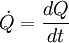Заглавная страница Избранные статьи Случайная статья Познавательные статьи Новые добавления Обратная связь FAQ Написать работу КАТЕГОРИИ: ТОП 10 на сайте Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрацииТехника нижней прямой подачи мяча. Франко-прусская война (причины и последствия) Организация работы процедурного кабинета Смысловое и механическое запоминание, их место и роль в усвоении знаний Коммуникативные барьеры и пути их преодоления Обработка изделий медицинского назначения многократного применения Образцы текста публицистического стиля Четыре типа изменения баланса Задачи с ответами для Всероссийской олимпиады по праву 
Мы поможем в написании ваших работ! ЗНАЕТЕ ЛИ ВЫ?
Влияние общества на человека
Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрации Практические работы по географии для 6 класса Организация работы процедурного кабинета Изменения в неживой природе осенью Уборка процедурного кабинета Сольфеджио. Все правила по сольфеджио Балочные системы. Определение реакций опор и моментов защемления |
Other heat transfer mechanismsСодержание книги
Поиск на нашем сайте · Latent heat: Transfer of heat through a physical change in the medium such as water-to-ice or water-to-steam involves significant energy and is exploited in many ways: steam engine, refrigerator etc. · Heat pipes: Using latent heat and capillary action to move heat, heat pipes can carry many times as much heat as a similar sized copper rod. Originally invented for use in satellites, they are starting to have applications in personal computers. Heat transfer rate or heat flow per unit time, is denoted by:
It is measured in watts. Heat flux is defined as rate of heat transfer per unit cross-sectional area, and is denoted q, resulting in units of watts per square metre, though slightly different notation conventions can be used.
ACTIVE VOCABULARY
heat transfer – теплообмен; теплоотдача; теплопередача equilibrium – равновесие, баланс to exchange – обменивать to equalize – делать равными; выравнивать; уравнивать interaction – взаимодействие internal energy – внутренняя энергия to tend – иметь тенденцию (к чему-л.); клониться, склоняться (к чему-л.) to occur – происходить, случаться, совершаться conduction – теплопроводность radiation – излучение, радиация a solid – твёрдое тело heat flux – тепловой поток electric current – электрический ток conductivity – проводимость; ratio – коэффициент; степень convection – конвекция
movement – движение (вообще или какой-л. вид); передвижение, перемещение fluid – текучая среда (жидкость, газ) to distinguish – различить gravity – сила тяжести buoyancy – плавучесть absence – недостаток, отсутствие to charge – заряжать emission – распространение surface – поверхность to emit – испускать, выделять to involve – привлекать, вовлекать втягивать, влечь за собой heat pipe – тепловая труба to carry – нести, переносить to denote – отмечать (знаком, меткой), обозначать to measure – измерять, мерить satellite – сателлит, спутник
X. Find the Russian for: fluid flow, rapidly moving atom, forced convection, a path function, buoyant convection, thermal equilibrium, heat transfer rate, electromagnetic radiation, phonon vibrations, net transfer of energy, the absence of work interaction, capillary action, electron fluid, convective heat transfer, conductive solid
XI. Find the English for: поток тепла, естественная конвекция, энергетический поток, выталкивающая сила, точечная функция, тепловое излучение, определение температуры воспламенения, заряженная частица, тепловой контакт, изменение физических свойств, фононный поток, тепловое равновесие, теплопроводность
XII. Translate the following sentences into Russian:
1) Heat flows between systems that are not in thermal equilibrium with each other. 2) When two bodies of different temperature come into thermal contact, they will exchange internal energy until their temperatures are equalized. 3) The term convective heat transfer is used to describe the combined effects of conduction and fluid flow. 4) In conduction hot, rapidly moving atoms and molecules interact with neighboring atoms and molecules, transferring some of their energy to these neighboring atoms. 5) The Peltier-Seebeck effect exhibits the propensity of electrons to conduct heat through an electrically conductive solid. 6) In convection, enthalpy transfer occurs by the movement of hot or cold portions of the fluid together with heat transfer by conduction. 7) Thermal radiation is a direct result of the movements of atoms and molecules in a material. 8) The movements of charged particles result in the emission of electromagnetic radiation, which carries energy away from the surface. 9) Using latent heat and capillary action to move heat, heat pipes can carry many times as much heat as a similar sized copper rod. 10) Heat flux is defined as rate of heat transfer per unit cross-sectional area, and is denoted q, resulting in units of watts per square metre.
XIII. Fill in the blanks with appropriate words:
1. Heat spontaneously flows from the areas of … temperature to areas of … temperature. 2. By the thermal contact two bodies reach thermal …. 3. Conduction is the most significant means of … in …. 4. In insulators the … is carried almost entirely by … vibrations. 5. Thermoelectricity is caused by the relationship between electrons, … and electrical …. 6. In free convection … and … forces drive the fluid movement. 7. … is the only means of heat transfer through a vacuum. 8. Heat pipes use … and … to move heat. 9. … is defined as rate of heat transfer per unit cross-sectional area. 10. Heat transfer rate is … in watts.
XIV. Translate into English, using the active vocabulary:
1. Два тела с разной температурой обмениваются внутренней энергией, пока их температуры не сравняются. 2. При отсутствии взаимодействия с другими тела теплота сохраняется в теле в виде внутренней энергии. 3. Существуют три механизма теплообмена: теплопроводность, излучение и конвекция. 4. Теплопроводность – это средство передачи тепла в твердых телах. 5. Тепло- и электропроводность большинства металлов имеет почти один и тот же коэффициент. 6. Конвекция – это преобладающая форма теплообмена в жидкостях и газах. 7. Различают два типа конвекции: естественная и вынужденная. 8. Излучение – это единственная форма теплопередачи, которая может происходить в отсутствии какой-либо среды. 9. Теплопередача посредством изменения физических свойств привлекает значительное количество энергии. 10. Интенсивность теплопередачи измеряется в ваттах.
XV. Answer the questions:
1. Where does heat flow? 2. When do two bodies exchange internal energy? 3. What is thermal equilibrium? 4. What are three mechanisms of heat transfer? 5. What is conduction? 6. When does conduction occur? 7. What is convection? 8. How does heat transfer occur in convection? 9. What types of convection do you know? 10. In which convection do gravity and buoyancy forces drive the fluid movement? 11. What form of heat transfer can occur in the vacuum? 12. What is thermal radiation? 13. What results in the emission of electromagnetic radiation? 14. What is heat transferred through in the medium such as water-to -ice? 15. What do heat pipes use to move heat?
XVI. Tell us about heat and heat transfer.
XV. a) Skim through the text and say in one sentence what the message of the text is. Answer the questions which follow. A related principle, Newton's law of cooling, states that the rate of heat loss of a body is proportional to the difference in temperatures between the body and its surroundings. The law is
Q = Heat transfer in Watts h = Heat transfer coefficient A = Surface area of the heat being transferred T 0 = Temperature of the object's surface Ta = Temperature of the surroundings This form of heat loss principle is sometimes not very precise; an accurate formulation may require analysis of heat flow, based on the (transient) heat transfer equation in a nonhomogeneous, or else poorly conductive, medium. The following simplification may be applied so long as it is permitted by the Biot number, which relates surface conductance to interior thermal conductivity in a body. If this ratio permits, it shows that the body has relatively high internal conductivity, such that (to good approximation) the entire body is at same uniform temperature as it is cooled from the outside, by the environment. If this is the case, then it is easy to derive from these conditions the behavior of exponential decay of temperature of a body. In such cases, the entire body is treated as lumped capacitance heat reservoir, with total heat content which is proportional to simple total heat capacity, and the temperature of the body. For example, simplified climate models may use Newtonian cooling instead of a full (and computationally expensive) radiation code to maintain atmospheric temperatures. * * * 1. What does Newton’s law of cooling state? 2. What does the Biot number relate? 3. Why is the form of heat loss principle sometimes not very precise?
b) Scan the text for details. Say what depends on the Biot number.
UNIT 8
|
||
|
Последнее изменение этой страницы: 2017-02-09; просмотров: 355; Нарушение авторского права страницы; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! infopedia.su Все материалы представленные на сайте исключительно с целью ознакомления читателями и не преследуют коммерческих целей или нарушение авторских прав. Обратная связь - 216.73.216.214 (0.009 с.) |