Заглавная страница Избранные статьи Случайная статья Познавательные статьи Новые добавления Обратная связь КАТЕГОРИИ: ТОП 10 на сайте Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрацииТехника нижней прямой подачи мяча. Франко-прусская война (причины и последствия) Организация работы процедурного кабинета Смысловое и механическое запоминание, их место и роль в усвоении знаний Коммуникативные барьеры и пути их преодоления Обработка изделий медицинского назначения многократного применения Образцы текста публицистического стиля Четыре типа изменения баланса Задачи с ответами для Всероссийской олимпиады по праву 
Мы поможем в написании ваших работ! ЗНАЕТЕ ЛИ ВЫ?
Влияние общества на человека
Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрации Практические работы по географии для 6 класса Организация работы процедурного кабинета Изменения в неживой природе осенью Уборка процедурного кабинета Сольфеджио. Все правила по сольфеджио Балочные системы. Определение реакций опор и моментов защемления |
Selling vs Marketing ConceptСтр 1 из 5Следующая ⇒
Selling vs Marketing Concept Selling concept: v Output “Sold” to Consumers v Looks at Individual, Single Consumer v Seeks Sales Rather than Profit v Short-Term Goal Orientation v Concerned with Current Inventory Reduction v Narrower View of Consumer Needs v Little Adaptation to Environment v Informal Planning and Feedback Marketing concept v Consumer-Oriented v Stresses Research and Consumer Analysis v Looks at Groups of Consumers v Profit-Oriented v Directed to Long-Range Goals v Two-Way Interactive v Process v Appropriate Adaptation to Marketing Environment v Broad View of Consumer Needs v Integrated Planning and Feedback
Marketing business functions ⅓, ⅔, 3/3 Marketing business functions ⅓ • Environmental analysis and marketing research • monitoring and adapting to external factors that affect success or failure, such as the economy and competition; and collecting data to resolve specific marketing issues. • Broadening the Scope of Marketing • deciding on the emphasis to place, as well as the approach to take, on societal issues, global marketing, and the Web. • Consumer analysis: • examining and evaluating consumer characteristics, needs and purchase processes; and selecting the roup(s) of consumers at which to aim marketing efforts. Marketing business functions ⅔ • Product planning (including goods, services, organizations, people, places, ideas) • developing and maintaining products, product assortments, product images, brands, packaging, and optional features, and deleting faltering products • Distribution planning • forming logistical relationships with intermediaries, physical distribution, inventory management, warehousing, transportation, allocating goods and services, wholesaling, and retailing • Promotion planning • communicating with customers, the general public, and others through some type of advertising, public relations, personal selling, and/or sales promotion Marketing business functions 3/3 • Price planning • determining price levels and ranges, pricing techniques, terms of purchase, price adjustments, and the use of price as an active or passive factor • Marketing management • planning, implementing, and controlling the marketing program (strategy) and individual marketing functions; appraising the risks and benefits in decision making; and focusing on total quality Marketing mix
Ps marketing mix evolution Marketing Mix Four Ps → Modern Marketing Management Four Ps Produce, Place, Promotion, Price → People, Processes, Programs, Performance Current Marketing realities Three Major Market Forces: Technology, Globalization, Social Responsibility Two Key Market Outcomes: New Consumer Capabilities, New Company Capabilities Four Fundamental Pillars of Holistic Marketing: Relationship Marketing, Internal Marketing, Performance Marketing #2. Marketing environment GDP and macro-environment Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the market value of all final goods and services produced in a period (quarterly or yearly) of time.
Factors affecting organization in Macro environment are known as PESTEL, that is: Political, Economical, Social, Technological, Environmental and Legal. Business cycle Revival -> Prosperity -> Liquidation -> Depression (Возрождение ->Процветание ->Ликвидация ->Депрессия) Market trends 1. A-COMMERCE Here’s what comes after e-commerce and m-commerce. 2. ASSISTED DEVELOPMENT Post-demographic consumers are crafting new narratives of adulthood. 3. VIRTUAL COMPANIONS Virtual entities make the leap from assistants to companions. 4. FORGIVING BY DESIGN Post-purchase forgiveness is a must-have feature. 5. GLASS BOX WRECKING BALLS A revolution in transparency is just getting started Marketing environment Macroenvironment refers to the broad demographic, societal, economic, political, technological forces that an organization faces. Microenvironment refers to the forces close to an organization that have a direct impact on its ability to serve its customers. Internal environment refers to inner setting of the organization Uncontrollable factors
Controllable factors
Marketing directs
Marketing myopia · It is an ineffective marketing approach · It is a short sighted, narrow-minded view of marketing and its environment · Avoid Myopia by thoroughly studying and adapting to the environment #3. Marketing strategy Total quality approach Ø This is a process- and out-put related philosophy, striving to satisfy customers effectively Ø It always: seeks to satisfy customers Ø has a top management commitment Ø emphasizes continuous improvement Ø requires support from employees, suppliers, and distribution intermediaries Strategic marketing process 1. Organization mission determination 2. Setting marketing objectives 3. Situation analysis 4. Marketing strategy development 5. Tactical implementation planning 6. Monitoring results #1. Organization mission determination Defining the organizational mission refers to a long term commitment to a type of business and a place in the market. It “describes the scope of the firm and its dominant emphasis and values,” based on a firm’s history, current management preferences, resources, and distinctive competence, and on environmental factors.
#2. Setting marketing objectives Marketing objectives establish the firm’s goals for each SBU. Objectives are described in both quantitative terms (dollar sales, percentage profit growth, and market share), and qualitative terms (image, level of innovativeness, and industry leadership role). Without clearly identified objectives, firms often fail. #3. Situation analysis Analysis methods used for uncontrollable factors: PEST, PEESTLE, PESTEL etc. Both uncontrollable and controllable factors: SWOT, BCG, GE/Mckinsey, Ansoff Matrix, 5 Porter market forces, Value chain, GAP #3.1. PESTEL analysis
#3.2. SWOT analysis The theory seems simple enough, you use it to evaluate the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities and Threats that is involved in a marketing or business project. You will specify the objective for the project and then identify the internal and external factors that will have a positive as well as negative impact on the objective. Users of the SWOT analysis can therefore use the first two sections (Strengths and Weaknesses) to help them identify all of the internal factors. The last two sections (Opportunities and Threats) will be used to identify all the external factors.
#4. Market strategy development A marketing strategy outlines the way in which the marketing mix is used to attract and satisfy the target market. Strategic planning approaches are (examples): BCG, GE/Mckinsey, Ansoff Matrix, 5 Porter market forces, Value chain, GAP.
The Boston Consulting group’s product portfolio matrix (BCG matrix) is designed to help with long-term strategic planning, to help a business consider growth opportunities by reviewing its portfolio of products to decide where to invest, to discontinue or develop products. It is also known as the Growth/Share Matrix. The Matrix is divided into 4 quadrants derived on market growth and relative market share, as shown in the diagram below 1. Dogs: These are products with low growth or market share 2. Question marks or Problem Child: Products in high growth markets with low market share. 3. Stars: Products in high growth markets with high market share. 4. Cash cows: Products in low growth markets with high market share
#4.2. GE/McKinsey analysis
GE-McKinsey nine-box matrix is a strategy tool that offers a systematic approach for the multi business corporation to prioritize its investments among its business units. GE-McKinsey is a framework that evaluates business portfolio, provides further strategic implications and helps to prioritize the investment needed for each business unit (BU)
Ansoff’s Matrix shows four strategies used to grow. It also helps to analyze the risks associated with each one. The idea is that, each time you move into a new quadrant (horizontally or vertically), risk increases. Market penetration, in the lower left quadrant, is the safest of the four options. Here, you focus on expanding sales of your existing product in your existing market: you know the product works, and the market holds few surprises for you. Product development, in the lower right quadrant, is slightly more risky, because you're introducing a new product into your existing market. With market development, in the upper left quadrant, you're putting an existing product into an entirely new market. You can do this by finding a new use for the product, or by adding new features or benefits to it. Diversification, in the upper right quadrant, is the riskiest of the four options, because you're introducing a new, unproven product into an entirely new market that you may not fully understand #4.4. 5 Porter’s market forces This model helps marketers and business managers to look at the ‘balance of power’ in a market between different types of organizations, and to analyze the attractiveness and potential profitability of an industry sector. It is a strategic tool designed to give a global overview, rather than a detailed business analysis technique. It helps review
#4.5. Value chain
Value chain represents the internal activities a firm engages in when transforming inputs into outputs.
Gap analysis involves the comparison of actual performance with potential or desired performance. If an organization does not make the best use of current resources, or forgoes investment in capital or technology, it may produce or perform below its potential. This concept is similar to an economy's production being below the production possibilities frontier. Gap analysis identifies gaps between the optimized allocation and integration of the inputs (resources), and the current allocation-level. This may reveal areas that can be improved. Gap analysis involves determining, documenting, and approving the difference between business requirements and current capabilities. Gap analysis naturally flows from benchmarking and from other assessments. Once the general expectation of performance in an industry is understood, it is possible to compare that expectation with the company's current level of performance. This comparison becomes the gap analysis. Such analysis can be performed at the strategic or at the operational level of an organization.
Gap analysis is a formal study of what a business is doing currently and where it wants to go in the future. It can be conducted, in different perspectives, as follows: 1. Organization (e.g., Human Resources) 2. Business direction 3. Business processes 4. Information technology #5. tactical implementation planning A tactical plan specifies the short-run actions (tactics) that a firm undertakes in implementing a given marketing strategy. It has three basic elements: • specific tasks • time frame • resource allocation #6. monitoring results Monitoring results compares the actual performance of a firm, SBU, or product against the planned performance for a specified period. Successful companies often employ the following strategies to assure success: • continuous monitoring of performance • regular use of proper strategy adjustments • maintenance of a customer-oriented focus • stressing positive written and oral communication among employees and channel members #4. Marketing research Market research objects § demand analysis - consumer studies § competition - rivals analysis § performance analysis Market research data types 1. Secondary data: internal and external Internal: business plans, P&L statements, invoices, +other relevant internal paperwork External: open sources publications, WEB 2. Primary data: big data, survey, experiment, simulation, panel ↓ ↓ ↓ in person, telephone mechanical online Pros Inexpensive (almost free to obtain) Widely available Easy and quick to procure Credible sources Aids exploratory research Cons may be obsolete, goes obsolete quite quickly may lack suitability questionable methodologies undisclosed findings conflicting results reliability may not be proven reflects the viewpoint of the researcher, journalist #3. primary data collection Primary data relate to a specific marketing issue. Primary data are: § collected to solve specific problem at hand § § necessary when available secondary data may be insufficient § usually required for conclusive research #3.1. primary data pros.&cons Pros precise current known methodology exclusive domain reliable Cons high costs time consuming perspective may be limited corporate limitations Research design § who collects data? § what information: exploratory/ conclusive? § who or what to be studied? T § echnique to be used? (survey/ observation experiment/simulation) other considerations: cost factors? methodology? § time frame? § when & where? #4. data analysis and implications § questionnaire information is coded and numbered § response categories are labeled § tabulations calculate summary data for each response category § analysis is the evaluation of responses, usually by statistical techniques, pertaining to the question under investigation #4.1. data analysis methods in marketing § means comparison § Levene’s T-test § ANOVA § Mann-Whitney, Kolmogorov-Smirnov tests § regression analysis § taxonomy analysis § cluster § factor § discriminant § structural equation modelling (SEM) #5. Recommendations § firm's future actions are based on research findings § the report is written in language for the intended audience § they incorporate a rationale and findings § research reports should be kept in the data warehouse of a firm’s marketing intelligence network for future reference #5. Decision making § research reports represent feedback to marketing managers § these managers are responsible for utilizing findings to achieve short-term and long-term goals § implementation works best when marketing managers take part in research design, have broad control over marketing decisions, and have confidence that results are accurate
Big data research and analysis Big data analytics is the process of examining large and varied data sets -- i.e., big data -- to uncover hidden patterns, unknown correlations, market trends, customer preferences and other useful information that can help organizations make more-informed business decisions. Driven by specialized analytics systems and software, big data analytics can point the way to various business benefits, including new revenue opportunities, more effective marketing, better customer service, improved operational efficiency and competitive advantages over rivals. Big data analytics applications enable data scientists, predictive modelers, statisticians and other analytics professionals to analyze growing volumes of structured transaction data, plus other forms of data that are often left untapped by conventional business intelligence (BI) and analytics programs. That encompasses a mix of semi-structured and unstructured data -- for example, internet clickstream data, web server logs, social media content, text from customer emails and survey responses, mobile-phone calldetail records and machine data captured by sensors connected to the internet of things. #5. Developing a target market strategy § what is consumer segmentation § STP - segmentation, targeting, positioning § consumer segmentation criteria § targeting consumers
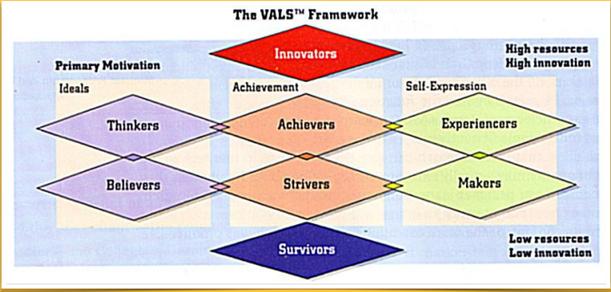
VALS framework
Targeting consumers Undifferentiated Marketing (Mass Marketing). The firm tries to reach a wide range of consumers with one basic marketing plan. These consumers are assumed to have a desire for similar goods and service attributes. One product for everybody. Concentrated Marketing. The firm concentrates on one group of consumers with a distinct set of needs and uses a tailor-made marketing plan to attract this single group. One product to one market niche. Differentiated Marketing (Multiple Segmentation). The firm aims at two or more different market segments, each of which has a distinct set of needs, and offers a tailor-made marketing plan for each segment. Two or more products to two or more groups. #6. marketing planning § organizational planning logic § critical planning elements § marketing planning process § audit in marketing planning Organizational planning logic:
Critical planning elements Well-integrated marketing plan = clear organizational mission, stability over time, coordination of marketing mix, compatible short and long plans, precisely defined target market, long-term competitive advantage Stability over time o a marketing plan must have a certain degree of stability over time to be implemented and evaluated properly o the plan should be consistent with the firm’s mission and guide the firm’s long-term efforts o the plan should be fine-tuned regularly and be consistent with the firm’s total quality approach Benchmarking Customer satisfaction ü customer satisfaction is the degree to which there is a match between a customer’s expectations of a good or service and its actual performance. It “is undoubtedly one of the top strategic issues in the new decade.” ü the largest ongoing research project is the American Customer Satisfaction Index (ACSI), a joint effort by the University of Michigan, the American Society for Quality Control, and CFI Group ü to compute ACSI, 50,000 consumers are surveyed annually regarding 200 companies and government agencies in 34 different industries. ü ACSI links customer expectations, perceived quality, and perceived value to customer satisfaction Marketing audit a marketing audit is a systematic critical impartial review and appraisal of the basic goals and policies of the marketing function, and of the organization, methods, procedures, and personnel employed to implement the policies and achieve the goals Marketing audit process 1.The audit is conducted by company specialists, company division or department managers, or outside specialists. 2. It may be done at the end of a calendar year, the of the annual reporting year, or when doing a physical inventory. 3. A horizontal audit studies the overall performance of a firm, emphasizing the interrelationship of variables. A vertical audit is an in-depth analysis of one aspect of a firm’s marketing strategy. 4. Audit forms list the topics to be examined and the exact information required to evaluate each topic. 5. Implementation decisions include: the timing and duration, employee awareness, when and how audit is performed, and how the audit report will be prepared. 6. Findings and recommendations are given to management. #7. integrated marketing communications promotion mix: ü Advertising ü Personal selling ü Sales Promotion ü Public Relations ü Direct Marketing Advertising advertising is paid, nonpersonal communication regarding goods, services, organizations, people, places, and ideas that is transmitted through various media by business firms, government and other nonprofit organizations, and individuals who are identified in the advertising message as the sponsor. The message is generally controlled by the sponsor.
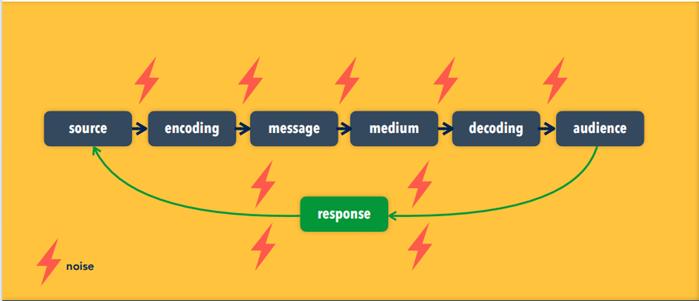
PR public relations includes any communication to foster a favorable image for goods, services, organizations, people, places, and ideas among their publics. It may be nonpersonal, personal, paid or non-paid, and sponsor controlled or not controlled. publicity is the form of public relations that entails nonpersonal communication passed on via various media but not paid for by an identified sponsor. personal selling personal selling involves oral communication with one or more prospective buyers by paid representatives for the purpose of making sales in sophisticated B2B sales SPIN approach to selling proved to be quite an effective technique sales promotion Sales promotion involves paid marketing communication activities (other than advertising, publicity, or personal selling) intended to stimulate purchases and dealer effectiveness. Included are trade shows, premiums, incentives, giveaways, demonstrations, and other efforts direct marketing Direct marketing is a form of advertising where organizations communicate directly to customers through a variety of media including cell phone text messaging, email, websites, online adverts, database marketing, fliers, catalog distribution, promotional letters and targeted television, newspaper and magazine advertisements as well as outdoor advertising. Among practitioners, it is also known as direct response. The prevalence of direct marketing and the unwelcome nature of some communications has led to regulations and laws such as the CAN-SPAM Act, requiring that consumers in the United States be allowed to opt out. Communication channel
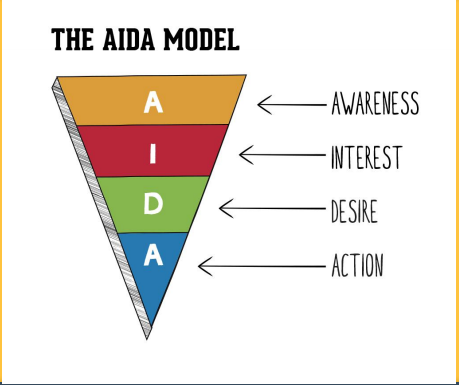
AIDA model
media planning and budgeting All-You-Can-Afford Method firm first allots funds for other elements of marketing, remaining marketing funds then go to the promotion budget Incremental Method a percentage is added to or subtracted from this year’s budget to determine next year’s Competitive Parity Method promotion budget is raised or lowered according to competitors’ actions. Percentage-of-Sales Method promotion budget is tied to sales revenue. Objective-and-Task Method firm sets promotion goals, determines the activities needed to satisfy them, and then establishes the proper budget. Selling vs Marketing Concept Selling concept: v Output “Sold” to Consumers v Looks at Individual, Single Consumer v Seeks Sales Rather than Profit v Short-Term Goal Orientation v Concerned with Current Inventory Reduction v Narrower View of Consumer Needs v Little Adaptation to Environment v Informal Planning and Feedback Marketing concept v Consumer-Oriented v Stresses Research and Consumer Analysis v Looks at Groups of Consumers v Profit-Oriented v Directed to Long-Range Goals v Two-Way Interactive v Process v Appropriate Adaptation to Marketing Environment v Broad View of Consumer Needs v Integrated Planning and Feedback
Marketing business functions ⅓, ⅔, 3/3 Marketing business functions ⅓ • Environmental analysis and marketing research • monitoring and adapting to external factors that affect success or failure, such as the economy and competition; and collecting data to resolve specific marketing issues. • Broadening the Scope of Marketing • deciding on the emphasis to place, as well as the approach to take, on societal issues, global marketing, and the Web. • Consumer analysis: • examining and evaluating consumer characteristics, needs and purchase processes; and selecting the roup(s) of consumers at which to aim marketing efforts. Marketing business functions ⅔ • Product planning (including goods, services, organizations, people, places, ideas) • developing and maintaining products, product assortments, product images, brands, packaging, and optional features, and deleting faltering products • Distribution planning • forming logistical relationships with intermediaries, physical distribution, inventory management, warehousing, transportation, allocating goods and services, wholesaling, and retailing • Promotion planning • communicating with customers, the general public, and others through some type of advertising, public relations, personal selling, and/or sales promotion Marketing business functions 3/3 • Price planning • determining price levels and ranges, pricing techniques, terms of purchase, price adjustments, and the use of price as an active or passive factor • Marketing management • planning, implementing, and controlling the marketing program (strategy) and individual marketing functions; appraising the risks and benefits in decision making; and focusing on total quality Marketing mix
Ps marketing mix evolution Marketing Mix Four Ps → Modern Marketing Management Four Ps Produce, Place, Promotion, Price → People, Processes, Programs, Performance Current Marketing realities Three Major Market Forces: Technology, Globalization, Social Responsibility Two Key Market Outcomes: New Consumer Capabilities, New Company Capabilities Four Fundamental Pillars of Holistic Marketing: Relationship Marketing, Internal Marketing, Performance Marketing #2. Marketing environment GDP and macro-environment Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the market value of all final goods and services produced in a period (quarterly or yearly) of time. Factors affecting organization in Macro environment are known as PESTEL, that is: Political, Economical, Social, Technological, Environmental and Legal. Business cycle Revival -> Prosperity -> Liquidation -> Depression (Возрождение ->Процветание ->Ликвидация ->Депрессия) Market trends 1. A-COMMERCE Here’s what comes after e-commerce and m-commerce. 2. ASSISTED DEVELOPMENT Post-demographic consumers are crafting new narratives of adulthood. 3. VIRTUAL COMPANIONS Virtual entities make the leap from assistants to companions. 4. FORGIVING BY DESIGN Post-purchase forgiveness is a must-have feature. 5. GLASS BOX WRECKING BALLS A revolution in transparency is just getting started Marketing environment Macroenvironment refers to the broad demographic, societal, economic, political, technological forces that an organization faces. Microenvironment refers to the forces close to an organization that have a direct impact on its ability to serve its customers. Internal environment refers to inner setting of the organization Uncontrollable factors
Controllable factors
Marketing directs
Marketing myopia · It is an ineffective marketing approach · It is a short sighted, narrow-minded view of marketing and its environment · Avoid Myopia by thoroughly studying and adapting to the environment #3. Marketing strategy
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Последнее изменение этой страницы: 2021-01-08; просмотров: 124; Нарушение авторского права страницы; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! infopedia.su Все материалы представленные на сайте исключительно с целью ознакомления читателями и не преследуют коммерческих целей или нарушение авторских прав. Обратная связь - 18.119.125.7 (0.291 с.) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
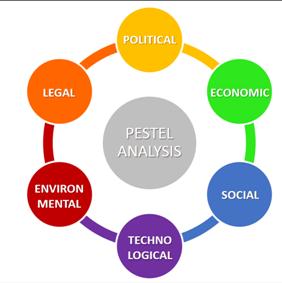 A PESTEL analysis is a framework or tool used by marketers to analyze and monitor the macroenvironmental (external marketing environment) factors that have an impact on an organization. The result of which is used to identify threats and weaknesses which is used in a SWOT analysis.
A PESTEL analysis is a framework or tool used by marketers to analyze and monitor the macroenvironmental (external marketing environment) factors that have an impact on an organization. The result of which is used to identify threats and weaknesses which is used in a SWOT analysis.
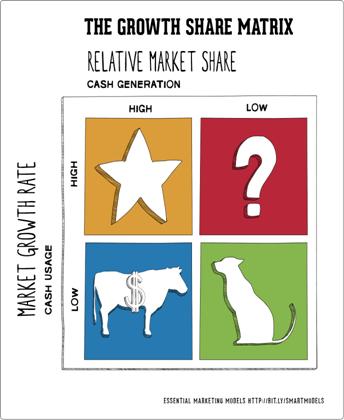 #4.1. Boston consulting group (BCG) analysis
#4.1. Boston consulting group (BCG) analysis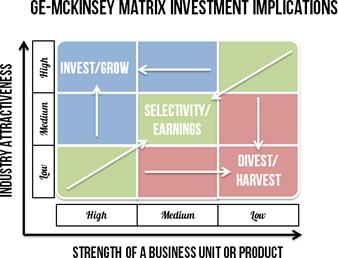
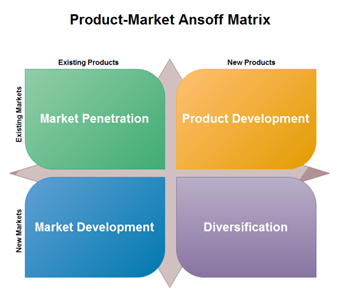 #4.3. Ansoff matrix analysis
#4.3. Ansoff matrix analysis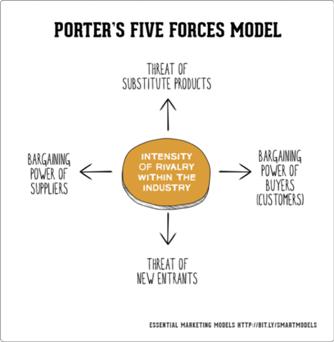
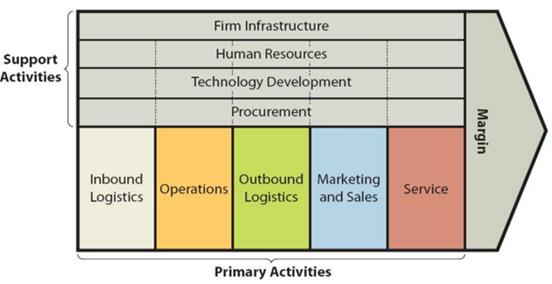 Value chain analysis (VCA) is a process where a firm identifies its primary and support activities that add value to its final product and then analyze these activities to reduce costs or increase differentiation.
Value chain analysis (VCA) is a process where a firm identifies its primary and support activities that add value to its final product and then analyze these activities to reduce costs or increase differentiation. #4.6. GAP analysis
#4.6. GAP analysis