
Заглавная страница Избранные статьи Случайная статья Познавательные статьи Новые добавления Обратная связь КАТЕГОРИИ: ТОП 10 на сайте Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрацииТехника нижней прямой подачи мяча. Франко-прусская война (причины и последствия) Организация работы процедурного кабинета Смысловое и механическое запоминание, их место и роль в усвоении знаний Коммуникативные барьеры и пути их преодоления Обработка изделий медицинского назначения многократного применения Образцы текста публицистического стиля Четыре типа изменения баланса Задачи с ответами для Всероссийской олимпиады по праву 
Мы поможем в написании ваших работ! ЗНАЕТЕ ЛИ ВЫ?
Влияние общества на человека
Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрации Практические работы по географии для 6 класса Организация работы процедурного кабинета Изменения в неживой природе осенью Уборка процедурного кабинета Сольфеджио. Все правила по сольфеджио Балочные системы. Определение реакций опор и моментов защемления |
From the history of architectureСтр 1 из 11Следующая ⇒
Старостина Н. А.
HISTORY OF ARCHITECTURE ИСТОРИЯ АРХИТЕКТУРЫ
Учебно-методическое пособие По английскому языку
Москва 2017
УДК 72.03=111/076.5 ББК 812-923 Англ. И. 90
Рецензенты кандидат филологических наук, доцент Пономарева М.Н., кандидат филологических наук, Пономарев В.В.
И. 90 История архитектуры. Учебно-методическое пособие по английскому языку для студентов 2 курса направления 08.03.01 «Строительство» очной и заочной форм обучения/сост. Н.А. Старостина; ООО «Технологии рекламы», г. Москва, 2017. – 99с.
Пособие предназначено для самостоятельной работы по английскому языку студентов направления 08.03.01 «Строительство» очной и заочной форм обучения. Основной целью издания является развитие навыков чтения, а также навыков устной речи, развитие навыков извлечения информации, ее обработки и получения дополнительных знаний из соответствующих областей технической науки. В текстах нашли отражение наиболее интересные моменты истории архитектуры, самые замечательные архитектурные стили, история возникновения и использования наиболее распространенных строительных материалов.
УДК 72.03=111/076.5 ББК 812-923 Англ.
© ООО «Технологии рекламы», 2017 © Старостина Н.А., 2017 Complete the following sentences. 1. Geographical, geological, climatic, religious influences _________________ the formation of a particular style. 2. Geography, geology, climate, religion and many others factors __________________ the development of architecture. 3. Architecture ________________ the mother of the arts of sculpture, painting, and the allied decorative crafts. 4. Architecture _______________ the art with which we all are in daily contact 5. The history of architecture ____________________ a record of continuous evolution. 6. A glance along the past ages _________________________ architecture as a history of social condition progress. 7. Architectural styles ____________________________naturally into several groups.________________ To aim at, to contribute to, to be, to fall, to influence on, to be, to reveal 4. Answer the questions: 1. What does the history of architecture aim at? ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
2. What does influence on architecture? ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 3. What is the best way to learn about architecture? ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 4. What is architecture? ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 5. What is the history of architecture? ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 6. What is architecture connected in all periods with? ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 7. What groups do architectural styles fall? ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 5. Continue the following sentences: 1. The history of architecture________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 2. The best way to learn about architecture_____________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 3. Architecture is _________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 4. Architectural styles _____________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 6. Explain in English. Use the following phrases to express your opinion: It seems to me that.... I would like to say that.... I guess that... I suppose that... I am sure that 1. The best way to learn about architecture is to study actual buildings and museums. ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 2. The history of architecture is a record of continuous evolution. ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ Give your opinion on the topic _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 8. Give a short summary of the text. _______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ Give annotation of the text _____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
CIVIL ENGINEERING The term «civil engineering» was first used to distinguish the work of the engineer with a non-military purpose from military engineering. But increasing specialization has led to subdivision of engineering into civil, mechanical, electrical, and other forms, and the term «civil engineering» is usually applied to such as excavation and embankment, the construction of railways, bridges, docks, and harbours, the control of water by dams and reservoirs, canals, aqueducts, and pipelines, and the reclamation of land. Civil engineering did not develop until the rise of Rome. The Cloaca Maxima, the great drain of Rome, was built in the sixth century В. С. It is in existence today, but the oldest part still standing probably dates from the third century В. С. Like most ancient drains and sewers, it was at first open, but was later enclosed. The original purpose of Rome's sewers was to drain off waste waters. For efficiency, the sewers were built along the lines of the natural streams. Of the approximately 200 aqueducts the Romans built throughout their Empire, at least nine were in Rome. Though they were able to deliver 85 million gallons of water per day, consumption averaged only 40 million. Like other ancient systems, the Romans' set-up had no main pipe leading from the reservoir to the town. Instead, the water flowed from the source partly along conduits which were often of considerable length, and partly over aqueducts to the water tower. The water tower interior was divided into four compartments — the tank itself and three subsidiary tanks. Two of the smaller tanks supplied the baths and the private houses of the rich. The third tank supplied the public fountains, where the majority of the people drew their water. Lead or clay pipes were used to conduct water to the houses. The lead pipes (4 1/4 inch in diameter), were made from sheet-lead, bent around a core. Walls were 1/4 inch thick. The Romans, although they did not invent paved roads, advanced road building to a new height. The total length of the roads built by the Romans in Britain is estimated at over 47,000 miles. They were constructed to last forever and many are in use today; some have simply been resurfaced. In the construction of their road network, the Romans aimed at the shortest route, regardless of obstacles. Rocks were cleared away, tunnels were dug through hills, and swamps were drained. At first the Romans built timber roads, then somewhat later, a timber road mounted on stakes, many having a covering of pavement. Roman bridges, at first made of wood, were later built of stone. Typical Roman style was a semicircular arch and short span. The bridge builders' chief problem was to provide solid foundations. Town building was based on camp tradition, and some towns arose out of army camps. The typical Roman city had a rectangular plan and resembled a Roman military camp with two main streets—the cardo (north-south) and the decumanus (east-west)—a grid of smaller streets dividing the town into blocks, and a wall circuit with gates. A typical town built this way was Manchester, England.
Roman theaters first appeared in the late Republic. They were semicircular in plan and consisted of a tall stage building abutting a semicircular orchestra and tiered seating area (caved). Unlike Greek theaters, which were situated on natural slopes, Roman theaters were supported by their own framework of piers and vaults and thus could be constructed in the hearts of cities.
The Colosseum in Rome (70-82) is best known for its multilevel system of vaults made of concrete. It is called the Colosseum for a colossal statue of Nero that once stood nearby, but its real name is the Flavian Amphitheater. It was used for staged battles between lions and Christians, among other spectacles, and is one of the most famous pieces of architecture in the world. Fusion of Roman and North European traditions was reflected in many ways. Buildings combined the Roman arch and the steep peaked roof of Northern Europe. Roman traditions were continued in an architectural form known as Romanesque. London bridge, finished in 1209, took thirty-three years to build. It consisted of nineteen irregular pointed arches, its piers resting on broad foundations designed to withstand the Thames' current. The first significant advance over Roman methods, however, was the invention of the ribbed vault. The ribs were built independently of the wall and supported the stone-vault web.
The use of pointed arches was another advance upon Roman methods, yet the medieval bridge was not as great an engineering achievement as was the cathedral. Providing for only one-way traffic, the typical bridge was narrow. It was not adapted to heavy vehicles.
New vocabulary: Subdivision — подразделение excavation - земляные работы embankment - дамба, набережная aqueduct – акведук pipeline – трубопровод reclamation - осушка, мелиорация drain - дренажная труба sewer – коллектор waste water - сточная вода interior – внутренний lead – свинец clay – глина regardless of - не обращая внимания на obstacle - помеха, преграда swamp – болото built timber - строительный материал pavement – тротуар semi- - полу- arch - арка, свод span – пролет fusion – слияние rib – выступ ribbed vault - веерный свод 1. Translate the words into Russian: Civil engineering _________________________ purpose _________________________ subdivision of engineering _________________________ civil _________________________ mechanical __________________________ electrical __________________________ excavation and embankment __________________________ railways __________________________ bridges __________________________ docks __________________________ harbour __________________________
reservoirs __________________________ canals __________________________ aqueduct __________________________ pipeline __________________________ reclamation of land __________________________ drain __________________________ sewers __________________________ enclose __________________________ natural streams __________________________ consumption __________________________ 2. Find the English equivalents: Дорожная сеть _______________________________ строительный лес _______________________________ тротуар _______________________________ скала _______________________________ убирать прочь _______________________________ арка _______________________________ пролет _______________________________ лагерная традиция _______________________________ веерный свод _______________________________ свинцовые или глиняные трубы _______________________________ доставлять воду к _______________________________ не обращая внимания _______________________________ средневековый мост _______________________________ собор _______________________________ тяжелый транспорт _______________________________ деление (отсек) _______________________________ 3. Practise the pronunciation of the words and word-combinations: Specialization, excavation, embankment, aqueduct, the Cloaca Maxima, ancient, approximately, reservoir, sewer, subsidiary. Give annotation of the text ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ARCHITECTURAL STYLES The natural products, such as timber, brick, clay and stone, largely determine the character of Egyptian Architecture. Stone, including limestone, sandstone and alabaster, as well as the harder granite or porphyry, was the material chiefly employed, not only for constructive and decorative work, but also for vases and even for personal ornaments, as the country was poor in metal and there was little building timber. The gigantic scale which distinguishes Egyptian architecture was made possible not only by the materials, but also by the methods of quarrying, transporting and raising enormous blocks of stone into position.
The architecture of Egypt is characterized by massive walls, close-spaced columns carrying stone lintels which, in their turn, support the flat roof. The Pyramids, which are amongst the oldest monuments, were religious in origin and reveal not only the religious faith but also the social and industrial conditions in those far-off days; for such massive buildings would have not been possible without a despotic government and the forced labour of a vast population of slaves and captives. The architecture of Western Asia also reflects national characteristics. Here, again, the colossal nature of building undertakings points to the social conditions that prevailed. European architecture up to this period may be divided into three main types, differentiated by important constructive principles. The Greek or trabeated style, consisting of column and beam. The Roman or composite style combining column and semicircular arch and vault. The Gothic or arcuated style is that, in which the pointed arch prevailed. Greek Architecture. The chief mineral wealth of Greece was in her marble - - the most beautiful and monumental of all building materials. The Greeks attached so much importance to the quality of fine-grained marble for producing exact outlines and smooth surfaces, that they even coated coarse-grained limestone with a layer of marble «stucco» in order to secure this effect, which is the great characteristic of their architecture. The architecture of Greece reflects each stage of Greek history with remarkable accuracy and her architecture has influenced all styles down to our own day. The Greek style consists of column and beam.
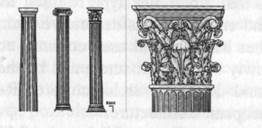
Roman Architecture. In addition to marble the Romans could quarry terracotta, stone, and brick, all of which they used even for important buildings. In the neighbour hood of Rome there was travertine, a hard limestone from Tivoli, tufa, a volcanic substance of which the hills of Rome are mainly composed, besides excellent sand and gravel. The building material, however, which led to great structural innovations, was concrete formed of pozzolana, a clean sandy earth which has a peculiar property when mixed with lime. It was exceedingly hard and cohesive concrete. Not only domes and vaults but also walls were frequently formed of this concrete, and they were faced with brick, stone, alabaster, porphyry and other marbles.
The architecture of Rome was largely influenced by the Etruscan arch so that a complex type resulted from blending the Greek column and entablature as decorative facings to piers with semicircular arches but they still used columns constructively. By the use of the newly invented concrete and by the employment of the arch, vault and dome the architecture of Rome became the foundation of European architecture. Gothic Architecture. The establishment of Christianity as the state religion resulted in the construction in Rome of over thirty churches. It gave an impetus to the marvellous architectural developments of the Medieval period which were in their turn developed from Romanesque architecture, and to which the name of Gothic has since been given. Gothic architecture of the thirteenth century is mainly distinguished from Romanesque architecture by the introduction and general use of the pointed arch and by employing small stones held together with thick mortar joints.

New vocabulary: Largely - зд. в значительной степени to determine the character определять характер limestone – известняк sandstone – песчаник alabaster – алебастр porphyry – порфир personal ornaments - личных украшений the gigantic scale - гигантский масштаб to distinguish – отличать quarry -разработка карьеров in their turn - в их очередь to be in origin - быть по происхождению to reveal the religious faith - показывать религиозную веру the forced labour - принудительный труд to reflect – отражать undertaking – предприятие prevail – преобладать trabeated style – стиль характеризующийся beam – балка антаблементом (фриз и карниз) arcuated style - арочный стиль marble – мрамор to attach – прилагать terracotta – терракота travertine – известковый туф pozzolana – пуццолана a peculiar property - специфическое свойство lime – известь exceedingly – чрезвычайно cohesive - способный к сцеплению concrete – бетон an impetus – стимул marvelous – изумительным the Medieval – средневековье mortar - известняковый раствор 1. Translate the words into Russian: Timber __________________________________________________________________ brick __________________________________________________________________ clay and stone __________________________________________________________________ granite __________________________________________________________________
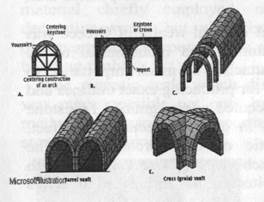
constructive and decorative work __________________________________________________________________ to be poor in metal __________________________________________________________________ building timber __________________________________________________________________ to raise enormous blocks of stone into position __________________________________________________________________ slaves and captives __________________________________________________________________ to point to the social conditions __________________________________________________________________ differentiated by important constructive principles __________________________________________________________________ semicircular arch and vault __________________________________________________________________ the quality of fine-grained marble for producing exact outlines and smooth surfaces __________________________________________________________________ «stucco» __________________________________________________________________ remarkable accuracy __________________________________________________________________ the neighbourhood __________________________________________________________________ great structural innovations __________________________________________________________________ establishment of Christianity __________________________________________________________________ 2. Translate the words, word combinations and sentences into English: 1. Для архитектуры Египта характерны массивные стены, близко расположенные друг к другу колонны, несущие каменные перемычки которые, в свою очередь, поддерживают плоскую крышу; __________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 2. в те отдаленные дни; ________________________________________________________________ 3. европейская архитектура до этого периода может быть разделена на три главных типа; __________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 4. наиболее красиво и монументально из всех строительных материалов; __________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 5. важности к качеству мелкозернистого мрамора для создания точных основ и гладких поверхностей; __________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 6. архитектура Греции отражает каждую стадию Греческой истории с замечательной точностью, а ее архитектура повлияла на все стили до наших дней. _______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ Give annotation of the text ______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ THE ORIGIN OF SHELLS It is impossible to open a magazine devoted to the building arts without coming across some reference to shells and shell technology. Where did they come from? What do they mean to the building arts? The history of the origin of shells begins about five thousand years ago in Egypt. It was at this time and place that the first architect constructed the stepped pyramid which is today the oldest existing building in the world. There is no direct connection between this pyramid and shells. These prototype buildings do not exist as structures, but archaeologists, reconstructing shapes from fragments, have theorized that some of these prototype structures had barrel vaulted roofs. Little or nothing remains now of any shells constructed by the Ancient Egyptians. The Romans did not invent the round or segmental arch but they developed the art of arch, dome and vault building to a peak of perfection. They built domes, half domes and barrel vaults. Their work with domes and vaults laid the foundation for an empirical system of shell technology. However the shift of culture to the East brought new ideas. These new ideas resulted in a revival of shell technology and a far wider use of shells than had existed to this time. One of the buildings of this or any other time is the Saint Sophia. Architects for this church, solved the problem of fitting a round dome on a square base. Five to seven hundred years passed after the construction of Saint Sophia with little or no progress in shell technology. Then the cathedral builders began the construction of the pointed vaults of the Gothic Period. Notre Dame and many other cathedrals were built and added to the empirical techniques of construction of the vault and shell.

Even early experience with the construction of shell-roofed buildings proved to be economical. Nowadays a lot of projects of this nature are being constructed. New vocabulary: Shell - зд. корпус, свод barrel vault - цилиндрический свод dome – купол vault – свод pointed vault - стрельчатый, готический свод 1. Translate the word combinations into Russian: shell technology _______________________________ to devote _______________________________ reference _______________________________ shape _______________________________ a peak of perfection _______________________________ an empirical system _______________________________ the shift _______________________________ revival _______________________________ splendid _______________________________ barrel vaulted roof _______________________________ the round and segmental arch _______________________________ half dome _______________________________ to fit on _______________________________ 2. Find the English equivalents: Невозможно __________________________________________________________________ строительное искусство __________________________________________________________________ самое старое из существующих сооружение в мире __________________________________________________________________ прямая связь __________________________________________________________________ прототип зданий __________________________________________________________________ оставаться __________________________________________________________________ положить основу __________________________________________________________________ решать проблему __________________________________________________________________ здания с крышей в виде свода-оболочки __________________________________________________________________ быть экономичным __________________________________________________________________ снабжать __________________________________________________________________ 3. Practise the pronunciation of the new words and word-combinations: Egypt, archaeologist, theorized, the Ancient Egyptians, perfection, revival, far -wider use, the Saint Sophia, church, Notre Dame, the Renaissance, Michael Angela's Dome of Saint Peter, project. Give annotation of the text _____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ Give annotation of the text _______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ BUILDING MATERIALS The availability of suitable materials fostered the crafts to exploit them and influenced the shapes of buildings. Large areas of the world were once forested, and their inhabitants developed carpentry. Although it has become relatively scarce, timber remains an important building material. Many kinds of stone lend themselves to building. Stone and marble were chosen for important monuments because they are incombustible and can be expected to endure. Stone is also a sculptural material; stone architecture was often integral with stone sculpture. The use of stone has declined, however, because a number of other materials are more amenable to industrial use and assembly. Some regions lack both timber and stone; their peoples used the earth itself, tamping certain mixtures into walls or forming them into bricks to be dried in the sun. Later they baked these substances in kilns, producing a range of bricks and tiles with greater durability. Thus, early cultures used substances occurring in their environment and invented the tools, skills, and technologies to exploit a variety of materials, creating a legacy that continues to inform more industrialized methods. Building with stones or bricks is called masonry. The elements cohere through sheer gravity or the use of mortar, first composed of lime and sand. The Romans found a natural cement that, combined with inert substances, produced concrete. They usually faced this with materials that would give a better finish. In the early 19th century a truly waterproof cement was developed, the key ingredient of modern concrete. In the 19th century also, steel suddenly became abundant; rolling mills turned out shapes that could make structural frames stronger than the traditional wooden frames. Moreover, steel rods could be positioned in wet concrete so as to greatly improve the versatility of that material, giving impetus early in the 20th century to new forms facilitated by reinforced concrete construction. The subsequent profusion of aluminum and its anodized coatings provided cladding (surfacing) material that was lightweight and virtually maintenance free. Glass was known in prehistory and is celebrated for its contributions to Gothic architecture. Its quality and availability have been enormously enhanced by industrial processing, which has revolutionized the exploitation of natural light and transparency. The requirements to be fulfilled by concrete vary to a great extent. One of the essential properties of concrete is its compressive strength. From the time of its first production more than a century ago there was a steady and gradual improvement in the compressive strength of Portland cement until the beginning of the war. With the cements now available much higher strengths can be obtained than some 40 or 50 years ago. The increase in strength is partly due to the increased fineness to which modern cements are ground. Cement develops heat during hydration. This is of considerable importance in certain types of concrete construction, particularly in structures of large volume, such as dams, massive retaining walls and the like. A very high rate of heat development is advantageous in work done in cold weather, so as to protect the fresh concrete from the effect of low temperatures. It should be noted, of course, that not ail properties desired can be obtained in any one cement. Selection of the cement alone does not ensure concrete with the properties desired, which depend also on the choice of aggregates and mixes, the control of the quantity of water added to the mix, and on a series of other factors. Silicon is one of the most abundant elements found in the earth's crust. It is second to oxygen in abundance. Silicon never occurs free, but in combination with oxygen or with oxygen and metals. It forms a great variety of organic and inorganic compounds. Elementary silicon is used as an alloying constituent to strengthen aluminum, copper, magnesium and other metals. It has a deoxidizing effect on steel. Silica (quartz) is a crystalline form of silicon dioxide. Silica bricks, made of nearly pure silica, are extensively used in metallurgical industry. Silica is also used as one of the raw materials for the manufacture of common glass. New vocabulary: The availability – пригодность suitable – подходящий carpentry - плотницкие работы scarce – недостаточный incombustible – невоспламеняющийся to endure – терпеть to decline – снизиться amenable – поддающийся to lack - испытывать недостаток kiln – печь durability – долговечность substances – вещества legacy – наследство masonry – каменный to cohere – сцеплять gravity - сила тяжести mortar - известковый раствор truly waterproof cement - настоящий abundant – избыточный водонепроницаемый цемент moreover - кроме того steel rods - стальные пруты impetus - стимул 1. Translate the word combinations into Russian: to foster the crafts __________________________________________________________________ to be forested __________________________________________________________________ remain __________________________________________________________________ to occur in the environment __________________________________________________________________ the availability of suitable materials their inhabitants developed carpentry __________________________________________________________________ tamping certain mixtures into walls or forming them into bricks to be dried in the sun __________________________________________________________________ to invent the tools __________________________________________________________________ skills and technologies __________________________________________________________________ to exploit a variety of materials __________________________________________________________________ creating a legacy that continues to inform more industrialized methods __________________________________________________________________ 2. Find the English equivalents: 1. древесина остается важным строительным материалом; __________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 2. камень - также скульптурный материал; _____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 3. построения из камня или кирпича называются каменными; _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 4. в начале 19-ого столетия был разработан действительно водонепроницаемый цемент; _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 5. кроме того, стальные пруты могли быть помещены во влажный бетон, чтобы улучшить многосторонность этого материала. _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 3. Practise the pronunciation of the new words and word-combinations: carpentry, stone sculpture, assembly, durability, masonry, subsequent, profusion, cladding Give annotation of the text ____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ REINFORCED CONCRETE The first reference to Portland cement concrete reinforced with steel or iron bars appeared in November 1855 in the magazine «The Engineer» in which Francois Coignet described his experiments with concrete and also with plain concrete houses that he had built eight years previously and a house that he had built near Paris, which had a roof-span of 23 ft of concrete reinforced with iron bars. In 1861 Coignet published a book on concretes of different mixtures placed in situation and insisted on the influence of the water-cement ratio on the strength of concrete. In this book he also describes his method of using reinforced concrete slabs. In the same book Coignet describes methods for the construction of pipes, reservoirs and walls of concrete reinforced with metal sheets, bars and chains. Coignet took out no patent for his ideas: he was interested only in the advancement of science. At the same time as Coignet was working on his reinforced concrete roof, another inventor was constructing his boat which appeared in the Paris Exhibition and was probably the first application of reinforced concrete. A few years later a French gardener Monier had the idea of replacing wooden-flower-boxes by those made of an iron mesh covered with cement, and he took out a patent for it. The greatest development of reinforced concrete construction took place at the turn of the century. In Britain, as well as in the United States, early interest in reinforced concrete was for fireproof construction. The first results of tests of reinforced concrete beams were published in 1877. Since that time the development of reinforced concrete work has made good progress. The-post-war necessity to increase the productivity of the building /industry has resulted in the rapid development of precast and prestressed members. Some of the many bridges, tall buildings with reinforced concrete frames, shell roofs, industrial structures are being built throughout the world of reinforced concrete. New vocabulary: Cement – цемент concrete reinforced – арматура the water-cement ratio - водно - цементная пропорция the strength of concrete - крепость бетона slab – плита to work on his reinforced concrete roof - работать iron mesh - железная сетка над арматурной крышей fireproof construction - противопожарные конструкции reinforced concrete beams – арматурные балки shell roofs - сводчатые потолки precast and prestressed members - изготовленные reinforced concrete frames - арматурные каркасы (рамы) заранее части 1. Translate the word combinations into Russian: reference to _______________________________ previously _______________________________ to take out _______________________________ in the advancement of science ______________________________ application ______________________________ to take place at ______________________________ rapid development ______________________________ industrial structures ______________________________ 2. Find the English equivalents: цементная арматура со стальными или железными брусками __________________________________________________________________ пролет крыши __________________________________________________________________ деревянные цветочные горшки __________________________________________________________________ результаты испытания были опубликованы __________________________________________________________________ послевоенная необходимость __________________________________________________________________ Парижская выставка __________________________________________________________________ по всему миру __________________________________________________________________ 3. Practise the pronunciation of the new words and word-combinations: concrete, reinforced, Francois Coignet, Paris, reservoirs, advancement, Monier, reinforced concrete frames, precast and prestressed members Give annotation of the text _____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Последнее изменение этой страницы: 2021-05-12; просмотров: 71; Нарушение авторского права страницы; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! infopedia.su Все материалы представленные на сайте исключительно с целью ознакомления читателями и не преследуют коммерческих целей или нарушение авторских прав. Обратная связь - 13.58.39.23 (0.355 с.) |







