Заглавная страница Избранные статьи Случайная статья Познавательные статьи Новые добавления Обратная связь КАТЕГОРИИ: ТОП 10 на сайте Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрацииТехника нижней прямой подачи мяча. Франко-прусская война (причины и последствия) Организация работы процедурного кабинета Смысловое и механическое запоминание, их место и роль в усвоении знаний Коммуникативные барьеры и пути их преодоления Обработка изделий медицинского назначения многократного применения Образцы текста публицистического стиля Четыре типа изменения баланса Задачи с ответами для Всероссийской олимпиады по праву 
Мы поможем в написании ваших работ! ЗНАЕТЕ ЛИ ВЫ?
Влияние общества на человека
Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрации Практические работы по географии для 6 класса Организация работы процедурного кабинета Изменения в неживой природе осенью Уборка процедурного кабинета Сольфеджио. Все правила по сольфеджио Балочные системы. Определение реакций опор и моментов защемления |
III. Answer the questions according to the text.
1. When and where was Lomonosov born? 2. Was he eager to study? Prove it. 3. Where did Lomonosov study? 4. Did Lomonosov study only in Russia? 5. What scientific degrees did Lomonosov receive? 6. What did he develop? 7. What was founded on the initiative of Lomonosov in 1755? 8. What age did he die at?
IV. Translate the sentences paying attention to the word "time". 1. For a long time people did not know that lightning find atmospheric electricity are one and the same thing. 2. These students work in the laboratory two times a week. 3. Lomonosov lectured at the University and at the same time worked in different fields of science. 4. Five times four is twenty. 5. We had a good time last summer. 6. One of the spheres is five times as large as the other one. V. Retell the text. TEST YOURSELF Подберите правильные переводы для слов левой колонки.
Упр.1 1. apply 1. добавлять 2. produce 2. применять 3. depend 3. увеличивать 4. require 4. приглашать 5. develop 5. зависеть 6. invent 6. развивать 7. add 7. требовать 8. производить 9. указывать 10. изобретать
Упр.2 1. transmit 1. измерять 2. transform 2. соединять 3. measure 3. передавать 4. observe 4. применять 5. solve 5. преобразовывать 6. improve 6. наблюдать 7. connect 7. получать 8. решать 9. улучшить 10. определять
Упр.3 1. production 1. прибор 2. improvement 2. улучшение 3. voltage 3. решение 4. appliance 4. свойство 5. solution 5. производство 6. science 6. развитие 7. condition 7. действие 8. условие 9. напряжение 10. наука
Упр.4 1. scientist 1. тепло 2. inventor 2. дуга 3. discovery 3. изобретатель 4. importance 4. свет 5. phenomenon 5. ученый 6. heat 6. сила 7. arc 7. явление 8. важность 9. время 10. открытие
Упр.5 1. wave 1. свет 2. pressure 2. тепло 3. engineering 3. применение 4. line 4. зависимость 5. connection 5. волна 6. development 6. давление 7. dependence 7. линия 8. соединение 9. техника
10. развитие
Упр.6 1. communication 1. передача 2. impossible 2. простой 3. difficult 3. наблюдение 4. important 4. полезный 5. various 5. различный 6. observation 6. связь 7. transmission 7. важный 8. невозможный 9. трудный 10. главный
Упр.7 1. в действительности 1. by means of 2. за последние годы 2. power grid 3. несмотря на 3. in addition to 4. кроме 4. obtain 5 благодаря 5. times 6. посредством 6. in spite of 7. раз 7. in fact 8. in recent years 9. thanks to 10. research
Упр.8 1. играть роль 1. electrical engineering 2. сделать вклад 2. equal 3. электротехника 3. power engineering 4. линия передачи 4. heat engineering 5. электростанция 5. play a part 6. энергетика 6 power plant 7. теплотехника 7. make continuation to 8. obtain 9. require 10. transmission line
9. Выберите правильный ответ:
M. V. Lomonosov P. N. Lebedev A. S. Popov
William Gilbert G.Galilei P.N.Yablochkov
A. G. Stoletov A. N. Lodygin K. Tsiolkovsky 1. Who did the study of electricity begin with? a) Galileo; b) Dr.Gilbert; c) Yablochkov. 2. Who created the principle of transformer? a) Lomonosov; b)Yablochkov. c) Lebedev. 3. What did Dr.Gilbert describe in his book about? a) experiments on static electricity; b) experiments on electricity and magnetism; c) experiments on electricity in motion; 4. Who discovered and measured the pressure of light? a) Tsiolkovsky; b) Lebedev; c) Lodygin. 5. Where did the first book on electricity publish? a) in Germany; b) in France; c) in Russia; 6. Who was the inventor of an electric lamp? a) Lomonosov; b) Lebedev; c) Lodygin 7. Who transmitted signals by means of electromagnetic waves? a) Stoletov; b) Popov; c) Lodygin 8. Where was first discovered the electric arc? a) in Germany; b) in Russia; c) in France;
9. Where was Yablochkov born? a) in Moscow; b) in St.Petersburg; c) in Saratov Province; 10. Who was the first scientist in the world who observed the electric arc? a) Petroff; b) Popov; c) Stoletov.
Упр.10. Определите по суффиксам, какие слова являются существительными, и укажите их номера. 1. transformer; 2. observe; 3. inventor; 4. industrial; 5. powerful: 6. scientist: 7. dependence; 8. requirement: 9. strong; 10. transmission Упр. 11. Определите по суффиксам, какие слова являются прилагательными. и укажите их номера.
1. various; 2. possibility; 3. centre; 4. active; 5. magnetic; 6, electrical; 7, peaceful; 8. activeness; 9. transmit; 10. transformation Упр. 12. Переведите предложения на русский язык, укажите грамматическое время.
1. We must use a transformer to change high voltage into lower one. 2. A motor changes electrical energy into mechanical energy. 3. The small electric power plant in Obninsk has become the symbol of peaceful atomon our globe. 4. The workers will have already repaired the engine before you come. 5. We can transmit electricity for long distances. 6. The appliances willbe working when you come. 7. In fact engineers are fulfilling major production tasks and solving problems of state and economic importance.
Упр. 13. Поставьте вопросы к подчеркнутым словам. 1. The students observed this phenomenon in the laboratory. 2. The students may take foreign magazines in the library. 3. The 750 kv a.c. line connects Kanakoyo and Moscow. 4. The students will make this experiment in the laboratory next week. 5. His friend has translated twoEnglish articles
UNIT II. MAGNETISM.
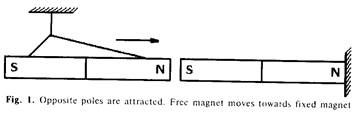
Lesson 1. Text. Kinds of magnets. Loadstone is classified as a natural magnet. It was discovered many centuries ago and one of the earliest practical uses made of the ore was in making compasses. Its use in the compass was known the world over by the time of Columbus. Artificial magnets may be made by rubbing a piece of steel with a piece of loadstone. The steel may be in the form of a straight bar, or it may be bent much like a horseshoe with the ends or poles a short distance apart. Any magnet has a much stronger field when the ends or poles are close together, thus reducing the air gap. Permanent magnets may be made by running an electric current through a coil of insulated wire wound around the piece of hard steel to be magnetized. Poles If a magnet is dipped into iron filings most of the filings will be attracted near the ends and only a few near the middle. Therefore, magnetism is stronger at the ends where it enters and leaves the magnet. These ends are called the poles of the magnet. If the bar magnet is hung by a string so that it swings freely with no other metal or magnet near, it will come to rest with one end pointing North and the other end pointing South. Such action is due to the influence of the earth's magnetism which is always on the earth surface. Thus one end of a bar magnet is usually marked "N" and the other is marked "S". In fact, these two poles are very different in action, the north pole of one magnet will attract the south pole of another but will repel the north pole. Let us suspend a bar magnet with marked poles, as in Fig. 1, by a string. Hold a second magnet a.s shown and observe the action. Notice, that the closer the magnets are together, the stronger the action. Remember then that: Like poles are repelled. Unlike poles are attracted.
|
||||||
|
Последнее изменение этой страницы: 2020-11-11; просмотров: 459; Нарушение авторского права страницы; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! infopedia.su Все материалы представленные на сайте исключительно с целью ознакомления читателями и не преследуют коммерческих целей или нарушение авторских прав. Обратная связь - 18.188.175.182 (0.017 с.) |