Заглавная страница Избранные статьи Случайная статья Познавательные статьи Новые добавления Обратная связь КАТЕГОРИИ: ТОП 10 на сайте Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрацииТехника нижней прямой подачи мяча. Франко-прусская война (причины и последствия) Организация работы процедурного кабинета Смысловое и механическое запоминание, их место и роль в усвоении знаний Коммуникативные барьеры и пути их преодоления Обработка изделий медицинского назначения многократного применения Образцы текста публицистического стиля Четыре типа изменения баланса Задачи с ответами для Всероссийской олимпиады по праву 
Мы поможем в написании ваших работ! ЗНАЕТЕ ЛИ ВЫ?
Влияние общества на человека
Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрации Практические работы по географии для 6 класса Организация работы процедурного кабинета Изменения в неживой природе осенью Уборка процедурного кабинета Сольфеджио. Все правила по сольфеджио Балочные системы. Определение реакций опор и моментов защемления |
По лингвострановедению Великобритании и СШАСтр 1 из 26Следующая ⇒
ГОСУДАРСТВЕННОЕ БЮДЖЕТНОЕ ОБРАЗОВАТЕЛЬНОЕ УЧРЕЖДЕНИЕ ВЫСШЕГО ПРОФЕССИОНАЛЬНОГО ОБРАЗОВАНИЯ «СТАВРОПОЛЬСКИЙ ГОСУДАРСТВЕННЫЙ МЕДИЦИНСКИЙ УНИВЕРСИТЕТ» МИНИСТЕРСТВА ЗДРАВООХРАНЕНИЯ РОССИЙСКОЙ ФЕДЕРАЦИИ Кафедра иностранных языков
ПРАКТИКУМ ПО ЛИНГВОСТРАНОВЕДЕНИЮ ВЕЛИКОБРИТАНИИ И США УЧЕБНОЕ ПОСОБИЕ ДЛЯ СТУДЕНТОВ ENGLISH
Ставрополь ГОСУДАРСТВЕННОЕ БЮДЖЕТНОЕ ОБРАЗОВАТЕЛЬНОЕ УЧРЕЖДЕНИЕ ВЫСШЕГО ПРОФЕССИОНАЛЬНОГО ОБРАЗОВАНИЯ «СТАВРОПОЛЬСКИЙ ГОСУДАРСТВЕННЫЙ МЕДИЦИНСКИЙ УНИВЕРСИТЕТ» МИНИСТЕРСТВА ЗДРАВООХРАНЕНИЯ РОССИЙСКОЙ ФЕДЕРАЦИИ Кафедра иностранных языков
ПРАКТИКУМ ПО ЛИНГВОСТРАНОВЕДЕНИЮ ВЕЛИКОБРИТАНИИ И США УЧЕБНОЕ ПОСОБИЕ ДЛЯ СТУДЕНТОВ
Ставрополь УДК 371.3:802.0(075.5) ББК 74.268.1:81.2 англ я73 ПРАКТИКУМ ПО ЛИНГВОСТРАНОВЕДЕНИЮ ВЕЛИКОБРИТАНИИ И США. Учебное пособие для студентов. – Ставрополь: Изд-во: СтГМУ. – 2016. – 106 с. Составители: Знаменская Стояна Васильевна, кандидат педагогических наук, доцент, заведующий кафедрой иностранных языков, декан факультета иностранных студентов ГБОУ ВПО «Ставропольский государственный медицинский университет». Агафонова Елена Сергеевна, кандидат педагогических наук, старший преподаватель кафедры иностранных языков ГБОУ ВПО «Ставропольский государственный медицинский университет». Науменко Валентина Анатольевна, старший преподаватель кафедры иностранных языков ГБОУ ВПО «Ставропольский государственный медицинский университет». Финенко Татьяна Николаевна, старший преподаватель кафедры иностранных языков ГБОУ ВПО «Ставропольский государственный медицинский университет».
Учебное пособие по лингвострановедению Великобритании и США предназначено для студентов СтГМУ, а также для всех, кто интересуется английским языком и страноведением англоязычных стран. Оно знакомит студентов с особенностями истории, образования, различными сторонами семейной и социокультурной жизни Великобритании и США. Учебное пособие составлено в соответствии с рабочими учебными программами по дисциплине и является дополнением к централизованным учебникам по английскому языку.
УДК 371.3:802.0(075.5)
ББК 74.268.1:81.2 англ я73 Рецензенты: Шибкова Оксана Сергеевна – доктор филологических наук, профессор, заведующий кафедрой иностранных языков естественнонаучных и экономических специальностей ФГАОУ ВПО «Северо-Кавказский федеральный университет» Министерства образования и науки Российской Федерации Маяцкая Наталья Константиновна, кандидат педагогических наук, доцент, заведующий кафедрой дефектологии и русского языка ГБОУ ВПО «Ставропольский государственный медицинский университет» Министерства здравоохранения Российской Федерации. Рекомендовано к печати редакционно-издательским советом Ставропольского государственного медицинского университета
Ó Ставропольский государственный медицинский университет, 2016 ПРЕДИСЛОВИЕ Целью данного учебного пособия является познакомить обучающихся с особенностями и отдельными сторонами социокультурной жизни таких англоязычных стран как Великобритания и США, включая наиболее важные факты и сведения о национальном характере, образе жизни, образовании и психологии населения этих стран. Практикум состоит из трех модулей: – Great Britain (Великобритания). – United States of America (Соединенные Штаты Америки). – Free Reading (Свободное чтение). Основу модулей и тем составляют тексты страноведческой и культурологической тематики. Каждый текст снабжен словарем и комментариями страноведческих реалий и терминов, включая перевод наиболее употребительных и важных слов и словосочетаний, представляющих трудность для понимания. Отдельные трудные для понимания слова и выражения, а также названия неизвестных обучающимся явлений и понятий, встречающихся в текстах, снабжены краткими объяснительными примечаниями. К каждой теме пособия предлагаются обзорные вопросы и задания для контроля усвоения изученного материала и развития навыков спонтанной, неподготовленной устной речи. Наряду с этим в большинстве разделов есть задания, направленные на анализ и комментарий отдельных высказываний юмористического характера с последующим написанием эссе на предложенные темы. Практикум может быть использован как на занятиях по английскому языку в аудитории, так и для самостоятельного изучения обучающимися, углубляющими знание британской и американской действительности в различных областях страноведения, включая культуру и образование.
По своей направленности и большому количеству фоновых сведений он может использоваться в качестве дополнительного материала при написании эссе, проведении семинаров и лекций по культурологии и страноведению Великобритании и США. В учебном пособии представлены фотографии, схемы и карты, иллюстрирующие различные области жизни стран, дающие наглядное представление о границах и мультикультурных традициях Великобритании и США, в зависимости от их географического положения и исторической судьбы.
Методические рекомендации по работе с учебным пособием Все темы пособия имеют определенную структуру. Порядок подачи материала каждой темы одинаков, задания четко сформулированы, что нацеливает и дает установку обучающимся на их выполнение. Рекомендуется следующая методика работы по каждой теме: – тщательная отработка произношения вокабуляра темы; – заучивание значения слов, словосочетаний темы и речевых клише; – отработка чтения основных текстов темы, их адекватный перевод на русский язык; – выполнение всех упражнений и заданий к теме в письменной и устной форме; – текст на свободное чтение дополняет лексически и тематически основной текст темы. Работа над ним проводится под руководством преподавателя на занятии; – ознакомление с заданиями в конце темы и их выполнение; – заключительным этапом работы по каждой теме является участие в беседе, составление монологов и диалогов в разнообразных ситуациях общения по заданной тематике с использованием дополнительных аудио и видео материалов. ЧАСТЬ I GREAT BRITAIN
PОPULATION OF GREAT BRITAIN Task 1. Learn the following words and expressions:
Population of Great Britain
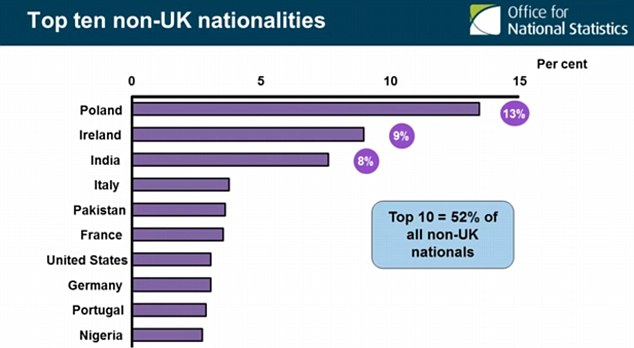
Great Britain is the fourth most populous country in Europe. People of English origin constitute about 50% of the nation's inhabitants. The Scots make up 8%, and there are smaller groups of Welsh (about 4.5%) and Irish (2.7%). Great Britain's population has shown increasing ethnic diversity since the 1970s, when people from the West Indies, India, Pakistan, Africa, and China began immigrating; in the 21st century these groups accounted for more than 10% of the population. There is also a significant number of Poles, who arrived after Poland joined the European Union. English is the universal language of Great Britain. In addition, about a quarter of the inhabitants of Wales speak Welsh and there are about 60,000 of the Scots, which speak Gaelic in Scotland.
The Church of England, also called the Anglican Church, is the officially established church in England (it was disestablished in Wales in 1914); the monarch is its supreme governor. The Presbyterian Church of Scotland is legally established in Scotland. There is complete religious freedom throughout Great Britain. By far the greatest number of Britons (some 27 million) is Anglicans, followed by Roman Catholics and other Christians. Muslims are the next biggest religious group and have grown in the last decade. There are also smaller minorities of Hindus, Jews, and Buddhists.
Who are the British people? Britain is somehow difficult country to understand. For tourists, British life, traditions and customs are weird. What is life like for ordinary people in Britain? How are things changing during the last decades? British people live in the UK. They are people who live in England, Scotland, Wales or Northern Ireland. British people can also be either the English, the Scots, the Welsh, or the Irish (from Northern Ireland only). The British are said to be reserved in manners, dress and speech. They are famous for their politeness, self-discipline and especially for their sense of humor. British people have a strong sense of humor, which sometimes can be hard for foreigners to understand. v -What is the longest word in the English language? – "Smiles". Because there is a mile between its first and last letters! v What's the definition of a pessimist? – A pessimist is a well-informed optimist. v Do you have any grandchildren? – No, all my children are just ordinary.
Britain is a country of mixed cultures. London has the largest non-white population of any European city and over 250 languages are spoken there. Therefore not all British people are White or Christians. Британцы Валлийцы
Ирландцы Шотландцы Elizabeth II
Despite the controversies and scandals surrounding her children and other members of the royal family, she remains a respected head of state. In 2015, Elizabeth celebrated 63 years on the throne and her 89th birthday. The Queen meets thousands of people each year in the UK and overseas. Before meeting Her Majesty, many people ask how they should behave. The simple answer is that there are no obligatory codes of behavior – just courtesy. Task 7. Learn the following words:
David Cameron David Cameron, in full David William Donald Cameron was born on October 9, 1966, London, England.
David Cameron married Samantha Sheffield in 1996. Their son Ivan was born in 2002 with cerebral palsy and epilepsy; Ivan died on 25 February 2009. They have three other children: Nancy (b. 2004), Arthur (b. 2006) and Florence (b. 2010). Тема 4. СИСТЕМА ОБРАЗОВАНИЯ В ВЕЛИКОБРИТАНИИ Education in Great Britain
Compulsory education begins at the age of 5 when children go to primary school. Primary education lasts for 6 years. It is divided into two periods: · infant schools (pupils from 5 to 7 years old) and · junior schools (pupils from 7 to 11 years old). In infant schools children don't have real classes. They mostly play and learn through playing. But when pupils are 7, real studying begins. They don't already play so much as they did it in infant school. Now they have real classes, when they sit at desks, read, write and answer the teacher's questions. Compulsory secondary education begins when children are 11 or 12 and lasts for 5 years. Secondary school is traditionally divided into 5 forms. Children study English, Mathematics, Science, History, Art, Geography, Music, a Foreign Language and have lessons of Physical training. Religious education is also provided. English, Mathematics and Science are called "core" subjects. At the age of 7, 11 and 14 pupils take examinations in the core subjects. There are 3 types of state secondary schools in Great Britain. They are: · · grammar schools**, which give secondary education of a very high standard. Entrance is based on the test of ability, usually at 11. Grammar schools are single sexed schools; · modern schools***, which don't prepare pupils for universities. Education in such schools gives good prospects for practical jobs. After five years of secondary education, at the age of 16, pupils take the General Certificate of Secondary Education (GCSE) examination. When they are in the third or in the fourth form, they begin to choose their exam subjects and prepare for them. After finishing the fifth form pupils can make their choice: they may either leave school and go to a Further Education College or continue their education in the sixth form. Those who stay at school after GCSE, study for 2 more years for "A" (Advanced) Level Exams in two or three subjects which is necessary to get a place at one of British universities. There are about 500 private schools in Great Britain. Most of these schools are boarding ones, where children live and study. Education in such schools is very expensive, that's why only 5 % of schoolchildren attend them. Private schools are also called preparatory (for children up to 13 years old) and public schools (for pupils from 13 to 18 years old). Any pupil can enter the best university of the country after leaving this school. The most famous British public schools are Eton, Harrow and Winchester. There is a considerable enthusiasm for post-school education in Britain. The aim of the government is to increase the number of students who enter into higher education. The driving force for this has been mainly economy. It is assumed that the more people who study at degree level, the more likely the country are to succeed economically. A large proportion of young people – about a third in England and Wales and almost half in Scotland – continue education at a more A-level beyond the age of 18. Nearly every university offers access and foundation courses before enrolment on a course of higher education of prospective students who do not have the standard entry qualifications.
Higher education in Britain is traditionally associated with universities, though education of University standard is also given in other institutions such as colleges and institutes of higher education, which have the power to award their own degrees. So after leaving secondary school young people can apply to a university, a polytechnic or a college of further education.
There are 126 universities in Britain. They are divided into some types: · The Old ones, which were founded before the 19th century, such as Oxford and Cambridge; · The Red Brick, which were founded in the 19th or 20th century; · The Plate Glass, which were founded in 1960s; · The Open University is the only university offering extramural education. The best universities, in view of "The Times" and "The Guardian", are the University of Oxford, the University of Cambridge, London School of Economics, London Imperial College, and London University College. Universities usually select students basing on their A-level results and an interview. After three years of study a university graduates get the Degree of a Bachelor of Arts, Science or Engineering. Many students then continue their studies for a Master's Degree and then a Doctor's Degree (PhD). ____________________________ * comprehensive schools – единая школа, которая охватывает наибольшее количество учеников. Учебные заведения данного типа предлагают образовательную программу, где можно получить как теоретические, так и практические навыки.
** grammar schools –грамматические школы, в которых акцентируется внимание на академической составляющей, то есть детей готовят к поступлению и дальнейшему обучению в вузах.
*** modern schools – cовременные школы − учебные заведения, которые дают практическую подготовку для того, чтобы в ускоренном режиме получить профессиональную квалификацию.
Task 3. Find the answers to these questions in the text: 1. When do British boys and girls begin to go to school? 2. What subjects do they study at school? 3. How long does the secondary education last? 4. What subjects are called "core" subjects? 5. At what age do children have their exams? 6. What's the difference between modern and grammar schools? 7. What are the private schools? 8. Would you like to study in Britain? Why? 9. Compare British and Russian education. 10. What types of British universities do you know?
Special Training
Special Training is subdivided into two parts: general professional and basic specialized. At the period of training and practice doctors work in the system of National Health. After full registration received, all practical doctors become qualified as SHO (senior house officer— senior medical grade with a full registration, taking specialized training.). Usually this title is awarded for a period of two or three years and is considered to be one of the stages of principal professional training. In this time training for examinations into various royal colleges is according to specialization. This is a natural requirement for getting higher stage of qualification, called specialist registrar (SpR) grade. Training programs corresponding to this grade are determined in accordance with qualification; such training may last from 4 to 6 years. At the time of specialized training all doctors are invited to take part in science programs to be familiar with methodologies of scientific research. Many of them acquire diplomas and degrees, but this is not a requirement condition for taking higher position.
Economy of Great Britain About 25% of Britain's land is arable, and almost half is suitable for meadows and pastures. Its agriculture is highly mechanized and extremely productive; about 2% of the labor force produces 60% percent of the country's food needs. Barley, wheat, rapeseed, potatoes, sugar beets, fruits, and vegetables are the main crops. The widespread dairy industry produces milk, eggs, and cheese. Beef cattle and large numbers of sheep, as well as poultry and pigs, are produced throughout much of the country. There is also a sizable fishing industry with cod, haddock, mackerel, whiting, trout, salmon and shellfish making up the bulk of the catch.
Within the manufacturing sector, the largest industries include machine tools and railroad equipment; ships; aircraft; motor vehicles and parts; electronic and communications equipment; metals; chemicals; coal; petroleum; paper and printing; food processing; textiles; and clothing. During the 1970s and 1980s, nearly 3.5 million manufacturing jobs were lost, but in the 1990s over 3.5 million jobs were created in service-related industries. By the early 21st cent., banking, insurance, business services, and other service industries accounted for almost three fourths of the gross domestic product and employed 80% of the workforce. This trend was also reflected in a shift in Great Britain's economic base, which has benefited the southeast, southwest, and Midlands regions of the country, while the north of England and Northern Ireland have been hard hit by the changing economy. The main industrial and commercial areas are the great conurbations, where about one third of the country's population lives. The administrative and financial center and most important part is Greater London*, which also has various manufacturing industries. London is Europe's foremost financial city. Great Britain has abundant supplies of coal, oil, and natural gas. Production of oil from offshore wells in the North Sea began in 1975, and the country is self-sufficient in petroleum. Other mineral resources include iron ore, tin, limestone, salt, china clay, oil shale, gypsum, and lead. The country's chief exports are manufactured goods, fuels, chemicals, food and beverages, and tobacco. The chief imports are manufactured goods, machinery, fuels, and foodstuffs. Since the early 1970s, Great Britain's trade has shifted from the United States to the European Union, which now accounts for over 50% of its trade. The United States, Germany, France, and the Netherlands are the main trading partners, and the Commonwealth countries are also important. ____________________________ * Greater London – Большой Лондон – особая административно-территориальная единица, состоит из Лондона и его пригородов.
Task 3. Answer the following questions: 1. How much percent of Britain's land is arable? 2. What does the widespread dairy industry produce in Great Britain? 3. What are the largest industries in Great Britain? 4. What does Greater London mean? 5. What kinds of goods does Great Britain export? 6. What are the main trading partners of Great Britain?
The National Health Service Good points of the NHS 1) Medical care costs very little to the individual and there is no question that the public is satisfied. 2) The previously full time physicians in the hospitals receive a better income than before and are given the importance they deserve. Many of them are happy about the change. 3) The out-patient departments are given greater importance and better organization. 4) The most competent section of the medical profession, professors, consultants, and top research workers are given more importance than formerly in the advisory committees, in the organization and the development of the service. 5) It appears that that the British doctors have a reasonable income and are much happier in comparison with the rest of English society. Weak points of the NHS 1) One of the most important failures of the NHS lies in its artificial administrative division into the three branches of the hospital services, general medical services, and public health, without any integration at any level. There is very little relationship between the consultant in the hospitals, the general practitioner and the public health officer. This often leads to misunderstanding and mutual ignorance. 2) Because of the number of certificates required and the impersonal character of hospital care, professional secrecy and discretion are in many instances things of the past. 3) Surgeons are paid by operating sessions and receive the same payment whether they do one appendectomy per operating session or four gastrectomies. 4) In the care of the aged, tuberculous patients, the chronically sick, the infirm and the patients with infected tonsils the situation is so bad that there is a waiting period of non-urgent cases of 6 months to 2 years before admission to the hospital and during that time the patient becomes a burden on the general practitioner.
British Families
In the past, people got married and stayed married. Divorce was very difficult, expensive and took a long time. Today, people's views on marriage are changing. Many couples, mostly in their twenties or thirties, live together (cohabit) without getting married. Only about 60% of these couples will eventually get married. In the past, people married before they had children, but now about 50% of children in Britain are born to unmarried (cohabiting) parents. In 2012, around a quarter of unmarried people between the ages of 16 and 59 were cohabiting in Great Britain. Cohabiting couples are also starting families without first being married. Before 1960 this was very unusual, but in 2012 around 30 per cent of births in the UK were to cohabiting couples. People are generally getting married at a later age now and many women do not want to have children immediately. They prefer to concentrate on their jobs and put off having a baby until late thirties. The number of single-parent families is increasing. This is mainly due to more marriages ending in divorce, but some women are also choosing to have children as lone parents without being married. The trend nowadays is to marry later. Many couples are living together first for all sorts of reasons such as finance.
Weddings
Most weddings take place on Saturday afternoons; this is the "peak period" in any week for getting married. Before the Wedding brides have "Hen" nights and bridegrooms have "Stag" parties. For couples getting married in a church, "banns" announcing and read aloud in the church three Sundays before the wedding. The groom chooses a Best Man who will look after the couple rings during the wedding ceremony. The Wedding Day It is unlucky for the groom to see the bride on the wedding day before the service. Traditionally the bride wears a white dress and the groom wears a suit (top hat and ties), the bride may be attended by bridesmaids and pageboys. The groom and the bride say their vows. They give each other rings. They sign a wedding register. After the wedding ceremony guests are invited to attend a meal and further celebrations. This is known as the Wedding Reception. Guests leave presents for the bride and groom on a table in the room where the reception in taken place. It is traditional for the Best Man, Brides Father and the Groom to give a speech at the wedding reception. Traditionally there is a special wedding cake at the reception, often it has two or more tiers – each tier may be made of a different type of cake to satisfy the tastes of all your wedding guests. The Honeymoon It is traditional for the bride and groom to go away on a holiday, called a Honeymoon, after the wedding has taken place. Family Size On average 2 or 4 people live as a family in one home Britain. This is smaller than most other European countries. Most British children live with their parents at least until they finish school at the age of 17 or 18. Then many go away to college, leaving some parents sad and lonely and enjoying their release from parental responsibilities. But many adults stay with their parents during their college years or return home after graduation. Today's parents cannot even be sure that their married children have moved out forever. After a divorce they may return to the parental home temporarily or even for a long-term. Older people take pride in their independence, enjoy their freedom and don't want to be a burden to their children. The telephone, the car and the airplane keep them in close contact even when they live in different parts of the country. Members of family — grandparents, aunts, uncles, cousins-keep in touch, but they see less of each other than they used to. This is because people often move away from home town to work and so the family becomes scattered. Christmas is the traditional season for reunions. Although the family group is smaller nowadays than it used to be, relatives often travel many miles in order to spend the holiday together. Family parties may be very joyous (радостный) when they bring together relatives who haven't seen each other for a while.
Place of Living
Most people in GB live in urban areas. Towns and cities are spreading into surrounding environment to cope with the increase populations. In England, an average of 7,000 hectares of farmland, countryside and green space were converted to urban use every year. This is almost the equivalent size of 9,600 international football pitches! Who owns houses in Great Britain? Now people are buying their own homes more than in the past. About two thirds of the people have their own homes or are in the process of buying it. Most others live in houses or flats that they rent from a private landlord the local council, or housing association. People buying their property almost always pay for it with a special loan called a mortgage, which they must repay, over a long period of time, usually 25 years. What are houses in Great Britain like? Most houses in England are made of stone or brick from the local area where the houses are built. The colors of the stones and bricks may vary across the country. Great Britain has many types of homes. In the large cities, people often live in apartments, which are called flats. In most towns, there are streets of houses joined together in long rows. They are called terraced houses (таунхауз). The main types of houses in Great Britain are: · Detached (особняк) (a house not joined to another house); · Semi-detached (двухквартирный) (two houses joined together); · Terrace (дом ленточной застройки) (several houses joined together); · Flats (apartments). The most popular type of home in England is semi-detached (more than 27% of all homes). Almost half of London's households are flats, maisonettes or apartments. Cost of Houses A big problem in England is the rising cost of houses. In 1990 first-time buyers paid an average of around £40,000, in 2001 this had more than doubled to £85,000 and in 2015 to £196,565. The cost of housing in England has increased much faster than people's wages. Average wage per year: £23,244. Average house price: £196,924.
Task 3. Answer the questions: 1. What is the typical British family? 2. What was the problem about British family between 1971 and 2012? 3. What can you tell about institute of marriage in GB nowadays? 4. What is the legal age for marrying in the UK? 5. Where can marriage take place? 6. What kinds of wedding traditions in UK do you know? 7. What is the usual family size in UK? 8. Where do the most British people live? 9. What kinds of houses in UK do you know? ЧАСТЬ II The American Flag
Every country has its own flag. In 1776 the thirteen colonies declared their independence from Great Britain. So the United States were born. George Washington was a general of the American Army. He decided that the United States also needed a flag. There is a story that General George Washington asked Betsy Ross* to make the flag. She used three colors: red, white, and blue. The red color was for courage, white was for liberty, and blue was for justice. She sewed thirteen red and white stripes and thirteen white stars in a circle on a blue square. Thirteen stars and stripes stood for the number of states at the beginning of the United States. On June 14, 1777, the Congress confirmed this flag as the National Flag. Later new states joined the United States. And in 1818 the Congress made another law about the flag. The thirteen stripes stayed the same, but for each new state there was a new star. Today there are fifty stars on the flag. Hawaii Island was the last star in 1959. __________________________________ *Elizabeth Phoebe " Betsy " Ross (January 1, 1752– January 30, 1836), is widely known with making the first American flag purportedly in 1776, according to family tradition, upon a visit from General George Washington, Commander-in-Chief of the Continental Army, and changing the shape of the stars described on the flag from six-pointed to easier-to-produce five-pointed stars. However, there is no archival evidence or other recorded verbal tradition to substantiate this story of the first American flag, and it appears that the story first surfaced in the writings of her grandson in the 1870s (a century after the fact), with no mention or documentation in earlier decades. The Fifty States
In the area of the United States covers every type of land, there are forests, deserts, mountains, and flat land. The area of the United States also covers every type of climate. The size of each state is different, too. Alaska is the biggest state. Rhode Island is the smallest one. Alaska is 500 times bigger than Rhode Island. About 250 million people live in the United States. The people of the United States come from all over the world. People often name new cities after those where they come from. For example, in the United States you will find Paris, Rome, Delhi, and Frankfurt. The state with the highest population is California. The state with the lowest population is Alaska. Each state has its own name. More than a half of the states have names of American Indian origin. Each state also has a flag with colors that have a special meaning for the state. The flag is the symbol of the state. There are also state flowers, trees, and birds.
Тема 8. НАСЕЛЕНИЕ США THE POPULATION OF THE USA Task 1. Learn the words and expressions:
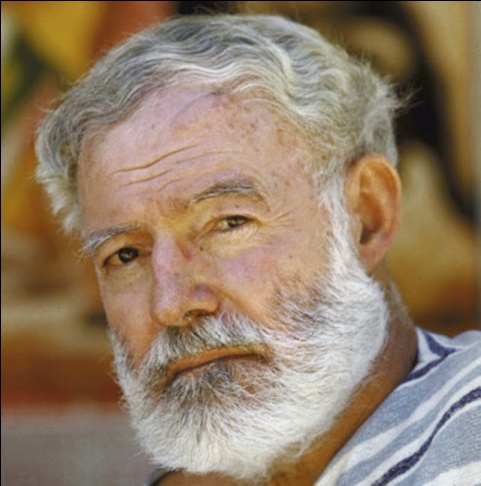
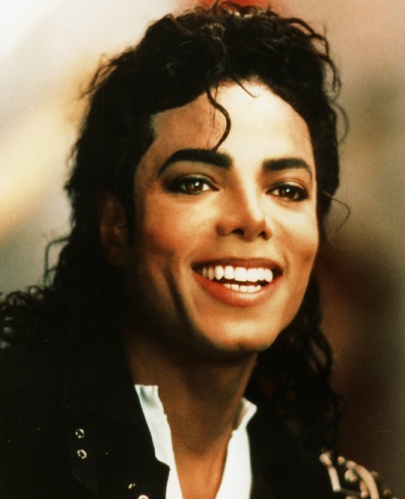
The Famous American People 1. Marilyn Monroe (1926 – 1962) – a model, actress, singer and arguably one of the most famous women of the twentieth century. 2. Abraham Lincoln (1809 – 1865) – US President during American civil war. 3. Mother Teresa (1910 – 1997) was a Roman Catholic nun, who devoted her life to serving the poor and destitute around the world. She spent many years in Calcutta, India, where she founded the Missionaries of Charity, a religious congregation devoted to helping those in great need. In 1979, Mother Teresa was awarded the Nobel Peace Prize and has become a symbol of charitable selfless work. She was beatified in 2003, the first step on the path to sainthood, within the Catholic Church. 4. Bill Gates (1955 –). As founder of Microsoft, Bill Gates is one of the most influential and richest people on the planet. Recent estimates of his wealth put it at $56 billion; this is the equivalent of the combined GDP of several African economies. In recent years he has retired from working full time at Microsoft, instead he has concentrated on working with his charitable foundation "The Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation". 5. Muhammad Ali (1942 –). American boxer and civil rights campaigner. Ali was crowned "Sportsman of the Century" by Sports Illustrated. He won the World Heavyweight Boxing championship three times, and won the North American Boxing Federation championship as well as an Olympic gold medal. 6. Elvis Presley (1935 – 1977) was an American singer, musician and actor. Elvis Presley became one of the most influential cultural icons of a generation. He is commonly referred to as the "The King of Rock ‘n’ Roll" and epitomizes the post-war pop generation. 7. Walt Disney (1901 – 1966) was a film producer, media magnate, and co-founder of the Walt Disney Company. He was an iconic figure in the Twentieth Century media and entertainment industry, helping to produce many films. With his staff, he created famous cartoon characters, such as Mickey Mouse and Donald Duck; his name was also used for the successful Disney Theme Parks. During his lifetime, he received a record 59 Nominations for the Academy Awards, winning 22 Awards. 8. Ernest Hemingway (1899 – 1961) was an American author and journalist whose unique writing style had a strong influence on 20th century fiction and culture. Many of his books are considered classics of American literature. 9. Henry Ford (1863 – 1947) was an industrialist who changed the face of automobile manufacture in America, becoming the epitome of American Capitalism. He lent his name to "Fordism" – efficient mass production.
Mother Teresa Marilyn Monroe Ernest Hemingway
Michael Jackson Abraham Lincoln Bill Gates 10. Michael Jackson (1958 – 2009) was an American singer, dancer, entertainer, and recording artist. Michael Jackson epitomized the era of pop in the 70s, 80s and 90s, earning himself the title the King of Pop. He remained a global icon until his untimely death in 2009. 11. Madonna (1958 –) – a famous American Pop singer. POLITICAL SYSTEM IN THE USA Task 1. Learn the following words and word combinations:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Последнее изменение этой страницы: 2017-02-08; просмотров: 2487; Нарушение авторского права страницы; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! infopedia.su Все материалы представленные на сайте исключительно с целью ознакомления читателями и не преследуют коммерческих целей или нарушение авторских прав. Обратная связь - 3.145.58.169 (0.219 с.) |






 Elizabeth II became queen of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland in 1952. In addition, she is the head of the Commonwealth. Elizabeth was born on 21 April 1926 in London, the first child of Albert, Duke of York, and his wife, formerly Lady Elizabeth Bowes-Lyon. (Ле́ди Елизаве́та Бо́уз-Ла́йон). She initially had little prospect of succeeding to the throne until her uncle, Edward VIII, abdicated in December 1936. Her father then became George VI and she became heir.
Elizabeth II became queen of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland in 1952. In addition, she is the head of the Commonwealth. Elizabeth was born on 21 April 1926 in London, the first child of Albert, Duke of York, and his wife, formerly Lady Elizabeth Bowes-Lyon. (Ле́ди Елизаве́та Бо́уз-Ла́йон). She initially had little prospect of succeeding to the throne until her uncle, Edward VIII, abdicated in December 1936. Her father then became George VI and she became heir. Elizabeth and her younger sister Margaret were educated at home. On the outbreak of war in 1939, they were evacuated to Windsor Castle. In 1945, Elizabeth joined the war effort, training as a driver in the Women's Auxiliary Territorial Service (WATS). In November 1947, she married a distant cousin, Philip Mountbatten (formerly Prince Philip of Greece and Denmark), who was created duke of Edinburgh. The couple has four children. George VI died on 6 February 1952 while Elizabeth and Philip were in Kenya. She returned home immediately, and was crowned at Westminster Abbey in June 1953. For more than 50 years, during a period of great change in Britain, the Queen has carried out her political duties as the head of state, the ceremonial responsibilities of the sovereign and a large annual program of visits in the United Kingdom as well as numerous foreign tours.
Elizabeth and her younger sister Margaret were educated at home. On the outbreak of war in 1939, they were evacuated to Windsor Castle. In 1945, Elizabeth joined the war effort, training as a driver in the Women's Auxiliary Territorial Service (WATS). In November 1947, she married a distant cousin, Philip Mountbatten (formerly Prince Philip of Greece and Denmark), who was created duke of Edinburgh. The couple has four children. George VI died on 6 February 1952 while Elizabeth and Philip were in Kenya. She returned home immediately, and was crowned at Westminster Abbey in June 1953. For more than 50 years, during a period of great change in Britain, the Queen has carried out her political duties as the head of state, the ceremonial responsibilities of the sovereign and a large annual program of visits in the United Kingdom as well as numerous foreign tours. David Cameron is the Conservative Party leader who has been Prime Minister of the United Kingdom since May of 2010. David Cameron was born in London but grew up in Berkshire, England. He attended Eton and then received a first class degree in Philosophy, Politics and Economics from Oxford in 1988. After Oxford, Cameron came into politics with a job in the research department of the Conservative Party. David Cameron was elected as a Member of Parliament for Witney, Oxfordshire in 2001 and became a party leader in 2005. He was often compared to Tony Blair, who played a similarly rejuvenating role for the Labor Party a decade earlier. The Conservative Party made an unexpectedly strong showing in the elections of 6 May 2010, and Cameron was asked by Queen Elizabeth II to form a new government when Gordon Brown resigned on 11 May 2010. In 2015 he was retained as a prime minister after the Conservative Party won, what the BBC called a "shock election victory"; the Conservatives instead won 331 seats, a clear majority of the 650 seats in Parliament.
David Cameron is the Conservative Party leader who has been Prime Minister of the United Kingdom since May of 2010. David Cameron was born in London but grew up in Berkshire, England. He attended Eton and then received a first class degree in Philosophy, Politics and Economics from Oxford in 1988. After Oxford, Cameron came into politics with a job in the research department of the Conservative Party. David Cameron was elected as a Member of Parliament for Witney, Oxfordshire in 2001 and became a party leader in 2005. He was often compared to Tony Blair, who played a similarly rejuvenating role for the Labor Party a decade earlier. The Conservative Party made an unexpectedly strong showing in the elections of 6 May 2010, and Cameron was asked by Queen Elizabeth II to form a new government when Gordon Brown resigned on 11 May 2010. In 2015 he was retained as a prime minister after the Conservative Party won, what the BBC called a "shock election victory"; the Conservatives instead won 331 seats, a clear majority of the 650 seats in Parliament. Twelve million children attend about 40 000 schools in Britain. Education in Great Britain is compulsory and free for all children between the ages of 5 and 16. There are many children who attend a nursery school from the age of 3, but it is not compulsory. In nursery schools they learn some elementary things such as numbers, colours, and letters. Apart from that, babies play, have lunch and sleep there. Whatever they do, there is always someone keeping an eye on them.
Twelve million children attend about 40 000 schools in Britain. Education in Great Britain is compulsory and free for all children between the ages of 5 and 16. There are many children who attend a nursery school from the age of 3, but it is not compulsory. In nursery schools they learn some elementary things such as numbers, colours, and letters. Apart from that, babies play, have lunch and sleep there. Whatever they do, there is always someone keeping an eye on them. comprehensive schools*, which take pupils of all abilities without exams. In such schools pupils are often put into certain sets or groups, which are formed according to their abilities for technical or humanitarian subjects. Almost all senior pupils (around 90 per cent) go there;
comprehensive schools*, which take pupils of all abilities without exams. In such schools pupils are often put into certain sets or groups, which are formed according to their abilities for technical or humanitarian subjects. Almost all senior pupils (around 90 per cent) go there;


 Great Britain is one of the world's leading industrialized nations. It has achieved this position despite the lack of most raw materials needed for industry. It imports 40% of its food supplies. Thus, its prosperity has been dependent upon the export of manufactured goods in exchange for raw materials and foodstuffs.
Great Britain is one of the world's leading industrialized nations. It has achieved this position despite the lack of most raw materials needed for industry. It imports 40% of its food supplies. Thus, its prosperity has been dependent upon the export of manufactured goods in exchange for raw materials and foodstuffs. The family institution in Britain is changing. The typical British family headed by two parents has undergone substantial changes during the twentieth century. In particular there has been a rise in the number of single-person, which increased from 18 to 29 per cent of all households between 1971 and 2012. By the year 2020, it is estimated that there will be more single people than married people. Fifty years ago this would have been socially unacceptable in Britain.
The family institution in Britain is changing. The typical British family headed by two parents has undergone substantial changes during the twentieth century. In particular there has been a rise in the number of single-person, which increased from 18 to 29 per cent of all households between 1971 and 2012. By the year 2020, it is estimated that there will be more single people than married people. Fifty years ago this would have been socially unacceptable in Britain. Over half the weddings in the UK take place in local register offices and the rest are religious ceremonies. A few years ago changes in the law allowed couples to get married in all sorts of places (known as a civil Wedding Ceremony).
Over half the weddings in the UK take place in local register offices and the rest are religious ceremonies. A few years ago changes in the law allowed couples to get married in all sorts of places (known as a civil Wedding Ceremony).
 The "Stars and Stripes" is a popular name for the red, white and blue flag of the United States. Another popular name is the "Star Spangled Banner". This is also the name of the National Anthem of the United States.
The "Stars and Stripes" is a popular name for the red, white and blue flag of the United States. Another popular name is the "Star Spangled Banner". This is also the name of the National Anthem of the United States. The fifty states have joined to make one nation. The United States did not always have fifty states. At first there were thirteen. As the United States grew, more states joined the union. The last two states to join were Alaska and Hawaii. They both joined in 1959.
The fifty states have joined to make one nation. The United States did not always have fifty states. At first there were thirteen. As the United States grew, more states joined the union. The last two states to join were Alaska and Hawaii. They both joined in 1959.








