): 1. An ohm is a unit used in the international system of measurements to measure resistance. 2. The symbol for Ohm is the Greek letter Delta. 3. George Ohm was an American physicist in the early 19th century. 4. Ohm is one of the great fathers of electricity. 5. Ohm was well-trained in mathematics and physical training.
UNIT 2 METROLOGY TEXT A I Read and remember the words and their translation: 1. to embrace – охоплювати 2. subfield – підгрупа 3. traceability – єдність вимірювань 4. to ensure – гарантувати, забезпечувати 5. comparisons – порівняння 6. hardness – твердість 7. gemstones – дорогоцінне каміння II Read and translate the following text: METROLOGY Metrology derives from Greek “metron” – measure and “logos” – science. Metrology is the science of measurement. Measurements come in different forms. Gemstones can be measured for hardness or carat size. Pieces of wood can be measured for length. Electricity can be measured in amps, volts and watts. Metrology includes all theoretical and practical aspects of measurement. In 1950s it was necessary to bring unity to measurement in the manufacturing process. As a result, the International Organization of Legal Metrology was created. Today dozens of countries are members of this organization. Their common goal is to unify manufacturing and business throughout the world. Metrology is defined by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures, as the science of measurement, embracing both experiment and theoretical determinations at any level in any field of science and technology. Metrology is a very broad field and may be divided into three subfields: Scientific or fundamental metrology concerns the establishment of measurement units, unit systems and the development of new measurement methods, realization of measurement standards and the transfer of traceability from these standards to users in society. Applied or industrial metrology concerns the application of measurement science to manufacturing and other processes and their use in society, ensuring the suitability of measurement instruments, their calibration and quality control of measurements. Legal metrology concerns requirements of measurements and measuring instruments for the protection of health, public safety, environment, enabling taxation, protection of consumers and fair trade.
III Answer the questions: 1. What is metrology? 2. What does metrology include? 3. How is metrology defined? 4. Is metrology an old science? 5. What subfields of metrology do you know? 6. What do you know about applied and industrial metrology? 7. What is legal metrology?
IV Complete the sentences with the words from the text: 1. Metrology is … of measurement. 2. Metrology is defined by … 3. Metrology is very broad field and … 4. Scientific and fundamental … of measurement. 5. Legal metrology … protection of health. V Find the English equivalents to the words: Споживач, прототип, підгрупа, визначення, маркування, гарантування, дорогоцінне каміння, твердість, єдність вимірювань, охоплювати, прикладна метрологія.
VI Match the words with their Ukrainian equivalents: 1. science a. споживач 2. determinations b. еволюціонувати 3. quality control c. прототип 4. comparisons d. безпека 5. scales e. порівняння 6. prototype f. ваги 7. consumer g. наука 8. evolve h. підгрупа 9. subfield i. контроль якості 10. safety j. визначення
VII True or false statements: 1. Metrology is the science of measurement. 2. Metrology is defined by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures as the science of weight. 3. Traditionally Metrology is divided into three subfields. 4. Legal metrology concerns the application of measurement science to manufacturing and the processes and their use in society. 5. Applied or industrial metrology concerns requirements of measurements and measuring instruments for the protection of health, public safety. VIII Translate into English: 1. Метрологія – це наука про вимірювання. 2. Метрологія включає всі теоретичні і практичні аспекти вимірювань. 3. Метрологія визначена Міжнародним Бюро Мір і Ваги, як наука про вимірювання. 4. Найвідомішою одиницею вимірювання ваги є кілограм. 5. Наукова метрологія займається розробкою вимірювальних апаратів та їх майбутнім патентуванням.
IX Make up sentences with the terms: Consumer, to determine, scales, legal metrology, carat size, unity, the International Bureau of Weights and Measures, traceability, the International Organization of Legal Metrology, taxation. X Speak on the topic using the following words and word-combinations: Derives from, the science of measurement, gemstones, applied, industrial, electricity, legal, the International Organization of Legal Metrology, broad field, scientific, fundamental, a core concept, traceability, to coordinate, national laboratories.
TEXT B I Read and remember: 1. sustainable – життєздатний, раціональний 2. purchase – купівля 3. weighing – зважування 4. ongoing – постійний 5. maintenance – підтримка II Read text and define the main idea of it: TEXT C I. Mind the following words and word - combinations: 1. dimensional – просторовий 2. gauging – вимірювання 3. caliper – штангенциркуль 4. comparator – компаратор 5. interface – взаємозв’язок
II Listen to the text ” THE WORLD’S LARGEST METROLOGY COMPANY “MITUTO” and decide if the statements are true (T) or false (F): 1. The world's largest metrological company was founded in 1954. 2. Today Mituto presents 5000 products. 3. Mituto American Corporation was formed in 1973. 4. Mituto's philosophy was to make the best mechanical micrometer in the world. 5. The world's largest metrology company was founded by Yean Nowata with just one product. UNIT 3 METRIC SYSTEM TEXT A I Read and remember the words and their translation: 1. aspiration– сильне бажання досягти чогось 2. decimal – десятинна система 3. to be aware – бути в курсі справ 4. earthly – земний 5. arc – арка, веселка 6. meridian – меридіан 7. pendulum – маятник 8. immutable – постійний 9. simultaneously – синхронно 10. counterbalances – врівноважені дії 11. density – компактність 12. light – світло 13. to subdivide – розділятися на групи 14. Are – Ар (міра земельної площі, дорівнює 100 м2) 15. oka – одиниця ваги в Єгипті(дорівнює 2, 34 англ. фунти) II Read and translate the following text: METRIC SYSTEM The aspiration of many European scientists for the creation of a new single and uniform metrical system fulfilled at the duration of French Revolution. King Louis the sixteenth (XVI) proposed the creation of a decimal metrical system. In 1670 Gabriel Mouton, famous scientist, being aware of the fact that this new metrical system should be based on earthly measurement, proposed a decimal metrical system, which would be based on the length of a thin arc of meridian. Later in 1671 Jean Packard, a French astronomer, proposed one unit of length based in pendulum. Nevertheless one century had to pass up to the creation of metric system. In 1790 the French national assembly assigned to French Academy of Sciences to create immutable models for all the meters and all the weights. The academy created a system of units that was simultaneously simple and scientifically based on the proposal of Gabriel Mouton. In June, 1799 the metric system was adopted. Finally the basis unit of length – meter was defined. The new units of surface and volume resulted from the meter were the square and cubic meter respectively. Also as a basic unit of weight was the gram.The gram is equal to the mass of a cubic centimeter of clean water in the temperature of biggest density (4° C) The liter, resulted from the volume of cube with length of each side equal to 10 centimeters. Multiples of square meter are: the Are, the Acre (10 are) and the hectare (100 are). Even though the metric system was not accepted with enthusiasm, its adoption from other nations began to increase regularly after its obligatory use in France 1840. It is not accidental that the growth of metrical system coincided with the technological growth in Europe and America. At the end of 1860 the need for existence of more precise and explicitly determined units became obvious, because of the requirements being created by the new scientific discoveries. This became possible with the Meter Convention in 1875. Meter Convention is an international treaty in which participated 17 countries. 35 nations had officially accepted the metric system. This treaty determined the units as well as the mechanisms for the constitution and adoption of further determinations in the metric system. The metric models were manufactured and distributed in each nation that ratified the treaty. The duty of the international office in France is the permanent secretariat of the Treaty of Meter as well as the exchange of information referring to the use and the improvement of metrical system. In 1921 the office extended the work of international standardization in electric models, in 1933 in the models of lighting and in the models of measurement of radiation in 1960. The same year (1960) a generalized simplification of metric system as well as its denomination in to the International System of Units was decided. The International System of Units has been established worldwide following simultaneously the continuously created scientific needs for the determination of new and more precise metrical units. In Greece the complete establishment of Metric System took place on the 1st of April in 1959 when the unit of weight known as oka was used until then was replaced by the kilogram. III Answer the questions: 1. Who proposed the creation of a decimal metrical system? 2. When did Jean Packard, a French astronomer, propose one unit of length based on pendulum? 3. When was the metric system adopted? 4. When was the metric system officially accepted by 35 nations? 5. Who created a system of units that was simultaneously simple and scientifically based on the proposal of Mouton? IV Complete the sentences: 1. The … created a system of units that was …simple and scientific based…Mouton. 2. In … the complete establishment of Metric System … on the 1st of April in 1959. 3. The...of many European scientists for … of a new single and uniform metrical system fulfilled at the… of French Revolution. 4. The duty of the… in France is the permanent secretariat of the Treaty of Meter as well as the exchange of information referring to the use and the … of metrical system. 5. …the sixteenth (XVI) proposed the …of a decimal …system.
V Find the English equivalents to the words: Маятник, розділятися на групи, десятинна система, компактність, бути в курсі, меридіан, постійний, синхронно, врівноважені дії
VI Match the English words with their Ukrainian equivalents: 1. immutable a.маятник 2. pendulum b.десятинна система 3. earthly c.бути в курсі 4. decimal d.сильне бажання досягти чогось 5. density e.земний 6. simultaneously f.веселка 7. to be aware g.синхронно 8. aspiration h.світло 9. arc i.постійний 10. light g.компактність VII True or false statements: 1. The meter resulted from the volume of cube with length of each side equal to 10 centimeters. 2. Also the basic unit of weight was the kilogram. 3. Multiples of square meter are: the Are, the Acre and the hectare. 4. King Louis the sixteenth (XVI) proposed the creation of a decimal metrical system. 5. Multiple of square meter is the Are.
VIII Translate into English: 1. Король Луї XVI запропонував створення десяткової метричної системи. 2. Багато Європейських учених прагнули створити нову і загальноприйняту метричну систему. 3. У Греції прийняття метричної системи відбулося 1-го квітня 1959 року. 4. Основною одиницею довжини в метричній системі був метр. 5. Офіційно, 35 країн світу ратифікували метричну систему. IX Make up sentences with the terms: Simultaneously, metric system, arc of meridian, decimal, a basic unit of weight, kilogram, aspiration, scientific discoveries, pendulum, counterbalances, Are. X Speak on the topic using the following words and word - combinations: The aspiration, French Revolution, King Louis the sixteenth, Meter Convention, decimal metrical system, meter, International System of Units, the need for existence, oka, kilogram, complete establishment, officially accepted, multiples of square meter, a thin arc of meridian.
TEXT B I Read and remember: 1. frustrate – розчаруватися 2. neatly – уміло, чітко 3. familiarity – фамільярність II Read text and define the main idea of it: SMALL-UNIT METRIC SYSTEM The small-unit metric system is based on three fundamental units: the centimeter, which quantifies displacement, the gram, which quantifies mass and the second, which quantifies time. The small-unit metric system is so-called because one centimeter is equal to 0.01 meter (10 -2 m), and one gram is equal to 0.001 kilogram (10 -3 kg). The CGS system, like the metric system, was originally developed by scientists who were frustrated with the English (foot-pound-second) system. The CGS units of displacement and mass lend themselves neatly to calculations in scientific notation, while English units generally do not. Time remains somewhat messy in all systems; there are 60 seconds in a minute, 60 minutes in an hour, and 24 hours in a day. The Standard International System of Units has officially supplanted the small-unit metric system as well as the metric system. But it is good to have passing familiarity with the small-unit metric system, because that scheme is still used by some astronomers and physicists, and many older scientific books and papers were written with a preference for it. Today's International System provides formal definitions for the meter, kilogram, second and also specifies and defines four additional units: the Kelvin for temperature, the ampere for electric current, the candela for luminous intensity, and the mole for material quantity. TEXT C I Mind the following words and word - combinations: 1. span – пядь (відстань від кінчика великого пальця до кінчика мізинця) 2. seek – шукати, дізнаватися 3. to alleviate – зменшувати,полегшувати 4. to devise – розробляти 5. simplicity – простота 6. inefficiency – неефективність 7. volume – об’єм II Listen to the text” THE METRIC SYSTEM “and decide if the statements are true (T) or false (F): 1. By the eighteenth century, dozens of different units of measurement were commonly used throughout the world. 2. Length could be measured in feet, inches, miles, spans, cubits, hands and more. 3. In 1779, the French National Assembly commissioned the Academy of Science to design a simple decimal-based system of units. 4. The most common base units in the metric system are the meter, gram, and liter. 5. The liter is a unit of length. UNIT 4 TEXT A I Read and remember the words and their translation: 1. non-metric – не метричний 2. to maintain – утримувати 3. transition – перехід 4. luminous – світловий 5. negligible – незначний 6. cross-section – поперечний розріз 7. charge – заряд 8. capacitance – ємкість 9. resistance – супротив, протидія 10. steradian – стерадіан 11. conductance – провідність 12. flux – потік 13. density – густина 14. inductance – індуктивність 15. lumen – люмен(одиниця світлового потоку) 16. lux – люкс(одиниця освітленості) 17. luminance – яскравість II Read and translate the following text:
SI Base Units
Other international units are called derived units. There are 22 derived units: · the radian and steradian for plane and solid angles; · the Newton for force and the Pascal for pressure; · the joule for energy and the watt for power; · the degree Celsius for everyday measurement of temperature; · units for measurement of electricity: the coulomb (charge), Volt (potential), farad (capacitance), Ohm (resistance), and siemens (conductance); · units for measurement of magnetism: the Weber (flux), Tesla (flux density), and Henry (inductance); · the lumen for flux of light and the lux for luminance; · the hertz for frequency of regular events and the Becquerel for rates of radioactivity; · the katal, a unit of catalytic activity used in biochemistry. Each international unit is represented by a symbol. The use of unit symbols is regulated by precise rules. These symbols are the same in every language of the world. However, the names of the units themselves vary in spelling according to national conventions. Therefore, it is correct for Americans to write meter and Germans to write Meter, and it is also correct for the British to write metre, Italians to write metro, and Poles to write metr. III Answer the questions: 1.What is the key agreement in the sphere of international measurements? 2. What base units do you know? 3. What derived units do you know? 4. How is each unit represented? 5. What is Meter Convention? IV Complete the sentences: 1. All systems of …, metric and non-metric are linked through a network of international agreements supporting the …. 2. The … is maintained by a small agency in Paris, the… 3. There are … base units. 4. Each SI … is represented by a …. V Find the English equivalents to the words: Незначний, перехід, світловий, густина, індуктивність, Ампер, потік, метричний, агентство, Міжнародне Бюро, фізична величина.
VI Match the English words with their Ukrainian equivalents: 1. physical quantity a. потік 2. maintain b. температура 3. density c. Ампер 4. inductance d. бюро 5. flux e. супротив 6. charge f. фізична величина 7. Ampere g. утримувати 8. resistance h. заряд 9. bureau i. індуктивність 10. temperature g. густина VII True or false statements: 1. The International System is maintained by a small agency in Poland. 2. The use of unit symbols is regulated by the international rules. 3. The 23rd CGPM met in 2007. 4. Each SI unit is represented by a symbol. 5. The next General Conference will be in 2015.
VIII Translate into English: 1. Всі метричні і не метричні системи вимірювання пов’язані між собою міжнародними угодами. 2. Метр – це одиниця вимірювання відстані. 3. Основними одиницями вимірювання є: метр, кілограм, секунда. 4. Вольт, Ом та Цельсій відомі як вторинні одиниці вимірювання. 5. Кожна одиниця вимірювання Міжнародної системи одиниць позначається символом. IX Make up sentences with the terms: Resistance, kilogram, physical quantity, temperature, inductance, bureau, charge, Ampere, flux, a symbol, Celsius, length. X Speak on the topic using the following words and word - combinations: Metric, metric club, international agreements, non-metric, industrialized countries, charter member, the International Bureau of Weights and Measures, industrial countries, constant current, an abbreviation, luminous intensity, the thermodynamic temperature, the Newton, force, the Pascal, SI base units, pressure, capacitance, SI derived units, a symbol, precise rules.
TEXT B
I Read and remember: 1. ray – промінь 2. Statute mile – британська статутна миля 3. Ammeter – амперметр 4. to consume – займати 5. to intend – мати на увазі II Read text and define the main idea of it: METER The meter is the international unit of displacement or length. One meter is the distance traveled by a ray of electromagnetic energy through a vacuum in 1/299,792,458 (3.33564095 x 10-9) of a second. The meter was originally defined as one ten-millionth (0.0000001 or 10-7) of the distance, as measured over the earth's surface in a great circle passing through Paris, France, from the geographic North Pole to the equator. One meter is a little more than three English feet, or about 39.37 inches. One foot is approximately 0.3048 meter. There are about 1609 meters in a statute mile. The official span was at one time formally defined as the separation between two scratches on a platinum bar in Paris. This was, of course, intended mainly for show, and not for use in the laboratory. In engineering applications and also in an everyday sense, the term meter refers to any instrument used to measure the magnitude of a quantity. Examples include the volume-unit meter in home audio systems, the ammeter to measure electric current, and the kilowatt-hour meter to measure electrical energy consumed over a period of time. TEXT C I Mind the following words and word - combinations: 1. heat – тепло 2. to melt – танути 3. to boil – кипіти 4. atmospheric pressure – атмосферний тиск 5. centigrade – стоградусний
II Listen to the text” HOW IS TEMPERATURE MEASURED? “and decide if the statements are true (T) or false (F): 1. Temperature is the heat of an object, measured by its intensity or degree on a defined scale. 2. There are several scales used to measure temperature, and the most common in use today are Celsius, Fahrenheit. 3. English scientist Sir Isaac Newton invented the Newton Scale in 1780. 4. Newton’s temperature scale fixed the degrees by defining the two points of melting snow and boiling water as 0 and 43 respectively. 5. Fahrenheit invented the scale currently used for non-scientific temperature measurement in France. UNIT 5 ENGLISH SYSTEM OF UNITS TEXT A I Read and remember the words and their translation: 1. to emanate – походити 2. to expand – розширятися 3. avoirdupois – евердьюпойс (Англійська система вимірювання ваги для всіх товарів, крім благородних металів, дорогоцінних каменів та ліків) 4. ounce (oz) – унція (28,3 г) 5. ton – тонна 6. short ton – мала тонна (907,2 кг) 7. dram – драхма 8. long ton – велика тонна (1016,06кг) 9. precious metals – дорогоцінні метали 10.pennyweight – пеннівейт,міра ваги (1,555 г) 11. grain – гран (0,0648г) 12. scruple – скрупул(міра ваги, яка застосовувалася в аптекарській діяльності) 13. fraction – частина 14. bushel – бушель, міра ємкості (36,3 л) 15. gallon – галон,міра рідких та сипучих тіл 16.English gallon – англійський галон (4,54 л) 17. American gallon – американський галон (3.78 л) 18. quart – кварта, (одиниця виміру рідини, 1/4галона) 19. peck – пек, міра сипучих тіл (1/4бушеля) 20. cu in – (cubic inch)-кубічний дюйм (16,39 см3) 21. survey – огляд 22. drawback – недолік 23. complexity – тяжкість 24. to convert – конвертувати 25. apothecary – аптека 26. customary system – звична система
II Read and translate the following text:
ENGLISH SYSTEM OF UNITS The English System has its roots in the Roman system, which used as a base the number twelve. Also from the Romans emanated the names of certain English metrical units such as the inch. The English System developed progressively, and in 19th century the English metrical system was established in various parts of the world, including America. At the heart of the English system of Units is a short list of base units: Units of Weight The pound (lb) is the basic unit of weight which is proportional to mass. Within the English units of measurement there are three different systems of weights. In the avoirdupois system, the most widely used of the three, the pound is divided into 16 ounces and the ounce into 16 drams. The ton, used to measure large masses, is equal to 2,000 lb. The troy system is used only for precious metals. The troy pound is divided into 12 ounces and the troy ounce into 20 pennyweights or 480 grains. The troy pound is thus 5,760 grains. The grain is also a unit in the avoirdupois system, 1 avoirdupois pound being 7,000 grains, so that the troy pound is 5,760/7,000 of an avoirdupois pound. Apothecaries' weights are based on troy weights. Units of Length and Area The basic unit of length is the yard. Fractions of the yard are the inch and the foot and commonly used multiples are the rod, the furlong and the mile. The acre, equal to 4,840 square yards or 160 square rods, is used for measuring land area. Units of Liquid Measure For liquid measure or liquid capacity the basic unit is the gallon. Gallon is divided into 4 quarts, 8 pints, or 32 gills. The U.S. gallon, or wine gallon, is 231 cubic inches. The British imperial gallon is the volume of 10 lb of pure water at 62°F and is equal to 277.42 cu in. The British units of liquid capacity are thus about 20% larger than the corresponding American units. Units of Dry Measure For dry measure or dry capacity, the basic unit is the bushel. Bushel is divided into 4 pecks, 32 dry quarts, or 64 dry pints. The U.S. bushel is 2,150.42 cu in. and is about 3% smaller than the British imperial bushel with a similar difference existing between the U.S. and British subdivisions. The barrel is a unit for measuring the capacity of larger quantities and has various legal definitions depending on the quantity being measured. TEXT B
I Read and remember: 1. Vitruvian Man – Вітрувіанський чоловік 2. world-renown – всесвітньо відомий 3. to depict – зображувати 4. correlation – взаємовідношення 5. ink – чорнило 6. to superimpose – накладати(одне на одне) 7. to inscribe – вписувати 8. treatise – трактат 9. to accompany – супроводжувати 10. width – ширина II Read text and define the main idea of it: VITRUVIAN MAN
According to Leonardo's notes in the accompanying text, it was made as a study of the proportions of the human body as described in Vitruvius: · a palm is the width of four fingers; · a foot is the width of four palms; · a cubit is the width of six palms; · a pace is four cubits; · a man's height is four cubits (and thus 24 palms); · the length of a man's outspread arms (arm span) is equal to his height; · the distance from the hairline to the bottom of the chin is one-tenth of a man's height; · the distance from the top of the head to the bottom of the chin is one-eighth of a man's height; · the distance from the bottom of the neck to the hairline is one-sixth of a man's height; · the maximum width of the shoulders is a quarter of a man's height; · the distance from the middle of the chest to the top of the head is a quarter of a man's height; · the distance from the elbow to the tip of the hand is a quarter of a man's height; · the distance from the elbow to the armpit is one-eighth of a man's height; · the length of the hand is one-tenth of a man's height; · the distance from the bottom of the chin to the nose is one-third of the length of the head; · the distance from the hairline to the eyebrows is one-third of the length of the face; · the length of the ear is one-third of the length of the face; · the length of a man's foot; TEXT C I Mind the following words and word - combinations: 1. to rub – терти 2. fur – хутро 3. current – потік 4. insulator – ізолятор II Listen to the text” WHO DISCOVERED THE ELECTRICITY? “and decide if the statements are true (T) or false (F): 1. The history of electricity goes back more than four thousand years. 2. By the 17th century, many electricity-related discoveries had been made, such as the invention of an early electrostatic generator. 3. In 1700, English physician William Gilbert coined the term electric. 4. English scientist Michael Faraday created the electric dynamo, a crude precursor of modern power generators. 5. In 1900, Italian physicist Alessandro Volta constructed the voltaic pile, later known as the electric battery. UNIT 6 TEXT A I Read and remember the words and their translation: 1. observers – експерти, спостерігачі 2. guidelines – рекомендації 3. elaboration – розвиток 4. credibility – правдоподібність, можливість 5. liaison – зв’язок 6. appropriate – підходящий 7. implementation – виконання, реалізація 8. simultaneously – одночасно 9. contradictory – суперечливий
II Read and translate the following text:
TEXT B
I Read and remember: 1. National Metrology Institutes (NMI) – Національний Метрологічний Інститут 2. to designate – визначати 3. backbone – основа 4. distributed – розгалужений II Read text and define the main idea of it:
BIPM and CIPM Recognising the need to work towards internationally agreed measurement standards, in 1875 governments from 17 countries worldwide signed the treaty and agreed to create and finance a permanent, scientific institute, the International Bureau of Weights and Measures as the centre for coordination of world measurement. The central coordination role for worldwide metrology is undertaken by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures with individual countries represented by National Metrology Institutes. The International Committee of Weights and Measures was established to oversee the International Bureau of Weights and Measures. Today there are 51 Member States of the Metre Convention. 23 Associate States take part in the General Conference of Weights and Measures. TEXT C I Mind the following words and word - combinations: 1. membership – членство 2. establishment – організація 3. Subcommittees – підкомітети 4. requirements – вимоги 5. intergovernmental – міжурядовий 6. authority – влада 7. guidance – управління 8. to accept – прийняти II Listen to the text” WHAT IS OIML? “ and decide if the statements are true (T) or false (F): 1. The International Organization of Legal Metrology is an intergovernmental treaty organization whose membership includes member States, countries which participate actively in technical activities. 2. The International Organization of Legal Metrology was established in 1965. 3. The International Organization of Legal Metrology was established in order to promote the global harmonization of legal metrology procedures. 4. Legal metrology comprises all activities for which legal requirements are prescribed on measurement, units of measurement, measuring instruments and methods of measurement. 5. The OIML is an observer in the WTO TBT Committee. UNIT 7
TEXT A I Read and remember the words and their translation: 1. developer – розробник 2. publisher – видавець 3. acronym – акронім (слово, яке формується з перших букв словосполучення, яке воно замінює) 4. non-governmental – недержавний 5. to mandate – надавати повноваження 6. friendliness – дружелюбність 7. reliability – надійність 8. efficiency – ефективність, результативність 9. unreliable – ненадійний 10. uniquely – однозначно 11. broad – широкий 12. absent – відсутній 13. incompatible – несумісний 14. to facilitate – сприяти 15. partnership – партнерство, співпраця 16. interchangeability – взаємозамінність
II Read and translate the following text: TEXT B
I Read and remember: 1. to disseminate – розповсюджувати 2. a broad choice – широкий вибір 3. to underpin – підтримувати 4. to diverge – відрізнятися, відхилятися 5. know-how – ноу-хау 6. to preserve – охороняти II Read text and define the main idea of it:
BENEFITS OF ISO STANDARDS For businesses, the widespread adoption of International Standards means that suppliers can develop and offer products and services meeting specifications that have wide international acceptance in their sectors. Therefore, businesses using International Standards can compete on many more markets around the world. For innovators of new technologies they speed up the dissemination of innovations and their development into manufacturable and marketable products. The worldwide compatibility of technology which is achieved when products and services are based on International Standards gives customers a broad choice of offers and insures quality, safety and reliability of products and services. They also benefit from the effects of competition among suppliers. The technological and scientific bases underpinning health, safety and environmental legislation are provided by ISO standards for the benefit of governments. They are also an important source of technological know-how. By defining the characteristics that products and services will be expected to meet on export markets, International Standards give developing countries a basis for making the right decisions when investing their resources and thus avoid squandering them. For trade officials, International Standards create “a level playing field” for all competitors on those markets. The existence of divergent national or regional standards can create technical barriers to trade. International Standards are the technical means by which political trade agreements can be put into practice. The International Standards contribute to the quality of life in general by ensuring that the transport, machinery and tools we use are safe and standards on air, water and soil quality, on emissions of gases and radiation and environmental aspects of products can contribute to efforts to preserve the environmen t. TEXT C I Mind the following words and word - combinations: 1. strength – сила 2. to maintain – підтримувати 3. eligible – підходящий II Listen to the text” WHO CAN JOIN ISO? “ and decide if the statements are true (T) or false (F): 1.Membership of ISO is open to national standards institutes most representative of standardization in their country, two members in each country. 2. Correspondent members pay reduced membership fees. 3. International organizations and associations, both non-governmental and representing industry sectors, can apply for liaison status to a technical committee. 4. Individuals may be selected by national member institutes. 5. Full members are known as member bodies. UNIT 8
GLOBAL COORDINATION OF METROLOGY AND THE CIPM
TEXT A I Read and remember the words and their translation: 1. reliability – надійність, достовірність 2. comparison – порівняння 3. to launch – починати, запускати 4. boundary – межа 5. peer-reviewed – рецензований людьми 6. calibration – маркування 7. signatory – сторона, що підписала документ 8. International Committee for Weights and Measures (CIPM) – Рада Міжнародного Управління 9. whilst – доки 10. coverage – сфера дії 11. uncertainties – коливання 12. signatory – сторона, що підписала документ 13. National Metrological Institute (NMI) – Національний Метрологічний Інститут 14. International Bureau of Weights and Measures – Міжнародне Бюро Вимірів і Ваги 15. General Conference of Weights and Measures – Загальна Конференція Вимірів і Ваги
II Read and translate the following text:
GLOBAL COORDINATION OF METROLOGY AND THE CIPM
The reliability of the international measurement system depends on work by each national metrology institute to base its measurements and measurement uncertainties on the International System, and to compare its realizations of the base units of the IS with those of other national metrology institutes. To establish such mutual equivalence, the National metrology institutes will regularly participate in measurement comparisons. In order to extend and fully document the practice of comparisons and to provide objective evidence on which to base declarations of equivalence, in 1999 the International Committee for Weights and Measures launched a Mutual Recognition Arrangement between National metrology institutes from Member States of the Meter Convention and Associate States and Economies of the General Conference of Weights and Measures. The CIPM MRA establishes a formal system within which National Metrological Institutes signatories and other designated institutes establish the degree of equivalence of their national measurement standards via a peer-review of their technical capabilities, as well as the mutual recognition of their calibration and measurement certificates. This degree of equivalence is technically supported through a series of “key” measurement comparisons which establish a basis for comparing and linking measurements across international boundaries. The CIPM MRA commits metrology to provide an essential support for global trade through a mutual recognition framework, which can help eliminate technical barriers to trade and regulatory affairs. To support the CIPM MRA the International Bureau of Weights and Measures key comparison database provides free public access to the results of key comparisons and the peer-reviewed, IS traceable, calibration and measurement capabilities, and the degrees of equivalence of participating laboratories in many areas of chemistry and physics. The launch of the CIPM MRA was a major step for the Meter Convention. As a result, metrology laboratories are now more confident of the technical basis for their calibration services, and their listing provides National metrology institutes with internationally recognized competence. It is already proving its value in the world of NMI metrology and a number of international and national organizations have already committed themselves to use it as evidence of technical equivalence at the highest levels, or for wider agreements negotiated for international trade, commerce or regulatory affairs. Whilst the technical coverage of the CIPM MRA is presently focused on physics, engineering and chemistry, the future will see related developments in the areas of laboratory medicine and food as the established framework can be applied to these new sectors. Already in laboratory medicine, the Joint Committee for Traceability in Laboratory Medicine (JCTLM) is creating a similar database of reference materials and processes. Key and other comparisons are underway to help provide the technical underpinning for this work. In this way, sound metrology practice will be applied to new activities, which contribute to human health and the quality of life.
III Answer the questions: 1. What does the reliability of the international measurement system depend on? 2. What was the reason of launching a Mutual Recognition Arrangement? 3. What does CIPM MRA establish? 4. What helps to eliminate technical barrier to trade and regulatory affairs? 5. What is the result of launching CIPM MRA? 6. What areas is CIPM MRA presently focused on? IV Complete the sentences: 1. To establish the mutual equivalence... 2. NMI signatories establish the degree.... 3….is supported through a series of.... 4….commits metrology to provide support for.... 5….was a major step for the Meter Convention. 6. The future will see related developments in areas of.... V Find the English equivalents to the words: Межа, внесення до списку, огляд, структура, достовірність, маркування, запускати, рецензувати, сторона, що підписала документ, безпечний для здоров’я, довкілля, глобальна координація, корекція вимірювань. VI Match the English words with their Ukrainian equivalents: 1. mutual a) сторона, що підписала документ 2. signatory b) кордон 3. equivalence c) внесення до списку 4. peer-review d) взаємний 5. framework e) огляд 6. listing f) реалізація 7. realization g) структура 8. boundary h) еквівалентність VII True or false statements: 1. NMI regularly participates in measurement comparison to establish mutual equivalence. 2. CIPM MRA was launched in 1990. 3. The equivalence of NMI signatories and other designed institutes is supported through measurement comparison. 4. The CIPM MRA will not help to eliminate technical barriers to trade. 5. Presently CIPM is focused on laboratory medicine and food areas.
VIII Translate into English: 1. Для встановлення взаємної еквівалентності Міжнародні Метрологічні Інститути щорічно здійснюють корекцію вимірювань. 2. Надійність міжнародної системи вимірювання залежить від роботи кожного Інституту Метрології. 3. Рада Міжнародного Управління здійснює підтримку міжнародної торгівлі. 4. Найвідомішим Інститутом Метрології в Україні є Держспоживстандарт. 5. Інститути Метрології розробляють стандарти, яким повинні відповідати всі товари та послуги. IX Make up sentences with the terms: International measurement, the International Committee of Weights and Measures, global trade, to establish, measurement certificates, National metrology institute. X Speak on the topic using the following words and word - combinations: Reliability, international measurement system, national metrology institute, to base realizations of the base units, national metrology institutes, to establish, mutual equivalence, comparisons, to extend, declarations of equivalence, Mutual Recognition Arrangement, the technical coverage, focused on, physics, engineering, chemistry, laboratory medicine, framework, to be applied, new sectors, to provide the technical underpinning, human health, the quality of life, CIPM, MRA, a formal system, the degree of equivalence, national measurement standards, recognition, measurement certificates, degree of equivalence. TEXT B
I Read and remember: 1. to endure – витримуват
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Последнее изменение этой страницы: 2016-12-28; просмотров: 177; Нарушение авторского права страницы; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! infopedia.su Все материалы представленные на сайте исключительно с целью ознакомления читателями и не преследуют коммерческих целей или нарушение авторских прав. Обратная связь - 18.222.110.231 (0.012 с.) |

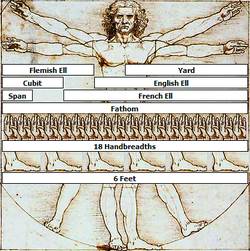 The Vitruvian Man is a world-renowned drawing created by Leonardo da Vinci in 1487. The drawing, which is in pen, and ink on paper, depicts a male figure in two superimposed positions with his arms and legs apart and simultaneously inscribed in a circle and square. The drawing and text are sometimes called the Canon of Proportions or, less often, Proportions of Man. It is stored in the Gallery de Academia in Venice. The drawing is based on the correlations of ideal human proportions with geometry described by the ancient Roman architect Vitruvius in Book III of his treatise “De Architectura”. Vitruvius described the human figure as being the principal source of proportion among the classical orders of architecture.
The Vitruvian Man is a world-renowned drawing created by Leonardo da Vinci in 1487. The drawing, which is in pen, and ink on paper, depicts a male figure in two superimposed positions with his arms and legs apart and simultaneously inscribed in a circle and square. The drawing and text are sometimes called the Canon of Proportions or, less often, Proportions of Man. It is stored in the Gallery de Academia in Venice. The drawing is based on the correlations of ideal human proportions with geometry described by the ancient Roman architect Vitruvius in Book III of his treatise “De Architectura”. Vitruvius described the human figure as being the principal source of proportion among the classical orders of architecture.



