Заглавная страница Избранные статьи Случайная статья Познавательные статьи Новые добавления Обратная связь КАТЕГОРИИ: ТОП 10 на сайте Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрацииТехника нижней прямой подачи мяча. Франко-прусская война (причины и последствия) Организация работы процедурного кабинета Смысловое и механическое запоминание, их место и роль в усвоении знаний Коммуникативные барьеры и пути их преодоления Обработка изделий медицинского назначения многократного применения Образцы текста публицистического стиля Четыре типа изменения баланса Задачи с ответами для Всероссийской олимпиады по праву 
Мы поможем в написании ваших работ! ЗНАЕТЕ ЛИ ВЫ?
Влияние общества на человека
Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрации Практические работы по географии для 6 класса Организация работы процедурного кабинета Изменения в неживой природе осенью Уборка процедурного кабинета Сольфеджио. Все правила по сольфеджио Балочные системы. Определение реакций опор и моментов защемления |
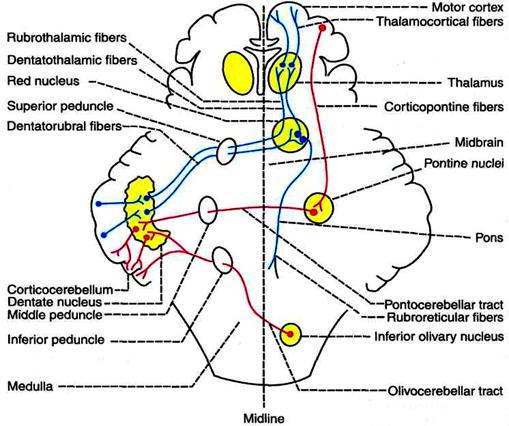
CORTICOCEREBELLUM (NEOCEREBELLUM)
Corticocerebellum is largest part of cerebellum. Because of its connection with cerebral cortex, it is called corticocerebellum or cerebrocerebellum. It is phylogenetically newer part of cerebellum. So, it is also called neocerebellum. It is concerned with planning, programming and coordination of skilled movements.
COMPONENTS OF CORTICOCEREBELLUM Corticocerebellum includes the lateral portions of cerebellar hemispheres.
Fig.28. Connections of corticocerebellum.
FUNCTIONS OF CORTICOCEREBELLUM Corticocerebellum is concerned with the integration and regulation of well coordinated muscular activities. The lesion in corticocerebellum leads to disturbances in movements. Corticocerebellum takes part in the integration and regulation of coordinated activities because of its afferent-efferent connection with cerebral cortex called the cerebro-cerebello-cerebral circuit. Apart from its connections with cerebral cortex, cerebellum also receives nerve fibers from proprioceptors in muscle. Thus, cerebellum receives feedback signals from the muscles during muscular activity. MECHANISM OF ACTION OF CORTICOCEREBELLUM Damping Action All the voluntary muscular activities are initiated by motor areas of cerebral cortex. Simultaneously, corticocerebellum receives impulses from motor cortex as well as feedback signals from the muscles as soon as the muscular activity starts. Corticocerebellum in turn sends impulses to cerebral cortex to discharge appropriate signals to the muscles so that, any extra or exaggeration of muscular activity is prevented and the movements become smooth and accurate. This action of corticocerebellum is called damping action. Control of Ballistic Movements The rapid alternate movements, which take place in different parts of the body while doing any skilled or trained work like typing, cycling, dancing, etc. are called ballistic movements. Corticocerebellum plays an important role in preplanning these movements during learning process. Timing and Programming the Movements While using a typewriter or while doing any other fast skilled work, a chain of movements occur rapidly in a sequential manner. During the learning processes of these skilled works, corticocerebellum plays an important role. The corticocerebellum plans the various sequential movements. It also plans the time duration of each movement and the time interval between movements. All the information from corticocerebellum are communicated to sensory motor area of cerebral cortex and stored in the form of memory. So, after the learning process is over, these activities are executed easily and smoothly in sequential manner. Servomechanism Once the skilled works are learnt, the sequential movements are executed without any interruption. Cerebellum lets the cerebral cortex to discharge the signals, which are already programmed and stored at sensory motor cortex, and, does not interfere much. However, if there is any disturbance or interference, the corticocerebellum immediately influences the cortex and corrects the movements. This action of corticocerebellum is known as servomechanism. Comparator Function The integration and coordination of the various muscular activities are regulated by the comparator function of the corticocerebellum. As already mentioned, it receives the representation of cortical impulses which are sent to the muscles and the feedback proprioceptive impulses coming from the muscles. By receiving the messages from both ends, corticocerebellum compares the actual cortical commands for muscular activity and the movements taking place in the muscles. Now, it sends impulses to the motor cortex to correct or modify the cortical signals to muscles, so that the movements become accurate and precise. This function of corticocerebellum is known as comparator function. Simultaneously, it also receives impulses from tactile receptors, eye and ear. Such additional information facilitates the comparator function of corticocerebellum.
Functions of cerebellum
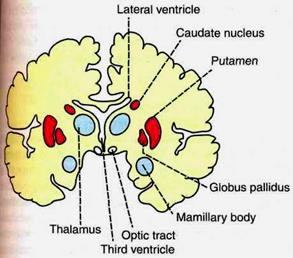
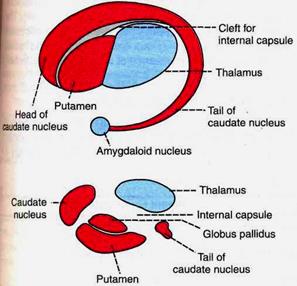
BASAL GANGLIA PHYSIOLOGY Basal ganglia are the scattered masses of gray matter submerged in subcortical substance of cerebral hemisphere. Basal ganglia form the part of extrapyramidal system, which is concerned with integration, and the regulation of motor activities. COMPONENTS 1) Corpus striatum 2) Substantia nigra and 3) Subthalamic nucleus of Luys. CORPUS STRIATUM It is a mass of gray matter situated at the base of cerebral hemispheres in close relation to the thalamus. The internal capsule incompletely divides the corpus striatum into two parts. 1. Caudate nucleus 2. Lenticular nucleus. 1. Caudate Nucleus This is an elongated arched gray mass, lying medial to internal capsule. Throughout its length, the caudate nucleus is related to lateral ventricle. Caudate nucleus has a head portion and a tail portion. The head is bulged into lateral ventricle and situated rostral to thalamus. The tail is long and arched. It extends along the dorsolateral surface of thalamus and ends in amygdaloid nucleus.
Fig.29. Basal ganglia.
Fig.30. Corpus striatum. 2. Lenticular Nucleus It is a wedge shaped gray mass, situated lateral to internal capsule. A vertical plate of white matter called the external medullary lamina, divides lenticular nucleus into two portions. a. The outer putamen and b. The inner globus pallidus Putamen and caudate nucleus are the phylogenetically newer parts of corpus striatum and these two parts are together called neostriatum or striatum. The globus pallidus is phylogenetically older part of corpus striatum. And, it is called pallidum or paleostriatum. The globus pallidus has two parts, an outer part and an inner part. SUBSTANTIA NIGRA This is situated below red nucleus. It is made up of small unpigmented and large pigmented cells. The pigments have high of quantity of iron. SUBTHALAMIC NUCLEUS OF LUYS This is situated lateral to red nucleus and dorsal to substantia nigra. BASAL GANGLIA CONNECTIONS The afferent and efferent connections of corpus striatum (Figs 29 and 30), substantia nigra and subthalamic nucleus of Luys are given in Table below In addition to afferent and efferent connections, the different components of corpus striatum of the same side are interconnected by intrinsic fibers. 1) Putamen to globus pallidus 2) Caudate nucleus to globus pallidus 3) Caudate nucleus to putamen The different components of corpus striatum in each side are connected to those of the opposite side by commissural fibers.
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Последнее изменение этой страницы: 2021-03-09; просмотров: 300; Нарушение авторского права страницы; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! infopedia.su Все материалы представленные на сайте исключительно с целью ознакомления читателями и не преследуют коммерческих целей или нарушение авторских прав. Обратная связь - 3.142.98.108 (0.008 с.) |