Заглавная страница Избранные статьи Случайная статья Познавательные статьи Новые добавления Обратная связь КАТЕГОРИИ: ТОП 10 на сайте Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрацииТехника нижней прямой подачи мяча. Франко-прусская война (причины и последствия) Организация работы процедурного кабинета Смысловое и механическое запоминание, их место и роль в усвоении знаний Коммуникативные барьеры и пути их преодоления Обработка изделий медицинского назначения многократного применения Образцы текста публицистического стиля Четыре типа изменения баланса Задачи с ответами для Всероссийской олимпиады по праву 
Мы поможем в написании ваших работ! ЗНАЕТЕ ЛИ ВЫ?
Влияние общества на человека
Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрации Практические работы по географии для 6 класса Организация работы процедурного кабинета Изменения в неживой природе осенью Уборка процедурного кабинета Сольфеджио. Все правила по сольфеджио Балочные системы. Определение реакций опор и моментов защемления |
Type A and Type B signalling ⇐ ПредыдущаяСтр 2 из 2
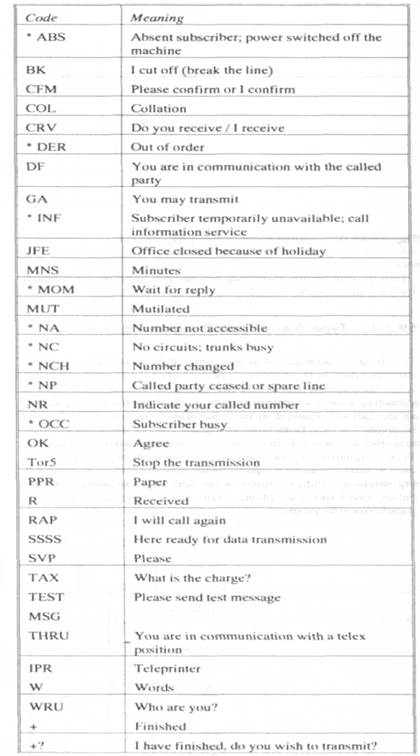
Two further subdivisions of the signalling systems have evolved, corresponding to the different types of national network employed. It has been agreed that, where two countries with different types of signalling system are trying to make connection, the country setting up the call will convert its outgoing signals to that of the country receiving the call. Both types of signals convey the same information, the difference is in the detail of implementation. In general Type A signalling has been used where the telex keyboard has been used lo send the address signals to the network and Type B signalling where the address signals were sent lo the network with dial pulses, much like a telephone. Figure 59.5 shows the sequence of signals in each system. Answerback CCITT recommendation F.60 specifies that every telex machine will have a unique answerback code made up of a one or two letter country code, telex line number and abbreviated subscriber's name. Sending a 'who are you' when connected through to the distant end will trigger the distant telex lo transmit the answerback aide embedded in the distant telex to the sending telex. This technique enables telex users to confirm that they have reached the correct distant party, before message transmission can begin, so protecting the confidentiality of the message. Telex protocol As telex signalling is machine to machine operation and the distant end may be unattended, then a protocol has been established. Several exist hut the ones given in Table 59.1 are generally internationally understood. All telex messages should commence with the sender's answerback so that the distant end can easily find the caller. The sequence of setting up a call on the telex network is seizing the line, receiving call confirmation and proceed to select indication from the telex network. The telex terminal then transmits the address information and if the call set up is successful the distant machine will automatically transmit to the caller the answerback code indicating it is ready to accept the message. If the call is unsuccessful for any reason the failure will be indicated by a service code of up to 3 letters transmitted from the telex network to the originating machine and printed out on the local record of the telex message. The telex network has facilities for testing the telex lines and can detect if a machine has its power disconnected or the line is out of order, and then send the corresponding service message from the network to the originating machine.
Figure 59.5 Type A and B signalling
Telex terminals Modern telex terminals are highly sophisticated pieces of equipment built around the principles of the personal computer. They comprise a microprocessor, disk drive, keyboard, VDU, and heavy duly printer with paper roll holder. These machines are still required to interwork with the older electromechanical machines, or paper tape transmitters or receivers, that exist on the telex networks. The modern telex terminal has in addition the ability to communicate with the telex network word processing software, to enable the telex operator to prepare messages, edit, store and finally transmit the messages. This makes the telex terminal a very powerful communication tool for business use.
Table59.l Telex protocol (indicates some of the typical service codes)
1. Learn the words & word combinations:
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Последнее изменение этой страницы: 2016-12-12; просмотров: 144; Нарушение авторского права страницы; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! infopedia.su Все материалы представленные на сайте исключительно с целью ознакомления читателями и не преследуют коммерческих целей или нарушение авторских прав. Обратная связь - 3.142.171.180 (0.005 с.) |