
Заглавная страница Избранные статьи Случайная статья Познавательные статьи Новые добавления Обратная связь КАТЕГОРИИ: ТОП 10 на сайте Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрацииТехника нижней прямой подачи мяча. Франко-прусская война (причины и последствия) Организация работы процедурного кабинета Смысловое и механическое запоминание, их место и роль в усвоении знаний Коммуникативные барьеры и пути их преодоления Обработка изделий медицинского назначения многократного применения Образцы текста публицистического стиля Четыре типа изменения баланса Задачи с ответами для Всероссийской олимпиады по праву 
Мы поможем в написании ваших работ! ЗНАЕТЕ ЛИ ВЫ?
Влияние общества на человека
Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрации Практические работы по географии для 6 класса Организация работы процедурного кабинета Изменения в неживой природе осенью Уборка процедурного кабинета Сольфеджио. Все правила по сольфеджио Балочные системы. Определение реакций опор и моментов защемления |
Exercise 7. Match word combinations in column A with those in column B.
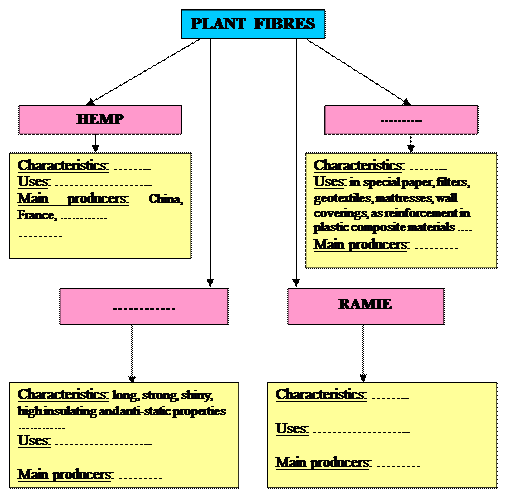
1) husk fibres a) поглинати вологу 2) natural anti-bacterial properties b) квіткова рослина 3) home furnishing textiles c) відділяти м’яку масу від волокна 4) chair coverings d) природні антибактеріальні властивості 5) absorb moisture e) волокна зі скоролупи, шелухи 6) flowering plant f) текстиль для домашнього використання 7) lightweight and silky fabrics g) покриття для стільців 8) plastic composite materials h) замінник асбеста 9) separate the pulp from the fibre i) легкі та шовковисті тканини 10) a substitute for asbestos j) композитний пластик Exercise 8. Find the international words in the text in paragraph 5, translate them to your native language. Exercise 9. Connect the parts given below in one sentence and translate them.
VI. Comprehension. Exercise 10. Agree or disagree with the following statements. Use phrases: You are right. I agree with you. I’m afraid you are wrong. I can’t agree with you. 1) Long, strong and durable, jute fibres are about 65% cellulose and contain low levels of lignin. 2) Bangladesh, West Bengal in India and Nepal are the world's main jute producers. 3) Ramie fibre is white with a silky lustre, it has high elasticity and dyes hardly. 4) S isal can be found in special paper, filters, geotextiles, mattresses, carpets, wall coverings, etc. Exercise 11. Find answers to the following questions in the text. Work in pairs
1) What is hemp fibre? Where is it used? 2) Where is jute grown? 3) What do you know about the production of jute fabrics? 4) Why are geotextiles from jute used so largely? 5) What properties does ramie possess? In what production is it used? 6) What is sisal fibre? Where is it cultivated?
VII. Oral practice. Exercise 12. Fill in the chart. Speak about the plant fibers and their usages in the textile industry.
VIII. Watching the video-material and comprehension. Exercise 13. a) Watch the video “Jute manufacturing”. Look through new words used in the video beforehand. Meads - луки; Barques – великі судна; Delivering-intensive method – метод трудомісткої доставки; Fibre-softening method – метод разм’ягшення волокна; Jute-batching oil – джутовий маслянистий розчин; Loom - верстат.
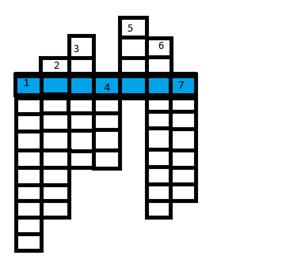
b) Answer the following questions according to the content of the video-material about jute in your native language. 1. Where was jute manufactured traditionally? 2. How was it transported? 3. What has happened to the old methods of delivery and processing nowadays? 4. What processes and methods are shown in the video-material? Name them. Exercise 14. Guess which of the words were used in the video-recording about jute manufacturing. Solve the crossword using these words and define the marked key-word.
IX. Oral practice. Exercise 15. a) Summarize the information you have studied about plant fibers at the lesson. b) Speak about the plant fibres grown in Ukraine and the textile fabrics made of them.
X. Home-task. Exercise 16. a) Retell the text “Plant fibres”, speak on their qualities and usage. b) Role-play: Act out a dialogue. Imagine that you are farmers from Mexico, India, China or some other country and you have your own farms. There you cultivate different plant fibres. A journalist arrives at your farm and wants to make an interview about your work. (Mind! While composing a dialogue, use Gerund where it is possible).
UNIT 2 CHEMICAL FIBERS
I. Practice. Exercise 1. Answer the following questions:
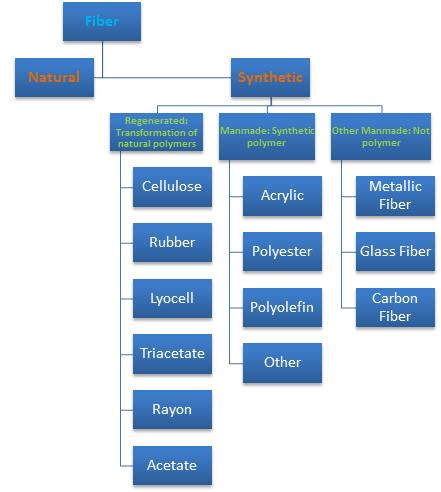
1. How are the materials used in the manufacture of clothing called? 2. Where is fibre found in nature? 3. What is the difference between the terms “fabric” and “cloth”? 4. What properties should textile fibres have? 5. Name the principal natural fibres. Why are they called natural fibres? 6. What fibres were developed in the 20th century? 7. Why are chemical fibres called man-made fibres? 8. How are fibres divided according to their origin? Give examples.
II. Language. Exercise 2. Read and memorize the following words and word combinations:
Exercise 3. Pay attention to the pronunciation of the following terms:
Exercise 4. Give English equivalents of the following: Вогнетривкий, сировина, обгортковий папір, поглинання води, покришки, деревна маса, неорганічне волокно, уникати тертя, захист від загинання тканини, природній полімер. Дуже важливі в промисловому сенсі, зростає з плином часу, переважають за показниками поглинання вологи, виробництво одягу, прасувати при низькій температурі, для створення композитних матеріалів, надзвичайна міцність.
Exercise 5. Make up derivatives, define the part of speech: industry, nature, deep, colour, artificial, produce, absorb, manufacture, near, resist, wide, chemical, architect, elastic, reinforce, acryl, conduct, vary, moist, advantage, frequent, attack.
Find antonyms: natural, coarse, advantage, man-made, increase, more, equal, fine, organic, decrease, weaken, unequal, disadvantage, reinforce, quality, less, inorganic, quantity. Find synonyms: produce, nylon, abundantly, manufacture, spandex, man-made, features, in large quantities, artificial, polyamide, characteristics, elastane. III. Grammar. Exercise 6. Find Participle I, II in the following sentences, set the functions and translate the sentences: 1. Nylon fibresare the fibers having the longest history among synthetic fibres. 2. Filament yarns are used for fabrics for women's clothing and linings. 3. The amount of production is continuing to increase year by year. 4. Fibres from Inorganic Materialsare the inorganic chemical fibres made from materials such as glass, metal, carbon or ceramic. 5. When dissolved with chemicals, cellulose contained in the wood pulp or cotton can be regenerated into fibres. 6. They are manufactured into fabrics, by blending with cotton, wool and linen fibres, making the use of each characteristic. 7. Comparing other synthetic fibres with nylon, scientists point out great advantages of nylon fibres.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Последнее изменение этой страницы: 2016-08-12; просмотров: 61; Нарушение авторского права страницы; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! infopedia.su Все материалы представленные на сайте исключительно с целью ознакомления читателями и не преследуют коммерческих целей или нарушение авторских прав. Обратная связь - 18.219.96.188 (0.017 с.) |

 IV. Reading.
IV. Reading.


