Заглавная страница Избранные статьи Случайная статья Познавательные статьи Новые добавления Обратная связь КАТЕГОРИИ: ТОП 10 на сайте Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрацииТехника нижней прямой подачи мяча. Франко-прусская война (причины и последствия) Организация работы процедурного кабинета Смысловое и механическое запоминание, их место и роль в усвоении знаний Коммуникативные барьеры и пути их преодоления Обработка изделий медицинского назначения многократного применения Образцы текста публицистического стиля Четыре типа изменения баланса Задачи с ответами для Всероссийской олимпиады по праву 
Мы поможем в написании ваших работ! ЗНАЕТЕ ЛИ ВЫ?
Влияние общества на человека
Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрации Практические работы по географии для 6 класса Организация работы процедурного кабинета Изменения в неживой природе осенью Уборка процедурного кабинета Сольфеджио. Все правила по сольфеджио Балочные системы. Определение реакций опор и моментов защемления |
The topic studied actuality. One can use potentials leads from body surface in clinical practice
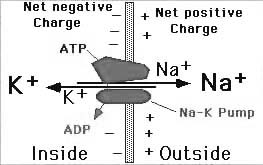
One can use potentials leads from body surface in clinical practice. The records received are called correspondingly to the potentials origin: electrocardiogram (ECG), electroencephalogram (EEG), electromyogram (MG) and so on. Tooth solid tissues electrical features determining is performed in dental practice for acute and chronic pulpitis diagnostics. This methodics is rather complicated. It requires measurements taking into account individual peculiarities of teeth morphological shape and geometric sizes as well as obligatory following the mot possible stimulus parameters. Nowadays one uses also possibility of oral mucosa biopotentials measurement for its functional state assessment. There was detected summary biopotentials age dynamics as well as their level change at parodontosis, oral mucosa diseases which is of important diagnostic value. Dentist can touch with potentials occurrence between similar metals (for instance, amalgame) of different content or between crowns made from the same metal if there is metal filling under them. Appearing microcurrents can be the reason of such a phenomenon named as galvanism. Sometimes pathological process is developed in years after denturing. It depends on the patient individual reactivity. Galvanism clinical symptoms are rather different. They can be divided into two big groups: subjective complaints which occur directly right after metallic fillings and crowns fixation in oral cavity. “Metallic taste” and some others belong to them. They are usually stopped in several days. Complaints which are appeared in prolonged time (sometimes in several years) belong to other group: metallic taste, pain. Oral mucosa inflammation can be developed: reddish color, tongue papillas swelling, erosions and ulcers appearance. 2. Study aims: To know: resting and action potentials physical and physiological characteristics, registrative methods, ionic mechanisms. To be able to: draw action and resting potentials developmental schemes during time; resting potential changings during membrane de-, re- and hyperpolarization as well as scheme of excitability changings during action potential development. 3. Pre-auditory self-work materials. 3.1.Basic knowledge, skills, experiences, necessary for study the topic:
3.2.Topic content. The muscle contracts when it is stimulated. Contraction of the muscle is a physical or mechanical event. In addition, various other changes occur in the muscle. The changes, which take place during muscular contraction are: 1.Electrical changes 2.Physical changes 3.Histological (molecular) changes 4.Chemical changes 5.Thermal changes Electrical changes during muscular contraction When the muscle is stimulated, electrical changes occur before onset of mechanical changes. Usually the electrical events in a muscle (or any living tissue) are measured by using a Cathode Ray Oscilloscope. Nowadays, sophisti cated electronic equipments like computerized polygraph are available to record and analyze the electrical activities of any tissue. RESTING MEMBRANE POTENTIAL The potential difference between inside and outside of the cell under resting condition is known as resting membrane potential.
Fig.2. Resting membrane potential.
When two electrodes are connected to a cathode ray oscilloscope through a suitable amplifier and placed over the surface of the muscle fiber, there is no potential difference. There is zero potential difference. But, if one of the electrodes is inserted into the interior of the muscle fiber, potential difference is observed across the sarcolemma (cell membrane). There is negativity inside the muscle fiber in relation to the outside. This potential difference is constant and is called resting membrane potential. The condition of the muscle during resting membrane potential is called polarized state. In human skeletal muscle, the resting membrane potential is -90 mV.
ACTION POTENTIAL When the muscle is stimulated, a series of changes occur in the membrane potential, which is called action potential. The action potential occurs in two phases. 1.Depolarization and 2.Repolarization. Depolarization When the impulse reaches the muscle, the polarized condition (-90 mV) is altered, i.e. the resting membrane potential is abolished. The interior of the muscle becomes positive and outside becomes negative. This condition is called depolarization. With other words, depolarisation is membrane potentials difference decreasing. Repolarization Within a short time, the muscle obtains the resting membrane potential once again. Interior of the muscle becomes negative and outside becomes positive. So, the polarized state of the muscle is re-established. This process is called repolarization. So, it is potentials difference restoration.
ACTION POTENTIAL CURVE Resting Membrane Potential The resting membrane potential is recorded as a straight baseline at -90 mV. Stimulus Artifact (local potential) When a stimulus is applied, there is a slight irregular deflection of baseline for a very short period. This is called stimulus artifact. Latent Period The stimulus artifact is followed by a short period without any change. This period is called latent period, which is about 0.5 to 1 millisecond.
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Последнее изменение этой страницы: 2021-03-09; просмотров: 63; Нарушение авторского права страницы; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! infopedia.su Все материалы представленные на сайте исключительно с целью ознакомления читателями и не преследуют коммерческих целей или нарушение авторских прав. Обратная связь - 3.145.17.20 (0.007 с.) |