
Заглавная страница Избранные статьи Случайная статья Познавательные статьи Новые добавления Обратная связь КАТЕГОРИИ: ТОП 10 на сайте Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрацииТехника нижней прямой подачи мяча. Франко-прусская война (причины и последствия) Организация работы процедурного кабинета Смысловое и механическое запоминание, их место и роль в усвоении знаний Коммуникативные барьеры и пути их преодоления Обработка изделий медицинского назначения многократного применения Образцы текста публицистического стиля Четыре типа изменения баланса Задачи с ответами для Всероссийской олимпиады по праву 
Мы поможем в написании ваших работ! ЗНАЕТЕ ЛИ ВЫ?
Влияние общества на человека
Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрации Практические работы по географии для 6 класса Организация работы процедурного кабинета Изменения в неживой природе осенью Уборка процедурного кабинета Сольфеджио. Все правила по сольфеджио Балочные системы. Определение реакций опор и моментов защемления |
Огсэ. 03 иностранный язык (английский)Стр 1 из 12Следующая ⇒
ОГСЭ. 03 ИНОСТРАННЫЙ ЯЗЫК (АНГЛИЙСКИЙ)
УЧЕБНОЕ ПОСОБИЕ для обучающихся очной формы обучения специальности: 34.02.01 «Сестринское дело»
Тюмень, 2020
Вторушина Ю.А. Учебное пособие для студентов 1 курса очной формы обучения специальности 34.02.01 «Сестринское дело» по темам: «Знакомство», «Медицинское образование», «Анатомия человека» – Тюмень,2020. – 92 с. Рецензенты: Айзятова Г.Г., преподаватель ГАПОУ ТО «Тюменский колледж транспортных технологий и сервиса». Виношкина Т.В., преподаватель ГАПОУ ТО «Тюменский медицинский колледж».
Учебное пособие предназначено для обучающихся 1 курса очной формы обучения специальности 34.02.01 «Сестринское дело». Пособие содержит теоретический и практический материал по учебной дисциплине в полном соответствии с рабочей программой. Оно включает тексты по темам, грамматические минимумы, лексико-грамматические упражнения. Пояснительная записка Данное учебно-методическое пособие предназначено для студентов первого курса медицинского колледжа специальности «Сестринское дело». Задача данного пособия — научить студентов- медиков навыкам разговорной речи на основные бытовые темы, а также темы, связанные с профессиональной деятельностью в области медицины. Основной целью учебного пособия, в соответствии с новыми государственными образовательными стандартами и действующей рабочей программой по дисциплине, является формирование иноязычной коммуникативной компетенции специалиста-медика, позволяющей использовать иностранный язык как средство профессионального и межличностного общения. Структура и содержание пособия ориентированы на взаимосвязанное решение коммуникативных, познавательных, развивающих и воспитательных задач и формирование у студентов- медиков профессиональной иноязычной коммуникативной компетенции. Структурной единицей учебного пособия является тема, состоящая: — из текста, который включает основную смысловую информацию урока и предназначен для развития навыков устной речи; — комплекса послетекстовых упражнений, направленных на развитие навыков разговорной речи (составление монологического и диалогического высказывания по изучаемой теме, формирование умений выразить свое собственное отношение к обсуждаемой проблеме); — грамматических заданий по темам рабочей программы. В учебном пособии представлен также глоссарий в соответствии с изучаемыми темами.
Настоящее учебно-методическое пособие предназначено для обучения английскому языку студентов как под руководством преподавателя, так и для самостоятельной работы.
Медицинские профессии — что может быть важнее? Содержание
Визитная карточка (VISITING CARD) Темы (Topics) Задание 1. Прочитайте и переведите текст (Read and translate the text):
A visiting card, also known as a calling card, is a small paper card with one's name printed on it. They first appeared in China in the 15th century, and in Europe in the 17th century. The footmen of aristocrats and of royalty would deliver these first European visiting cards to the servants of their prospective hosts solemnly introducing the arrival of their owners. Visiting cards became an indispensable tool of etiquette, with sophisticated rules governing their use. The essential convention was that one person would not expect to see another person in her own home (unless invited or introduced) without first leaving his visiting card for the person at her home. Upon leaving the card, he would not expect to be admitted at first, but might receive a card at his own home in response. This would serve as a signal that a personal visit and meeting at home would not be unwelcome. On the other hand, if no card was forthcoming in return, or if a card were sent in an envelope, a personal visit was thereby discouraged. As an adoption from French and English etiquette, visiting cards became common amongst the aristocracy of Europe, and also in the United States. The whole procedure depended upon there being servants to open the door and receive the cards and it was, therefore, confined to the social classes which employed servants. Some visiting cards included refined engraved ornaments, embossed lettering, and fantastic coats of arms. However, the standard form visiting card in the 19th century in the United Kingdom was a plain card with nothing more than the bearer's name on it. Sometimes the name of a gentlemen's club might be added, but addresses were not otherwise included. Visiting cards were kept in highly decorated card cases. The visiting card is no longer the universal feature of upper middle class and upper class life that it once was in Europe and North America. Much more common is the business card, in which contact details, including address and telephone number, are essential. This has led to the inclusion of such details even on modern domestic visiting cards, a practice endorsed by modern books of etiquette, such as Debrett's New Etiquette. Задание 2. Ответьте на вопросы (Answer the questions): 1. What is the visiting card? 2. What is its origin? / Where did it come from? 3. When did it appear in Europe? 4. What were they used for? 5. How could the visiting cards be decorated? 6. What is the business card? Задание 3. Составьте свою визитную карточку (Make your own Visiting Card):
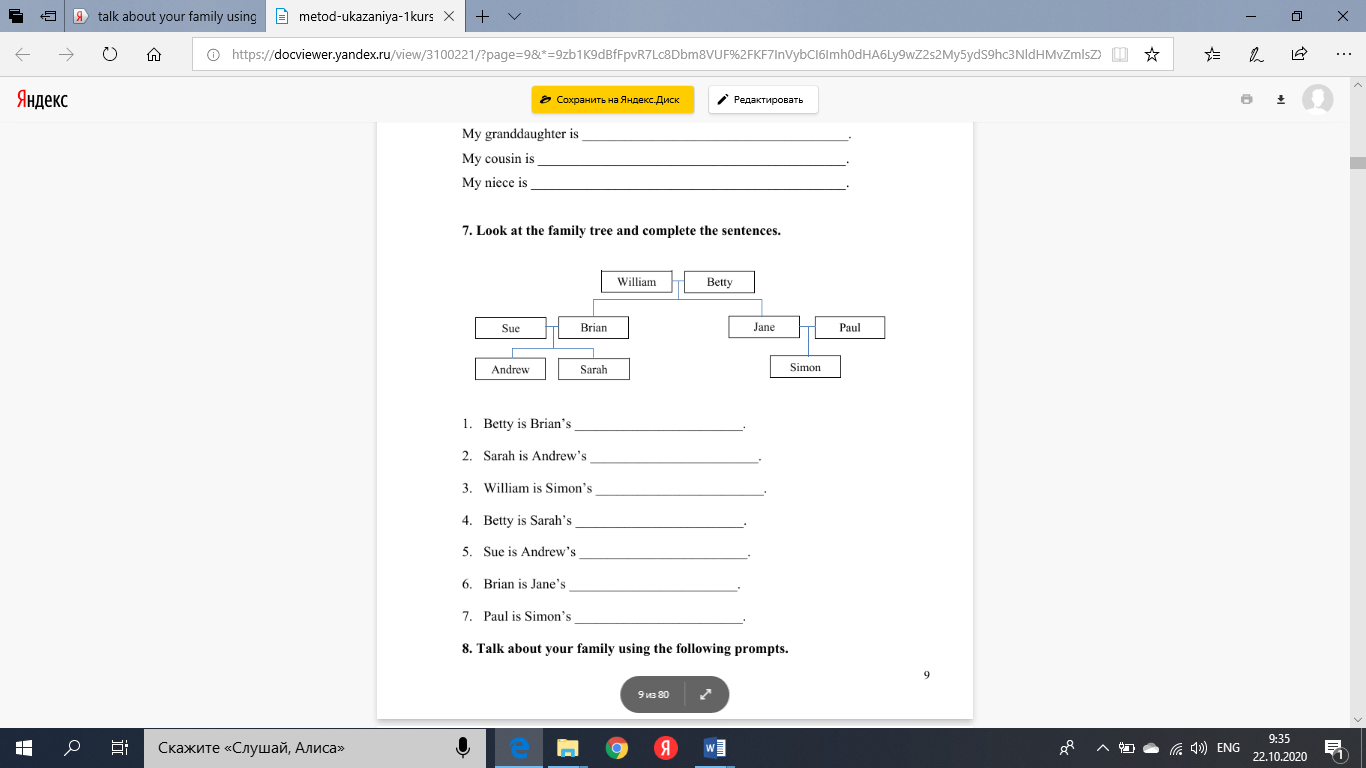
Моя семья (My Family) Задание 1. Прочитайте и переведите текст (Read and translate the text): My name is Danil. I am 16. I study at the Tyumen Medical College. It is my first year. Let me tell you about my family. I have got a big family. We are the Ivanovs. There are 4 members in my family. They are my mum, dad, brother and me. My mum’s name is Galina. She is 35. But she looks much younger. She is tall and slim. She is very attractive and charming. My mum is clever and kind. She is an accountant by profession. She works five days a week, from Monday to Friday. My Dad says she is as busy as a bee. She is always on the go. My mum is good at cooking and sawing. Every day she keeps the house and takes care of all of us. She washes the dishes, goes shopping and tidies up our flat. She likes singing. People say we look like two peas. My father’s name is Artem. My father is handsome and serious. He is a programmer. He works a lot. He works six days a week, from Monday to Saturday. He is a broad-shouldered, tall man with dark hair and blue eyes. My father is fond of playing computer games, reading books, and playing the guitar. My father always reads newspaper and watches news on TV in the evenings. At the weekends we sometimes play table-games together. Also, he helps me with my homework and my mum with housework. He is the best dad in the world! My brother is 11 years my younger. So he is 5 now. His name is Max. He looks like my dad. He is strong, clever and talented. He can swim and run. He likes watching cartoons on TV. Sometimes he is naughty. He enjoys breaking my old toy cars and drawing in my exercise-books. All in all we are a happy and friendly family. Задание 2. Посмотрите на генеалогическое древо и дополните предложения (Look at the family tree and complete the sentences): 1. 2. Sarah is Andrew’s ________________________. 3. William is Simon’s ________________________. 4. Betty is Sarah’s ________________________. 5. Sue is Andrew’s ________________________. 6. Brian is Jane’s ________________________. 7. Paul is Simon’s ________________________.
Задание 3. Расскажите о своей семье используя данные выражения (Talk about your family using the following prompts): My family is … (small/big). There are … (two/three/four) of us in the family: … We spend/ don’t spend a lot of time together. We go…, visit… My mum’s name is … She is a …(teacher). She works in/ at a… My dad’s name is… He is a… My brother(s)/sister(s) is (are)… We all have our duties about the house. I think our family is… Мой друг (My Friend) Задание 1. Прочитайте и переведите текст (Read and translate the text):
Friendship Friendship is a special relationship between people. People need this relationship because they expect help and comfort from each other. Those who have friends have less stress and maybe longer lives. Friendship is usually based on common interests and mutual understanding, true encouragement and sympathy. A friend is the one who has a tight relationship of trust with another person. Real friend can often make better an awful day and cheer you up because that is what friends exists for. A real friend is every time next to you, you can for sure count on his support and attention. You can have a lot of acquaintances, they come and go, but real friend is always there when you need a shoulder to cry on. Good friend is someone who helps you to see the truth even if it hurts, who keeps your secrets and shares things with you. People usually become friends when they have much in common, when they have much to tell each other, when they trust each other and rely on each other. If you feel depressed your friend will hang out with you to amuse you, to cheer you up and have a laugh with you. A good friend will not take offence at you if you disagree with him. I have a wide circle of friends who are on the same wavelength. I get on well with them because I respect their differences. It is good fun to be with them but my special friend is Alex. Alex is tall (well-built, pretty, handsome, plump, good-looking, slim) in his/her teens. Sasha has got an oval face with shoulder-length hair, greenish-blue eyes and full lips. Alex is an active and energetic person who enjoys running, dancing, swimming, playing sports games. He is also ambitious and works so hard at school to be successful in the future. All in all, Alex is very special to me as my best buddy is every time there when I need him/her. Задание 2. Переведите слова и выражения на английский язык (Translate into English): Нуждаться в помощи и поддержке, основываться на общих интересах и взаимопонимании, подбадривать, рассчитывать на поддержку и внимание, иметь много знакомых, хранить секреты, иметь много общего, доверять друг другу, проводить время, тусоваться, обижаться, большой круг друзей, на одной волне, амбиционный. Задание 3. Ответьте на вопросы (Answer the questions): 1. Why is it important to have the best friend? 2. Do you have a lot of friends? 3. What is the most important trait of character that your best friend has? 4. Describe your best friend. What things do you like to do together? Мое хобби (My Hobby) Задание 1. Прочитайте и переведите текст (Read and translate the text): Different people like doing different things. Different people have different hobbies. As for me, I am fond of reading. I have got many different books: fiction and historical novels. I have got many books about animals and birds. I have also books which can tell you about different countries and lands. I think many people can say that their hobby is reading. And I am sure it’s easy to explain why. We learn when we read books. My best friend, Tom, likes sport. He plays football from his childhood. Also he collects posters. His collection is thematic. The theme is his favourite football team. He keeps his posters on the wall. When you come into his room you can see them all there. My father collected coins when he was a boy. When he was in different countries he always brought home coins. Some people collect pictures, cups, toys, books and many other things. But collecting things is not the only hobby people have. Some people are fond of travelling or gardening. Many people are fond of sport or art and music. Задание 2. Ответьте н вопросы (Answer the questions): 1) What do you care for (увлекаешься)? Why do you like to do it? 2) Do you like to go to the cinema? What films do you prefer? 3) Can you draw very well? Did you attend an art school?
4) Can you sing or play some instruments? What kind of music do you listen to? 5) Can you dance very well? Do you like to go to discos in nightclubs? What kinds of dances do you like most of all? 6) Are you good at sports? How often do you work out? Задание 3. Составьте монологическое высказывание о своем хобби (Make up your own story about your hobby): Useful Phrases 1. To begin with… 2. Firstly, Secondary, Finally…. 3. Besides… 4. In any case… 5. As far as I know… 6. As for me… 7. I suppose… 8. From my point of view… 9. In conclusion… 10. To sum up… Грамматика (Grammar) 1.5. Глаголы to be/to have (Verbs to be/to have) Глагол to be Значения: 1) быть, существовать He is alive and happy. – Он (есть) жив и счастлив. 2) находиться Jake is in Tokyo now. – Джейк сейчас (находится) в Токио. 3) являться She is an outstanding artist. – Она (является, есть) выдающаяся художница. · am – форма первого лица единственного числа. Употребляется лишь в одном случае – с местоимением I. · is – форма третьего лица единственного числа. Используется вместе с местоимениями he, she, it, а также с любыми именами и предметами в единственном числе. · are – форма множественного числа настоящего времени. Употребляется с местоимениями you, we и they, а также с существительными во множественном числе. В настоящем простом времени эти формы выступают сказуемыми. Примеры: I am here just to help you. – Я здесь для того, чтобы помочь тебе. You are so kind and beautiful. – Ты так добра и красива. He is twenty two.- Ему двадцать два года. I have got a cat. It is red and fluffy. – У меня есть кошка. Она рыжая и пушистая. We are young, we are green. – Мы молоды и неопытны. You are still in the garden. – Вы все еще в саду. Вопросительная и отрицательная формы: В отрицательных предложениях частица “not” занимает место после to be. I am not a lazy bone. You (we, they) are not (aren’t) alone here. It (she, he) is not (isn’t) red, it is orange. В вопросительных предложениях подлежащее и глагол (в одной из 3 форм) меняются местами, на первое место выходит сама форма глагола, а подлежащее ставится за ним. Is he that very Olympic champion? Настоящее время (Present)
Прошедшее время (Past)
Будущее время (Future)
Упражнения (Exercises): Ex.1. Дополните предложения. Используйте am, is или are (C omplete the sentences. Use am, is or are .) My name (1) ______ Brenda Foster. I (2) ______ on the left in the picture. I (3) ______ ten years old and I (4) ______ in the fifth form. My birthday (5) _____ on the first of January. I (6) ______ from Santa Monica, California, USA. I (7) ______ American. My phone number (8) ______ 235-456-789. I live at 16 Park Street. My post code (9) ______ LA 30 SM. I’ve got a sister and a brother. Their names (10) ______ Gina and Paul. Gina (11) ______ 16 years old and Paul (12) ______ only three. I’ve also got a dog. His name (13) ______ Spot. He (14) ______ on the right in the picture. My Mum (15) ______ a doctor. She works at a hospital. My Dad (16) ______ a driver. He works in Los Angeles. We (17) ______ all friendly in our family. Ex.2. Дополните предложения (Write in is / isn’t, are / aren’t, am / ’m not.) 1. I __________ lazy. 2. My friend ___________ naughty. 3. My granny___________ kind.
4. My granddad ___________clever. 5. My teachers___________ funny. 6. I___________ a bad pupil. Ex.3. Дополните предложения (Write in was / were) 1. _______ your mum tired yesterday? 2. _______ you hungry yesterday evening? 3. _______ it cold yesterday? 4. _______ your teacher sad yesterday? 5. _______ your pet hungry yesterday? Ex.4. Дополните предложения формами глагола to be ( Fill in to be (Present Simple / Past simple / Future Simple) A. Hello! Му name ________ Alan. I________ thirteen. My friend’s name ________ David. He ________ thirteen, too. We ________ from Belarus. Last summer we ________ at the seaside. The weather ________ sunny. There________ many people on the beach. We had a good time. I hope next summer it ________ sunny and warm, too. There________ a lot of nice days. I ______ never ________ to other countries. Some day in future I ________ lucky to visit London and my holidays ________ great. B. 1. The animals ________ in danger. 2. There ________ only a few mountain gorillas in the world now. 3. It ________ the thirty-first today. 4. The wind ________ strong yesterday. 5. We________ at the end of Cliff Road when Alan fell down. 6. What ________ the weather like yesterday? 7. I hope your leg________ better soon. 8. ________ you________ at home tomorrow? 9. _______ you ever________ to London? 10. I ________ ill for a week. Глагол to have Основным значением слова является «иметь», «владеть», при переводе на русский язык чаще используют структуру «у (кого-то) есть». I have a delicious cake – у меня есть вкусный пирог. He has a new car – у него есть новая машина. Настоящее время (Present)
Прошедшее время (Past)
Будущее время (Future)
Упражнения (Exercises): Ex.1. Дополните предложения формами глагола have or has. (Fill in have or has).
Ex.2. Опишите своих одногруппников (Describe your groupmate. What does he/she have or not have?) Ex.3. Ответь на вопрос What will you have in your future? Темы (Topics) 2.1. Медицинский колледж (Medical College) Задание 1. Прочитайте и переведите текст (Read and translate the text): Medical College My name is Sveta Popova. I’m 17. I’m a student of the medical college. Our college is one of the oldest educational establishments of the region with its own traditions. Its graduates are considered to be the most highly trained specialists in the region. There are 7 departments in our college. I would like to tell you about them. “Nursing Affair” gives qualification of a nurse of general practice. A medical nurse is a chief assistant of a doctor. She provides uninterrupted medical health, including preventive and rehabilitation measures. Our graduates work at the polyclinics, hospitals, kindergartens, schools and houses for aged people. If you want to become a doctor assistant, you should study at the “Curative Affair” department. A doctor assistant of general practice is a highly-trained specialist who works independently in the policlinics, emergency ambulances and hospitals. His main task includes prescription and performance of preventive, curative and diagnostic measures. The graduates of this department are waited for at the stations of emergency medical help, in the country-side hospitals and in the military hospitals. “Obstetrician Affair” is another interesting department, it offers qualification of an obstetrician. An obstetrician provides preventive and curative medical help to the pregnant women and patients with gynaecological diseases. Boys and girls whose future profession is dentist study at the “Stomatology”. A dentist is a highly trained specialist who works independently or under the guidance of a senior doctor who provides preventive and curative medical help for the population. “Medical-prophylactic affair” gives qualification of a sanitary doctor assistant, who prevents appearance and spreading of infections and other kinds of the diseases. He controls the influence of the conditions of work and life on a person s health and takes some measures to prevent this harmful influence of the surroundings. They work in the centers of state sanitary inspectors and laboratories of different branches. A dental mechanic-while studying at the “Orthopedic stomatology” departments a future specialist learns to make artificial teeth and crowns, plastics and porcelain teeth. On graduating from the college they usually work in the denial mechanic laboratories. As for me 1 am a student of the “Pharmacy” department. My future profession is pharmaceutist. I’ll be provided the population with different medicines. My work will demand the knowledge of preventive rules, the rules of herb’s preparation and so on. The graduates of our department will be able to work in the chemist’s, pharmacological enterprises, laboratory. I like to study at our college very much. Задание 2. Ответьте на вопросы (Answer the questions): 1. Where does Sveta Popova study? 2. How many departments are there in the college? 3. What kind of qualification does the “Nursing affair” department give? 4. Who can work at the station of emergency medical help? 5. What does an obstertrician provide to the pregnant women and patients with gynaecological diseases? 6. Where do the sanitary doc tor assistants work? 7. What is Sveta’s future profession? Задание 3. Заполните таблицу (Fill in):
Задание 4. Расскажи о своем колледже (Tell about your college):
2.2. Рабочий день студента - медика (The Working Day of Medical Student) Задание 1. Прочитайте и переведите текст (Read and translate the text): I am very busy on my week-days. My week-days do not differ much one from another. On week-days my working day begins early in the morning. My school starts at 8 o’clock, so I have to get up at 7, to be ready in time. I never wake up myself, my mother always wakes me up. Sometimes I do my morning exercises, then I rush to the bathroom. I clean my teeth, wash my face. The cold water makes me feel not so sleepy. Then I go back to my room, make the bed. I switch on my radio, usually I listen to radio. I put on my clothes, comb my hair, put a little make-up. By that time my breakfast is ready (my mother cooks it for me). At a quarter to eight I grab my bag and rush to my school. My school starts at 8 o’clock and I don’t like to be late. Usually I have six or seven lessons a day, it lasts till 3 o’clock. After each lesson there is a break, so I can talk to my friends or eat my sandwich. When school is over I go home. First of all, I need to walk my dog. Then I have my dinner and a little rest. The teachers give us a lot of homework, so I start doing it about 16.30 or 17.00. As a rule, it takes me two or three hours to do my home assignments. My parents get home about six o’clock. We watch soap opera on TV, have supper together. We share all the news, I tell about the lessons and school. After it, I help my mother to do some work about the house — wash dishes, sweep the floor, clean the room. Twice a week in evenings I go play tennis. When I do not go to play tennis, I stay home and watch TV, listen to the music, read magazines. Sometimes my friends call me and we go for a walk. At eleven o’clock tired after a long working day I go to bed and fall asleep. Задание 2. Ответьте на вопросы (Answer the questions): 1. What time do you get up on your week-days? 2. Do you usually do your morning exercises? 3. Who cooks your breakfast? 4. What time do you leave your house to go to school? 5. How many lessons do you have a day? 6. Do you usually do your homework? 7. What do you do in the evening? 8. What time do you go to bed? Задание 3. Прочитайте текст «Мой рабочий день» (Read the text “ My week day ”): Many of you are either applying or thinking of applying to medical school — but what is it really like? I am a student. My dream has come true. A new life began. I guess it is not easy to study at the Medical College. Every day I have much work to do. My week-days don’t differ much one from another. My working day begins early. English people say: «Early to bed and early to rise makes a man healthy, wealthy and wise». I am not an early riser, but I have to get up at 7 a.m. At a quarter past 8 a.m. I leave the hostel for the college. I go to there on foot as it is not far from the hostel where I live. Many of our students live at home. They go to the college by bus or trolley bus. Our classes usually begin at 8.30 a.m. Every medical school has a different curriculum. A student goes to college for 4–8 hours of a traditional lecture-based format, and then comes home and studies. Medical school is difficult due to the large amount of material presented and tested in each course. The students have practical classes, lectures and seminars in numerous theoretical and special subjects. For most students, the hardest course, right at the beginning, appears to be Biochemistry taught in the first semester of the first year. Physiology, Pathology and Pharmacology are also very intense course. Like most of our students I attend all the lectures as they are delivered by qualified teachers, and are very interesting and important. We work much in class, at our laboratories and library to get deep knowledge. As the students want to become not ordinary but good specialists they must study not only their text-books but read special medical literature in Russian and foreign languages. So English, German and French are taught at our college. To know some foreign language is necessary for every person because its knowledge also helps to learn more about culture, science, life and other events abroad. The students carry out research work and then make reports at the conferences. My classes are over either at 2.40 or 4.10 p.m. Right after classes I go straight to the hostel. Sometimes I go to the library to take some books or articles necessary for my studies. Задание 4. Дополните предложения (Complete the sentences): 1. At a quarter past 8 a.m.... 2. They carry out research work … 3. Right after classes … 4. English people say … 5. As a rule we … 6. I am not an early riser but … 7. We work much in … 8. In the evening I … Задание 5. Ответьте на вопросы и расскажите одногруппникам о своем рабочем дне (Answer the questions and tell your groupmates about your working day): 1) What are you? 2) When does your working day begin? 3) Are you an early riser or a heavy sleeper? 4) When do you leave home for the college? 5) How do you get to the college? 6) Are you late for classes? 7) When do your classes usually begin? 8) Do you miss lectures? 9) What subjects are you studying in the 1st year? 10) When are your classes over? 11) Where do you go right after classes? Задание 1. Прочитайте и переведите текст (Read and translate the text): Before the 1850s nursing in England was classed with the lowest kind of work. Women who worked in public hospitals were regarded as rough, ignorant and dirty. Florence Nightingale was brought up in a wealthy family. In those days girls like her were expected to marry well and produce children. Florence’s parents were horrified when she told them that she wanted to become a professional nurse and she went abroad. She spent three months in Germany and a short time in Paris observing their methods. To gather information about hospital administration she devoted a lot of time writing to institutions in various European countries. In 1853 she took over the administration of a women’s hospital in London and reorganized it with great success. The following year England went to war with Russia. Florence Nightingale was asked to help and in the autumn of 1854 she sailed for the Crimea with a party of 38 other nurses. The hospital was a crumbling old building. Many were lying on the bloodstained floors because there were not enough beds. There was a shortage of everything including bandages, medicine, blankets, even soap and the wards were rat-infested-there was filth everywhere. Together with her team she set to work. Her nurses scrubbed the wards, corridors and lavatories. She reorganized the kitchens and set up a laundry. For months she worked up to twenty hours a day, ending each day by visiting the wounded soldiers, carrying a lamp in her hand. Queen Victoria offered her a reward for the work she had done. Instead Florence Nightingale asked people to give money to set up schools to train nurses. The money poured in. In 1860 a nursing school was opened in London and similar training schools were soon set up in other places. The student nurses were carefully chosen. They had to be literate, honest, hardworking and willing to live under strict discipline. Even their personal diaries were regularly inspected to see how they were behaving themselves. Florence Nightingale opened up a whole new field of work for women. By 1900 Britain had 64,000 skilled nurses, ensuring that their hospitals were efficient and hygienic. Florence Nightingale lived to the age of 90 and died in 1910. Задание 2. Выберете один верный ответ (Chose the right answer): 1) Florence Nightingale was: a) an English nurse; b) a Russian nurse; c) a French nurse; d) a Turkish nurse. 2) Florence was born in: a) autumn; b) winter; c) spring; d) summer. 3) Florence was called: a) the lady with the clock; b) the lady with the lamp; c) the lady with the flowers; d) the lady with the chair. 4) She studied the method of: a) jumping; b) nursing; c) teaching children; d) swimming. 5) She worked in: a) hospitals; b) shops; c) schools; d) offices. 6) In 1854 she worked in the hospital in London in … Street. a) Oxford Street; b) Fleet Street; c) Westminster; d) Harley 7) In 1854 Florence went to the Crimean War together with … nurses to help soldiers get better. a) 10; b) 100; c) 50; d) 38 8) In 1860 she opened a school for nurses at St. Thomas’ hospital in: a) Paris; b) London; c) Moscow; d) St. Petersburg. 9) Florence got the King’s red Crist in: a) 1883; b) 1903; c) 1803; d) 2013. 10) She was in Britain … woman to be awarded the Order of Merit in 1907. a) the first; b) the second; c) the third; d) the fourth 11) She died in … at the age of 90. a) 1920; b) 1910; c) 1935; d) 1905 2.4. Медицинское образование в Великобритании (Medical Education in Great Britain) Задание 1. Прочитайте и переведите текст (Read and translate the text). Задание 2. Найдите в тексте эквиваленты к словам и выражениям (Find in the text equivalents). Терапевты, факультет, семестр, посещают лекции; учебный год, оплачиваются, длительность, лаборатория, проходят практику, клинические предметы, начиная с 3-его курса, после сдачи государственных экзаменов, диссертация. Задание 3. Ответьте на вопросы (Answer the questions). 1. Where are doctors trained in G.B.? 2. What examinations is it necessary to pass? 3. Is education in G.B. charged? 4. How many terms has the academic year? 5. What subjects do the students study? 6. What degrees are given to students in G.B. after passing the finals? 2.5. Медицинское образование в России (Medical Education in Russia) Задание 1. Прочитайте и переведите текст (Read and translate the text). MEDICAL EDUCATION IN RUSSIA All establishments of higher medical education are financed and guided by the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation. Doctors of different specialties are trained at medical institutions of higher education, at medical universities and academies. There are also pharmaceutical academies, which train specialists in pharmacy. Medical institutions of higher education offer various faculties and specialties which an entrant may choose according to his or her abilities and wishes. Nowadays a new examination system is being introduced. The so-called «The General State Exam» allows pupils to enter any institution of higher education according to its results. Medical colleges train paramedical personnel: nurses, midwives, dental technicians and doctor’s assistants. The course of studies is 3-4 years. The training at medical institutions of higher education takes 5 or 6 years. It consists of lectures, practical classes and medical practice. The attendance of lectures, practical classes and seminars4 is compulsory. Academic year begins on September the 1st and is divided into two semesters of four months each. At the end of each semester the students have to pass examinations and tests. If a student passes the exams well he gets a grant paid monthly. paramedical personnel. For the first two years, students study pre-clinical subjects such as: Physics, Chemistry, Biology, Social Sciences, Latin and so on. They also study Human Anatomy, Physiology, Histology, and Microbiology. Clinical subjects are taught from the third to the fifth or sixth year. The students have practical course at therapeutic, surgical and other departments in hospitals and clinics. They master practical skills in clinical conditions. They are taught how to take and record the patient’s case history, to carry on medical examination of the patient, to make diagnosis, to prescribe treatment and carry on different medical procedures. There are all facilities for talented students to carry on research work. They attend scientific societies at different departments where they are offered modern guidelines for research activity. Having passed state examinations graduates receive their diplomas and can apply for clinical internship. The post graduate course and the Institute of Post-Diploma and Additional Education are for doctors, paramedical personnel. During three years the post-graduate students prepare a thesis, defend it and obtain the degree of Candidate of Medical Sciences. Задание 2. Переведите слова и выражения на русский язык (Find Russian equivalents). The Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation; an entrant may choose according to his or her abilities and wishes; paramedical personnel; master practical skills in clinical conditions; to carry on research work. Задание 3. Ответьте на вопросы (Answer the questions). 1 Who finances and guides the higher medical education in Russia? 2. Where are the doctors trained? 3. Where are the specialists in pharmacy trained? 4. Who may enter a medical institution of higher education? 6. Whom do the medical colleges train? 7. What is the course of training at the medical institution of higher education? 8. How many semesters has the academic year? 9. What subjects does the curriculum include? 10. Where do the students have medical practice? 11. What are the students taught during medical practice? 12. Where do the students carry on research work? 13. When do the graduates receive their diplomas? 14. Where can the doctors improve their qualification? 15. For what degree does the post-graduate student defend a thesis? Грамматика (Grammar) Нарицательные (Common) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Конкретные (материальные, относящиеся к какому-то классу...) Concrete | Абстрактные Abstract | Собирательные Collective | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| a book a disk a computer children friends cities wood iron water jam paper oil | success news progress advice freedom love friendship democracy | police people clothes glasses team jeans company Mass Media |
|
Собственные (Proper) | |
| Личные Personal | Географические Geographic |
| Peter Nikitin Mary Brown Kate the Stones | Moscow Russia London England Italy Rome |
| Исчисляемые | Неисчисляемые | |
| ед. ч. — мн. ч. ед. ч. | ед. ч. | |
| an idea — ideas a fish — fish a child — children an apple — apples a printer — printers | Material | Abstract |
| milk sugar glass bread iron | news weather money information knowledge | |
Упражнения (Exercises):
Ex.1. Какие существительные относятся к исчисляемым/неисчисляемым? (What nouns are countable/uncountable?):
An orange, a person, an album, butter, cakes, juice, children, chalk, a fish1, wood, a sheep, a ship, iron, love, a piece, a mouse, a deer, books, a toy, petrol, gold, silver, meat, a key, time, progress, cream, paper, a paper, yogurt, money, gas, chairs, a case, a star, water, fruit.
Ex.2. Используйте is/ are. (Use is/ are):
1. Big money...................... hard to hide.
2. There...................... big fish in this river.
3. Clothes...................... very important to her.
4. It...................... front-page news.
5. The traffic...................... bumper to bumper today.
6. His hair...................... getting thin, though he is only thirty. 7. There...................... a hair on your plate.
8. Your earrings...................... so beautiful!
9. This news...................... hard to believe.
10. The fish in this river...................... dying.
11. The scissors...................... on the table.
12. These sunglasses...................... so cool!
Исключения:
1. Существительные, обозначающие время и расстояние: today’s newspaper, a mile’s distance. Названия стран и городов: Germany’s industry, New York’s streets.
2. Названия газет и организаций: the Guardian’s article, Red Cross’s volunteers.
3. Слова nation, country, city, town: country’s treasures.
4. Слова ship, car, boat: ship’s name, car’s speed.
5. Слова nature, water, ocean: ocean’s temperature, nature’s beauty.
6. Названия месяцев и времени года: January’s frosts, summer’s days.
7. Названия планет: Saturn’s rings.
8. Некоторые устойчивые выражения: at death’s door, at arm’s length, a hair’s breadth, at a snail’s pace и другие.
Родительный падеж передается при помощи предлога of:
The beginning of the summer was cold. Начало (чего?) лета было холодным.
The behavior of this new breed of mice is rather unusual. Поведение (кого?) этой новой породы мышей довольно необычно.
Упражнения ( Exercises):
Ex.1. Используйте притяжательный падеж существительных в данных предложениях (Use the Possessive Case of nouns):
1. The advice of my parents. 2. The games of her sons. 3. The marks of her children. 4. A fax from Felix. 5. A novel by Akunin. 6. The life of students. 7. A school for boys. 8. A magazine for women. 9. A club for men. 10. The climate of England. 11. The surface of the moon. 12. The history of the world. 13. A holiday for two weeks. 14. The news of today. 15. The problems of the country.
Ex.2. Используйте окончания -’ s, - s ’, -’ (Use -’ s, - s ’, -’ ):
1. We met at Mr. Harris house. 2. I need Bess phone number. 3. My sister husband is a broker. 4. We’ll have a children party next week. 5. I’ll spend the weekend at my friends house. 6. They need a month time to finish the project. 7. This is a women shop. 8. She works in a girls school. 9. Columbus discovery of America was a historic event. 10. Do you remember Pythagoras Theorem? 11. “Alice Adventures in Wonderland” was written by Lewis Carroll. 12. From the radio came Elvis voice. 13. My brother is now reading “Gulliver Travels”. 14. It’s teenagers style. 15. I work at Mr. Phillips office. 16. My grandparents house is very old.
Темы (Topics)
Задание 1. Прочитайте и переведите текст (Read and translate the text):
The Human Body
There are three chief parts of the human body, the head, the trunk and the limbs or extremities. The skeleton of the body is composed of 223 bones of various size and shapes, which give firm but flexible support to the soft tissues, muscles and organs. The bony framework of the head, enclosing the brain and supporting the face, is the skull. The skeleton of the trunk mainly consists of the spinal column made of a series of bony rings. The trunk is divided into two large cavities by the diaphragm. The chest is the upper of these cavities, the belly or abdomen – the lower.
The upper cavity contains heart and lungs. In the lower cavity there is stomach, liver, gall-bladder, kidneys, bladder and the intestines. The lungs belong to the respiratory system. Kidneys and bladder are part of the urinary system. The heart, the arteries, veins constitute the cardiovascular system.
The upper extremity is divided into the shoulder, the upper arm, the forearm, and the hand. Each hand has four fingers and one thumb.
The parts of the lower extremity are the thigh (hip), the lower leg and the foot.
Задание 2. Найдите в тексте слова и выражения (Find in the text words and word expressions):
Содержать, основные части, конечности, состоять из, поддерживать, туловище, быть разделенным, полость, составлять.
Задание 3. Дополните предложения данными словами (Complete the sentences with the words from the list):
Задание 1. Прочитайте текст, выпишите незнакомые слова и переведите их (Read the text, write out unknown words from it, translate them):
The Parts of the Human Body
The body is wonderfully made, like a complex, perfect machine. Each part is specially constructed to carry out its own function, and to work as a whole with the other parts. The body has a strong frame work of bones called the skeleton. The skeleton is covered by muscles and other soft tissues, and by skin on the outside. The human body consists of three parts. They are the head, the trunk and the limbs.
The main part of the head is called the skull. The forehead, the temples, the cheeks, the cheekbones, the two jaws and the mouth compose the face. The teeth and the tongue are loading in the mouth. One chews food with the teeth and tastes food with the tongue. The lips are the two margins of the mouth. We see with the eyes, breathe and smell with the nose. The trunk consists of the spine, the chest and the pelvic bones. The trunk is divided into two large cavities by diaphragm. The upper cavity of the trunk is called thorax and lower one is called the belly. The lungs and the heart are located above the diaphragms in the upper cavity. In the lower cavity we find interior organs such as stomach, liver, urinary bladder, gallbladder kidneys, spleen and intestines.
The upper limb is divided into the shoulder, the upper arm, the forearm and the hand. The join between upper arm and forearm we call the elbow. The wrist is the joint between forearm and hand. Each hand has five fingers: index, middle finger, ring finger, little finger and a thumb.
The lower limb consists of the thigh-bone, the shin-bone and the fibula. We call the calf the back of the lower leg. The join between the femur and the lower leg is called the knee-joint. This joint is protected by the knee-cap. The joints between lower legs and feet are the ankles. The foot consists of heel, sole and toes.
Задание 2. Найдите в тексте эквиваленты (Find English equivalents):
Составляют лицо; располагаются во рту; работаться как одно целое; покрыт мускулами и мягкими тканями; жевать еду; состоять из трех частей; внутренние органы; верхние конечности; нижние конечности.
Задание 3. Найдите в тексте эквиваленты (Find Russian equivalents):
To carry out its own function; complex machine; the teeth and the tongue are loading in the mouth; strong frame work of bones; upper cavity; lower cavity; tastes food with the tongue; joint between forearm and hand.
Задание 4. Прочитайте текст, определите, верны / неверны данные предложения (Decide whether the following statements are true or false according to the text):
1. Each part of the body carries out its own function.
2. The skeleton is covered by muscles on the outside.
3. The face is composed by the forehead, the temples, the cheeks and two jaws.
4. The food is tested with the tongue.
5. The upper cavity of the trunk is called the belly.
6. The elbow is the joint between forearm and hand.
7. The foot consists of heel, sole and toes.
Задание 1. Прочитайте и переведите текст (Read and translate the text):
All internal organs are situated in the chest and abdomen. The chest is separated from the abdomen by the diaphragm. The principal organs of the chest are the gullet, the heart and the lungs. The gullet connects the pharynx and the stomach. There are two lungs - one in each half of the chest. They differ in size. The right lung is larger than the left one. There is the heart between the lungs behind the breastbone. The heart pumps the blood to the whole body.
 Betty is Brian’s ________________________.
Betty is Brian’s ________________________.


