Заглавная страница Избранные статьи Случайная статья Познавательные статьи Новые добавления Обратная связь КАТЕГОРИИ: ТОП 10 на сайте Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрацииТехника нижней прямой подачи мяча. Франко-прусская война (причины и последствия) Организация работы процедурного кабинета Смысловое и механическое запоминание, их место и роль в усвоении знаний Коммуникативные барьеры и пути их преодоления Обработка изделий медицинского назначения многократного применения Образцы текста публицистического стиля Четыре типа изменения баланса Задачи с ответами для Всероссийской олимпиады по праву 
Мы поможем в написании ваших работ! ЗНАЕТЕ ЛИ ВЫ?
Влияние общества на человека
Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрации Практические работы по географии для 6 класса Организация работы процедурного кабинета Изменения в неживой природе осенью Уборка процедурного кабинета Сольфеджио. Все правила по сольфеджио Балочные системы. Определение реакций опор и моментов защемления |
Materials for Sealing Pits and Fissures
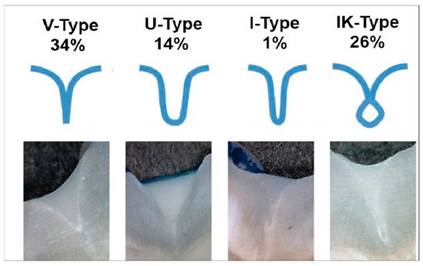
Thus, the advantages of sealing materials in the field of caries prophylaxis are undisputed. However, the material most suitable for the indication of pit and fissure sealing is still under question. Resin-based sealants and glass ionomer sealants are most commonly used as sealing materials [10]. Although resin-based sealants are composed of urethane dimethacrylate (UDMA) or Dent. J. 2018, 6, 18 3 of 8 bisphenol A-glycidyl mathacrylate (bis-GMA) monomers, glass ionomer sealants are composed of fluoroaluminosilicate glass powder and an aqueous-based polyacrylic acid solution [10,20]. The most prominent advantage of resin-based sealing materials is their good durability, while glass ionomer sealants show advantageous fluoride-releasing properties. The combination of the advantages of the two aforementioned materials was the aim of further materials. For example, compomers are resin-based materials with additional fluoride releasing properties, while resin-modified glass ionomers are glass ionomer sealants with additional resin components [10,40,41]. Older methods to protect against caries in the pits and fissure system include sealing with zinc phosphate cement, mechanical fissure eradication, prophylactic odontotomy, or chemical treatment with silver nitrate [10]. However, these methods are no longer routinely used thanks to the more convincing effects of sealing materials on the basis of resin or glass ionomer cement. However, resin-based sealants and glass ionomer sealants also have disadvantages when they are used as sealing materials. In terms of resin-based materials for sealing, one disadvantage includes polymerization shrinkage, potentially resulting in microleakage, which allows saliva and bacteria to penetrate the occlusal barrier [42,43]. Furthermore, a stronger biofilm accumulation seems to occur on resin-based materials [15]. In cases when glass ionomer cements are used for sealing fissures and pits, fractures of the material can occur due to its reduced ability to withstand occlusal forces [10]. However, the most important issue when placing sealing materials is the capability of adhesion of the single material to the hard substance of the tooth. Sealing materials are only effective in preventing caries when they perfectly adhere to the tooth surface. Methods to improve the retention of the sealing material on the tooth surface are, inter alia, a thorough cleaning of the occlusal surface with, for example, hydrogen peroxide, pumice, as well as air abrasion and pretreatment with acid [44]. With regard to the retention and long-term success of the sealing materials, numerous studies exist which compare different materials. A Cochrane review from 2013 also considered the effectiveness of different sealing materials. However, its authors did not come to a definite conclusion regarding the reduction of caries due to the use of a particular material for sealing pits and fissures [10,20]. Albeit, the results of various studies have shown that a reduced caries frequency is associated with an improved retention. Another Cochrane review from 2017 also stated that comparisons between glass ionomer to resin sealants remained inconclusive [45]. However, there is a clear advantage of resin-based sealing versus fluoridation, whereas no difference could be found between glass ionomer sealing and fluoridation [16]. This could be seen as an indirect suggestion for favoring resin-based sealing materials. Nevertheless, if it is impossible to isolate the teeth, for example, in the case of incompliant patients, children, or teeth in eruption, glass ionomer sealing materials should be preferred [46]. Nevertheless, a positive correlation between the good retention of the sealing material and the occurrence of caries seems to be undeniable. Critical for the successful retention of the sealing material is a successful penetration of the material into the pits and fissures. Interestingly, effective penetration of a resin-based sealing material is independent of the specific material used. However, the morphology of the fissures significantly influences the penetration of the sealing material [47]. Although “Y”-shaped fissures presented a low penetration of the sealing materials, a “U” or “V” shape allowed for good penetration of the sealant [47]. Differences of the fissure morphologies are visualized in Figure 1. Long-term success of the resin-based materials might also be influenced by the use of a bonding system [10,48,49] and various pretreatment strategies such as laser irradiation [50], air abrasion of the tooth surface [51], or preheating of the sealing material [52]. Dent. J. 2018, 6, 18
Figure 1. Different shapes of fissures.
|
||||
|
Последнее изменение этой страницы: 2020-12-19; просмотров: 76; Нарушение авторского права страницы; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! infopedia.su Все материалы представленные на сайте исключительно с целью ознакомления читателями и не преследуют коммерческих целей или нарушение авторских прав. Обратная связь - 3.145.93.136 (0.003 с.) |